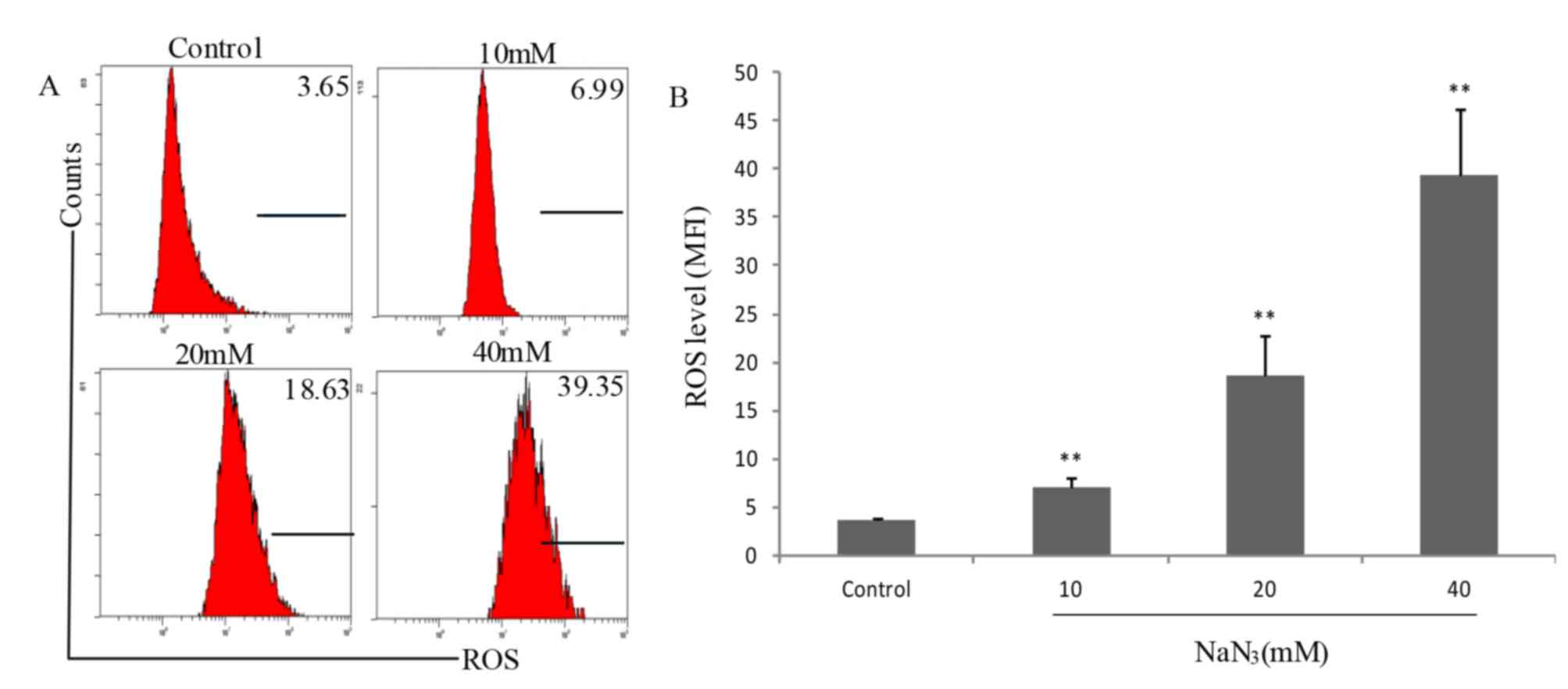
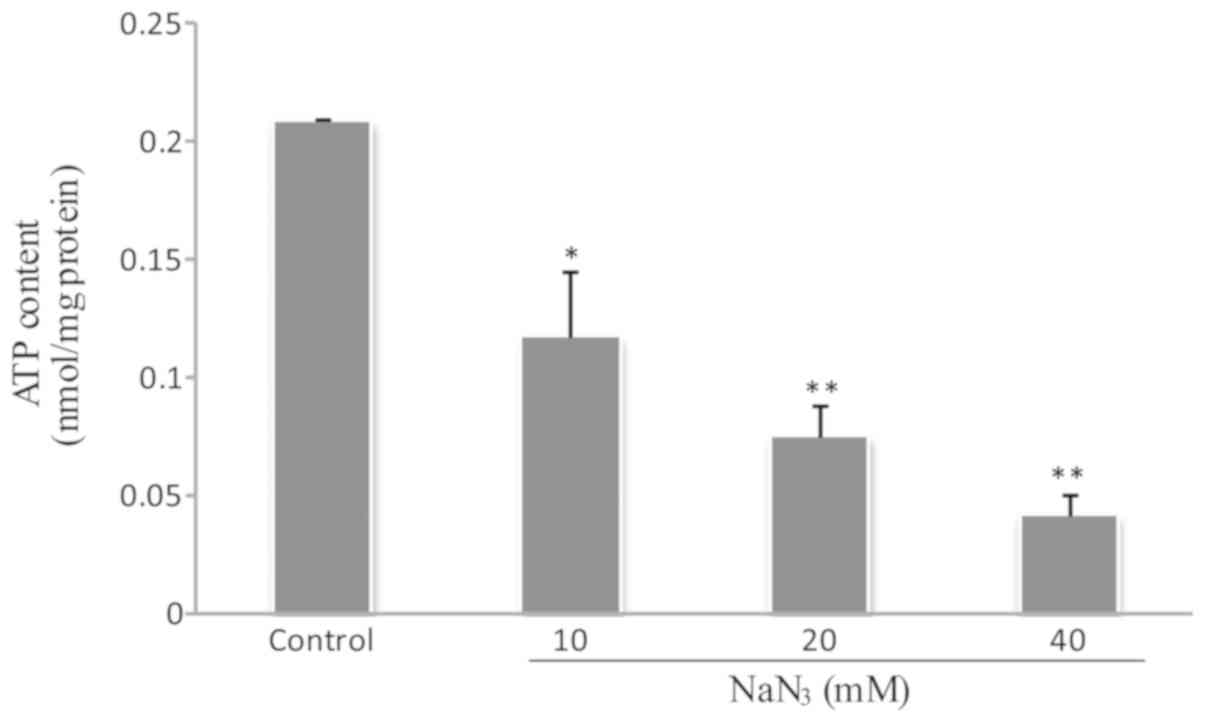
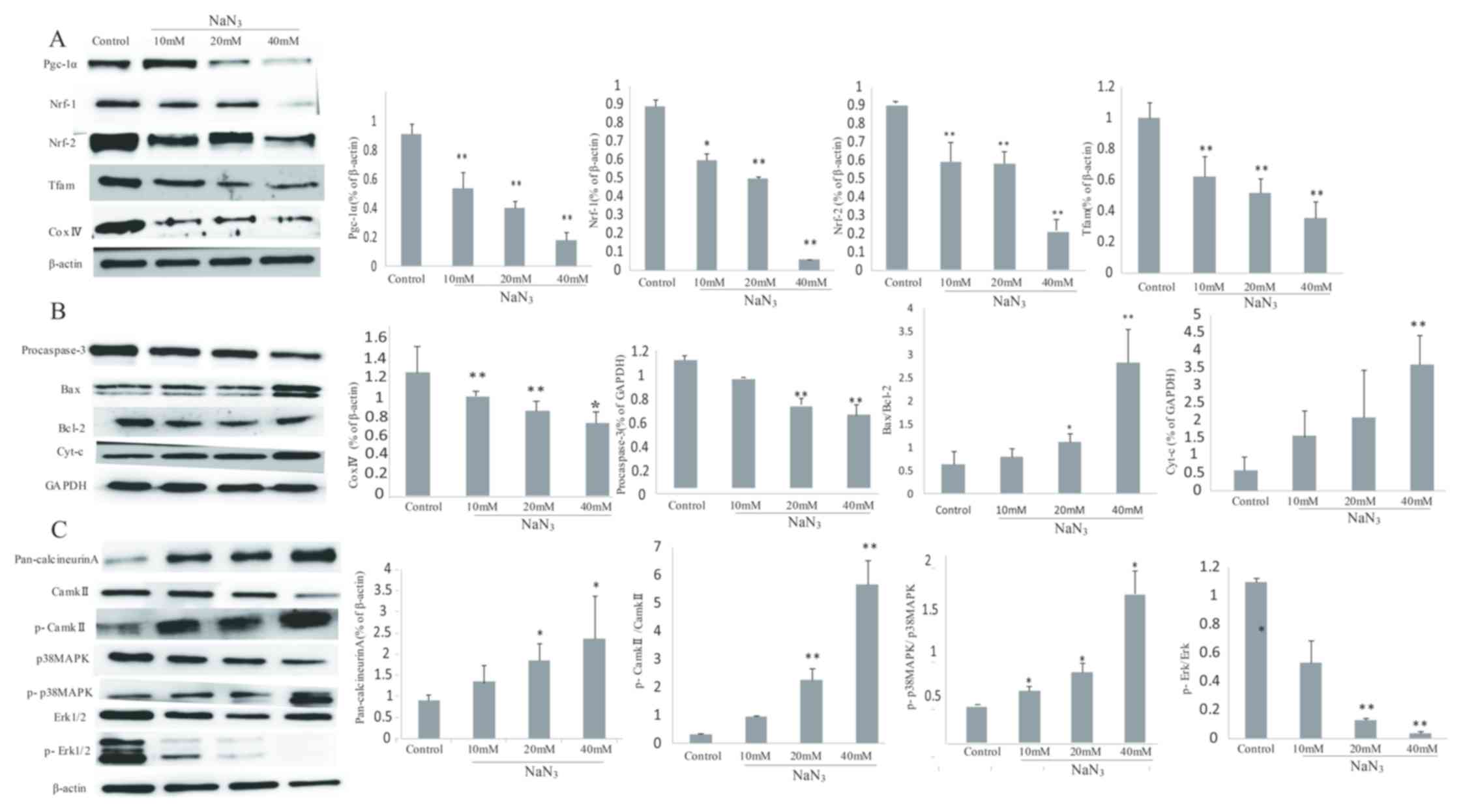
|
1
|
Herbold M, Schmitt G, Aderjan R and Pedal
I: Fatal sodium azide poisoning in a hospital: A preventable
accident. Arch Kriminol. 196:143–148. 1995.(In German). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Marquet P, Clément S, Lotfi H, Dreyfuss
MF, Debord J, Dumont D and Lachâtre G: Analytical findings in a
suicide involving sodium azide. J Anal Toxicol. 20:134–138. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chang S and Lamm SH: Human health effects
of sodium azide exposure: A literature review and analysis. Int J
Toxicol. 22:175–186. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Leary SC, Hills BC, Lyons CN, Carison CG,
Michaud D, Kraft CS, Ko K, Glerum DM and Moyes CD: Chronic
treatment with azide in situ leads to an irreversible loss of
cytochrome c oxidase activity via holoenzyme dissociation. J Biol
Chem. 277:11321–11328. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Grammatopoulos TN, Morris K, Bachar C,
Moore S, Andres R and Weyhenmeyer JA: AngiotensinII attenuates
chemical hypoxia-induced caspase-3 activation in primary cortical
neuronal cultures. Brain Res Bull. 62:297–303. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Scarpulla RC: Metabolic control of
mitochondrial biogenesis through the PGC-1 family regulatory
network. Biochim Biophys Acta 1813. 1269–1278. 2011.
|
|
7
|
Qian G, Guo JB and Li L: The role of
Pgc-1α and mitochondrial regulation in cardiovascular disease.
Chinese Pharmacol Bull. 29:1–5. 2013.
|
|
8
|
Jones AW, Yao Z, Vicencio JM,
Karkucinska-Wieckowska A and Szabadkai G: PGC-1 family coactivators
and cell fate: Roles in cancer, neurodegeneration, cardiovascular
disease and retrograde mitochondria-nucleus signaling.
Mitochondrion. 12:86–99. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kerr JFR, Winterford CM and Harmon BV:
Apoptosis: Its significance in cancer and cancer therapy. Cancer.
73:2013–2026. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chan DC: Mitochondria: Dynamic organelles
in disease, ageing and development. Cell. 125:1241–1252. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Islam MT: Oxidative stress and
mitochondrial dysfunctionlinked neurodegenerative disorders. Neurol
Res. 39:73–82. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chaturvedi RK and Flint BM: Mitochondrial
diseases of the brain. Free Radic Biol Med. 63:1–29. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Van Laar VS, Roy N, Liu A, Raiprohat S,
Arnold B, Dukes AA, Holbein CD and Berman SB: Glutamate
excitotoxicity in neurons triggers mitochondrial and endoplasmic
reticulum accumulation of Parkin and in the presence of N-acetyl
cysteine, mitophagy. Neurobiol Dis. 74:180–193. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu L, Peritore C, Ginsberg J, Shinh J,
Arun S and Donmez G: Protective role of SIRT5 against motor deficit
and dopaminergic degeneration in MPTP-induced mice model of
Parkinson's disease. Behav Brain Res. 281:215–221. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Palomo GM and Manfredi G: Exploring new
pathways of neurodegeneration in ALS: The role of mitochondria
quality control. Brain Res 1607. 36–46. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Youle RJ and Strasser A: The BCL-2 protein
family: Opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 9:47–59. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vercauteren K, Pasko RA, Gleyzer N, Marino
VM and Scarpulla RC: PGC-1-related coactivator: Immediate early
expression and characterization of a CREB/NRF-1 binding domain
associated with cytochrome c promoter occupancy and respiratory
growth. Mol Cell Biol. 26:7409–7419. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Scarpulla RC: Transcriptional paradigms in
mammalian mitochondrial biogenesis and function. Physiol Rev.
88:611–638. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Betts J, Lightowlers RN and Turnbull DM:
Neuropathological aspects of mitochondrial DNA disease. Neurochem
Res. 29:505–511. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tanji K, Kunimatsu T, Vu TH and Bonilla E:
Neuropathological features of mitochondrial disorders. Semin Cell
Dev Biol. 12:429–439. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Aluvila S, Mandal T, Hustedt E, Fajer P,
Choe JY and Oh KJ: Organization of the mitochondrial apoptotic BAK
pore: Oligomerization of the BAK homodimers. J Biol Chem.
289:2537–2551. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang E, Zha J, Jockel J, Boise LH,
Thompson CB and Korsmeyer SJ: Bad, a heterodimeric partner for
Bcl-XL and Bcl-2, displaces Bax and promotes cell death. Cell.
80:285–291. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hock MB and Kralli A: Transcriptional
control of mitochondrial biogenesis and function. Annu Rev Physiol.
71:177–203. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Handschin C, Rhee J, Lin J, Tarr PT and
Spieglman BM: An autoregulatory loop controls peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1alpha expression
in muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:7111–7116. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Schaeffer PJ, Wende AR, Magee CJ, Neilson
JR, Leone TC, Chen F and Kelly DP: Calcineurin and
calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase activate distinct
metabolic gene regulatory programs in cardiac muscle. J Biol Chem.
279:593–603. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Rohas LM, St-Pierre J, Uldry M, Jäger S,
Handschin S and Spiegelman BM: A fundamental system of cellular
energy homeostasis regulated by PGC-1 alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 104:7933–7938. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Puigserver P, Rhee J, Lin J, Wu Z, Yoon
JC, Zhang CY, Krauss S, Mootha VK, Lowell BB and Spiegelman BM:
Cytokine stimulation of energy expenditure through p38 MAP kinase
activation of PPARgamma coactivator-1. Mol Cell. 8:971–982. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|