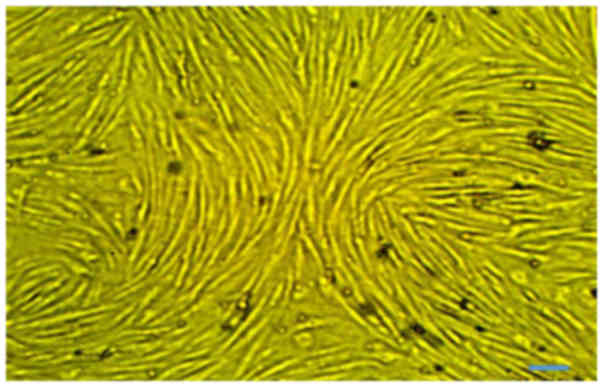
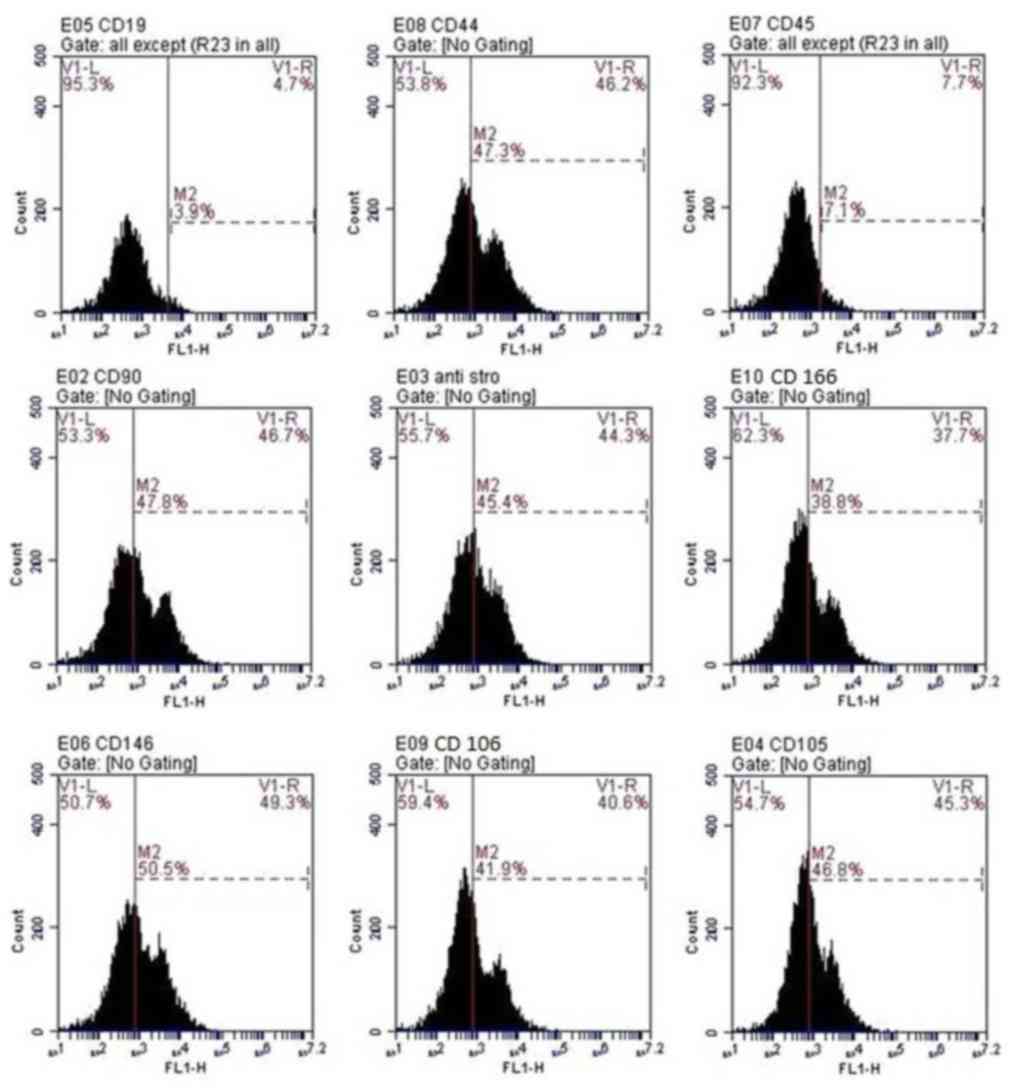
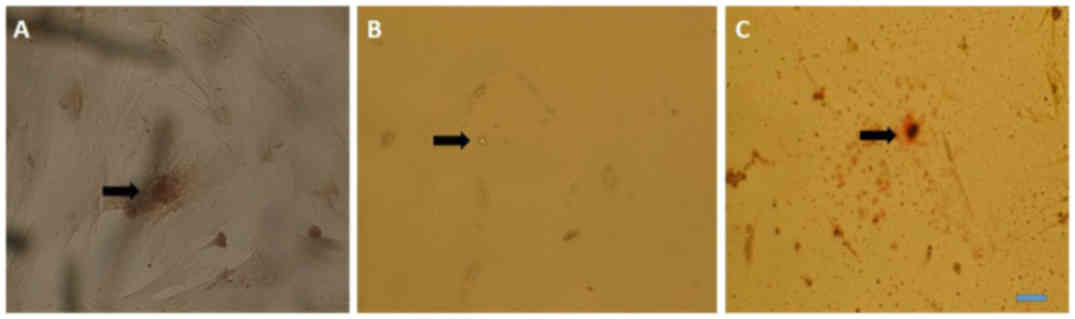
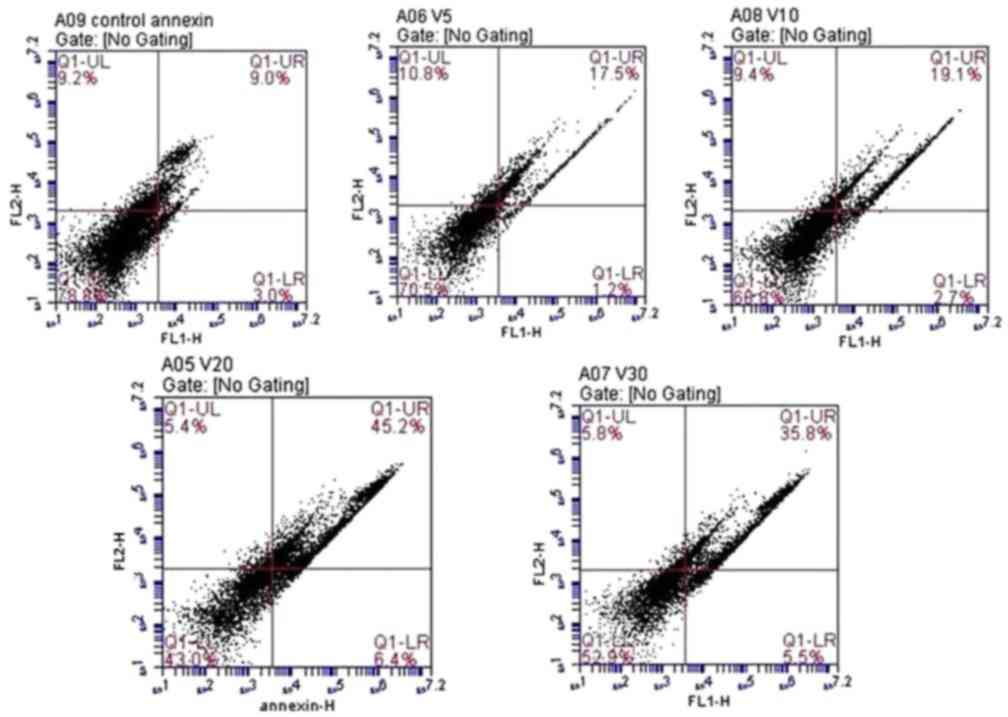
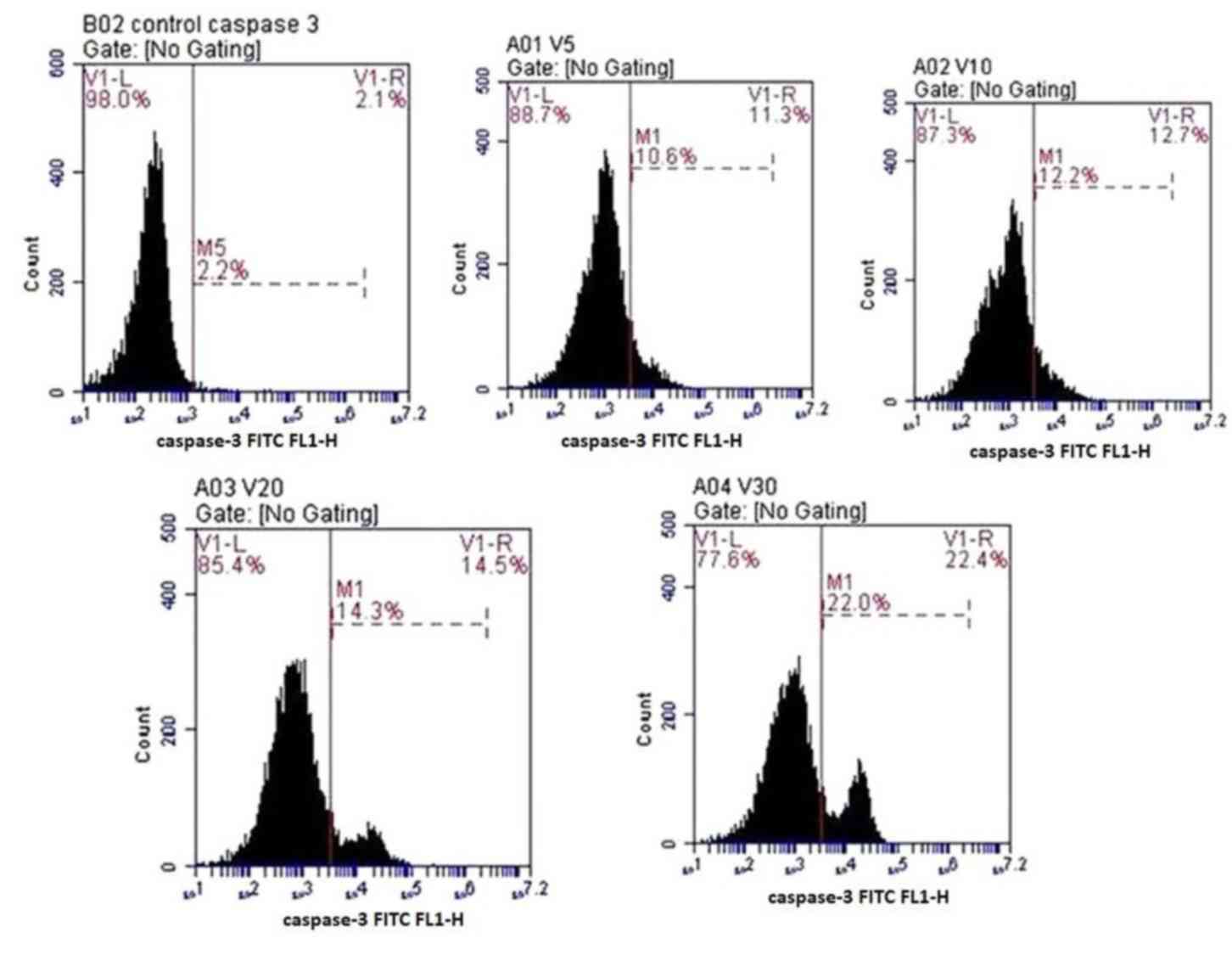
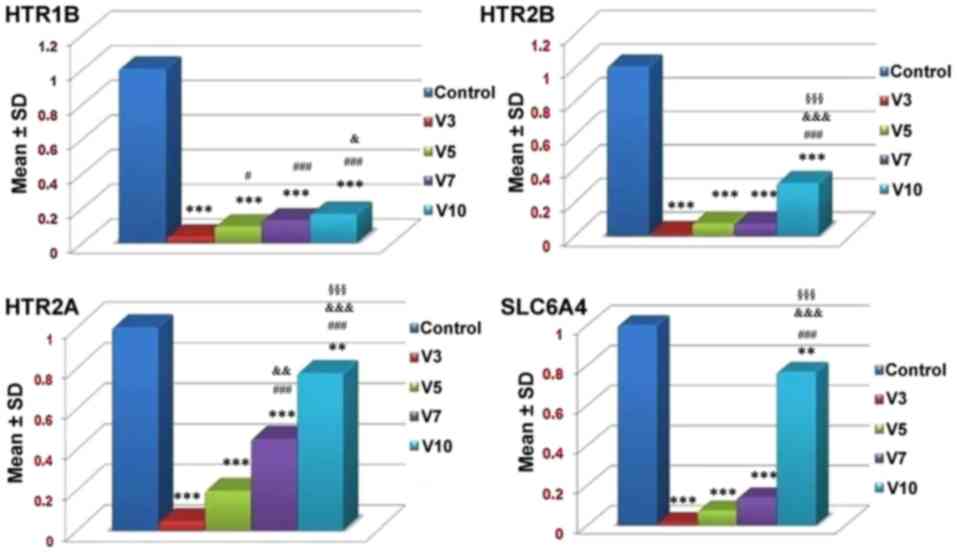
|
1
|
Haney EM, Chan BK, Diem SJ, Ensrud KE,
Cauley JA, Barrett-Connor E, Orwoll E and Bliziotes MM;
Osteoporotic Fractures in Men Study Group, : Association of low
bone mineral density with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
use by older men. Arch Intern Med. 167:1246–1251. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Haney EM, Warden SJ and Bliziotes MM: The
effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors on bone health
in adults: Time for recommendations about screening, prevention and
management? Bone. 46:13–17. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen F, Hahn TJ and Weintraub NT: Do SSRIs
play a role in decreasing bone mineral density? J Am Med Dir Assoc.
13:413–417. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bliziotes MM, Eshleman AJ, Zhang XW and
Wiren KM: Neurotransmitter action in osteoblasts: Expression of a
functional system for serotonin receptor activation and reuptake.
Bone. 29:477–486. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Westbroek I, van der Plas A, de Rooij KE,
Klein-Nulend J and Nijweide PJ: Expression of serotonin receptors
in bone. J Biol Chem. 276:28961–28968. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chau K, Atkinson SA and Taylor VH: Are
selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors a secondary cause of low
bone density? J Osteoporos. 2012:3230612012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bab I and Yirmiya R: Depression, selective
serotonin reuptake inhibitors, and osteoporosis. Curr Osteoporos
Rep. 8:185–191. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bradaschia-Correa V, Josephson AM, Mehta
D, Mizrahi M, Neibart SS, Liu C, Kennedy OD, Castillo AB, Egol KA
and Leucht P: The selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor fluoxetine
directly inhibits osteoblast differentiation and mineralization
during fracture healing in mice. J Bone Miner Res. 32:821–833.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zuk PA, Zhu M, Ashjian P, De Ugarte DA,
Huang JI, Mizuno H, Alfonso ZC, Fraser JK, Benhaim P and Hedrick
MH: Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol
Biol Cell. 13:4279–4295. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zimmerlin L, Donnenberg VS and Donnenberg
AD: Rare event detection and analysis in flow cytometry: Bone
marrow mesenchymal stem cells, breast cancer stem/progenitor cells
in malignant effusions, and pericytes in disaggregated adipose
tissue. Methods Mol Biol. 699:251–273. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Halvorsen YD, Franklin D, Bond AL, Hitt
DC, Auchter C, Boskey AL, Paschalis EP, Wilkison WO and Gimble JM:
Extracellular matrix mineralization and osteoblast gene expression
by human adipose tissue-derived stromal cells. Tissue Eng.
7:729–741. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Salamh M, Mehanna R, Hanafy Sh and Abdel
Ghafar H: The usage of liver extract verses growth factors in the
differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocyte like
cells. J Int Acad Res Multidisciplinary. 2:35–50. 2014.
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C (T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dale E, Bang-Andersen B and Sánchez C:
Emerging mechanisms and treatments for depression beyond SSRIs and
SNRIs. Biochem Pharmacol. 95:81–97. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tsapakis EM, Gamie Z, Tran GT, Adshead S,
Lampard A, Mantalaris A and Tsiridi E: The adverse skeletal effects
of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Eur Psychiatry.
27:156–169. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hodge JM, Wang Y, Berk M, Collier FM,
Fernandes TJ, Constable MJ, Pasco JA, Dodd S, Nicholson GC, Kennedy
RL and Williams LJ: Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors inhibit
human osteoclast and osteoblast formation and function. Biol
Psychiatry. 74:32–39. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ortuño MJ, Robinson ST, Subramanyam P,
Paone R, Huang YY, Guo XE, Colecraft HM, Mann JJ and Ducy P:
Serotonin-reuptake inhibitors act centrally to cause bone loss in
mice by counteracting a local anti-resorptive effect. Nat Med.
22:1170–1179. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Schaz U, Föhr KJ, Liebau S, Fulda S,
Koelch M, Fegert JM, Boeckers TM and Ludolph AG: Dose-dependent
modulation of apoptotic processes by fluoxetine in maturing
neuronal cells: An in vitro study. World J Biol Psychiatry.
12:89–98. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rafiei M, Sadeghian S, Torabinia N and
Hajhashemi V: Systemic effects of fluoxetine on the amount of tooth
movement, root resorption, and alveolar bone remodeling during
orthodontic force application in rat. Dent Res J (Isfahan).
12:482–487. 2017.
|
|
20
|
Gustafsson BI, Westbroek I, Waarsing JH,
Waldum H, Solligård E, Brunsvik A, Dimmen S, van Leeuwen JP,
Weinans H and Syversen U: Long-term serotonin administration leads
to higher bone mineral density, affects bone architecture, and
leads to higher femoral bone stiffness in rats. J Cell Biochem.
97:1283–1291. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dai SQ, Yu LP, Shi X, Wu H, Shao P, Yin GY
and Wei YZ: Serotonin regulates osteoblast proliferation and
function in vitro. Braz J Med Biol Res. 47:759–765. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nam SS, Lee JC, Kim HJ, Park JW, Lee JM,
Suh JY, Ums HS, Kim JY, Lee Y and Kim YG: Serotonin inhibits
osteoblast differentiation and bone regeneration in rats. J
Periodontol. 87:461–469. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Battaglino R, Vokes M, Schulze-Späte U,
Sharma A, Graves D, Kohler T, Müller R, Yoganathan S and Stashenko
P: Fluoxetine treatment increases trabecular bone formation in
mice. J Cell Biochem. 100:1387–1394. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mortazavi SH, Khojasteh A, Vaziri H,
Khoshzaban A, Roudsari MV and Razavi SH: The effect of fluoxetine
on bone regeneration in rat calvarial bone defects. Oral Surg Oral
Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 108:22–27. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|