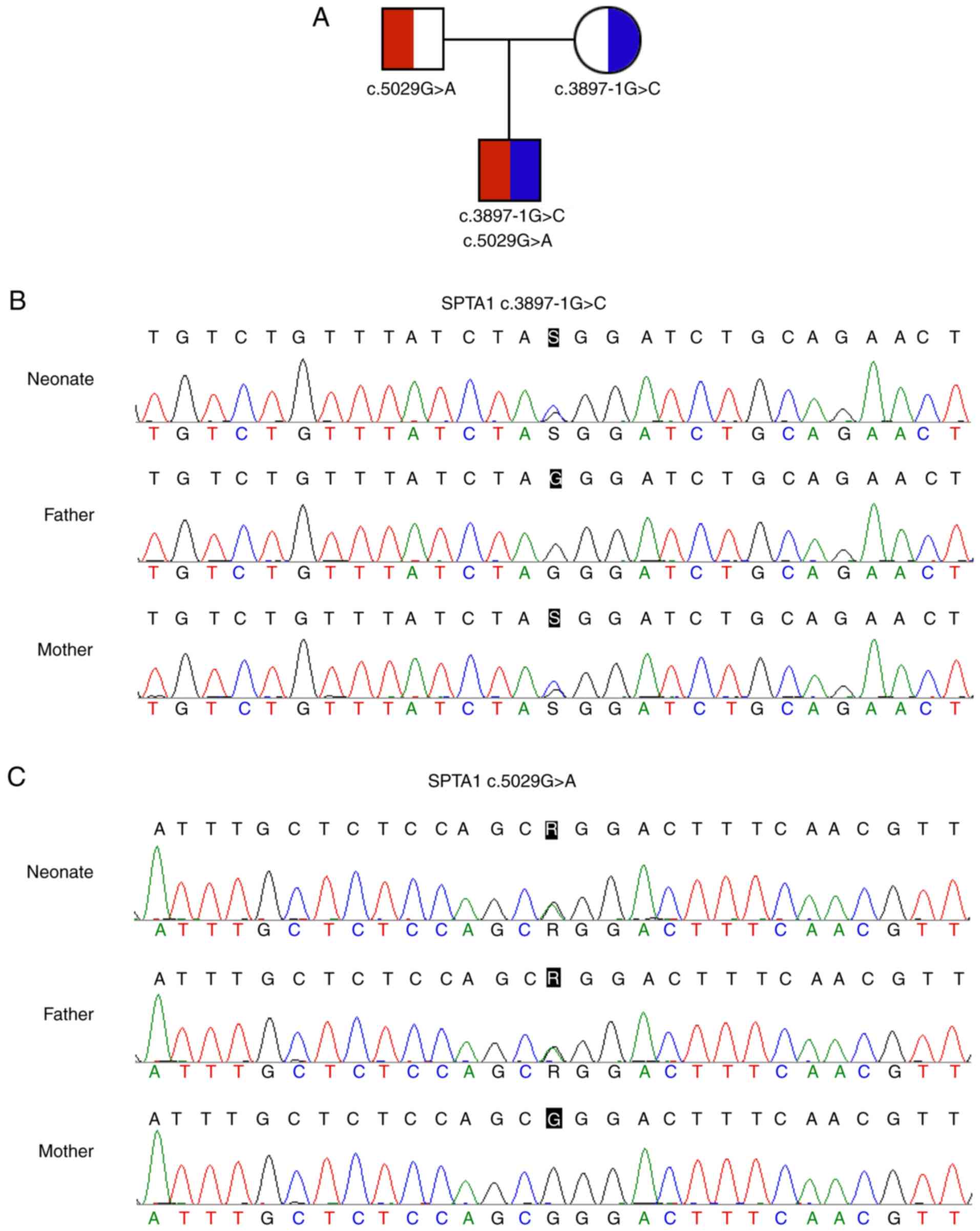
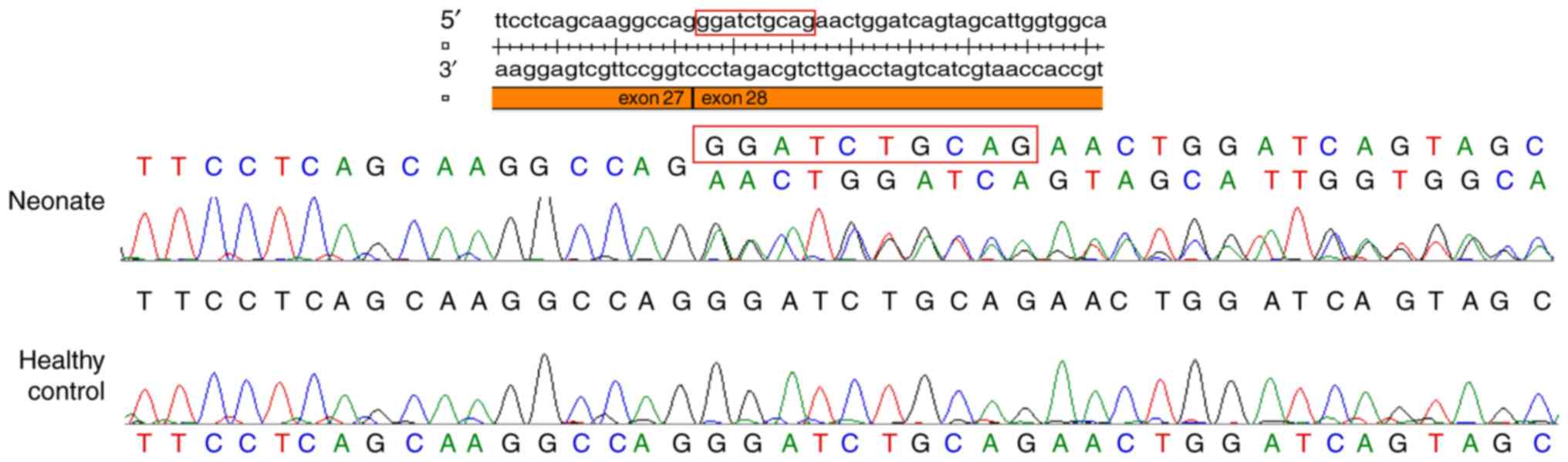
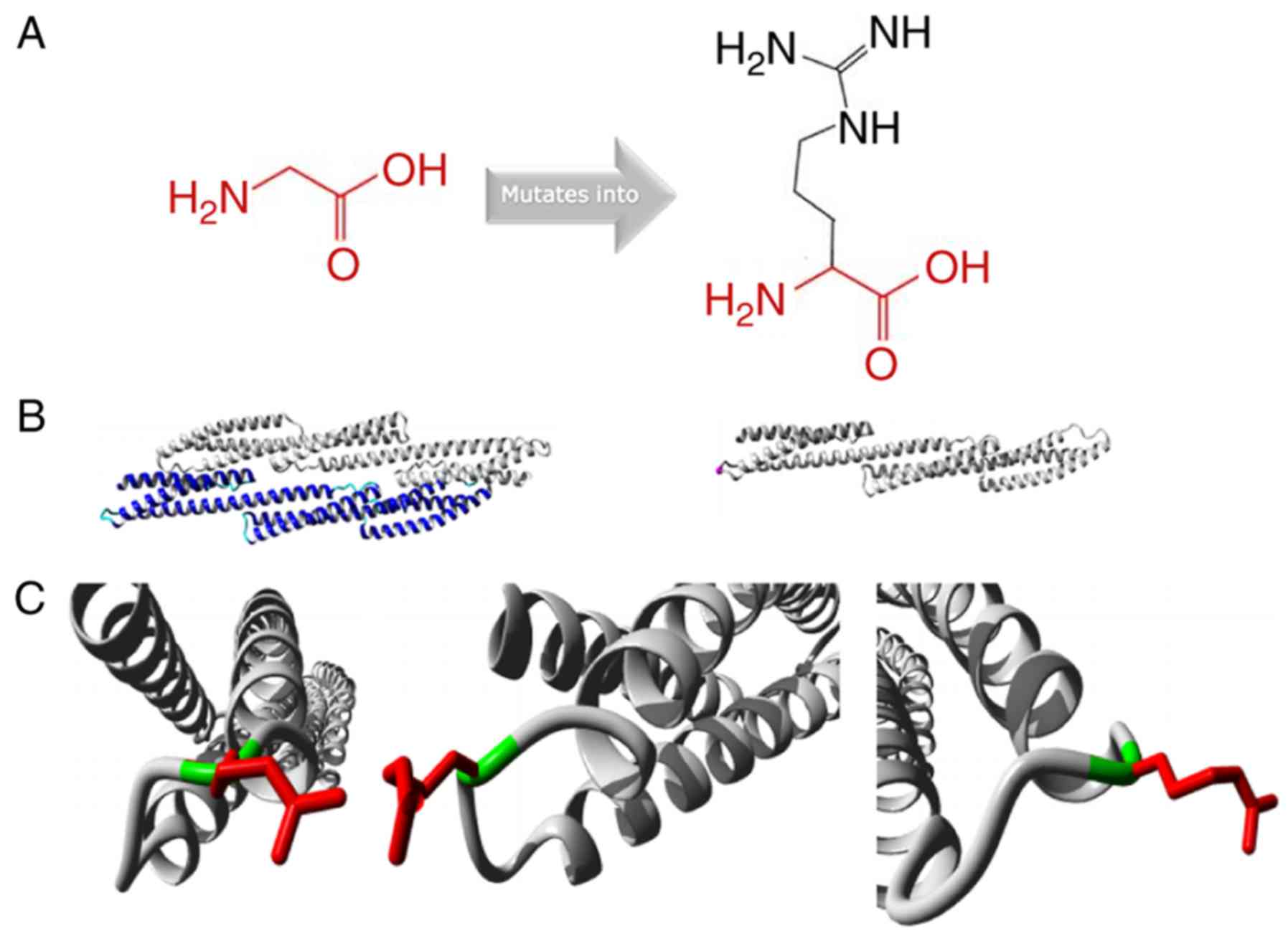
|
1
|
Da Costa L, Galimand J, Fenneteau O and
Mohandas N: Hereditary spherocytosis, elliptocytosis, and other red
cell membrane disorders. Blood Rev. 27:167–178. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang X, Shen N, Huang M, Lu Y and Hu Q:
Novel hereditary spherocytosis-associated splice site mutation in
the ANK1 gene caused by parental gonosomal mosaicism.
Haematologica. 103:e219–e222. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Iolascon A, Andolfo I, Barcellini W,
Corcione F, Garçon L, De Franceschi L, Pignata C, Graziadei G,
Pospisilova D, Rees DC, et al: Recommendations regarding
splenectomy in hereditary hemolytic anemias. Haematologica.
102:1304–1313. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Johnson L, Bhutani VK, Karp K, Sivieri EM
and Shapiro SM: Clinical report from the pilot USA kernicterus
registry (1992 to 2004). J Perinatol. 29 (Suppl 1):S25–S45. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gallagher PG: Disorders of red cell volume
regulation. Curr Opin Hematol. 20:201–207. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Christensen RD, Yaish HM and Gallagher PG:
A pediatrician's practical guide to diagnosing and treating
hereditary spherocytosis in neonates. Pediatrics. 135:1107–1114.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Andres O, Eber S and Speer CP: Early
postnatal diagnosis of hereditary spherocytosis by combining light
microscopy, acidified glycerol lysis test and eosin-5′-maleimide
binding assay. Ann Hematol. 94:1959–1964. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
An X and Mohandas N: Disorders of red cell
membrane. Br J Haematol. 141:367–375. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yawata Y, Kanzaki A, Yawata A, Doerfler W,
Ozcan R and Eber SW: Characteristic features of the genotype and
phenotype of hereditary spherocytosis in the Japanese population.
Int J Hematol. 71:118–135. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Speicher DW, DeSilva TM, Speicher KD,
Ursitti JA, Hembach P and Weglarz L: Location of the human red cell
spectrin tetramer binding site and detection of a related ‘closed’
hairpin loop dimer using proteolytic footprinting. J Biol Chem.
268:4227–4235. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lam VQ, Antoniou C, Rolius R and Fung LW:
Association studies of erythroid alpha-spectrin at the
tetramerization site. Br J Haematol. 147:392–395. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Narla J and Mohandas N: Red cell membrane
disorders. Int J Lab Hematol. 39 (Suppl 1):S47–S52. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Perrotta S, Gallagher PG and Mohandas N:
Hereditary spherocytosis. Lancet. 372:1411–1426. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li Q and Wang K: InterVar: Clinical
interpretation of genetic variants by the 2015 ACMG-AMP guidelines.
Am J Hum Genet. 100:267–280. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kumar P, Henikoff S and Ng PC: Predicting
the effects of coding non-synonymous variants on protein function
using the SIFT algorithm. Nat Protoc. 4:1073–1081. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schwarz JM, Cooper DN, Schuelke M and
Seelow D: MutationTaster2: Mutation prediction for the
deep-sequencing age. Nat Methods. 11:361–362. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Adzhubei I, Jordan DM and Sunyaev SR:
Predicting functional effect of human missense mutations using
PolyPhen-2. Curr Protoc Hum Genet Chapter. 7:Unit7.202013.
|
|
18
|
Wang X, Zhu Y, Shen N, Peng J, Wang C, Liu
H and Lu Y: Mutation analysis of a Chinese family with
oculocutaneous albinism. Oncotarget. 7:84981–84988. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Venselaar H, Te Beek TA, Kuipers RK,
Hekkelman ML and Vriend G: Protein structure analysis of mutations
causing inheritable diseases. An e-Science approach with life
scientist friendly interfaces. BMC Bioinformatics. 11:5482010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Auer PL, Reiner AP, Wang G, Kang HM,
Abecasis GR, Altshuler D, Bamshad MJ, Nickerson DA, Tracy RP, Rich
SS, et al: Guidelines for large-scale sequence-based complex trait
association studies: Lessons learned from the NHLBI exome
sequencing project. Am J Hum Genet. 99:791–801. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zheng-Bradley X and Flicek P: Applications
of the 1000 genomes project resources. Brief Funct Genomics.
16:163–170. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lek M, Karczewski KJ, Minikel EV, Samocha
KE, Banks E, Fennell T, O'Donnell-Luria AH, Ware JS, Hill AJ,
Cummings BB, et al: Analysis of protein-coding genetic variation in
60,706 humans. Nature. 536:285–291. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, Bick D, Das S,
Gastier-Foster J, Grody WW, Hegde M, Lyon E, Spector E, et al:
Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence
variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College
of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular
Pathology. Genet Med. 17:405–424. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Christensen RD, Nussenzveig RH, Yaish HM,
Henry E, Eggert LD and Agarwal AM: Causes of hemolysis in neonates
with extreme hyperbilirubinemia. J Perinatol. 34:616–619. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yaish HM, Christensen RD and Agarwal A: A
neonate with Coombs-negative hemolytic jaundice with spherocytes
but normal erythrocyte indices: A rare case of autosomal-recessive
hereditary spherocytosis due to alpha-spectrin deficiency. J
Perinatol. 33:404–406. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Christensen RD and Henry E: Hereditary
spherocytosis in neonates with hyperbilirubinemia. Pediatrics.
125:120–125. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sheffield MJ and Christensen RD:
Evaluating neonatal hyperbilirubinemia in late preterm Hispanic
twins led to the diagnosis of hereditary spherocytosis in them, and
in their sibling and in their mother. J Perinatol. 31:625–627.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Agarwal AM, Nussenzveig RH, Reading NS,
Patel JL, Sangle N, Salama ME, Prchal JT, Perkins SL, Yaish HM and
Christensen RD: Clinical utility of next-generation sequencing in
the diagnosis of hereditary haemolytic anaemias. Br J Haematol.
174:806–814. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang X, Yi B, Mu K, Shen N, Zhu Y, Hu Q
and Lu Y: Identification of a novel de novo ANK1 R1426* nonsense
mutation in a Chinese family with hereditary spherocytosis by NGS.
Oncotarget. 8:96791–96797. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
He Y, Jia S, Dewan RK and Liao N: Novel
mutations in patients with hereditary red blood cell membrane
disorders using next-generation sequencing. Gene. 627:556–562.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang R, Yang S, Xu M, Huang J, Liu H, Gu W
and Zhang X: Exome sequencing confirms molecular diagnoses in 38
Chinese families with hereditary spherocytosis. Sci China Life Sci.
61:947–953. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Farias MG: Advances in laboratory
diagnosis of hereditary spherocytosis. Clin Chem Lab Med.
55:944–948. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wichterle H, Hanspal M, Palek J and
Jarolim P: Combination of two mutant alpha spectrin alleles
underlies a severe spherocytic hemolytic anemia. J Clin Invest.
98:2300–2307. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nussenzveig RH, Christensen RD, Prchal JT,
Yaish HM and Agarwal AM: Novel α-spectrin mutation in trans
with alpha-spectrin causing severe neonatal jaundice from
hereditary spherocytosis. Neonatology. 106:355–357. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|