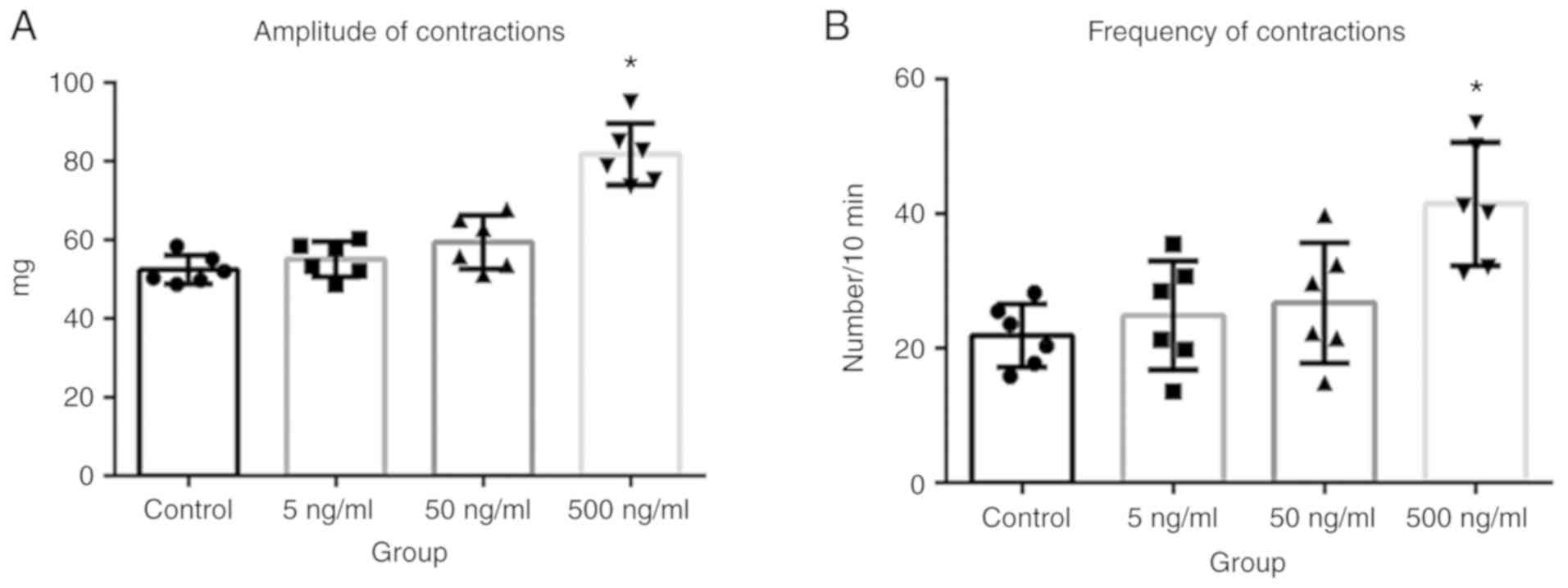
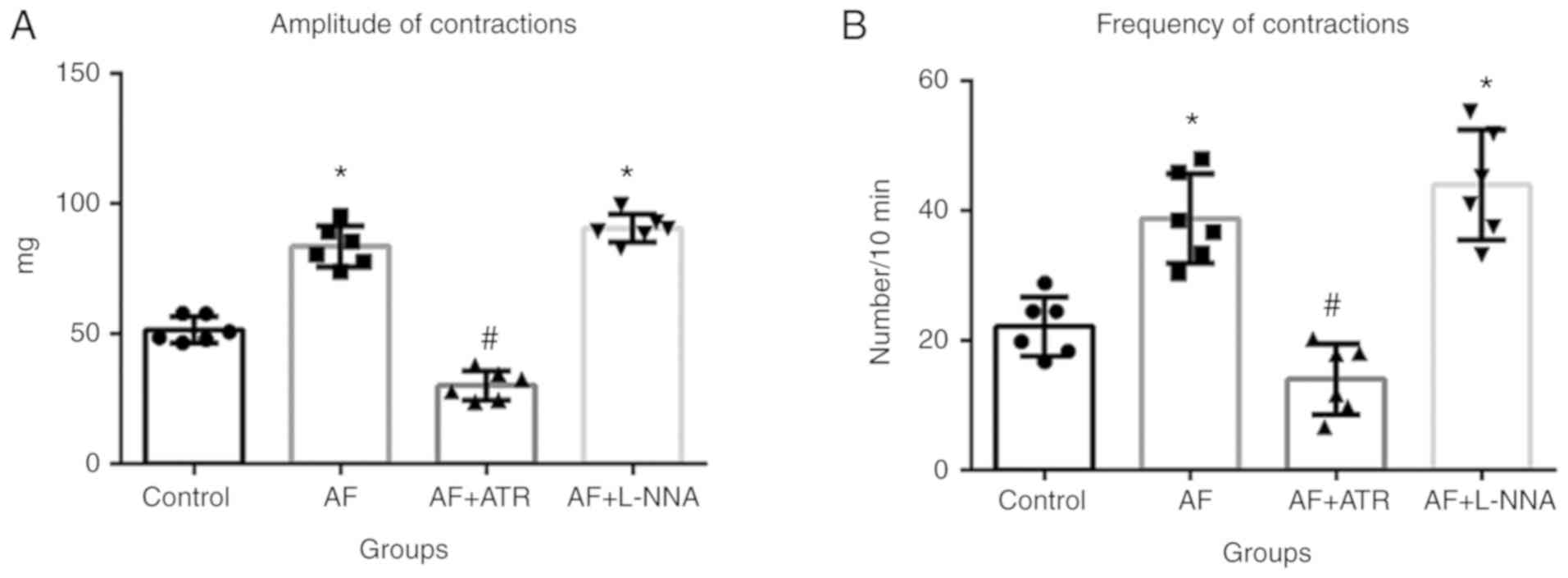
|
1
|
Sadowski DC, Ackah F, Jiang B and Svenson
LW: Achalasia: Incidence, prevalence and survival. A
population-based study. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 22:e256–e261.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Birgisson S and Richter JE: Achalasia in
Iceland, 1952–2002: An epidemiologic study. Dig Dis Sci.
52:1855–1860. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gennaro N, Portale G, Gallo C, Rocchietto
S, Caruso V, Costantini M, Salvador R, Ruol A and Zaninotto G:
Esophageal achalasia in the veneto region: Epidemiology and
treatment. Epidemiology and treatment of achalasia. J Gastrointest
Surg. 15:423–428. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Marlais M, Fishman JR, Fell JM, Haddad MJ
and Rawat DJ: UK incidence of achalasia: An 11 year national
epidemiological study. Arch Dis Child. 96:192–194. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Clark SB, Rice TW, Tubbs RR, Richter JE
and Goldblum JR: The nature of the myenteric infiltrate in
achalasia: An immunohistochemical analysis. Am J Surg Pathol.
24:1153–1158. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Villanacci V, Annese V, Cuttitta A,
Fisogni S, Scaramuzzi G, De Santo E, Corazzi N and Bassotti G: An
immunohistochemical study of the myenteric plexus in idiopathic
achalasia. J Clin Gastroenterol. 44:407–410. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Park W and Vaezi MF: Etiology and
pathogenesis of achalasia: The current understanding. Am J
Gastroenterol. 100:1404–1414. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mohamed AA, Lu XL and Mounmin FA:
Diagnosis and treatment of esophageal candidiasis: Current updates.
Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 20:35851362019.
|
|
9
|
Meijssen MA, Tilanus HW, van Blankenstein
M, Hop WC and Ong GL: Achalasia complicated by oesophageal squamous
cell carcinoma: A prospective study in 195 patients. Gut.
33:155–158. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Streitz JM, Ellis FH, Gibb SP and Heatley
GM: Achalasia and squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus:
Analysis of 241 patients. Ann Thorac Surg. 59:1604–1609. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tustumi F, Bernardo WM, da Rocha JRM,
Szachnowicz S, Seguro FC, Bianchi ET, Sallum RAA and Cecconello I:
Esophageal achalasia: A risk factor for carcinoma. A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Dis Esophagus. 30:1–8. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ghasemi-Kebria F, Joshaghani H, Taheri NS,
Semnani S, Aarabi M, Salamat F and Roshandel G: Aflatoxin
contamination of wheat flour and the risk of esophageal cancer in a
high risk area in Iran. Cancer Epidemiol. 37:290–293. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Marchese S, Polo A, Ariano A, Velotto S,
Costantini S and Severino L: Aflatoxin B1 and M1: Biological
properties and their involvement in cancer development. Toxins
(Basel). 24:E2142018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Rawal S, Kim JE and Coulombe R Jr:
Aflatoxin B1 in poultry: Toxicology, metabolism and prevention. Res
Vet Sci. 89:325–331. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Raisuddin S, Singh K, Zaidi S, Paul BN and
Ray PK: Immunosuppressive effects of aflatoxin in growing rats.
Mycopathologia. 124:189–194. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Marin D, Taranu I, Bunaciu RP, Pascale F,
Tudor DS, Avram N, Sarca M, Cureu I, Criste RD, Suta V and Oswald
IP: Changes in performance, blood parameters, humoral and cellular
immune responses in weanling piglets exposed to low doses of
aflatoxin. J Anim Sci. 80:1250–1257. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Park JW, Kim EK, Shon DH and Kim YB:
Natural co-occurrence of aflatoxin B1, fumonsin B1, and ochratoxin
A in barley and maize foods from Korea. Food Addit Contam.
19:1073–1080. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Inoue H, Minami H, Kobayashi Y, Sato Y,
Kaga M, Suzuki M, Satodate H, Odaka N, Itoh H and Kudo S: Peroral
endoscopic myotomy (POEM) for esophageal achalasia. Endoscopy.
42:265–271. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou PH, Li QL, Yao LQ, Xu MD, Chen WF,
Cai MY, Hu JW, Li L, Zhang YQ, Zhong YS, et al: Peroral endoscopic
remyotomy for failed heller myotomy: A prospective single-center
study. Endoscopy. 45:161–166. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Khashab MA, Messallam AA, Onimaru M,
Teitelbaum EN, Ujiki MB, Gitelis ME, Modayil RJ, Hungness ES,
Stavropoulos SN, El Zein MH, et al: International multi-center
experience with peroral endoscopic myotomy for the treatment of
spastic esophageal disorders refractory to medical therapy (with
video). Gastrointest Endosc. 81:1170–1177. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jones EL, Meara MP, Pittman MR, Hazey JW
and Perry KA: Prior treatment does not influence the performance or
early outcome of per-oral endoscopic myotomy for achalasia. Surg
Endosc. 30:1282–1286. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Inoue H, Sato H, Ikeda H, Onimaru M, Sato
C, Minami H, Yokomichi H, Kobayashi Y, Grimes KL and Kudo SE:
Per-Oral endoscopic myotomy: A series of 500 patients. J Am Coll
Surg. 221:256–264. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Minami H, Yamaguchi N, Matsushima K,
Akazawa Y, Ohnita K, Takeshima F, Nakayama T, Hayashi T, Inoue H,
Nakao K and Isomoto H: Improvement of endocytoscopic findings after
per oral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) in esophageal achalasia; does
POEM reduce the risk of developing esophageal carcinoma? Per oral
endoscopic myotomy, endocytoscopy and carcinogenesis. BMC
Gastroenterol. 30:222013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wang J and Liu XM: Assessment of dietary
aflatoxin exposure in Chinese residents. Chin J Food Hyg.
19:238–240. 2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
25
|
Eckardt V: Clinical presentations and
complications of achalasia. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am.
11281–292. (vi)2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pandolfino JE, Kwiatek MA, Nealis T,
Bulsiewicz W, Post J and Kahrilas PJ: Achalasia: A new clinically
relevant classification by high-resolution manometry.
Gastroenterology. 135:1526–1533. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Eckardt AJ and Eckardt VF: Treatment and
surveillance strategies in achalasia: An update. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 8:311–319. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ferri F, Brera C, De Santis B, Fedrizzi G,
Bacci T, Bedogni L, Capanni S, Collini G, Crespi E, Debegnach F, et
al: Survey on urinary levels of aflatoxins in professionally
exposed workers. Toxins (Basel). 9:E1172017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yard EE, Daniel JH, Lewis LS, Rybak ME,
Paliakov EM, Kim AA, Montgomery JM, Bunnell R, Abudo MU, Akhwale W,
et al: Human aflatoxin exposure in Kenya, 2007: A cross-sectional
study. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess.
30:1322–1331. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fujii T, Yamana H, Sueyoshi S, Fujita H,
Tanaka Y, Kubota M, Toh U, Mine T, Sasahara H, Shirouzu K, et al:
Histopathological analysis of non-malignant and malignant
epithelium in achalasia of the esophagus. Dis Esophagus.
13:110–116. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Leeuwenburgh I, Gerrits MM, Capello A, van
den Bogert B, van Dekken H, Steyerberg EW, Siersema PD and Kuipers
EJ: Expression of p53 as predictor for the development of
esophageal cancer in achalasia patients. Dis Esophagus. 23:506–511.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Peraica M, Radic B, Lucic A and Pavlović
M: Toxic effects of mycotoxins in humans. Bull World Health Organ.
77:754–766. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Luzi A, Cometa MF and Palmery M: Acute
effects of aflatoxins on guinea pig isolated ileum. Toxicol In
Vitro. 6:525–529. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Gursoy N, Durmus N, Bagcivan I, Sarac B,
Parlak A, Yildirim S and Kaya T: Investigation of acute effects of
aflatoxin on rat proximal and distal colon spontaneous
contractions. Food Chem Toxicol. 46:2876–2880. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gockel HR, Schumacher J, Gockel I, Lang H,
Haaf T and Nöthen MM: Achalasia: Will genetic studies provide
insights? Hum Genet. 128:353–364. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Boeckxstaens GE: Achalasia: Virus-induced
euthanasia of neurons? Am J Gastroenterol. 103:1610–1612. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rohof WO, Salvador R, Annese V, Bruley des
Varannes S, Chaussade S, Costantini M, Elizalde JI, Gaudric M,
Smout AJ, Tack J, et al: Outcomes of treatment for achalasia depend
on manometric subtype. Gastroenterology. 144:718–725. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Eckardt VF, Kohne U, Junginger T and
Westermeier T: Risk factors for diagnostic delay in achalasia. Dig
Dis Sci. 42:580–585. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
El-Takli I, O'Brien P and Paterson WG:
Clinical diagnosis of achalasia: How reliable is the barium x-ray?
Can J Gastroenterol. 20:335–337. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ghoshal UC, Daschakraborty SB and Singh R:
Pathogenesis of achalasia cardia. World J Gastroenterol.
28:3050–3057. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Moon EY and Pyo S: Aflatoxin B(1) inhibits
CD14-mediated nitric oxide production in murine peritoneal
macrophages. Int J Immunopharmacol. 22:237–246. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Moon EY, Rhee DK and Pyo S: Inhibition of
various functions in murine peritoneal macrophages by aflatoxin B1
exposure in vivo. Int J Immunopharmacol. 21:47–58. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Moon EY, Han JJ, Rhee DK and Pyo S:
Aflatoxin B1-induced suppression of nitric oxide production in
murine peritoneal macrophages. J Toxicol Environ Health A.
55:517–530. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Khajanchee YS, VanAndel R, Jobe BA, Barra
MJ, Hansen PD and Swanstrom LL: Electrical stimulation of the vagus
nerve restores motility in an animal model of achalasia. J
Gastrointest Surg. 7:843–849. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
de Souza EM, Rivera MT, Araujo-Jorge TC
and de Castro SL: Modulation induced by estradiol in the acute
phase of Trypanosoma cruzi infection in mice. Parasitol Res.
87:513–520. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ming Z and Davis CD: CD8+ T
lymphocytes required for enhanced survival of Trypanosoma
cruzi-infected mice at elevated environmental temperature. J
Parasitol. 89:630–632. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|