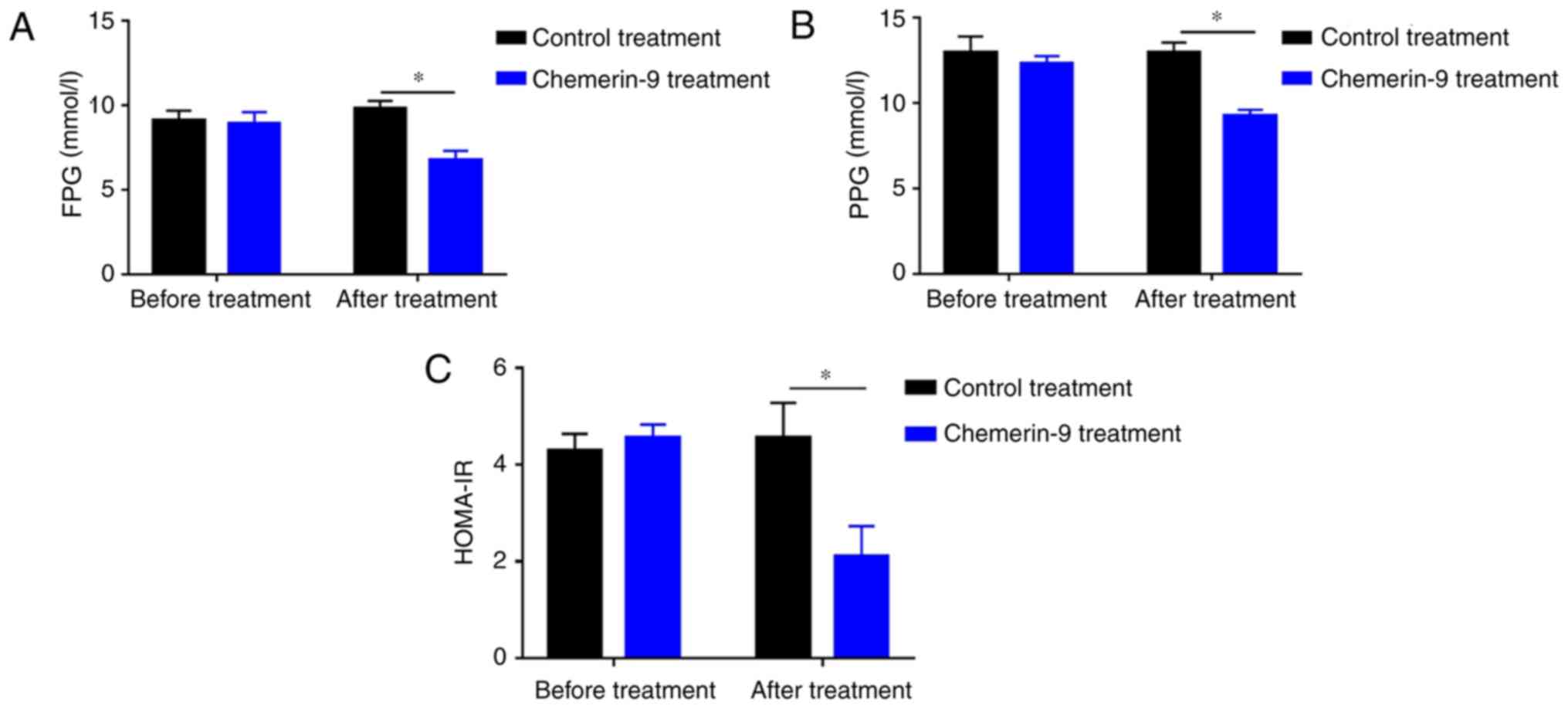
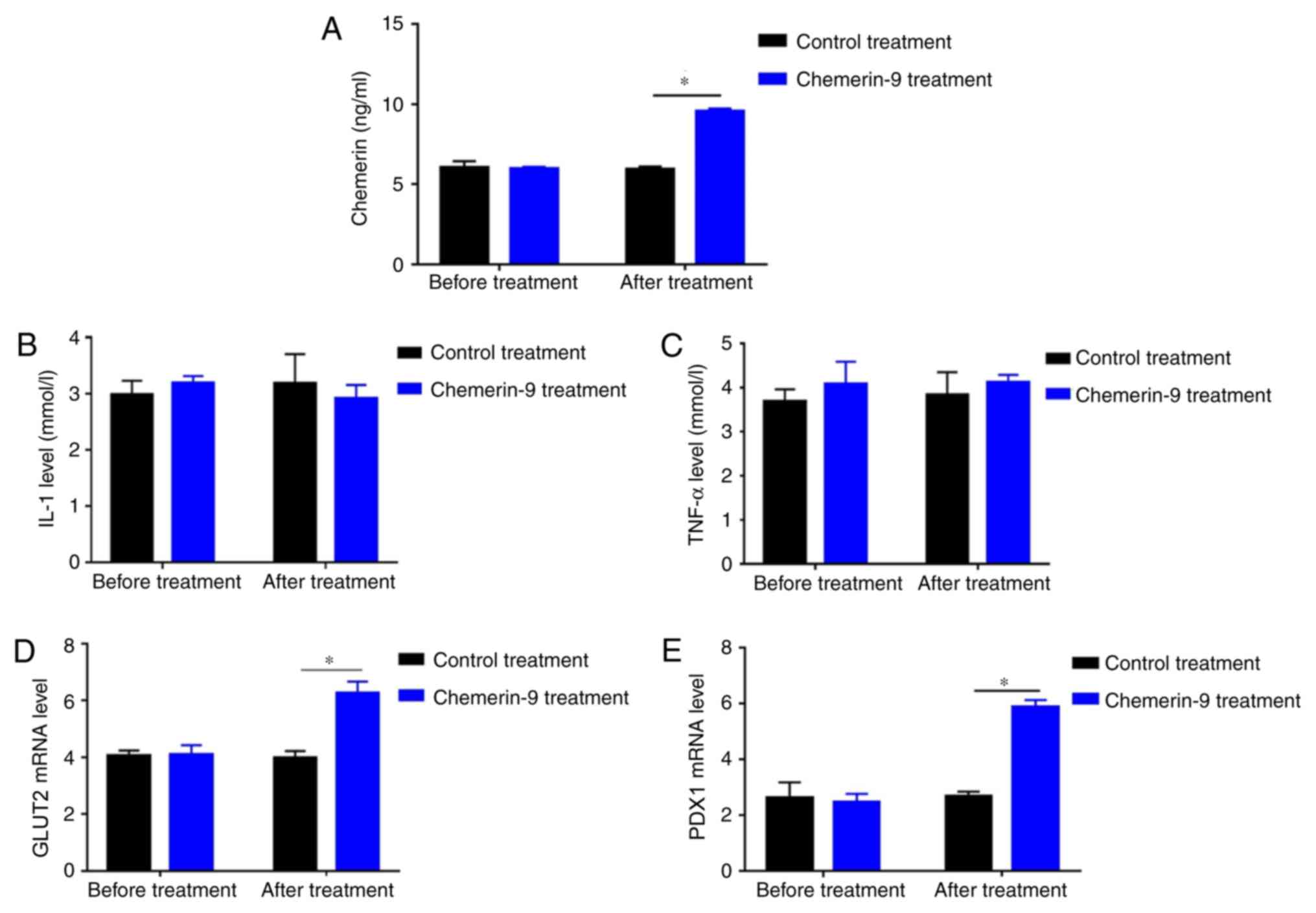
|
1
|
Wittamer V, Franssen JD, Vulcano M,
Mirjolet JF, Le Poul E, Migeotte I, Brézillon S, Tyldesley R,
Blanpain C, Detheux M, et al: Specific recruitment of
antigen-presenting cells by chemerin, a novel processed ligand from
human inflammatory fluids. J Exp Med. 198:977–985. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Goralski KB, McCarthy TC, Hanniman EA,
Zabel BA, Butcher EC, Parlee SD, Muruganandan S and Sinal CJ:
Chemerin, a novel adipokine that regulates adipogenesis and
adipocyte metabolism. J Biol Chem. 282:28175–28188. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Conde J, Scotece M, Gómez R, López V,
Gómez-Reino JJ, Lago F and Gualillo O: Adipokines: Biofactors from
white adipose tissue. A complex hub among inflammation, metabolism,
and immunity. Biofactors. 37:413–420. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ouchi N, Parker JL, Lugus JJ and Walsh K:
Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat Rev Immunol.
11:85–97. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ernst MC and Sinal CJ: Chemerin: At the
crossroads of inflammation and obesity. Trends Endocrinol Metab.
21:660–667. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bondue B, Wittamer V and Parmentier M:
Chemerin and its receptors in leukocyte trafficking, inflammation
and metabolism. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 22:331–338. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang R, Liu S, Guo B, Chang L and Li Y:
Chemerin induces insulin resistance in rat cardiomyocytes in part
through the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Pharmacology. 94:259–264.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Takahashi M, Takahashi Y, Takahashi K,
Zolotaryov FN, Hong KS, Kitazawa R, Iida K, Okimura Y, Kaji H,
Kitazawa S, et al: Chemerin enhances insulin signaling and
potentiates insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.
FEBS Lett. 582:573–578. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bozaoglu K, Bolton K, McMillan J, Zimmet
P, Jowett J, Collier G, Walder K and Segal D: Chemerin is a novel
adipokine associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome.
Endocrinology. 148:4687–4694. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yu S, Zhang Y, Li MZ, Xu H, Wang Q, Song
J, Lin P, Zhang L, Liu Q, Huang QX, et al: Chemerin and apelin are
positively correlated with inflammation in obese type 2 diabetic
patients. Chin Med J (Engl). 125:3440–3444. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chatterjee S and Davies MJ: Accurate
diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and new paradigms of classification.
Nat Rev Endocrinol. 14:386–387. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
American Diabetes Association: Diagnosis
and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 33 (Suppl
1):S62–S69. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and
Classification of Diabetes Mellitus: Report of the expert committee
on the diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes
Care. 26 (Suppl 1):S5–S20. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ewald N, Kaufmann C, Raspe A, Kloer HU,
Bretzel RG and Hardt PD: Prevalence of diabetes mellitus secondary
to pancreatic diseases (type 3c). Diabetes Metab Res Rev.
28:338–342. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ewald N and Bretzel RG: Diabetes mellitus
secondary to pancreatic diseases (Type 3c)-are we neglecting an
important disease? Eur J Intern Med. 24:203–206. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Weaver C, Bishop AE and Polak JM:
Pancreatic changes elicited by chronic administration of excess
L-arginine. Exp Mol Pathol. 60:71–87. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kennedy AJ, Yang P, Read C, Kuc RE, Yang
L, Taylor EJ, Taylor CW, Maguire JJ and Davenport AP: Chemerin
elicits potent constrictor actions via chemokine-like receptor 1
(CMKLR1), not G-protein-coupled receptor 1 (GPR1), in human and rat
vasculature. J Am Heart Assoc. 5(pii): e0044212016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang M, Yang G, Dong J, Liu Y, Zong H, Liu
H, Boden G and Li L: Elevated plasma levels of chemerin in newly
diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus with hypertension. J Investig
Med. 58:883–886. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pfau D, Stepan H, Kratzsch J, Verlohren M,
Verlohren HJ, Drynda K, Lössner U, Blüher M, Stumvoll M and
Fasshauer M: Circulating levels of the adipokine chemerin in
gestational diabetes mellitus. Horm Res Paediatr. 74:56–61. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hart PA, Bellin MD, Andersen DK, Bradley
D, Cruz-Monserrate Z, Forsmark CE, Goodarzi MO, Habtezion A, Korc
M, Kudva YC, et al: Type 3c (pancreatogenic) diabetes mellitus
secondary to chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Lancet
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1:226–237. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Andersen DK: The practical importance of
recognizing pancreatogenic or type 3c diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res
Rev. 28:326–328. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Araya AV, Pavez V, Perez C, Gonzalez F,
Columbo A, Aguirre A, Schiattino I and Aguillón JC: Ex vivo
lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, IL-6 and PGE2
secretion in whole blood from Type 1 diabetes mellitus patients
with or without aggressive periodontitis. Eur Cytokine Netw.
14:128–133. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Saxena M, Srivastava N and Banerjee M:
Association of IL-6, TNF-α and IL-10 gene polymorphisms with type 2
diabetes mellitus. Mol Biol Rep. 40:6271–6279. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hassani-Nezhad-Gashti F, Rysa J, Kummu O,
Näpänkangas J, Buler M, Karpale M, Hukkanen J and Hakkola J:
Activation of nuclear receptor PXR impairs glucose tolerance and
dysregulates GLUT2 expression and subcellular localization in
liver. Biochem Pharmacol. 148:253–264. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Beamish CA, Zhang L, Szlapinski SK, Strutt
BJ and Hill DJ: An increase in immature β-cells lacking Glut2
precedes the expansion of β-cell mass in the pregnant mouse. PLoS
One. 12:e01822562017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Khandelwal P, Sinha A, Jain V, Houghton J,
Hari P and Bagga A: Fanconi syndrome and neonatal diabetes:
Phenotypic heterogeneity in patients with GLUT2 defects. CEN Case
Rep. 7:1–4. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rathinam A and Pari L: Myrtenal
ameliorates hyperglycemia by enhancing GLUT2 through Akt in the
skeletal muscle and liver of diabetic rats. Chem Biol Interact.
256:161–166. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wei J, Ding D, Wang T, Liu Q and Lin Y:
MiR-338 controls BPA-triggered pancreatic islet insulin secretory
dysfunction from compensation to decompensation by targeting Pdx-1.
FASEB J. 31:5184–5195. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shi S, Zhao L and Zheng L: NSD2 is
downregulated in T2DM and promotes β cell proliferation and insulin
secretion through the transcriptionally regulation of PDX1. Mol Med
Rep. 18:3513–3520. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang BT, Dayeh TA, Volkov PA, Kirkpatrick
CL, Malmgren S, Jing X, Renström E, Wollheim CB, Nitert MD and Ling
C: Increased DNA methylation and decreased expression of PDX-1 in
pancreatic islets from patients with type 2 diabetes. Mol
Endocrinol. 26:1203–1212. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hao T, Zhang H, Li S and Tian H:
Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist ameliorates the insulin
resistance function of islet β cells via the activation of
PDX-1/JAK signaling transduction in C57/BL6 mice with high-fat
diet-induced diabetes. Int J Mol Med. 39:1029–1036. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|