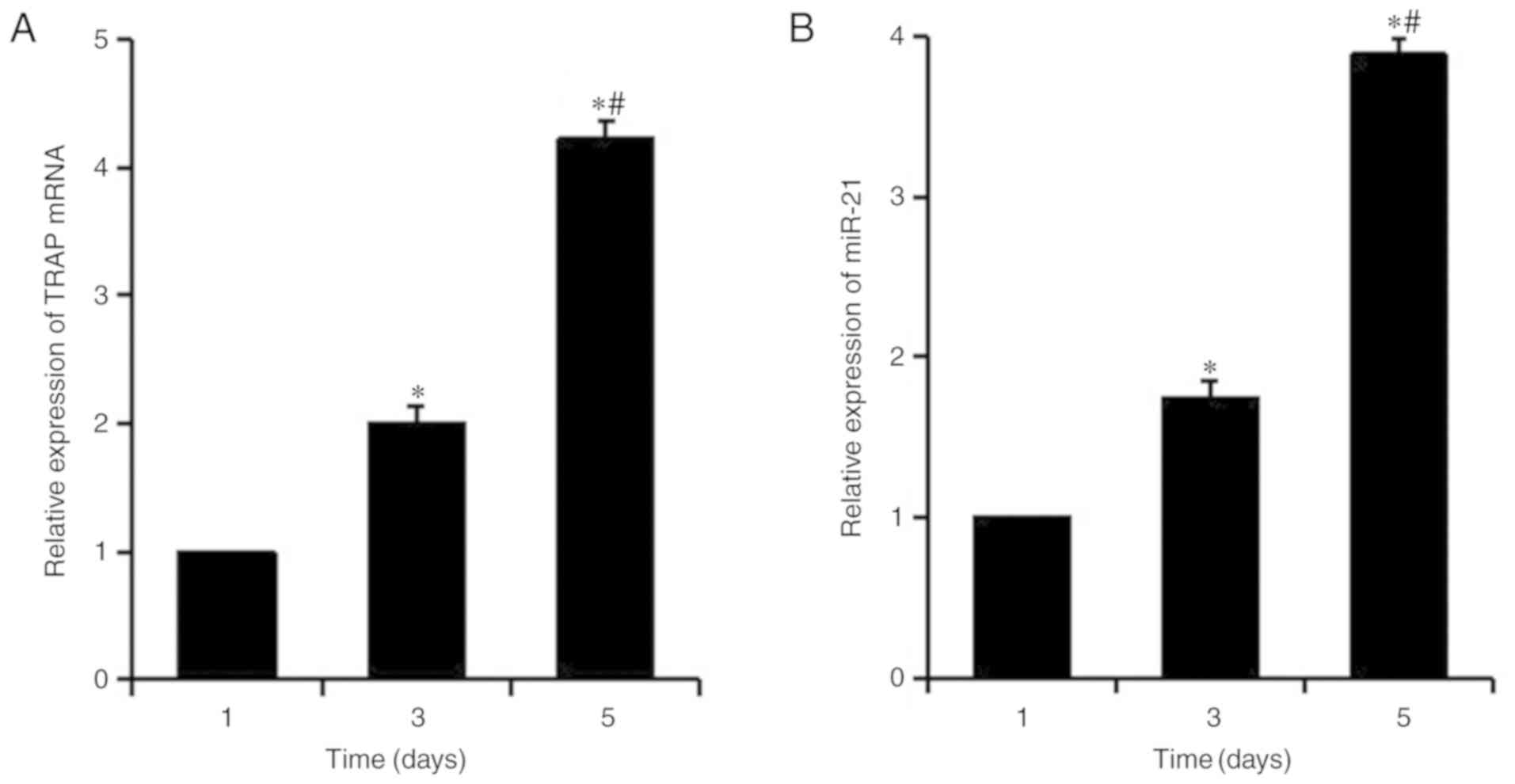
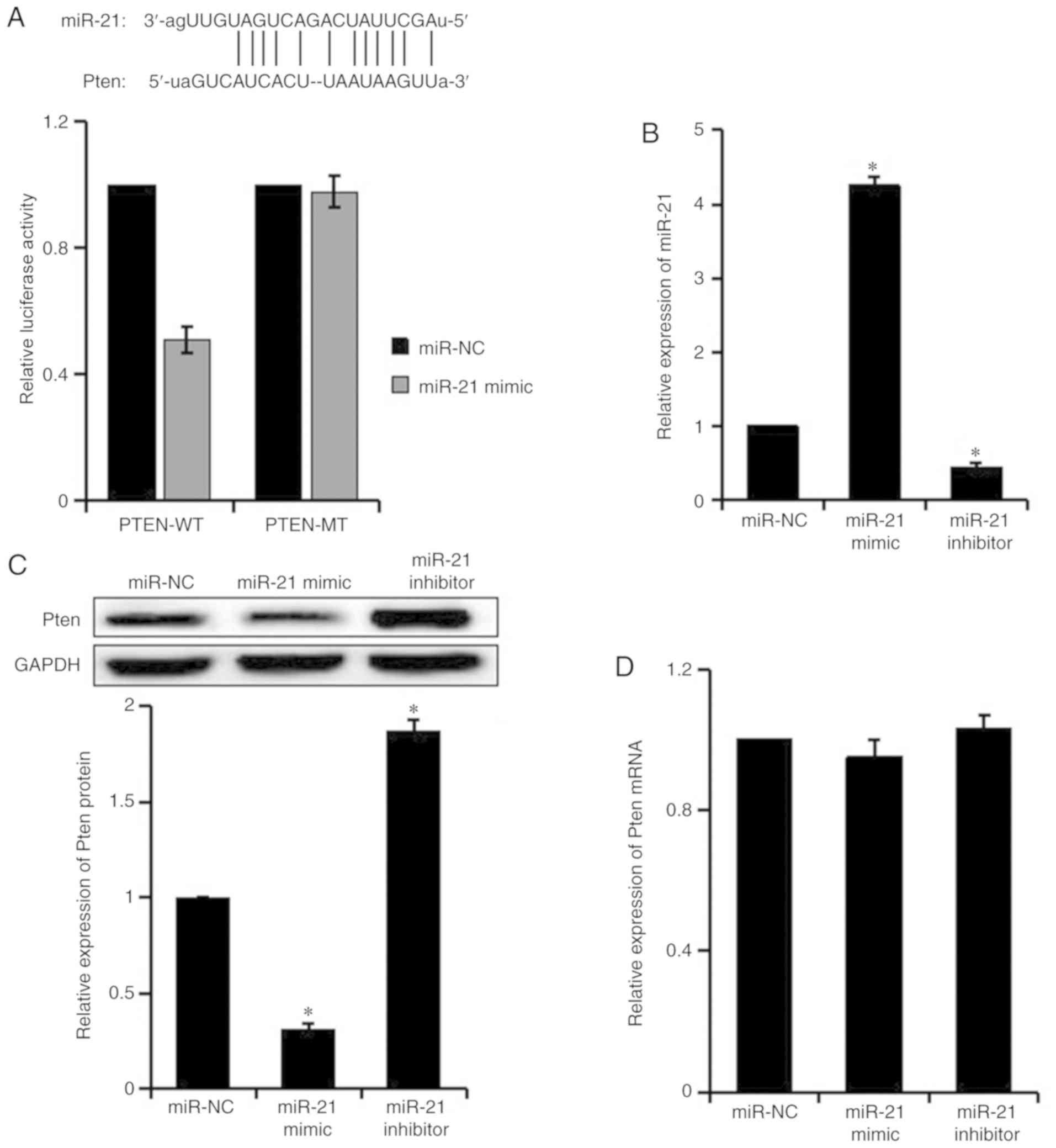
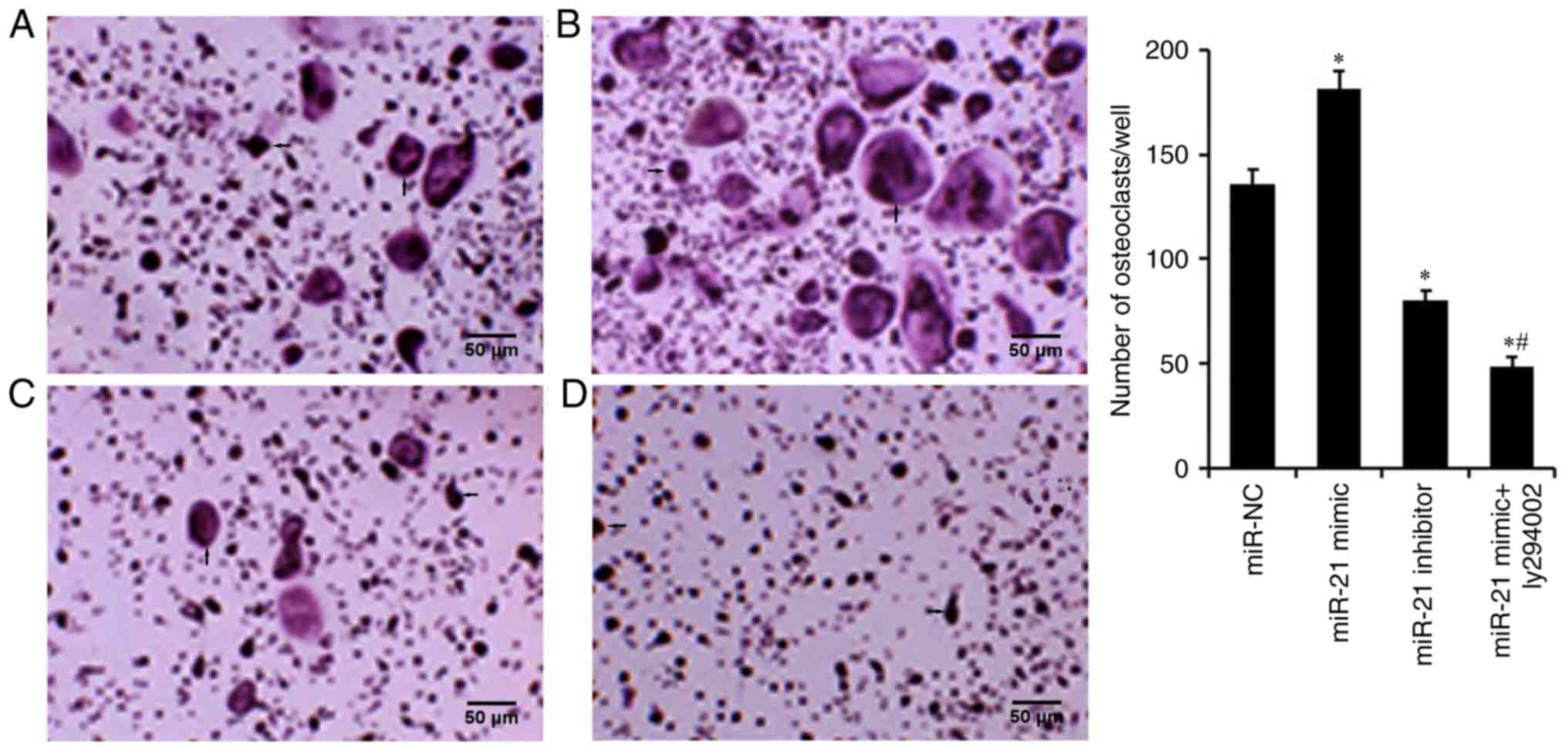
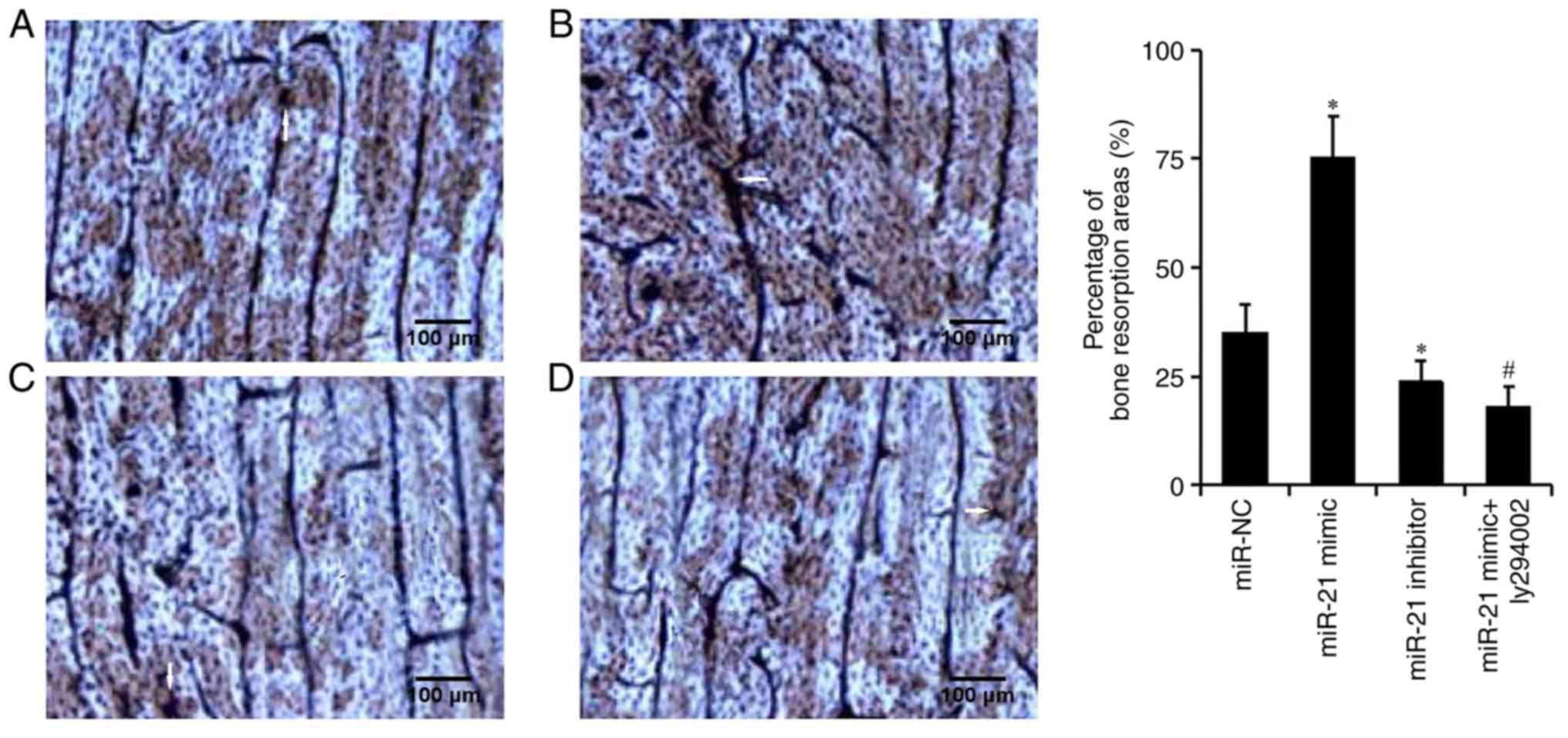
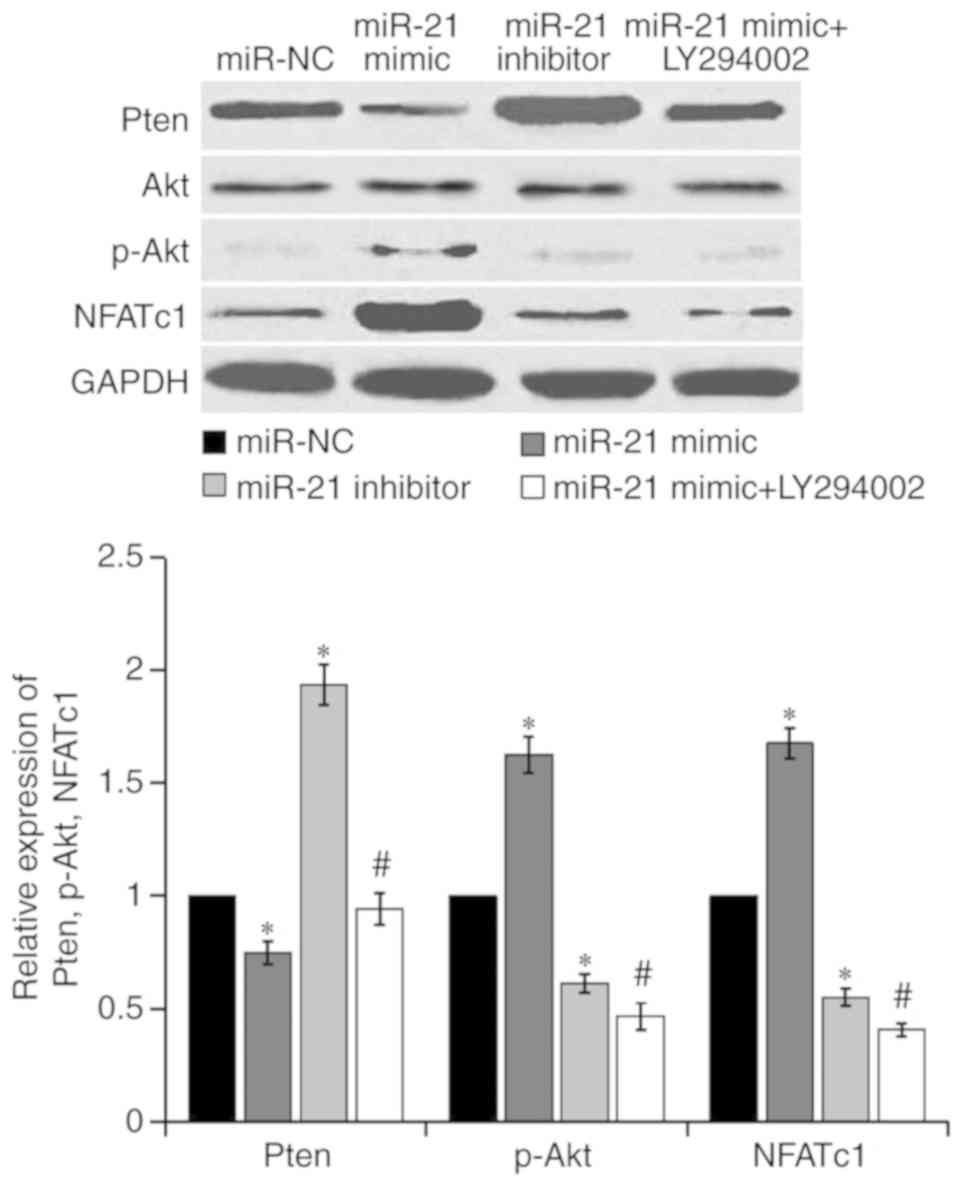
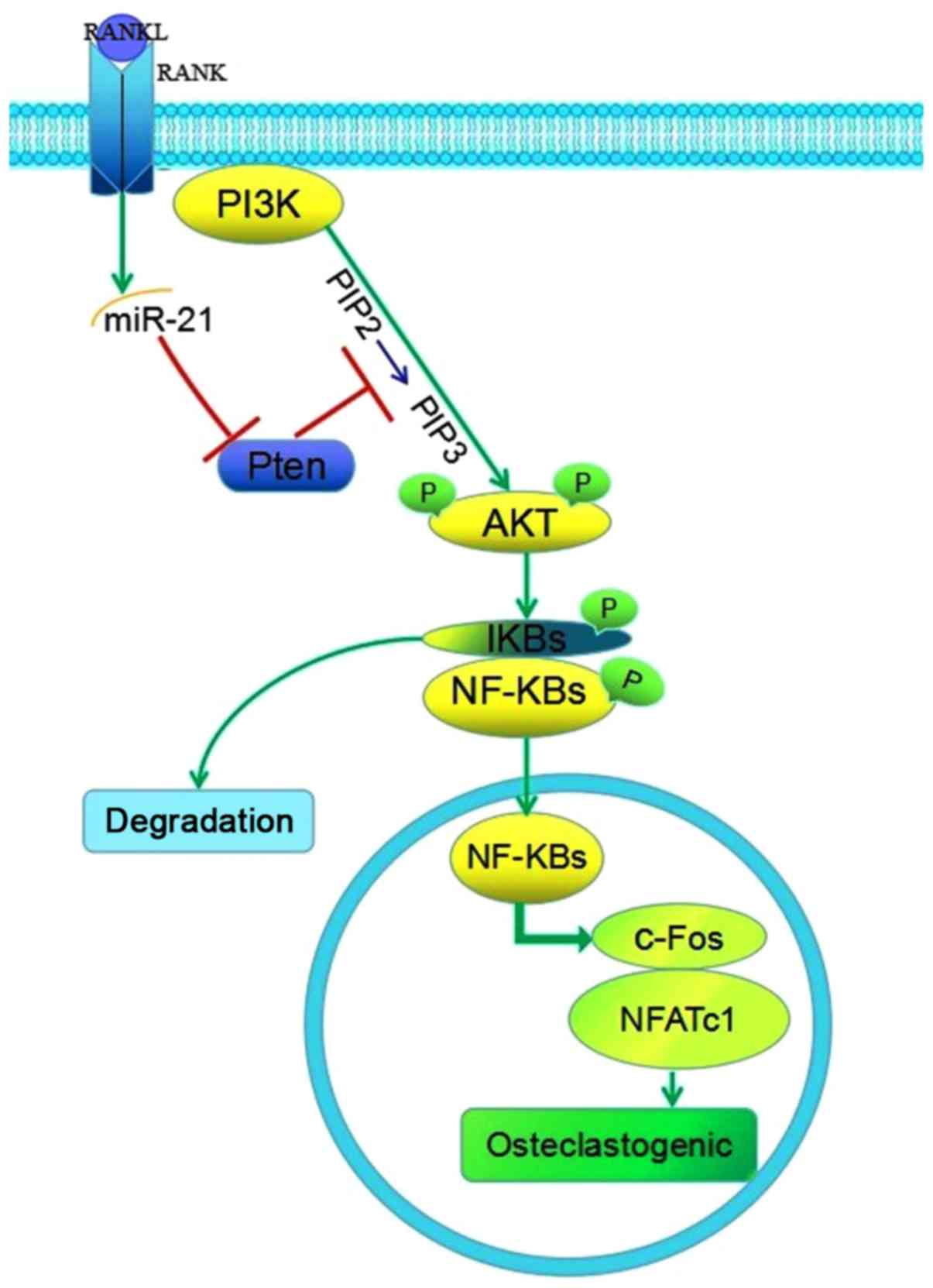
|
1
|
Drissi H and Sanjay A: The multifaceted
osteoclast; far and beyond bone resorption. J Cell Biochem.
117:1753–1756. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Boyce BF: Advances in the regulation of
osteoclasts and osteoclast functions. J Dent Res. 92:860–867. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hodge JM, Collier FM, Pavlos NJ, Kirkland
MA and Nicholson GC: M-CSF potently augments RANKL-induced
resorption activation in mature human osteoclasts. PLoS One.
6:e214622011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Takayanagi H, Kim S, Koga T, Nishina H,
Isshiki M, Yoshida H, Saiura A, Isobe M, Yokochi T, Inoue J, et al:
Induction and activation of the transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2)
integrate RANKL signaling in terminal differentiation of
osteoclasts. Dev Cell. 3:889–901. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen C, Cheng P, Xie H, Zhou HD, Wu XP,
Liao EY and Luo XH: MiR-503 regulates osteoclastogenesis via
targeting RANK. J Bone Miner Res. 29:338–347. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cheng P, Chen C, He HB, Hu R, Zhou HD, Xie
H, Zhu W, Dai RC, Wu XP, Liao EY and Luo XH: miR-148a regulates
osteoclastogenesis by targeting V-maf musculoaponeurotic
fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog B. J Bone Miner Res. 28:1180–1190.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mizoguchi F, Murakami Y, Saito T, Miyasaka
N and Kohsaka H: miR-31 controls osteoclast formation and bone
resorption by targeting RhoA. Arthritis Res Ther. 15:R1022013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ge J, Guo S, Fu Y, Zhou P, Zhang P, Du Y,
Li M, Cheng J and Jiang H: Dental follicle cells participate in
tooth eruption via the RUNX2-MiR-31-SATB2 loop. J Dent Res.
94:936–944. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang JH, Zheng WW, Cheng ST, Liu BX, Liu
FR and Song JQ: Correlation between microRNA21 and sprouty homolog
2 gene expression in multiple myeloma. Mol Med Rep. 11:4220–4224.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pitari MR, Rossi M, Amodio N, Botta C,
Morelli E, Federico C, Gullà A, Caracciolo D, Di Martino MT,
Arbitrio M, et al: Inhibition of miR-21 restores RANKL/OPG ratio in
multiple myeloma-derived bone marrow stromal cells and impairs the
resorbing activity of mature osteoclasts. Oncotarget.
6:27343–27358. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sugatani T and Hruska KA: Down-regulation
of miR-21 biogenesis by estrogen action contributes to osteoclastic
apoptosis. J Cell Biochem. 114:1217–1222. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ocana A, Vera-Badillo F, Al-Mubarak M,
Templeton AJ, Corrales-Sanchez V, Diez-Gonzalez L, Cuenca-Lopez MD,
Seruga B, Pandiella A and Amir E: Activation of the PI3K/mTOR/AKT
pathway and survival in solid tumors: Systematic review and
meta-analysis. PLoS One. 9:e952192014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang L and Guo X: Research advance in
signal pathways and signal factors during the process of osteoclast
differentiation. Chin J Osteoporo. 21:742–748. 2015.
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wan J, Ling X, Peng B and Ding G:
MiR-142-5p regulates CD4+ T cells in human non-small cell lung
cancer through PD-L1 expression via the PTEN pathway. Oncol Rep.
40:272–282. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jang HD, Noh JY, Shin JH, Lin JJ and Lee
SY: PTEN regulation by the Akt/GSK-3β axis during RANKL signaling.
Bone. 55:126–131. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kagiya T and Nakamura S: Expression
profiling of microRNAs in RAW264.7 cells treated with a combination
of tumor necrosis factor alpha and RANKL during osteoclast
differentiation. J Periodontal Res. 48:373–385. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Deng Z and Jin J: MicroRNAs in regulation
of bone metabolism: A literature review. Orthop J China.
24:1019–1022. 2016.
|
|
19
|
Zhang BG, Li JF, Yu BQ, Zhu ZG, Liu BY and
Yan M: microRNA-21 promotes tumor proliferation and invasion in
gastric cancer by targeting PTEN. Oncol Rep. 27:1019–1026. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Peacock O, Lee AC, Cameron F, Tarbox R,
Vafadar-Isfahani N, Tufarelli C and Lund JN: Inflammation and
MiR-21 pathways functionally interact to downregulate PDCD4 in
colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 9:e1102672014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu LF, Wu ZP, Chen Y, Zhu QS, Hamidi S and
Navab R: MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) regulates cellular proliferation,
invasion, migration, and apoptosis by targeting PTEN, RECK and
Bcl-2 in lung squamous carcinoma, Gejiu City, China. PLoS One.
9:e1036982014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sun Y, Xu L, Huang S, Hou Y, Liu Y, Chan
KM, Pan XH and Li G: mir-21 overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells
accelerate fracture healing in a rat closed femur fracture model.
Biomed Res Int. 2015:4123272015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hu CH, Sui BD, Du FY, Shuai Y, Zheng CX,
Zhao P, Yu XR and Jin Y: miR-21 deficiency inhibits osteoclast
function and prevents bone loss in mice. Sci Rep. 7:431912017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xu Z, Liu X, Wang H, Li J, Dai L, Li J and
Dong C: Lung adenocarcinoma cell-derived exosomal miR-21
facilitates osteoclastogenesis. Gene. 666:116–122. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sugatani T, Vacher J and Hruska KA: A
microRNA expression signature of osteoclastogenesis. Blood.
117:3648–3657. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fujita S, Ito T Mizutani T, Minoguchi S,
Yamamichi N, Sakurai K and Iba H: miR-21 gene expression triggered
by AP-1 is sustained through a double-negative feedback mechanism.
J Mol Biol. 378:492–504. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang P, Guan Q, Zhou D, Yu Z, Song Y and
Qiu W: miR-21 inhibitors modulate biological functions of gastric
cancer cells via PTEN/PI3K/mTOR pathway. Dna Cell Biol. 37:38–45.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xiong B, Cheng Y, Ma L and Zhang C: MiR-21
regulates biological behavior through the PTEN/PI-3 K/Akt signaling
pathway in human colorectal cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 42:219–228.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|