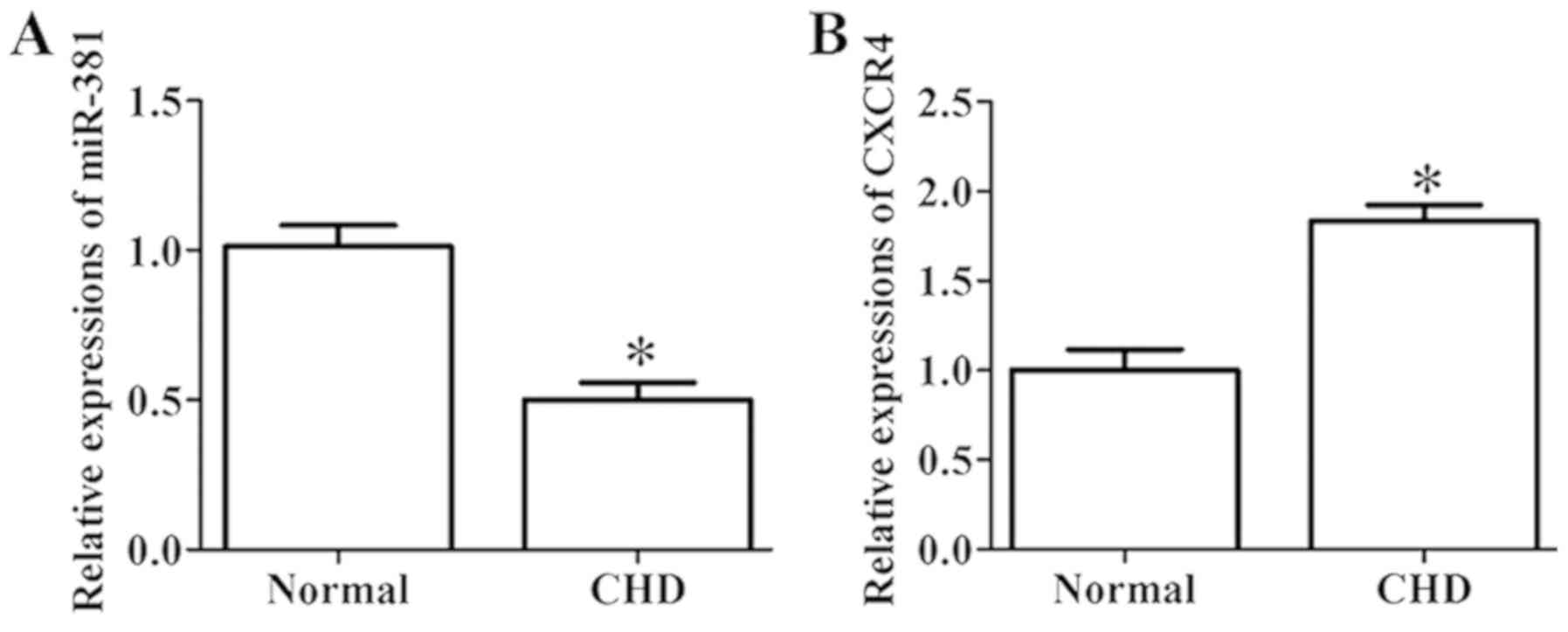
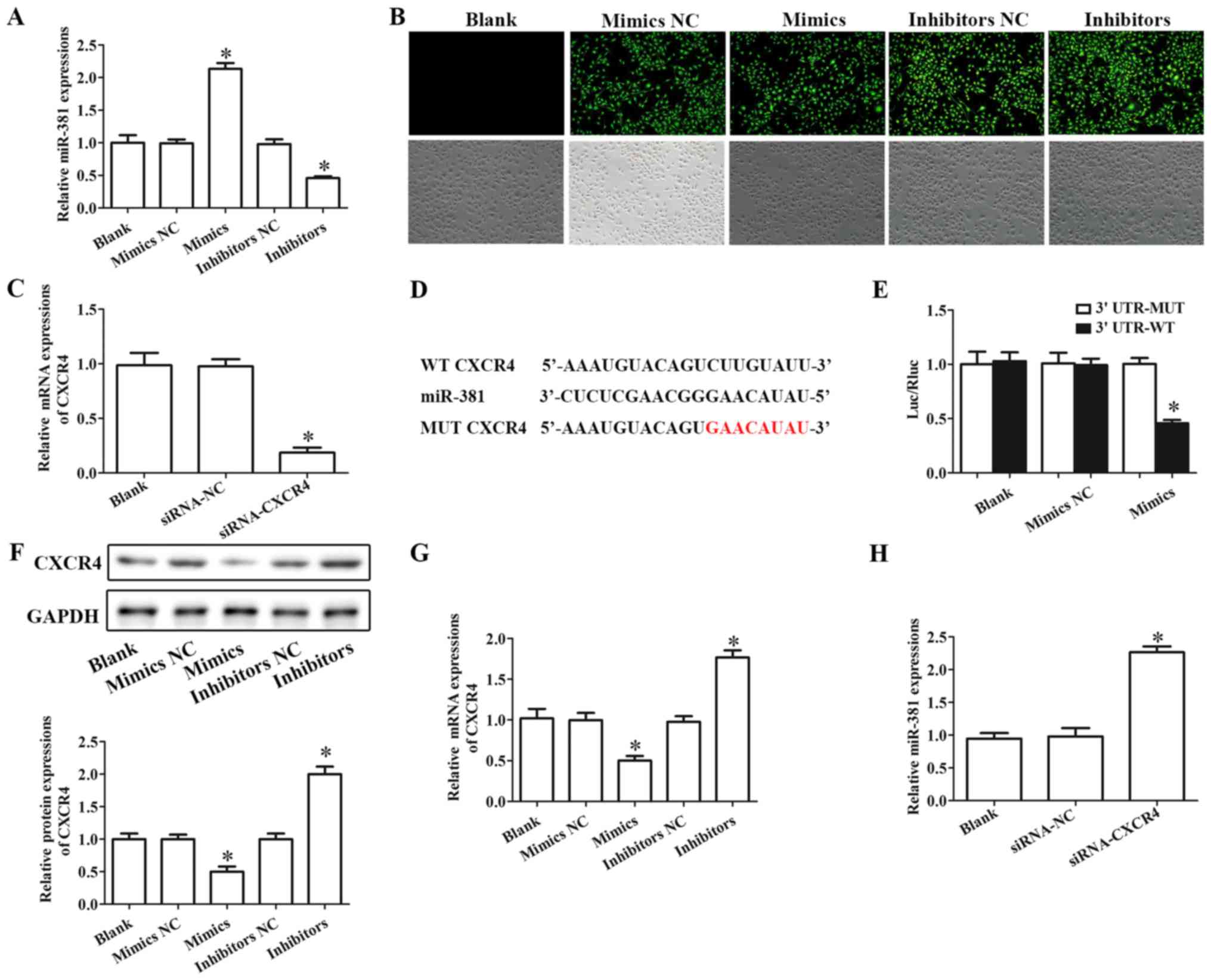
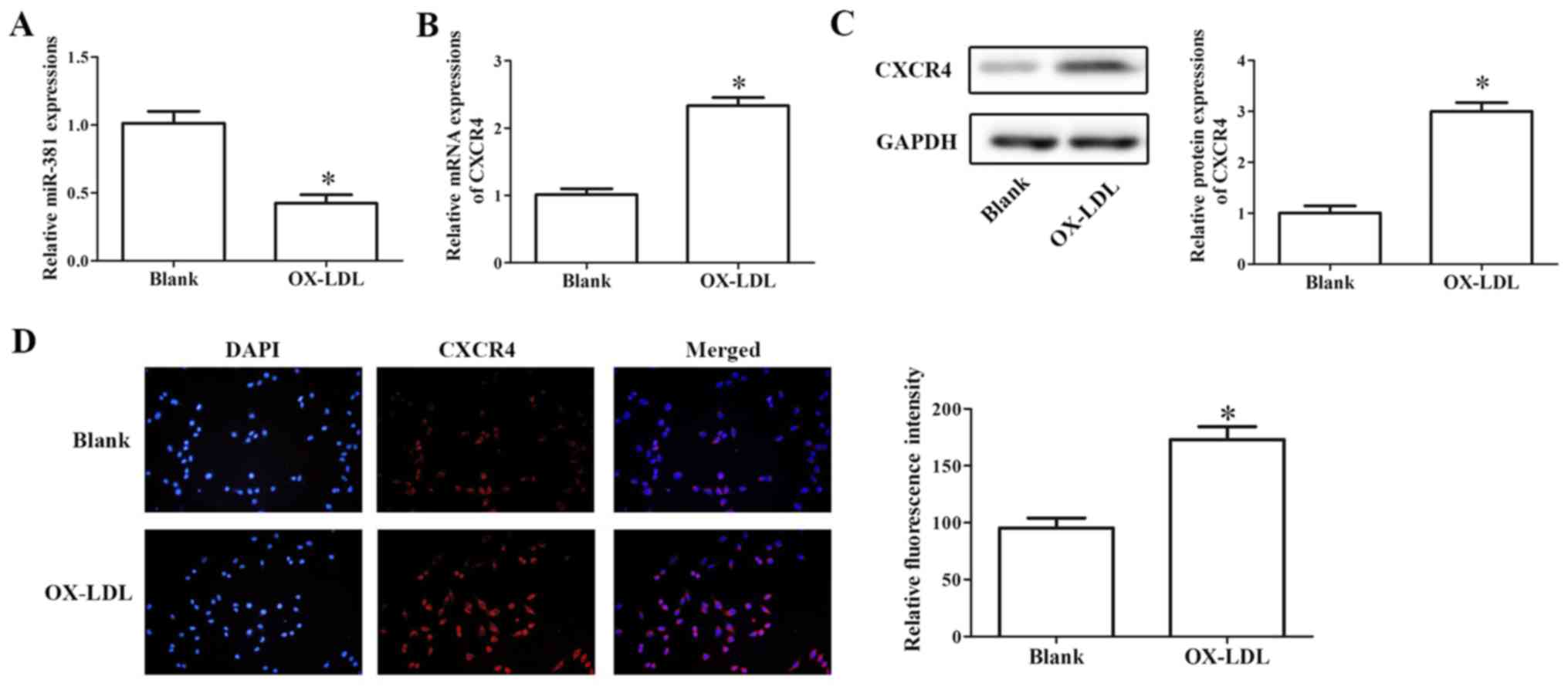
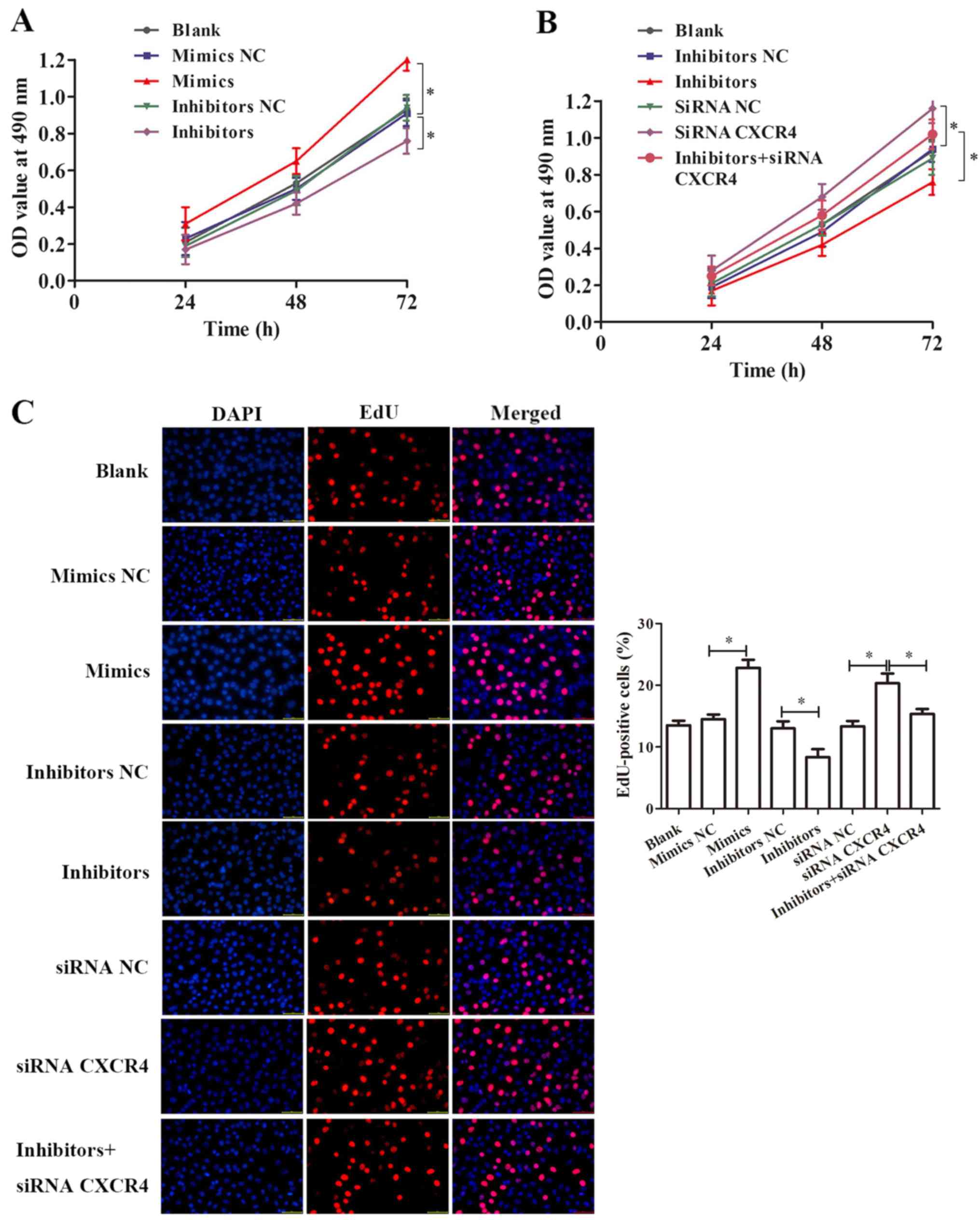
|
1
|
Writing Group Members, ; Mozaffarian D,
Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M, Das SR, de
Ferranti S, Després JP, Fullerton HJ, et al: Heart disease and
stroke statistics-2016 update: A report from the American Heart
Asociation. Circulation. 133:e38–e360. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Townsend N, Wilson L, Bhatnagar P,
Wickramasinghe K, Rayner M and Nichols M: Cardiovascular disease in
Europe: Epidemiological update 2016. Eur Heart J. 37:3232–3245.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Backshall J, Ford GA, Bawamia B, Quinn L,
Trenell M and Kunadian V: Physical activity in the management of
patients with coronary artery disease: A review. Cardiol Rev.
23:18–25. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tousoulis D, Kampoli AM, Papageorgiou N,
Androulakis E, Antoniades C, Toutouzas K and Stefanadis C:
Pathophysiology of atherosclerosis: The role of inflammation. Cur
Pharm Des. 17:4089–4110. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wang D, Wang Y, Ma J, Wang W, Sun B, Zheng
T, Wei M and Sun Y: MicroRNA-20a participates in the aerobic
exercise-based prevention of coronary artery disease by targeting
PTEN. Biomed Pharmacother. 95:756–763. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Peng Y, Song L, Zhao M, Harmelink C,
Debenedittis P, Cui X, Wang Q and Jiao K: Critical roles of
miRNA-mediated regulation of TGFβ signaling during mouse
cardiogenesis. Cardiovasc Res. 103:258–267. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yazdani-Bakhsh R, Javanbakht M, Sadeghi M,
Mashayekhi A, Ghaderi H and Rabiei K: Comparison of health-related
quality of life after percutaneous coronary intervention and
coronary artery bypass surgery. ARYA Atheroscler. 12:124–131.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Acunzo M, Romano G, Wernicke D and Croce
CM: MicroRNA and cancer a brief overview. Adv Biol Regul. 57:1–9.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang X, Xu X, Ma Z, Huo Y, Xiao Z, Li Y
and Wang Y: Dynamic mechanisms for pre-miRNA binding and export by
Exportin-5. RNA. 17:1511–1528. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sluijter JP, van Mil A, van Vliet P, Metz
CH, Liu J, Doevendans PA and Goumans MJ: MicroRNA-1 and −499
regulate differentiation and proliferation in human-derived
cardiomyocyte progenitor cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
30:859–868. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kota J, Chivukula RR, O'Donnell KA,
Wentzel EA, Montgomery CL, Hwang HW, Chang TC, Vivekanandan P,
Torbenson M, Clark KR, et al: Therapeutic microRNA delivery
suppresses tumorigenesis in a murine liver cancer model. Cell.
137:1005–1017. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Poliseno L, Tuccoli A, Mariani L,
Evangelista M, Citti L, Woods K, Mercatanti A, Hammond S and
Rainaldi G: MicroRNAs modulate the angiogenic properties of HUVECs.
Blood. 108:3068–3071. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang Y, Ouyang M, Wang Q and Jian Z:
MicroRNA-142-3p inhibits hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis
and fibrosis of cardiomyocytes by targeting high mobility group box
1. Int J Mol Med. 38:1377–1386. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Singh GB, Raut SK, Khanna S, Kumar A,
Sharma S, Prasad R and Khullar M: MicroRNA-200c modulates DUSP-1
expression in diabetes-induced cardiac hypertrophy. Mol Cell
Biochem. 424:1–11. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Carino A, De Rosa S, Sorrentino S,
Polimeni A, Sabatino J, Caiazzo G, Torella D, Spaccarotella C,
Mongiardo A, Strangio A, et al: Modulation of circulating MicroRNAs
levels during the switch from clopidogrel to ticagrelor. BioMed Res
Int. 2016:39682062016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Facini J, Ruidavets JB, Cordelier P,
Martins F, Maoret JJ, Bongard V, Ferrières J, Roncalli J, Elbaz M
and Vindis C: Circulating miR-155, miR-145 and let-7 cas diagnostic
biomarkers of the coronary artery disease. Sci Rep. 7:429162017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Karakas M, Schulte C, Appelbaum S, Ojeda
F, Lackner KJ, Münzel T, Schnabel RB, Blankenberg S and Zeller T:
Circulating miRNAs strongly predict cardiovascular death in
patients with coronary artery disease-results from the large
AtheroGene study. Eur Heart J. 38:516–523. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang J, Yan Y, Song D and Liu B: Reduced
plasma miR-146a is a predictor of poor coronary colateral
circulation in patients with coronary artery disease. Biomed Res
Int. 2016:42859422016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ming J, Zhou Y, Du J, Fan S, Pan B, Wang
Y, Fan L and Jiang J: miR-381 suppresses C/EBPα-dependent Cx43
expression in breast cancer cells. Biosci Rep. 35:e002662015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li Y, Zhao C, Yu Z, Chen J, She X, Li P,
Liu C, Zhang Y, Feng J, Fu H, et al: Low expression of miR-381 is a
favorite prognosis factor and enhances the chemosensitivity of
osteosarcoma. Oncotarget. 7:68585–68596. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xia B, Li H, Yang S, Liu T and Lou G:
MiR-381 inhibits epithelial ovarian cancer malignancy via YY1
suppression. Tumour Biol. 37:9157–9167. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liang Y, Zhao Q, Fan L, Zhang Z, Tan B,
Liu Y and Li Y: Down-regulation of MicroRNA-381 promotes cell
proliferation and invasion in colon cancer through up-regulation of
LRH-1. Biomed Pharmacother. 75:137–141. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xu Y, Ohms SJ, Li Z, Wang Q, Gong G, Hu Y,
Mao Z, Shannon MF and Fan JY: Changes in the expression of miR-381
and miR-495 are inversely associated with the expression of the
MDR1 gene and development of multi-drug resistance. PLoS One.
8:e820622013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Teicher BA and Fricker SP: CXCL12
(SDF-1)/CXCR4 pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 16:2927–2931.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen J, Chemaly E, Liang L, Kho C, Lee A,
Park J, Altman P, Schecter AD, Hajjar RJ and Tarzami ST: Effects of
CXCR4 gene transfer on cardiac function after ischemia-reperfusion
injury. Am J Pathol. 176:1705–1715. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Döring Y, Noels H, van der Vorst EPC,
Neideck C, Egea V, Drechsler M, Mandl M, Pawig L, Jansen Y,
Schröder K, et al: Vascular CXCR4 limits Atherosclerosis by
maintaining Arterial Integrity: Evidence from mouse and human
studies. Circulation. 136:388–403. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ivins S, Chappell J, Vernay B,
Suntharalingham J, Martineau A, Mohun TJ and Scambler PJ: The
CXCL12/CXCR4 axis plays a critical role in coronary artery
development. Dev Cell. 33:455–468. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tang Y, Zhao J, Shen L, Jin Y, Zhang Z, Xu
G and Huang X: Ox-LDL induces endothelial dysfunction by promoting
Arp2/3 complex expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 475:182–188.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Owens AP III and Mackman N: Sources of
tissue factor that contribute to thrombosis after rupture of an
atherosclerotic plaque. Thromb Res. 129 (Suppl 2):S30–S33. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gao S, Zhao D, Wang M, Zhao F, Han X, Qi Y
and Liu J: Association between circulating oxidized LDL and
atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: A Meta-analysis of
observational studies. Can J Cardiol. 33:1624–1632. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
O'Rourke RA, Brundage BH, Froelicher VF,
Greenland P, Grundy SM, Hachamovitch R, Pohost GM, Shaw LJ,
Weintraub WS and Winters WL Jr: American College of
Cardiology/American Heart Association Expert Consensus Document on
electron-beam computed tomography for the diagnosis and prognosis
of coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 36:326–340. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2 (-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hanifehpour R, Motevalli M, Ghanaati H,
Shahriari M and Aliyari Ghasabeh M: Diagnostic accuracy of coronary
calcium score less than 100 in excluding coronary artery disease.
Iran J Radiol. 13:e167052016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang YH, He K and Shi G: Effects of
microRNA-499 on the inflammatory damage of endothelial cells during
coronary artery disease via the targeting of PDCD4 through the
NF-Κβ/ TNF-α signaling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 44:110–124.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gerhardt S, Konig V, Doll M,
Hailemariam-Jahn T, Hrgovic I, Zoller N, Kaufmann R, Kippenberger S
and Meissner M: Dimethylfumarate protects against TNF-α-induced
secretion of inflammatory cytokines in human endothelial cells. J
Inflamm (Lond). 12:492015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Han F, Hui Z, Zhang S, Hou N, Wang Y and
Sun X: Induction of haemeoxygenase-1 improves FFA-induced
endothelial dysfunction in rat aorta. Cell Physiol Biochem.
35:1230–1240. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Garzon R, Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNAs
in cancer. Annu Rev Med. 60:167–179. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jha CK, Mir R, Elfaki I, Khullar N, Rehman
S, Javid J, Banu S and Chahal SMS: Potential impact of microRNA-423
gene variability in coronary artery disease. Endocr Metab Immune
Disord Drug Targets. 19:67–74. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu L, Cheng Z and Yang J: miR-23
regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis of vascular smooth
muscle cells in coronary heart disease. Pathol Res Pract.
214:1873–1878. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yamac AH, Huyut MA, Yilmaz E, Celikkale I,
Bacaksiz A, Demir Y, Demir AR, Erturk M, Bakhshaliyev N, Ozdemir R
and Kilic U: MicroRNA-199a is downregulated in patients after
coronary artery bypass graft surgery and is associated with
increased levels of sirtuin 1 (SIRT 1) protein and major adverse
cardiovascular events at 3-year follow-up. Med Sci Monit.
24:6245–6254. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang Y, Wang X, Liu Z and Yu L:
Dexmedetomidine attenuates lipopolysaccharide induced acute lung
injury by targeting NLRP3 via miR-381. J Biochem Mol Toxicol.
32:e222112018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu Y, Gao Y, Yang J, Shi C, Wang Y and Xu
Y: MicroRNA-381 reduces inflammation and infiltration of
macrophages in polymyositis via downregulating HMGB1. Int J Oncol.
53:1332–1342. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lu L, Zhang H, Dong W, Peng W and Yang J:
MiR-381 negatively regulates cardiomyocyte survival by suppressing
Notch signaling. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 54:610–619. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hu W, Lu H, Zhang J, Fan Y, Chang Z, Liang
W, Wang H, Zhu T, Garcia-Barrio MT, Peng D, et al: Krüppel-like
factor 14, a coronary artery disease associated transcription
factor, inhibits endothelial inflammation via NF-κB signaling
pathway. Atherosclerosis. 278:39–48. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hazzalin CA and Mahadevan LC:
MAPK-regulated transcription: A continuously variable gene switch?
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 3:30–40. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kaminska B: MAPK signalling pathways as
molecular targets for anti-inflammatory therapy-from molecular
mechanisms to therapeutic benefits. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1754:253–262. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Sini S, Deepa D, Harikrishnan S and
Jayakumari N: High-density lipoprotein from subjects with coronary
artery disease promotes macrophage foam cell formation: Role of
scavenger receptor CD36 and ERK/MAPK signaling. Mol Cell Biochem.
427:23–24. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Mirzaei H, Ferns GA, Avan A and Mobarhan
MG: Cytokines and microRNA in coronary artery disease. Adv Clin
Chem. 82:47–70. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|