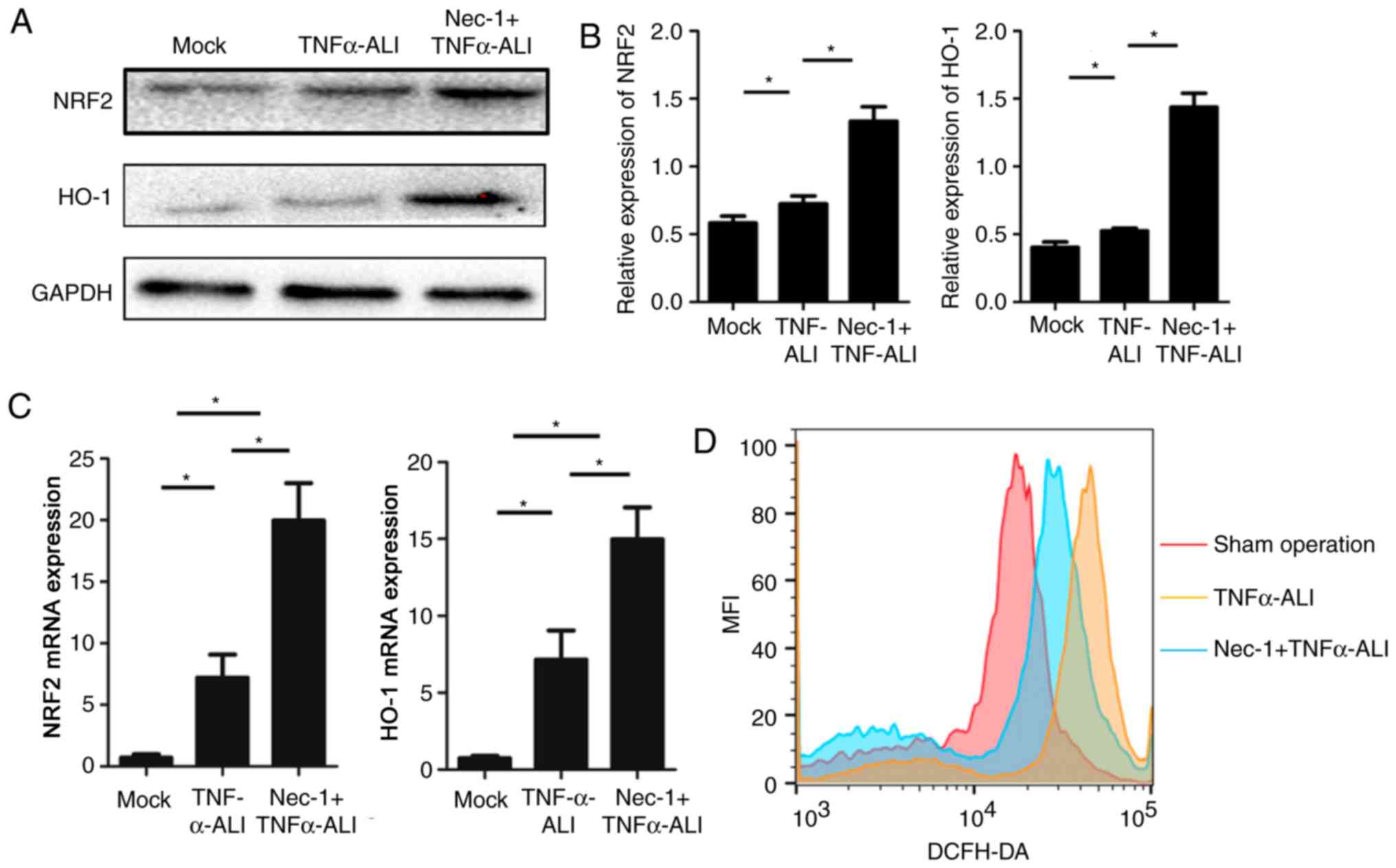
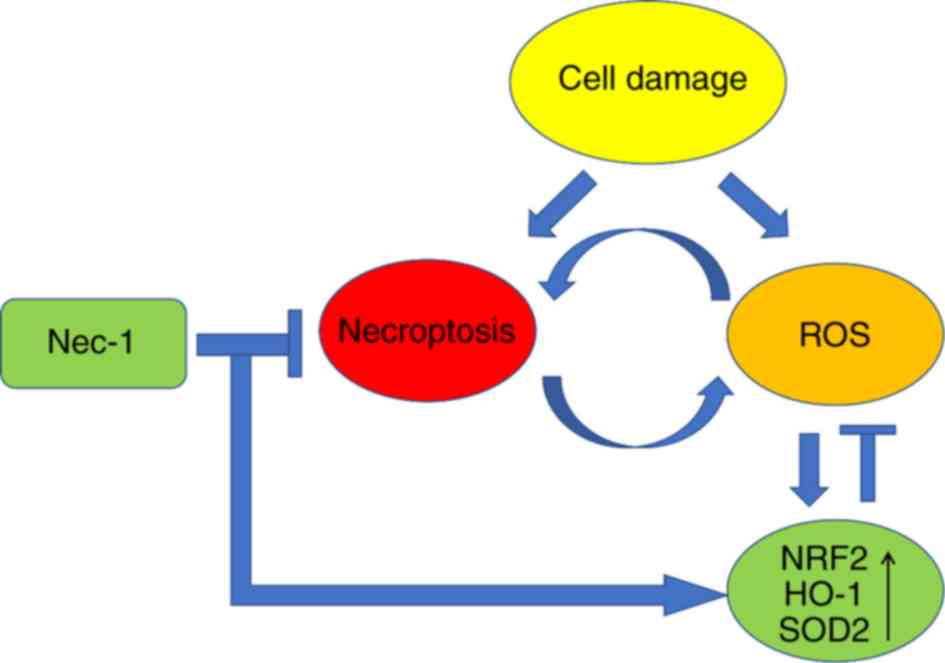
|
1
|
Wheeler AP and Bernard GR: Acute lung
injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome: A clinical
review. Lancet. 369:1553–1564. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Martin GS, Mannino DM, Eaton S and Moss M:
The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through
2000. N Engl J Med. 348:1546–1554. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zou C, Li J, Xiong S, Chen Y, Wu Q, Li Q,
Weathington NM, Han S, Snavely C, Chen BB and Mallampalli RK:
Mortality factor 4 like 1 protein mediates epithelial cell death in
a mouse model of pneumonia. Sci Transl Med. 7:311ra1712015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Coon TA, McKelvey AC, Lear T, Rajbhandari
S, Dunn SR, Connelly W, Zhao JY, Han S, Liu Y, Weathington NM, et
al: The proinflammatory role of HECTD2 in innate immunity and
experimental lung injury. Sci Transl Med. 7:295ra1092015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ayala P, Vivar R, Montalva R, Olmos P,
Meneses M and Borzone GR: Elastin degradation products in acute
lung injury induced by gastric contents aspiration. Respir Res.
19:1652018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Guo S, Jiang K, Wu H, Yang C, Yang Y, Yang
J, Zhao G and Deng G: Magnoflorine ameliorates
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via suppressing NF-κB
and MAPK activation. Front Pharmacol. 9:9822018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Morales-Ortiz J, Deal V, Reyes F,
Maldonado-Martínez G, Ledesma N, Staback F, Croft C, Pacheco A,
Ortiz-Zuazaga H, Yost CC, et al: TLT-1 is a prognostic indicator in
ALI/ARDS and prevents tissue damage in the lungs in a mouse model.
Blood. 132:2495–2505. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li X, Yu Y, Gorshkov B, Haigh S, Bordan Z,
Weintraub D, Rudic RD, Chakraborty T, Barman SA, Verin AD, et al:
Hsp70 suppresses mitochondrial reactive oxygen species and
preserves pulmonary Microvascular barrier integrity following
exposure to bacterial toxins. Front Immunol. 9:13092018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gorman AM, Healy SJ, Jäger R and Samali A:
Stress management at the ER: Regulators of ER stress-induced
apoptosis. Pharmacol Ther. 134:306–316. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dhuriya YK and Sharma D: Necroptosis: A
regulated inflammatory mode of cell death. J Neuroinflammation.
15:1992018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
He S and Wang X: RIP kinases as modulators
of inflammation and immunity. Nat Immunol. 19:912–922. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang Y, Zhang J, Yan R, Tian J, Zhang Y,
Zhang J, Chen M, Cui Q, Zhao L, Hu R, et al: Receptor-interacting
protein kinase 3 promotes platelet activation and thrombosis. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:2964–2969. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pasparakis M and Vandenabeele P:
Necroptosis and its role in inflammation. Nature. 517:311–320.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pavlosky A, Lau A, Su Y, Lian D, Huang X,
Yin Z, Haig A, Jevnikar AM and Zhang ZX: RIPK3-mediated necroptosis
regulates cardiac allograft rejection. Am J Transplant.
14:1778–1790. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lau A, Wang S, Jiang J, Haig A, Pavlosky
A, Linkermann A, Zhang ZX and Jevnikar AM: RIPK3-mediated
necroptosis promotes donor kidney inflammatory injury and reduces
allograft survival. Am J Transplant. 13:2805–2818. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu ZY, Wu B, Guo YS, Zhou YH, Fu ZG, Xu
BQ, Li JH, Jing L, Jiang JL, Tang J and Chen ZN: Necrostatin-1
reduces intestinal inflammation and colitis-associated
tumorigenesis in mice. Am J Cancer Res. 5:3174–3185.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu J, Huang Z, Ren J, Zhang Z, He P, Li Y,
Ma J, Chen W, Zhang Y, Zhou X, et al: Mlkl knockout mice
demonstrate the indispensable role of Mlkl in necroptosis. Cell
Res. 23:994–1006. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nikseresht S, Khodagholi F, Nategh M and
Dargahi L: RIP1 inhibition rescues from LPS-induced RIP3-mediated
programmed cell death, distributed energy metabolism and spatial
memory impairment. J Mol Neurosci. 57:219–230. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hwang S and Kim JK: Effects of NADPH
oxidase inhibitors and mitochondria-targeted antioxidants on
amyloid β1-42-induced neuronal deaths in mouse mixed cortical
cultures. Chonnam Med J. 54:159–166. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu Z, Ren Z, Zhang J, Chuang CC,
Kandaswamy E, Zhou T and Zuo L: Role of ROS and nutritional
antioxidants in human diseases. Front Physiol. 9:4772018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang C, Chen S, Zhang T, Li D, Huang Z,
Huang J, Qin Y, Chen B, Cheng G, Ma F and Zhou M: TLR3 ligand
PolyI:C prevents acute pancreatitis through the
interferon-β/Interferon-α/β receptor signaling pathway in a
Caerulein-induced pancreatitis mouse model. Front Immunol.
10:9802019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Han J, Kim YS, Lim MY, Kim HY, Kong S,
Kang M, Choo YW, Jun JH, Ryu S, Jeong HY, et al: Dual roles of
graphene oxide to attenuate inflammation and elicit timely
polarization of macrophage phenotypes for cardiac repair. ACS Nano.
12:1959–1977. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Morrison TJ, Jackson MV, Cunningham EK,
Kissenpfennig A, McAuley DF, O'Kane CM and Krasnodembskaya AD:
Mesenchymal stromal cells modulate macrophages in clinically
relevant lung injury models by extracellular vesicle mitochondrial
transfer. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 196:1275–1286. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sousse LE, Herndon DN, Andersen CR, Zovath
A, Finnerty CC, Mlcak RP, Cox RA, Traber DL and Hawkins HK:
Pulmonary histopathologic abnormalities and predictor variables in
autopsies of burned pediatric patients. Burns. 41:519–527. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Malaviya R, Sunil VR, Venosa A, Verissimo
VL, Cervelli JA, Vayas KN, Hall L, Laskin JD and Laskin DL:
Attenuation of nitrogen mustard-induced pulmonary injury and
fibrosis by anti-tumor necrosis factor-α antibody. Toxicol Sci.
148:71–88. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
McConnell AM, Yao C, Yeckes AR, Wang Y,
Selvaggio AS, Tang J, Kirsch DG and Stripp BR: p53 regulates
progenitor cell quiescence and differentiation in the airway. Cell
Rep. 17:2173–2182. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Malaviya R, Laskin JD and Laskin DL:
Anti-TNFα therapy in inflammatory lung diseases. Pharmacol Ther.
180:90–98. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Vanden Berghe T, Vanlangenakker N,
Parthoens E, Deckers W, Devos M, Festjens N, Guerin CJ, Brunk UT,
Declercq W and Vandenabeele P: Necroptosis, necrosis and secondary
necrosis converge on similar cellular disintegration features. Cell
Death Differ. 17:922–930. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Raju S, Whalen DM, Mengistu M, Swanson C,
Quinn JG, Taylor SS, Webster JD, Newton K and Shaw AS: Kinase
domain dimerization drives RIPK3-dependent necroptosis. Sci Signal.
11(pii): eaar21882018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shen C, Wang C, Han S, Wang Z, Dong Z,
Zhao X, Wang P, Zhu H, Sun X, Ma X, et al: Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2
deficiency negates chronic low-to-moderate alcohol
consumption-induced cardioprotecion possibly via ROS-dependent
apoptosis and RIP1/RIP3/MLKL-mediated necroptosis. Biochim Biophys
Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1863:1912–1918. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chauhan AK, Min KJ and Kwon TK:
RIP1-dependent reactive oxygen species production executes
artesunate-induced cell death in renal carcinoma Caki cells. Mol
Cell Biochem. 435:15–24. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shan B, Pan H, Najafov A and Yuan J:
Necroptosis in development and diseases. Genes Dev. 32:327–340.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang DW, Shao J, Lin J, Zhang N, Lu BJ,
Lin SC, Dong MQ and Han J: RIP3, an energy metabolism regulator
that switches TNF-induced cell death from apoptosis to necrosis.
Science. 325:332–336. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xu C, Qiao L, Ma L, Guo Y, Dou X, Yan S,
Zhang B and Roman A: Biogenic selenium nanoparticles synthesized by
Lactobacillus casei ATCC 393 alleviate intestinal epithelial
barrier dysfunction caused by oxidative stress via Nrf2
signaling-mediated mitochondrial pathway. Int J Nanomedicine.
14:4491–4502. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu Q, Lv H, Wen Z, Ci X and Peng L:
Isoliquiritigenin activates nuclear factor erythroid-2 related
factor 2 to suppress the NOD-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome
and inhibits the NF-κB pathway in macrophages and in acute lung
injury. Front Immunol. 8:15182017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lien CF, Lee WS, Wang IC, Chen TI, Chen TL
and Yang KT: Intermittent hypoxia-generated ROS contributes to
intracellular zinc regulation that limits ischemia/reperfusion
injury in adult rat cardiomyocyte. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 118:122–132.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|