|
1
|
Gladson CL, Prayson RA and Liu WM: The
pathobiology of glioma tumors. Annu Rev Pathol. 5:33–50. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zeng A, Hu Q, Liu Y, Wang Z, Cui X, Li R,
Yan W and You Y: IDH1/2 mutation status combined with Ki-67
labeling index defines distinct prognostic groups in glioma.
Oncotarget. 6:30232–30238. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
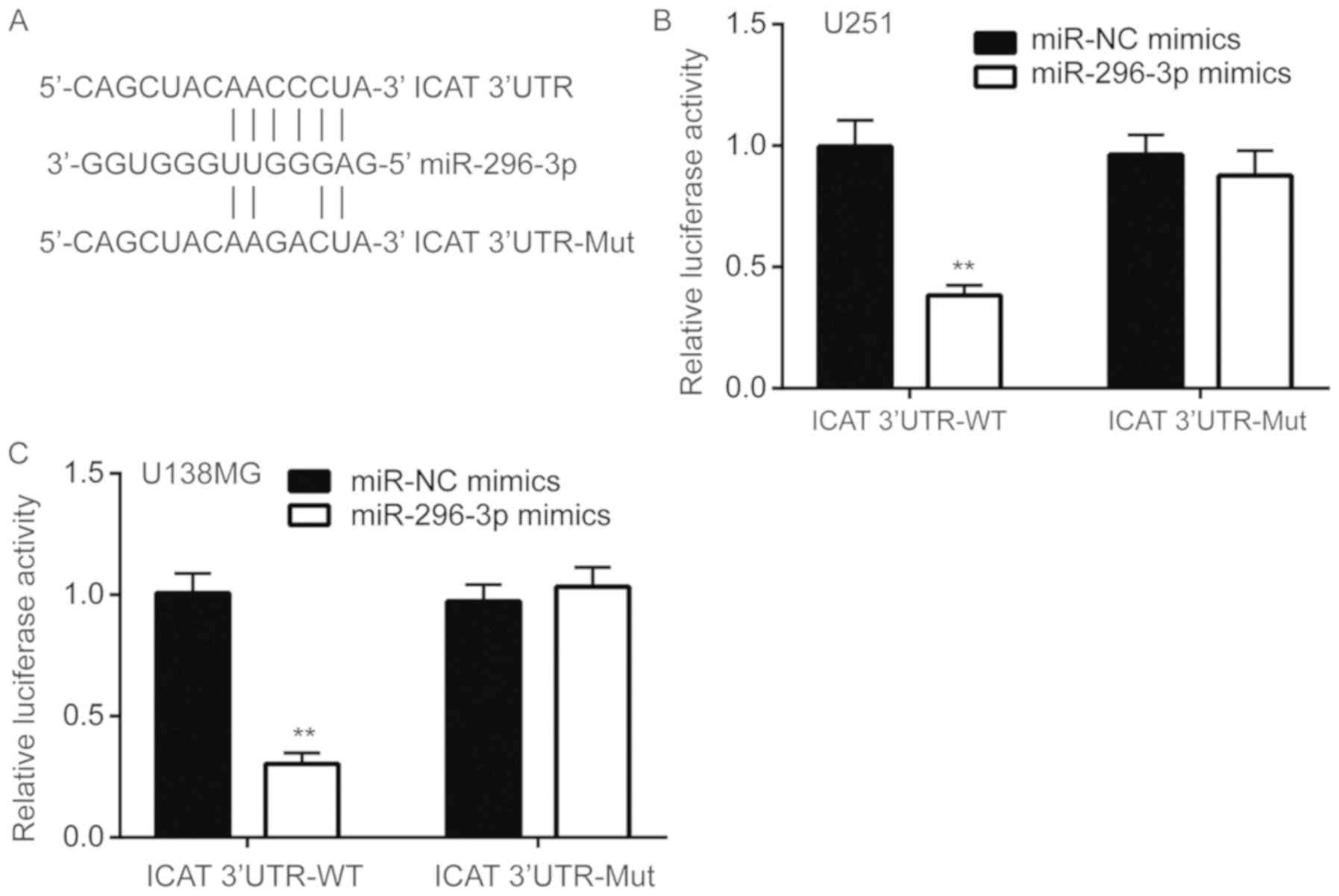
Van Gool S, Maes W, Ardon H, Verschuere T,
Van Cauter S and De Vleeschouwer S: Dendritic cell therapy of
high-grade gliomas. Brain Pathol. 19:694–712. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller
M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn
U, et al: Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide
for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 352:987–996. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cai T, Liu Y and Xiao J: Long noncoding
RNA MALAT1 knockdown reverses chemoresistance to temozolomide via
promoting microRNA-101 in glioblastoma. Cancer Med. 7:1404–1415.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang Z, Xu X, Liu N, Cheng Y, Jin W, Zhang
P, Wang X, Yang H, Liu H and Tu Y: SOX9-PDK1 axis is essential for
glioma stem cell self-renewal and temozolomide resistance.
Oncotarget. 9:192–204. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sethi A and Sholl LM: Emerging evidence
for MicroRNAs as regulators of cancer stem cells. Cancers (Basel).
3:3957–3971. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mendell JT: MicroRNAs: Critical regulators
of development, cellular physiology and malignancy. Cell Cycle.
4:1179–1184. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Markopoulos GS, Roupakia E, Tokamani M,
Alabasi G, Sandaltzopoulos R, Marcu KB and Kolettas E: Roles of
NF-kB signaling in the regulation of miRNAs impacting on
inflammation in cancer. Biomedicines. 6:E402018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li S, Chowdhury R, Liu F, Chou AP, Li T,
Mody RR, Lou JJ, Chen W, Reiss J, Soto H, et al: Tumor-suppressive
miR148a is silenced by CpG island hypermethylation in IDH1-mutant
gliomas. Clin Cancer Res. 20:5808–5822. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang R, Luo H, Wang S, Chen W, Chen Z,
Wang HW, Chen Y, Yang J, Zhang X, Wu W, et al: MicroRNA-377
inhibited proliferation and invasion of human glioblastoma cells by
directly targeting specificity protein 1. Neuro Oncol.
16:1510–1522. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang Y, Dutta A and Abounader R: The role
of microRNAs in glioma initiation and progression. Front Biosci
(Landmark Ed). 17:700–712. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sumazin P, Yang X, Chiu HS, Chung WJ, Iyer
A, Llobet-Navas D, Rajbhandari P, Bansal M, Guarnieri P, Silva J
and Califano A: An extensive microRNA-mediated network of RNA-RNA
interactions regulates established oncogenic pathways in
glioblastoma. Cell. 147:370–381. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Würdinger T, Tannous BA, Saydam O, Skog J,
Grau S, Soutschek J, Weissleder R, Breakefield XO and Krichevsky
AM: miR-296 regulates growth factor receptor overexpression in
angiogenic endothelial cells. Cancer Cell. 14:382–393. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee H, Hwang SJ, Kim HR, Shin CH, Choi KH,
Joung JG and Kim HH: Neurofibromatosis 2 (NF2) controls the
invasiveness of glioblastoma through YAP-dependent expression of
CYR61/CCN1 and miR-296-3p. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1859:599–611.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bai Y, Liao H, Liu T, Zeng X, Xiao F, Luo
L, Guo H and Guo L: MiR-296-3p regulates cell growth and multi-drug
resistance of human glioblastoma by targeting ether-à-go-go (EAG1).
Eur J Cancer. 49:710–724. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jiang Y, Ren W, Wang W, Xia J, Gou L, Liu
M, Wan Q, Zhou L, Weng Y, He T and Zhang Y: Inhibitor of β-catenin
and TCF (ICAT) promotes cervical cancer growth and metastasis by
disrupting E-cadherin/β-catenin complex. Oncol Rep. 38:2597–2606.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Koyama T, Tago K, Nakamura T, Ohwada S,
Morishita Y, Yokota J and Akiyama T: Mutation and expression of the
beta-catenin-interacting protein ICAT in human colorectal tumors.
Jpn J Clin Oncol. 32:358–362. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Imai M, Nakamura T, Akiyama T and Horii A:
Infrequent somatic mutations of the ICAT gene in various human
cancers with frequent 1p-LOH and/or abnormal nuclear accumulation
of beta-catenin. Oncol Rep. 12:1099–1103. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang Y, Li T, Guo P, Kang J, Wei Q, Jia
X, Zhao W, Huai W, Qiu Y, Sun L and Han L: MiR-424-5p reversed
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of anchorage-independent HCC
cells by directly targeting ICAT and suppressed HCC progression.
Sci Rep. 4:62482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
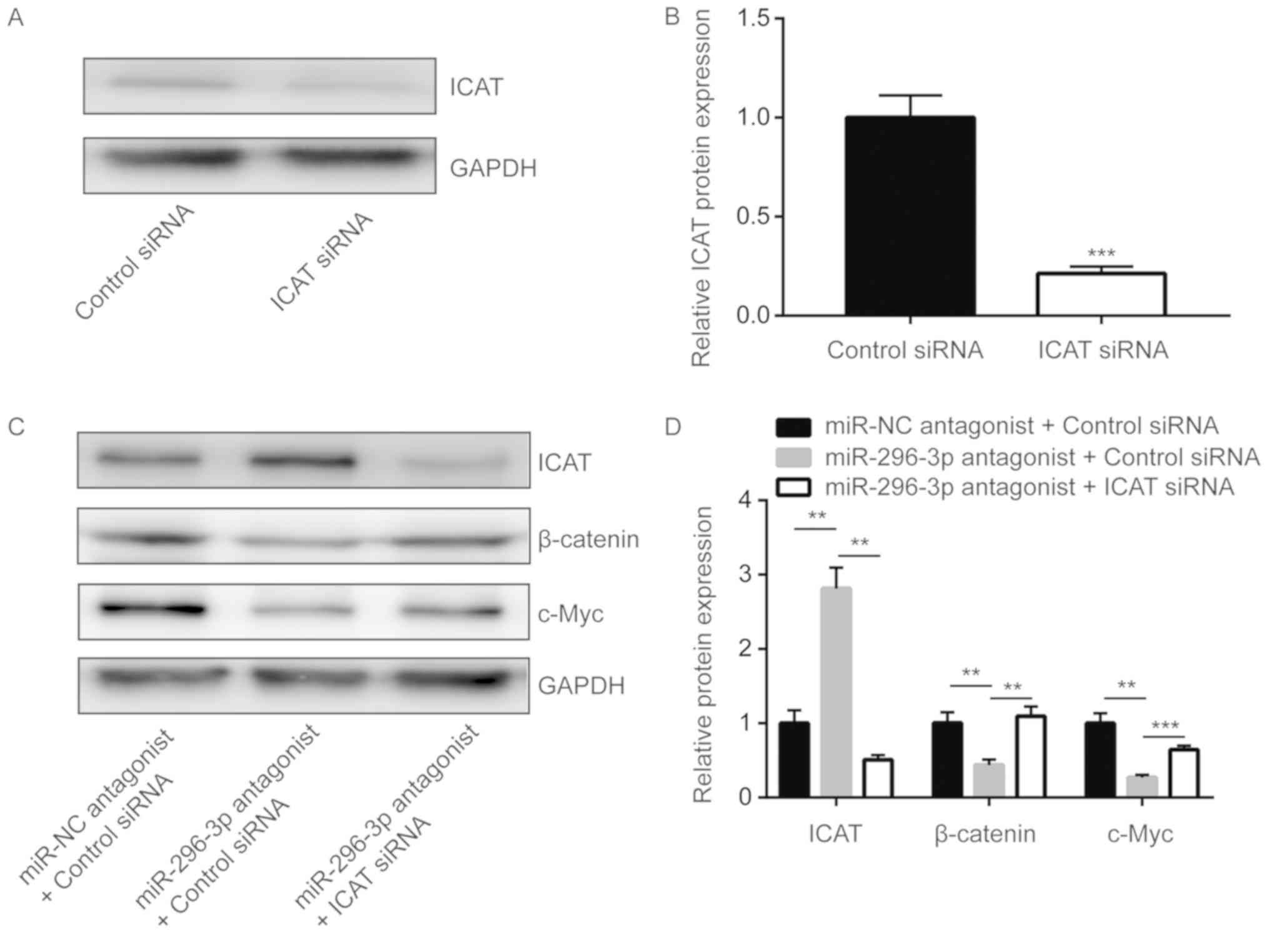
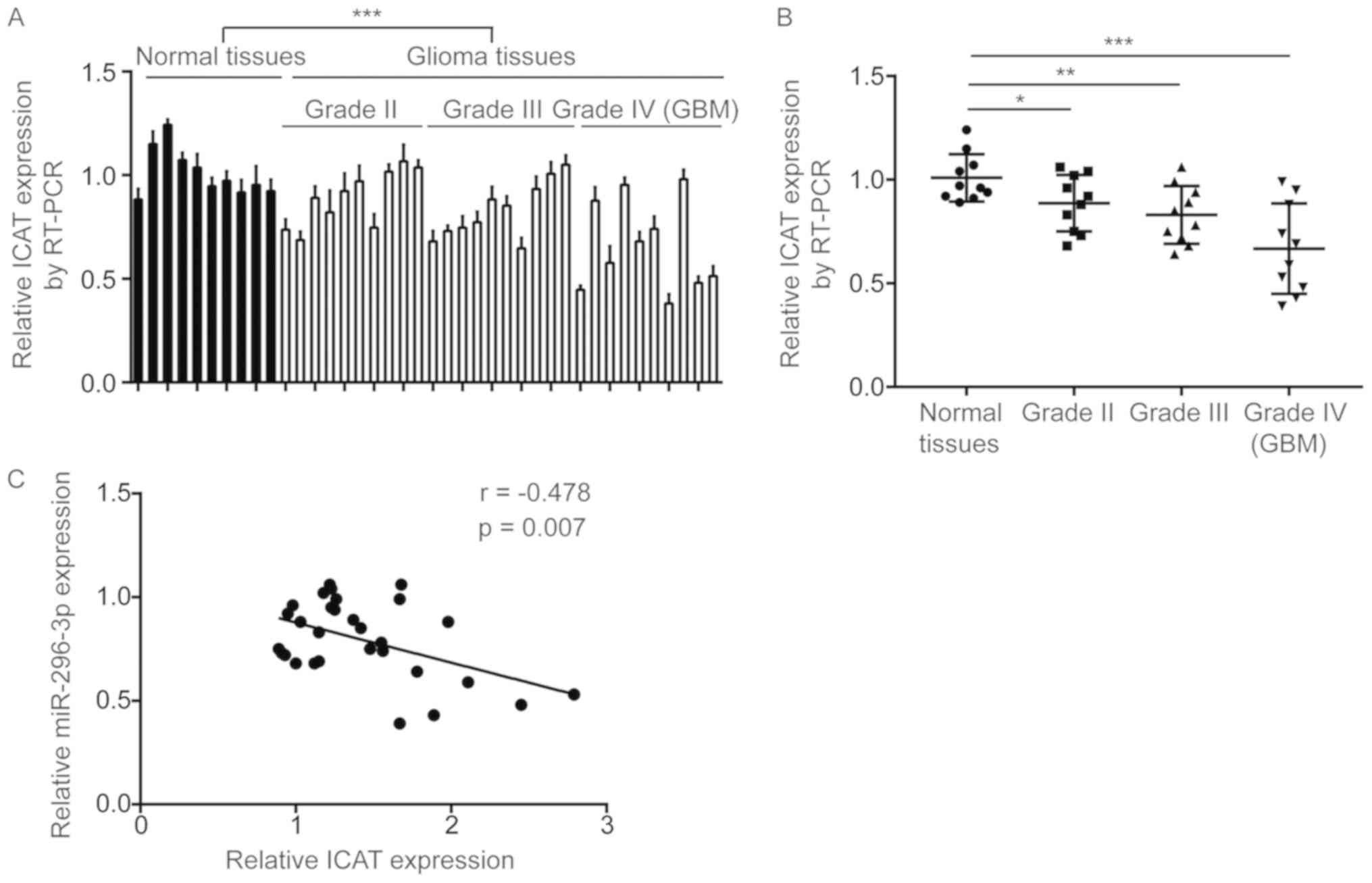
Zhang K, Zhu S, Liu Y, Dong X, Shi Z,
Zhang A, Liu C, Chen L, Wei J, Pu P, et al: ICAT inhibits
glioblastoma cell proliferation by suppressing Wnt/β-catenin
activity. Cancer Lett. 357:404–411. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tan Z, Zheng H, Liu X, Zhang W, Zhu J, Wu
G, Cao L, Song J, Wu S, Song L and Li J: MicroRNA-1229
overexpression promotes cell proliferation and tumorigenicity and
activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling in breast cancer. Oncotarget.
7:24076–24087. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee
WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, Scheithauer BW and Kleihues P: The 2007
WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta
Neuropathol. 114:97–109. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Betel D, Wilson M, Gabow A, Marks DS and
Sander C: The microRNA.org resource: Targets and expression.
Nucleic Acids Res. 36:D149–D153. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huang DW, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
Bioinformatics Resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Bioinformatics enrichment tools: Paths toward the comprehensive
functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res.
37:1–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ramis G, Villalonga-Planells R,
Serra-Sitjar M, Brell M, Fernández de Mattos S and Villalonga P:
The tumor suppressor FOXO3a mediates the response to EGFR
inhibition in glioblastoma cells. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 42:521–536.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Peng Y, He X, Chen H, Duan H, Shao B, Yang
F, Li H, Yang P, Zeng Y, Zheng J, et al: Inhibition of
microRNA-299-5p sensitizes glioblastoma cells to temozolomide via
the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. Biosci Rep. 38:BSR201810512018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang W, Shen C, Li C, Yang G, Liu H, Chen
X, Zhu D, Zou H, Zhen Y, Zhang D and Zhao S: miR-577 inhibits
glioblastoma tumor growth via the Wnt signaling pathway. Mol
Carcinog. 55:575–585. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zeng A, Yin J, Li Y, Li R, Wang Z, Zhou X,
Jin X, Shen F, Yan W and You Y: miR-129-5p targets Wnt5a to block
PKC/ERK/NF-kappaB and JNK pathways in glioblastoma. Cell Death Dis.
9:3942018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang G, Chen L, Khan AA, Li B, Gu B, Lin
F, Su X and Yan J: miRNA-124-3p/neuropilin-1(NRP-1) axis plays an
important role in mediating glioblastoma growth and angiogenesis.
Int J Cancer. 143:635–644. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen W, Kong KK, Xu XK, Chen C, Li H, Wang
FY, Peng XF, Zhang Z, Li P, Li JL and Li FC: Downregulation of
miR205 is associated with glioblastoma cell migration, invasion,
and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition, by targeting ZEB1 via
the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Int J Oncol. 52:485–495.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Huang SW, Ali ND, Zhong L and Shi J:
MicroRNAs as biomarkers for human glioblastoma: Progress and
potential. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 39:1405–1513. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yuan GQ, Wei NL, Mu LY, Wang XQ, Zhang YN,
Zhou WN and Pan YW: A 4-miRNAs signature predicts survival in
glioblastoma multiforme patients. Cancer Biomark. 20:443–452. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lu D, Li Y, Liu QR, Wu Q, Zhang H, Xie P
and Wang Q: Wls promotes the proliferation of breast cancer cells
via Wnt signaling. Med Oncol. 32:1402015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jang GB, Hong IS, Kim RJ, Lee SY, Park SJ,
Lee ES, Park JH, Yun CH, Chung JU, Lee KJ, et al: Wnt/β-catenin
small-molecule inhibitor CWP232228 preferentially inhibits the
growth of breast cancer stem-like cells. Cancer Res. 75:1691–1702.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gong A and Huang S: FoxM1 and
Wnt/β-catenin signaling in glioma stem cells. Cancer Res.
72:5658–5662. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Shin J, Shin Y, Oh SM, Yang H, Yu WJ, Lee
JP, Huh SO, Lee SH, Suh YH, Chung S and Kim HS: MiR-29b controls
fetal mouse neurogenesis by regulating ICAT-mediated Wnt/β-catenin
signaling. Cell Death Dis. 5:e14732014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu J, Han P, Gong J, Wang Y, Chen B, Liao
J and Tian D: Knockdown of KIAA1199 attenuates growth and
metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Discov.
4:1022018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gan CP, Sam KK, Yee PS, Zainal NS, Lee
BKB, Abdul Rahman ZA, Patel V, Tan AC, Zain RB and Cheong SC:
IFITM3 knockdown reduces the expression of CCND1 and CDK4 and
suppresses the growth of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cell
Oncol (Dordr). 42:477–490. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Deng X, Liu Z, Liu X, Fu Q, Deng T, Lu J,
Liu Y, Liang Z, Jiang Q, Cheng C and Fang W: miR-296-3p negatively
regulated by nicotine stimulates cytoplasmic translocation of c-Myc
via MK2 to suppress cell growth, metastasis and chemotherapy
resistance. Mol Ther. 26:1066–1081. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Fu Q, Song X, Liu Z, Deng X, Luo R, Ge C,
Li R, Li Z, Zhao M, Chen Y, et al: miRomics and proteomics reveal a
miR-296-3p/PRKCA/FAK/Ras/c-Myc feedback loop modulated by
HDGF/DDX5/β-catenin complex in lung adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer
Res. 23:6336–6350. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|