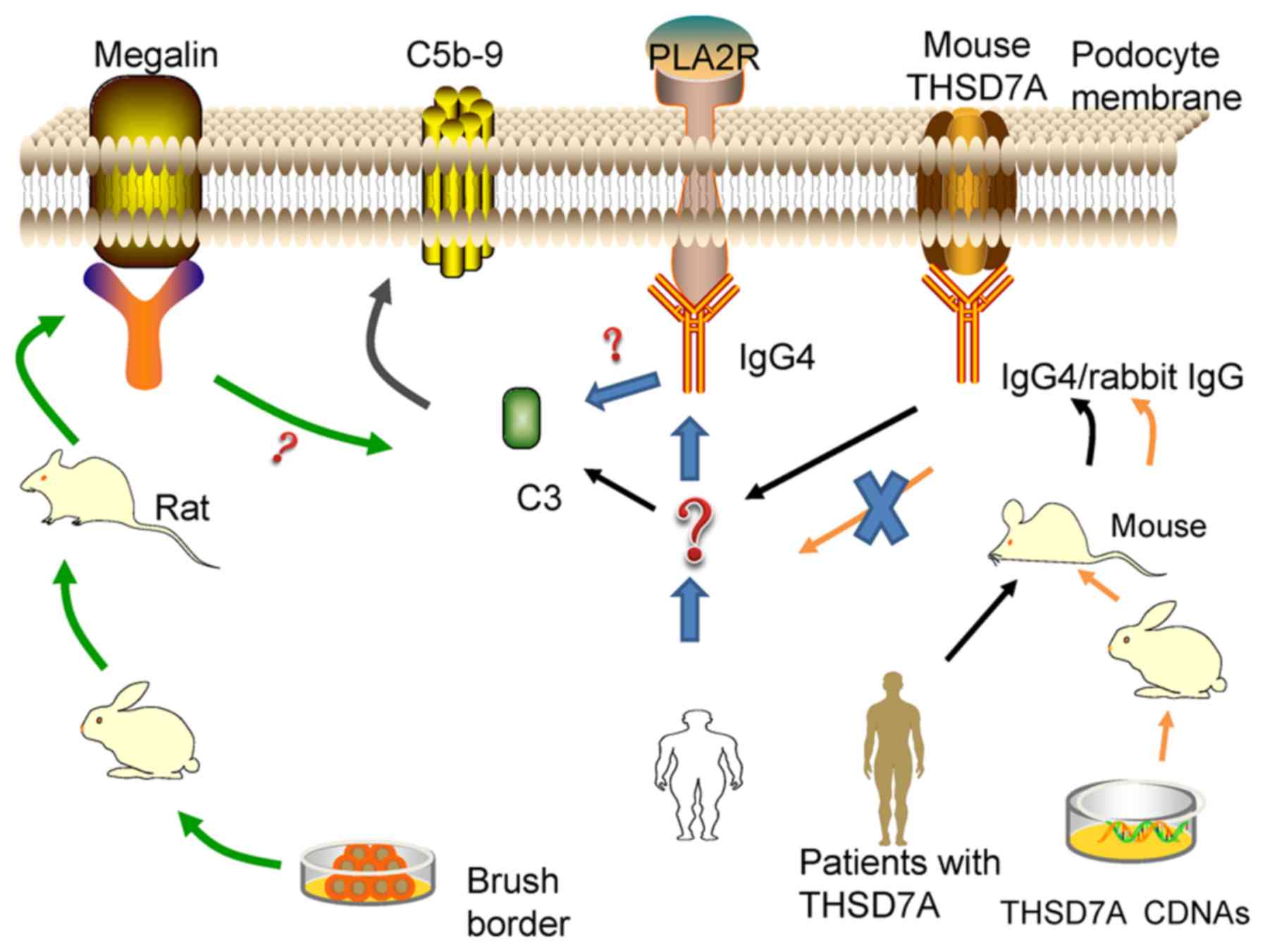
|
1
|
Cernaro V, Coppolino G, Visconti L, Rivoli
L, Lacquaniti A, Santoro D, Buemi A, Loddo S and Buemi M:
Erythropoiesis and chronic kidney disease-related anemia: From
physiology to new therapeutic advancements. Med Res Rev.
39:427–460. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen DQ, Cao G, Chen H, Argyopoulos CP, Yu
H, Su W, Chen L, Samuels DC, Zhuang S, Bayliss GP, et al:
Identification of serum metabolites associating with chronic kidney
disease progression and anti-fibrotic effect of
5-methoxytryptophan. Nat Commun. 10:14762019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen DQ, Cao G, Zhao H, Chen L, Yang T,
Wang M, Vaziri ND, Guo Y and Zhao YY: Combined melatonin and
poricoic acid A inhibits renal fibrosis through modulating the
interaction of Smad3 and β-catenin pathway in AKI-to-CKD continuum.
Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 10:20406223198691162019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
MacKinnon HJ, Wilkinson TJ, Clarke AL,
Gould DW, O'Sullivan TF, Xenophontos S, Watson EL, Singh SJ and
Smith AC: The association of physical function and physical
activity with all-cause mortality and adverse clinical outcomes in
nondialysis chronic kidney disease: A systematic review. Ther Adv
Chronic Dis. 9:209–226. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xiaofan H, Jing X, Chenni G, Yifan W,
Xialian Y, Li L, Hong R, Wen Z, Weiming W, Xiaoxia P, et al: New
risk score for predicting progression of membranous nephropathy. J
Transl Med. 17:412019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Petrosyan A, Cravedi P, Villani V,
Angeletti A, Manrique J, Renieri A, De Filippo RE, Perin L and Da
Sacco S: A glomerulus-on-a-chip to recapitulate the human
glomerular filtration barrier. Nat Commun. 10:36562019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Glassock RJ: The pathogenesis of
idiopathic membranous nephropathy: A 50-year odyssey. Am J Kidney
Dis. 56:157–167. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu X, Wang G, Chen N, Lu T, Nie S, Xu G,
Zhang P, Luo Y, Wang Y, Wang X, et al: Long-term exposure to air
pollution and increased risk of membranous nephropathy in China. J
Am Soc Nephrol. 27:3739–3746. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhu P, Zhou FD, Wang SX, Zhao MH and Wang
HY: Increasing frequency of idiopathic membranous nephropathy in
primary glomerular disease: A 10-year renal biopsy study from a
single Chinese nephrology centre. Nephrology (Carlton). 20:560–566.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pan X, Xu J, Ren H, Zhang W, Xu Y, Shen P,
Li X, Wang W, Chen X, Wu P, et al: Changing spectrum of
biopsy-proven primary glomerular diseases over the past 15 years: A
single-center study in China. Contrib Nephrol. 181:22–30. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen X, Chen Y, Shi K, Lv Y, Tong H, Zhao
G, Chen C, Chen B, Li D and Lu Z: Comparison of prognostic,
clinical, and renal histopathological characteristics of
overlapping idiopathic membranous nephropathy and IgA nephropathy
versus idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Sci Rep. 7:114682017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Maisonneuve P, Agodoa L, Gellert R,
Stewart JH, Buccianti G, Lowenfels AB, Wolfe RA, Jones E, Disney
AP, Briggs D, et al: Distribution of primary renal diseases leading
to end-stage renal failure in the United States, Europe, and
Australia/New Zealand: Results from an international comparative
study. Am J Kidney Dis. 35:157–165. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Latt KZ, Honda K, Thiri M, Hitomi Y, Omae
Y, Sawai H, Kawai Y, Teraguchi S, Ueno K, Nagasaki M, et al:
Identification of a two-SNP PLA2R1 Haplotype and HLA-DRB1 Alleles
as primary risk associations in idiopathic membranous nephropathy.
Sci Rep. 8:155762018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Couser WG: Primary Membranous Nephropathy.
Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 12:983–997. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Troyanov S, Wall CA, Scholey JW, Miller JA
and Cattran DC: Idiopathic membranous nephropathy: Definition and
relevance of a partial remission. Kidney International.
66:1199–1205. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cattran D and Brenchley P: Membranous
nephropathy: Thinking through the therapeutic options. Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 32:i22–i29. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fontecha-Barriuso M, Martin-Sanchez D,
Ruiz-Andres O, Poveda J, Sanchez-Niño MD, Valiño-Rivas L,
Ruiz-Ortega M, Ortiz A and Sanz AB: Targeting epigenetic DNA and
histone modifications to treat kidney disease. Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 33:1875–1886. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jefferson JA, Pippin JW and Shankland SJ:
Experimental models of membranous nephropathy. Drug Discov Today
Dis Models. 7:27–33. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Borza DB, Zhang JJ, Beck LH Jr,
Meyer-Schwesinger C and Luo W: Mouse models of membranous
nephropathy: The road less travelled by. Am J Clin Exp Immunol.
2:135–145. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tomas NM, Hoxha E, Reinicke AT, Fester L,
Helmchen U, Gerth J, Bachmann F, Budde K, Koch-Nolte F, Zahner G,
et al: Autoantibodies against thrombospondin type 1
domain-containing 7A induce membranous nephropathy. J Clin Invest.
126:2519–2532. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lim WH, Wong G, McDonald SP, Chakera A,
Luxton G, Isbel NM, Pilmore HL, Barbour T, Hughes P and Chadban SJ:
Long-term outcomes of kidney transplant recipients with end-stage
kidney disease attributed to presumed/advanced glomerulonephritis
or unknown cause. Sci Rep. 8:90212018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cybulsky AV, Quigg RJ and Salant DJ:
Experimental membranous nephropathy redux. Am J Physiol Renal
Physiol. 289:F660–F671. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ma H, Sandor DG and Beck LH Jr: The role
of complement in membranous nephropathy. Semin Nephrol. 33:531–542.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Heymann W, Hackel DB, Harwood S, Wilson SG
and Hunter JL: Production of nephrotic syndrome in rats by Freund's
adjuvants and rat kidney suspensions. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med.
100:660–664. 1959. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Salant DJ, Quigg RJ and Cybulsky AV:
Heymann nephritis: Mechanisms of renal injury. Kidney Int.
35:976–984. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Christiansen RE, Kolmannskog O, Leh S,
Iversen BM and Tenstad O: Glomerular charge barrier and development
of proteinuria in passive Heymann nephritis. Kidney Blood Press
Res. 31:203–209. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Salant DJ and Cybulsky AV: Experimental
glomerulonephritis. Methods Enzymol. 162:421–461. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kerjaschki D and Farquhar MG: The
pathogenic antigen of Heymann nephritis is a membrane glycoprotein
of the renal proximal tubule brush border. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
79:5557–5561. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kerjaschki D and Farquhar MG:
Immunocytochemical localization of the Heymann nephritis antigen
(GP330) in glomerular epithelial cells of normal Lewis rats. J Exp
Med. 157:667–686. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kerjaschki D, Ullrich R, Diem K,
Pietromonaco S, Orlando RA and Farquhar MG: Identification of a
pathogenic epitope involved in initiation of Heymann nephritis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 89:11179–11183. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Raychowdhury R, Zheng G, Brown D and
McCluskey RT: Induction of Heymann nephritis with a gp330/megalin
fusion protein. Am J Pathol. 148:1613–1623. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Couser WG: Mediation of immune glomerular
injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1:13–29. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Baker PJ, Ochi RF, Schulze M, Johnson RJ,
Campbell C and Couser WG: Depletion of C6 prevents development of
proteinuria in experimental membranous nephropathy in rats. Am J
Pathol. 135:185–194. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Prabakaran T, Nielsen R, Larsen JV,
Sørensen SS, Feldt-Rasmussen U, Saleem MA, Petersen CM, Verroust PJ
and Christensen EI: Receptor-mediated endocytosis of
α-galactosidase A in human podocytes in Fabry disease. PLoS One.
6:e250652011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Larsen C, Etzerodt A, Madsen M, Skjodt K,
Moestrup SK and Andersen CBF: Structural assembly of the
megadalton-sized receptor for intestinal vitamin B12
uptake and kidney protein reabsorption. Nat Commun. 9:52042018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ronco P and Debiec H: Pathophysiological
advances in membranous nephropathy: Time for a shift in patient's
care. Lancet. 385:1983–1992. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Vinaiphat A and Thongboonkerd V:
Characterizations of PMCA2-interacting complex and its role as a
calcium oxalate crystal-binding protein. Cell Mol Life Sci.
75:1461–1482. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Beausang JF, Fan HC, Sit R, Hutchins MU,
Jirage K, Curtis R, Hutchins E, Quake SR and Yabu JM: B cell
repertoires in HLA-sensitized kidney transplant candidates
undergoing desensitization therapy. J Transl Med. 15:92017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Rudkin FM, Raziunaite I, Workman H, Essono
S, Belmonte R, MacCallum DM, Johnson EM, Silva LM, Palma AS, Feizi
T, et al: Single human B cell-derived monoclonal anti-Candida
antibodies enhance phagocytosis and protect against disseminated
candidiasis. Nat Commun. 9:52882018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Natori Y, Shindo N and Natori Y:
Proteinuria induced by anti-dipeptidyl peptidase IV (gp108); role
of circulating and glomerular antigen. Clin Exp Immunol.
95:327–332. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hunter JL, Hackel DB and Heymann W:
Nephrotic syndrome in rats produced by sensitization to rat kidney
proteins: Immunologic studies. J Immunol. 85:319–327.
1960.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tomas NM, Beck LH Jr, Meyer-Schwesinger C,
Seitz-Polski B, Ma H, Zahner G, Dolla G, Hoxha E, Helmchen U,
Dabert-Gay AS, et al: Thrombospondin type-1 domain-containing 7A in
idiopathic membranous nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 371:2277–2287.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Glassock RJ: Pathogenesis of membranous
nephropathy: A new paradigm in evolution. Contrib Nephrol.
181:131–142. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tan K, Duquette M, Liu JH, Dong Y, Zhang
R, Joachimiak A, Lawler J and Wang JH: Crystal structure of the
TSP-1 type 1 repeats: A novel layered fold and its biological
implication. J Cell Biol. 159:373–382. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Allison SJ: Glomerular disease:
Thrombospondin type-1 domain-containing 7A-a new player in
membranous nephropathy. Nat Rev Nephrol. 11:632015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
De Vriese AS, Glassock RJ, Nath KA, Sethi
S and Fervenza FC: A Proposal for a serology-based approach to
membranous nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 28:421–430. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Godel M, Grahammer F and Huber TB:
Thrombospondin type-1 domain-containing 7A in idiopathic membranous
nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 372:10732015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Tomas NM, Meyer-Schwesinger C, von Spiegel
H, Kotb AM, Zahner G, Hoxha E, Helmchen U, Endlich N, Koch-Nolte F
and Stahl RAK: A Heterologous model of thrombospondin type 1
domain-containing 7A-associated membranous nephropathy. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 28:3262–3277. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Assmann KJ, van Son JP, Dijkman HB and
Koene RA: A nephritogenic rat monoclonal antibody to mouse
aminopeptidase A. Induction of massive albuminuria after a single
intravenous injection. J Exp Med. 175:623–635. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Dijkman HB, Gerlofs-Nijland ME, van der
Laak JA, Wetzels JF, Groenen PJ and Assmann KJ: Podocyte changes
after induction of acute albuminuria in mice by anti-aminopeptidase
A mAb. Nephron Exp Nephrol. 94:e85–e93. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Border WA, Ward HJ, Kamil ES and Cohen AH:
Induction of membranous nephropathy in rabbits by administration of
an exogenous cationic antigen. J Clin Invest. 69:451–461. 1982.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Liu B, Lu R, Li H, Zhou Y, Zhang P, Bai L,
Chen D, Chen J, Li J, Yu P, et al: Zhen-wu-tang ameliorates
membranous nephropathy rats through inhibiting NF-κB pathway and
NLRP3 inflammasome. Phytomedicine. 59:1529132019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Adler SG, Wang H, Ward HJ, Cohen AH and
Border WA: Electrical charge. Its role in the pathogenesis and
prevention of experimental membranous nephropathy in the rabbit. J
Clin Invest. 71:487–499. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Chen JS, Chen A, Chang LC, Chang WS, Lee
HS, Lin SH and Lin YF: Mouse model of membranous nephropathy
induced by cationic bovine serum albumin: Antigen dose-response
relations and strain differences. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
19:2721–2728. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Debiec H, Lefeu F, Kemper MJ, Niaudet P,
Deschênes G, Remuzzi G, Ulinski T and Ronco P: Early-childhood
membranous nephropathy due to cationic bovine serum albumin. N Engl
J Med. 364:2101–2110. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zhang JJ, Malekpour M, Luo W, Ge L, Olaru
F, Wang XP, Bah M, Sado Y, Heidet L, Kleinau S, et al: Murine
membranous nephropathy: Immunization with α3(IV) collagen fragment
induces subepithelial immune complexes and FcγR-independent
nephrotic syndrome. J Immunol. 188:3268–3277. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Hopfer H, Hunemorder S, Treder J, Turner
JE, Paust HJ, Meyer-Schwesinger C, Hopfer U, Sachs M, Peters A,
Bucher-Kocaoglu B, et al: Glomerulopathy induced by immunization
with a peptide derived from the goodpasture antigen α3IV-NC1. J
Immunol. 194:3646–3655. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Luo W, Olaru F, Miner JH, Beck LH Jr, van
der Vlag J, Thurman JM and Borza DB: Alternative pathway is
essential for glomerular complement activation and proteinuria in a
mouse model of membranous nephropathy. Front Immunol. 9:14332018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Hopfer H, Maron R, Butzmann U, Helmchen U,
Weiner HL and Kalluri R: The importance of cell-mediated immunity
in the course and severity of autoimmune anti-glomerular basement
membrane disease in mice. FASEB J. 17:860–868. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Meyer TN, Schwesinger C, Wahlefeld J,
Dehde S, Kerjaschki D, Becker JU, Stahl RA and Thaiss F: A new
mouse model of immune-mediated podocyte injury. Kidney Int.
72:841–852. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Tsai SF, Wu MJ and Chen CH: Low serum C3
level, high neutrophil-lymphocyte-ratio, and high
platelet-lymphocyte-ratio all predicted poor long-term renal
survivals in biopsy-confirmed idiopathic membranous nephropathy.
Scie Rep. 9:62092019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Meyer-Schwesinger C, Dehde S, Klug P,
Becker JU, Mathey S, Arefi K, Balabanov S, Venz S, Endlich KH,
Pekna M, et al: Nephrotic syndrome and subepithelial deposits in a
mouse model of immune-mediated anti-podocyte glomerulonephritis. J
Immunol. 187:3218–3229. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Beck LH Jr, Bonegio RG, Lambeau G, Beck
DM, Powell DW, Cummins TD, Klein JB and Salant DJ: M-type
phospholipase A2 receptor as target antigen in idiopathic
membranous nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 361:11–21. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Debiec H and Ronco P: Immune response
against autoantigen PLA2R is not gambling: Implications for
pathophysiology, prognosis, and therapy. J Am Soc Nephrol.
27:1275–1277. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Pandey P, Roy KK, Liu H, Ma G, Pettaway S,
Alsharif WF, Gadepalli RS, Rimoldi JM, McCurdy CR, Cutler SJ and
Doerksen RJ: Structure-based identification of potent natural
product chemotypes as cannabinoid receptor 1 inverse agonists.
Molecules. 23(pii): E26302018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wang J, Cui Z, Lu J, Probst C, Zhang YM,
Wang X, Qu Z, Wang F, Meng LQ, Cheng XY, et al: Circulating
antibodies against thrombospondin type-I domain-containing 7A in
Chinese patients with idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Clin J Am
Soc Nephrol. 12:1642–1651. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Liu W, Gao C, Dai H, Zheng Y, Dong Z, Gao
Y, Liu F, Zhang Z, Liu Z, Liu W, et al: Immunological pathogenesis
of membranous nephropathy: Focus on PLA2R1 and Its role. Front
Immunol. 10:18092019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Song JS, Kim YJ, Han KU, Yoon BD and Kim
JW: Zymosan and PMA activate the immune responses of Mutz3-derived
dendritic cells synergistically. Immunol Lett. 167:41–46. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Gawryl MS, Simon MT, Eatman JL and Lint
TF: An enzyme-linked immunoabsorbent assay for the quantitation of
the terminal complement complex from cell membranes or in activated
human sera. J Immunol Methods. 95:217–225. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Ishikawa S, Tsukada H and Bhattacharya J:
Soluble complex of complement increases hydraulic conductivity in
single microvessels of rat lung. J Clin Invest. 91:103–109. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Liu WJ, Li ZH, Chen XC, Zhao XL, Zhong Z,
Yang C, Wu HL, An N, Li WY and Liu HF: Blockage of the
lysosome-dependent autophagic pathway contributes to complement
membrane attack complex-induced podocyte injury in idiopathic
membranous nephropathy. Sci Rep. 7:86432017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Fearon DT and Austen KF: Activation of the
alternative complement pathway due to resistance of zymosan-bound
amplification convertase to endogenous regulatory mechanisms. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 74:1683–1687. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Tegla CA, Cudrici C, Patel S, Trippe R
III, Rus V, Niculescu F and Rus H: Membrane attack by complement:
The assembly and biology of terminal complement complexes. Immunol
Res. 51:45–60. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Harboe M, Garred P, Lindstad JK, Pharo A,
Müller F, Stahl GL, Lambris JD and Mollnes TE: The role of
properdin in zymosan- and Escherichia coli-induced complement
activation. J Immunol. 189:2606–2613. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Rawal N and Pangburn MK: C5 convertase of
the alternative pathway of complement. Kinetic analysis of the free
and surface-bound forms of the enzyme. J Biol Chem.
273:16828–16835. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Rawal N and Pangburn M: Formation of
high-affinity C5 convertases of the alternative pathway of
complement. J Immunol. 166:2635–2642. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Zhang MH, Fan JM, Xie XS, Deng YY, Chen
YP, Zhen R, Li J, Cheng Y and Wen J: Ginsenoside-Rg1 protects
podocytes from complement mediated injury. J Ethnopharmacol.
137:99–107. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Zhang C, Leng L, Zhang X, Zhao Y and Li Z:
Comprehensive identification of immune-associated biomarkers based
on network and mRNA expression patterns in membranous
glomerulonephritis. J Transl Med. 16:2102018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Bruschi M, Petretto A, Santucci L, Vaglio
A, Pratesi F, Migliorini P, Bertelli R, Lavarello C, Bartolucci M,
Candiano G, et al: Neutrophil Extracellular Traps protein
composition is specific for patients with Lupus nephritis and
includes methyl-oxidized alphaenolase (methionine sulfoxide 93).
Scie Rep. 9:79342019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Li LZ, Hu Y, Ai SL, Cheng L, Liu J, Morris
E, Li Y, Gou SJ and Fu P: The relationship between thyroid
dysfunction and nephrotic syndrome: A clinicopathological study.
Sci Rep. 9:64212019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Pozdzik A, Brocheriou I, David C, Touzani
F, Goujon JM and Wissing KM: Membranous nephropathy and
anti-podocytes antibodies: Implications for the diagnostic workup
and disease management. Biomed Res Int. 2018:62810542018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Borsos T: Immune complex mediated
activation of the classic complement pathway. Behring Inst Mitt.
93–101. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Cattran DC and Brenchley PE: Membranous
nephropathy: Integrating basic science into improved clinical
management. Kidney Int. 91:566–574. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Zhang Q, Huang B, Liu X, Liu B, Zhang Y,
Zhang Z, Hua J, Fan Y, Hu L, Meng M, et al: Ultrasensitive
quantitation of anti-phospholipase A2 receptor antibody as a
diagnostic and prognostic indicator of idiopathic membranous
nephropathy. Sci Rep. 7:120492017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Fresquet M, Jowitt TA, McKenzie EA, Ball
MD, Randles MJ, Lennon R and Brenchley PE: PLA2R binds
to the annexin A2-S100A10 complex in human podocytes. Sci Rep.
7:68762017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Vidarsson G, Dekkers G and Rispens T: IgG
subclasses and allotypes: From structure to effector functions.
Front Immunol. 5:5202014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Borza DB: Alternative pathway
dysregulation and the conundrum of complement activation by IgG4
immune complexes in membranous nephropathy. Front Immunol.
7:1572016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Wang Z, Wen L, Dou Y and Zhao Z: Human
anti-thrombospondin type 1 domain-containing 7A antibodies induce
membranous nephropathy through activation of lectin complement
pathway. Biosci Rep. 38(pii): BSR201801312018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Hayashi N, Okada K, Matsui Y, Fujimoto K,
Adachi H, Yamaya H, Matsushita M and Yokoyama H: Glomerular
mannose-binding lectin deposition in intrinsic antigen-related
membranous nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 33:832–840. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Garred P, Genster N, Pilely K,
Bayarri-Olmos R, Rosbjerg A, Ma YJ and Skjoedt MO: A journey
through the lectin pathway of complement-MBL and beyond. Immunol
Rev. 274:74–97. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Bally S, Debiec H, Ponard D, Dijoud F,
Rendu J, Fauré J, Ronco P and Dumestre-Perard C: Phospholipase A2
Receptor-related membranous nephropathy and mannan-binding lectin
deficiency. J Am Soc Nephrol. 27:3539–3544. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Hoxha E, Wiech T, Stahl PR, Zahner G,
Tomas NM, Meyer-Schwesinger C, Wenzel U, Janneck M, Steinmetz OM,
Panzer U, et al: A mechanism for Cancer-associated membranous
nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 374:1995–1996. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Matsumoto A, Matsui I, Namba T, Sakaguchi
Y, Mizuno H, Shirayama Y, Shimada K, Hashimoto N, Doi Y, Yamaguchi
S, et al: VEGF-A links angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia
(ALHE) to THSD7A membranous nephropathy: A report of 2 cases. Am J
Kidney Dis. 73:880–885. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Xu X, Wang G, Chen N, Lu T, Nie S, Xu G,
Zhang P, Luo Y, Wang Y, Wang X, et al: Long-term exposure to air
pollution and increased risk of membranous nephropathy in China. J
Am Soc Nephrol. 27:3739–3746. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Silliman CC, Moore EE, Zallen G, Gonzalez
R, Johnson JL, Elzi DJ, Meng X, Hanasaki K, Ishizaki J, Arita H, et
al: Presence of the M-type sPLA(2) receptor on neutrophils and its
role in elastase release and adhesion. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
283:C1102–C1113. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Granata F, Petraroli A, Boilard E, Bezzine
S, Bollinger J, Del Vecchio L, Gelb MH, Lambeau G, Marone G and
Triggiani M: Activation of cytokine production by secreted
phospholipase A2 in human lung macrophages expressing the M-type
receptor. J Immunol. 174:464–474. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Beck LH Jr: PLA2R and THSD7A: Disparate
paths to the same disease? J Am Soc Nephrol. 28:2579–2589. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Chiorazzo MG, Tunset HM, Popov AV,
Johansen B, Moestue S and Delikatny EJ: Detection and
differentiation of breast cancer Sub-types using a cPLA2α
activatable fluorophore. Sci Rep. 9:61222019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Pan Q, Lan Q, Peng Y, Cai J, Zheng J,
Dickerson C, Xiao H and Liu HF: Nature, functions, and clinical
implications of IgG4 autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus
and rheumatoid arthritis. Discov Med. 23:169–174. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Salant DJ: Unmet challenges in membranous
nephropathy. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 28:70–76. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Borza DB: Alternative pathway
dysregulation and the conundrum of complement activation by IgG4
immune complexes in membranous nephropathy. Front Immunol.
7:1572016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Liu D, Zhang J, Shi Y and Liu Z: Gene
polymorphism and risk of idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Life
Sci. 229:124–131. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Canadas-Garre M, Anderson K, McGoldrick J,
Maxwell AP and McKnight AJ: Genomic approaches in the search for
molecular biomarkers in chronic kidney disease. J Transl Med.
16:2922018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Kamyshova ES, Bobkova IN, Gorelova IA,
Каkhsurueva PA and Filatova EE: Genetic determinants of the
development and course of membranous nephropathy. Ter Arkh.
90:105–111. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Lan HY, Mu W, Tomita N, Huang XR, Li JH,
Zhu HJ, Morishita R and Johnson RJ: Inhibition of renal fibrosis by
gene transfer of inducible Smad7 using ultrasound-microbubble
system in rat UUO model. J Am Soc Nephrol. 14:1535–1548. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Fujii H, Li SH, Wu J, Miyagi Y, Yau TM,
Rakowski H, Egashira K, Guo J, Weisel RD and Li RK: Repeated and
targeted transfer of angiogenic plasmids into the infarcted rat
heart via ultrasound targeted microbubble destruction enhances
cardiac repair. Eur Heart J. 32:2075–2084. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Huang B, Wang L, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Zhang
Q, Xiao H, Zhou B, Sun Z, Cao YN, Chen Y, et al: A novel
Time-resolved Fluoroimmunoassay for the quantitative detection of
Antibodies against the phospholipase A2 receptor. Sci Rep.
7:460962017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Pan Y, Wan J, Liu Y, Yang Q, Liang W,
Singhal PC, Saleem MA and Ding G: sPLA2 IB induces human podocyte
apoptosis via the M-type phospholipase A2 receptor. Sci Re.
4:66602014.
|
|
109
|
Lambeau G and Lazdunski M: Receptors for a
growing family of secreted phospholipases A2. Trends Pharmacol Sci.
20:162–170. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Tamaru S, Mishina H, Watanabe Y, Watanabe
K, Fujioka D, Takahashi S, Suzuki K, Nakamura T, Obata JE, Kawabata
K, et al: Deficiency of phospholipase A2 receptor exacerbates
ovalbumin-induced lung inflammation. J Immunol. 191:1021–1028.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Chen DQ, Feng YL, Cao G and Zhao YY:
Natural products as a source for antifibrosis therapy. Trends
Pharmacol Sci. 39:937–952. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Chen DQ, Hu HH, Wang YN, Feng YL, Cao G
and Zhao YY: Natural products for the prevention and treatment of
kidney disease. Phytomedicine. 50:50–60. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Wang M, Chen DQ, Chen L, Cao G, Zhao H,
Liu D, Vaziri ND, Guo Y and Zhao YY: Novel inhibitors of the
cellular renin-angiotensin system components, poricoic acids,
target Smad3 phosphorylation and Wnt/beta-catenin pathway against
renal fibrosis. Br J Pharmacol. 175:2689–2708. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Chen Y, Deng Y, Ni Z, Chen N, Chen X, Shi
W, Zhan Y, Yuan F, Deng W and Zhong Y: Efficacy and safety of
traditional Chinese medicine (Shenqi Particle) for patients with
idiopathic membranous nephropathy: A multicenter randomized
controlled clinical trial. Am J Kidney Dis. 62:1068–1076. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Zhang L, Li P, Xing CY, Zhao JY, He YN,
Wang JQ, Wu XF, Liu ZS, Zhang AP, Lin HL, et al: Efficacy and
safety of Abelmoschus manihot for primary glomerular disease: A
prospective, multicenter randomized controlled clinical trial. Am J
Kidney Dis. 64:57–65. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Liu S, Li X, Li H, Liang Q and Chen J and
Chen J: Comparison of tripterygium wilfordii multiglycosides and
tacrolimus in the treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy: A
prospective cohort study. BMC Nephrol. 16:2002015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|