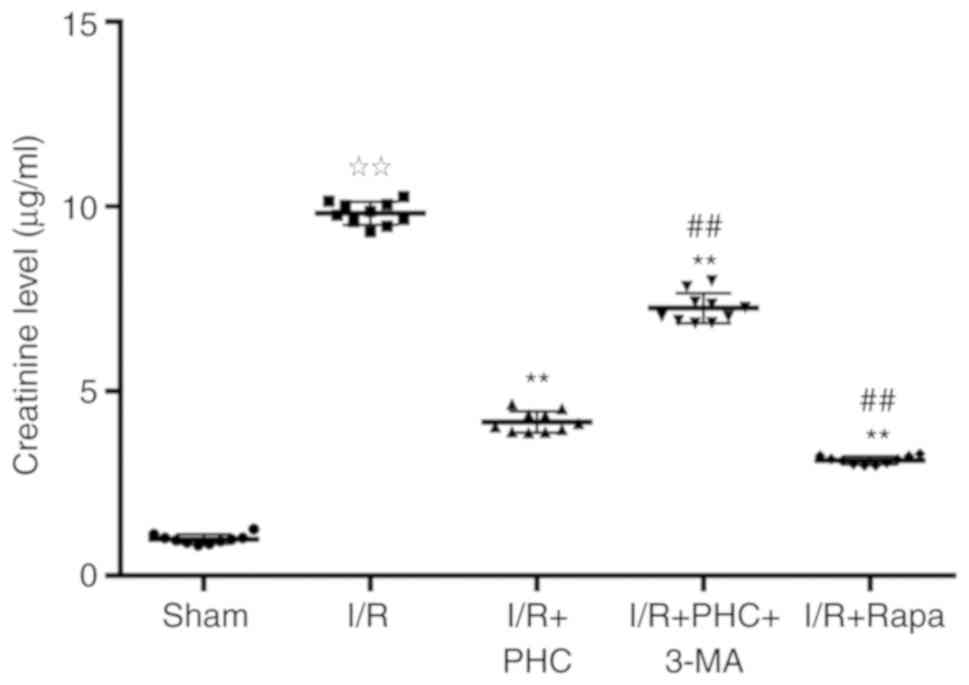
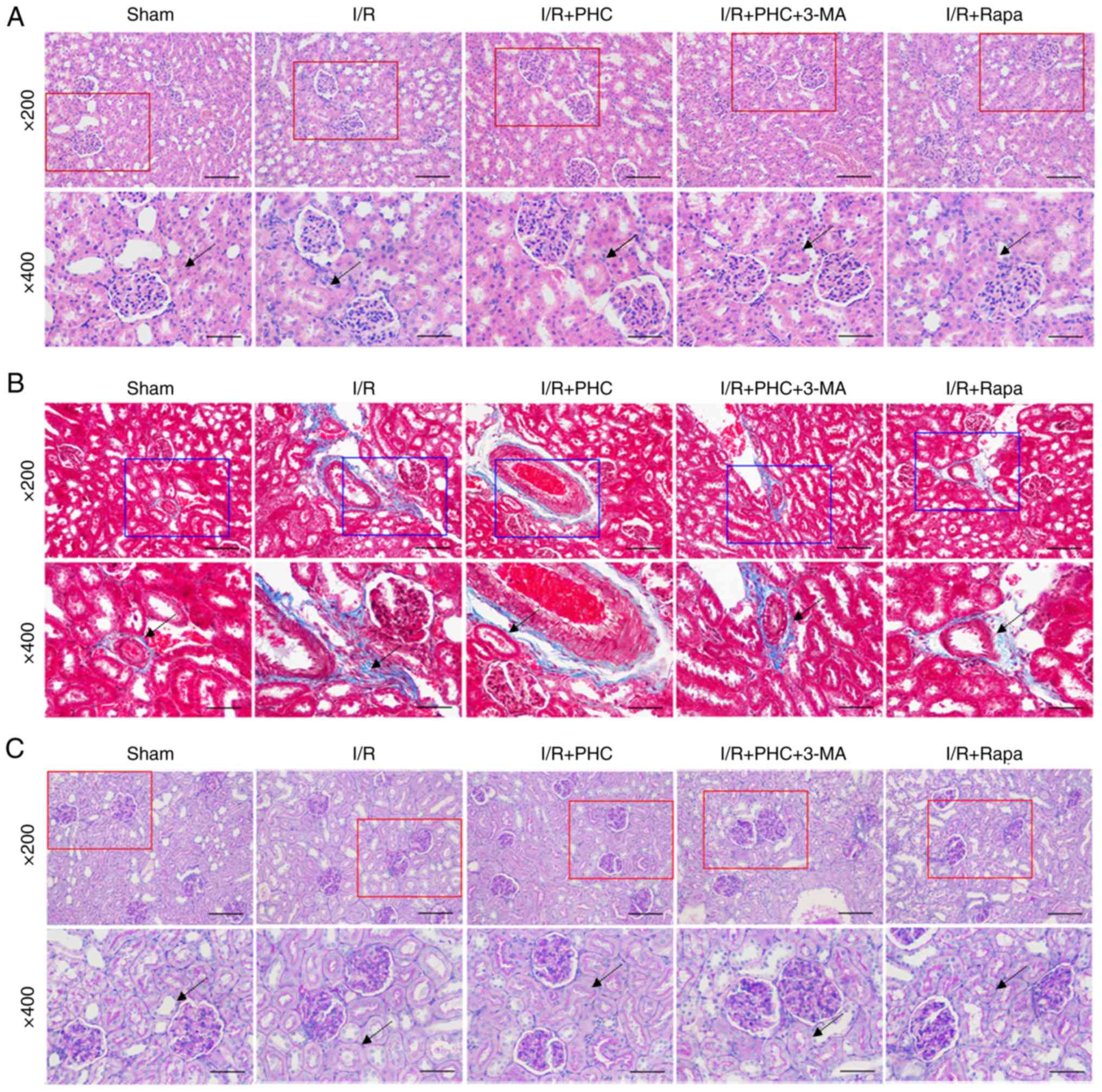
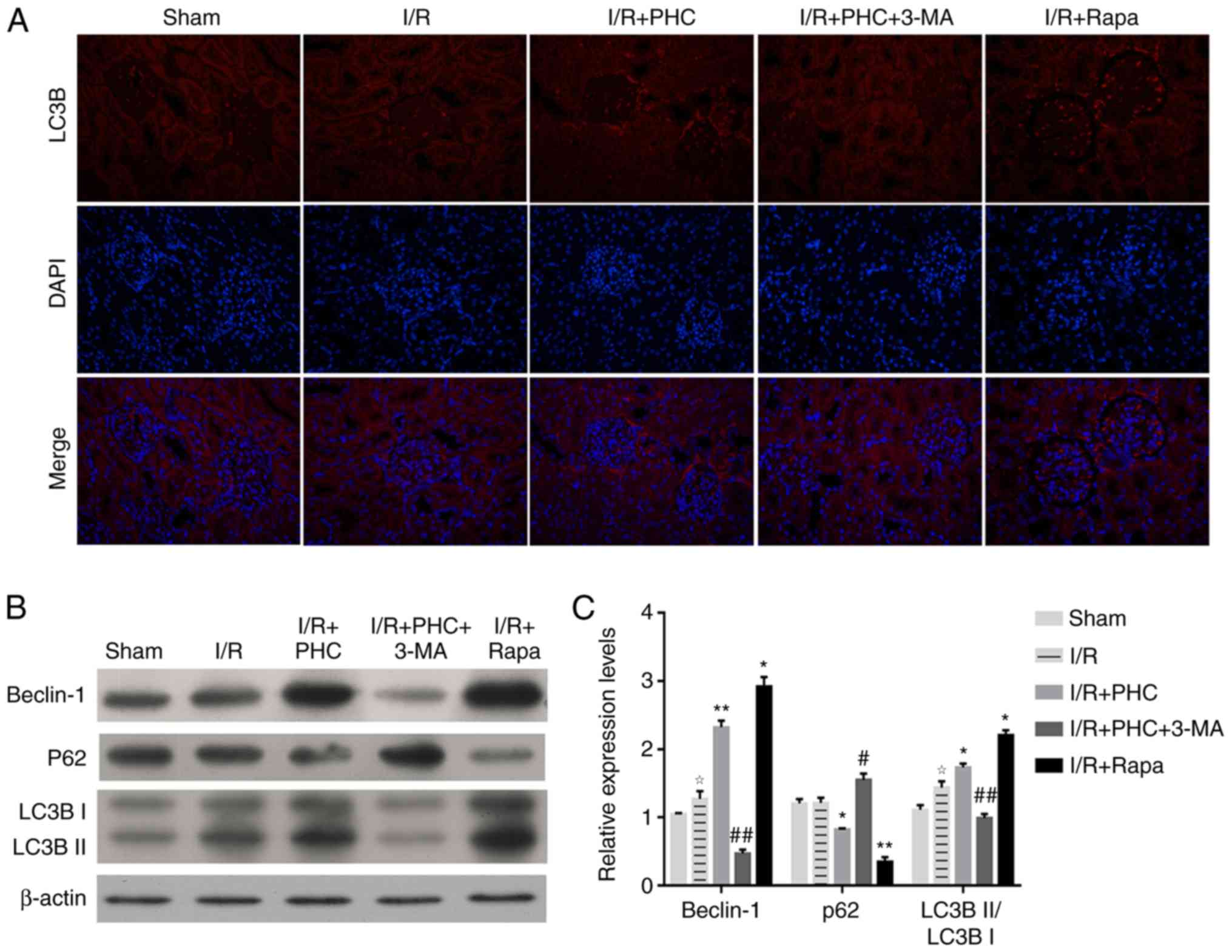
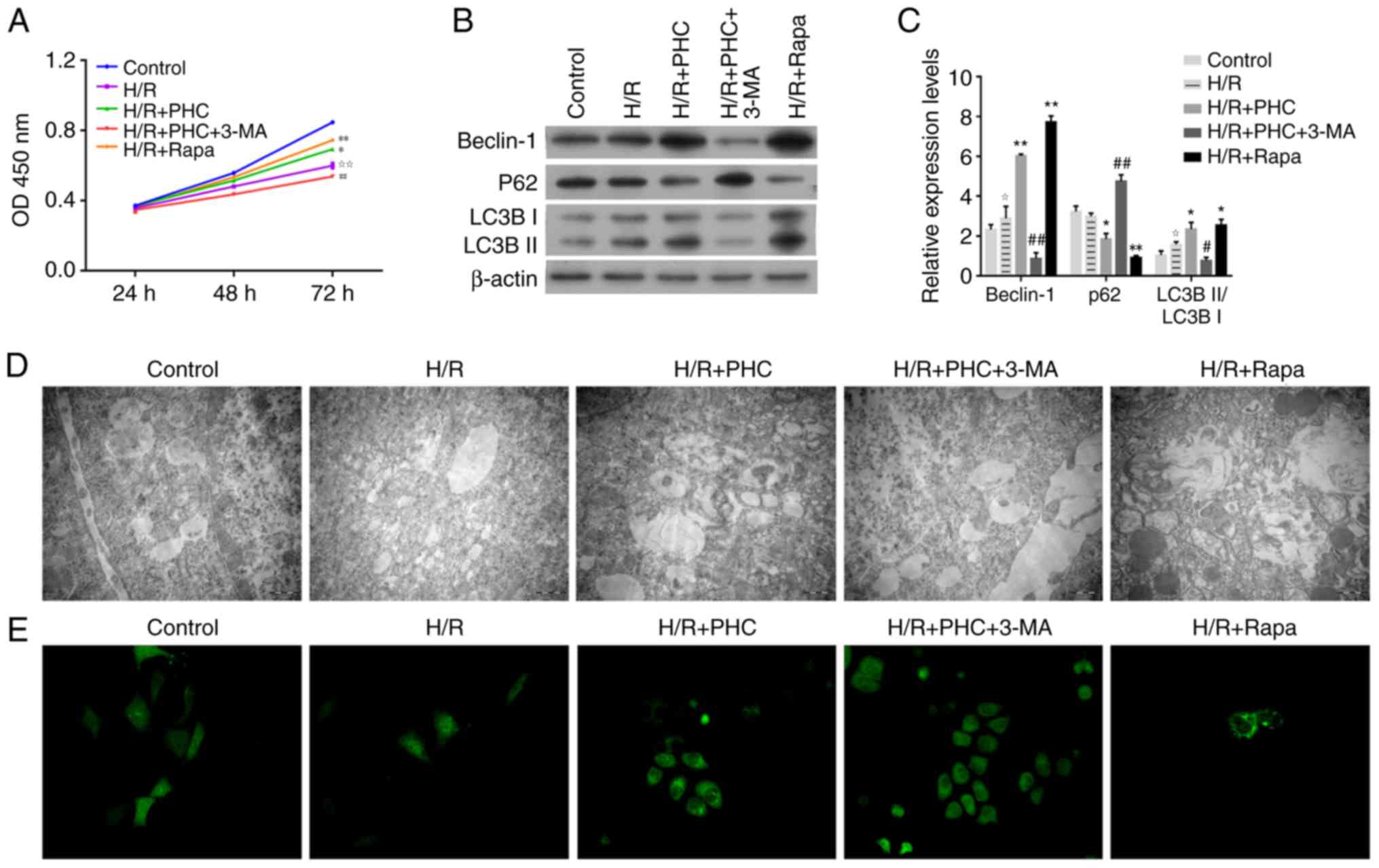
|
1
|
Malek M and Nematbakhsh M: Renal
ischemia/reperfusion injury; from pathophysiology to treatment. J
Renal Inj Prev. 4:20–27. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sharfuddin AA and Molitoris BA:
Pathophysiology of ischemic acute kidney injury. Nat Rev Nephrol.
7:189–200. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Danobeitia JS, Djamali A and Fernandez LA:
The role of complement in the pathogenesis of renal
ischemia-reperfusion injury and fibrosis. Fibrogenesis Tissue
Repair. 7:162014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kellum JA, Unruh ML and Murugan R: Acute
kidney injury. BMJ Clin Evid. 2011(pii): 20012011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ling H, Chen H, Wei M, Meng X, Yu Y and
Xie K: The effect of autophagy on inflammation cytokines in renal
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Inflammation. 39:347–356. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu D, Shang H and Liu Y: Stanniocalcin-1
protects a mouse model from renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by
affecting ROS-mediated multiple signaling pathways. Int J Mol Sci.
17(pii): E10512016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wen J, Shu Y and Zhang W: ROS, P53, and
ischemic acute kidney injury in diabetic models. Kidney Int.
88:198–199. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Qiao X, Chen X, Wu D, Ding R, Wang J, Hong
Q, Shi S, Li J, Xie Y, Lu Y and Wang Z: Mitochondrial pathway is
responsible for aging-related increase of tubular cell apoptosis in
renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci.
60:830–839. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Migita H, Yoshitake S, Tange Y,
Choijookhuu N and Hishikawa Y: Hyperbaric oxygen therapy suppresses
apoptosis and promotes renal tubular regeneration after renal
ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Nephrourol Mon. 8:e344212016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jie L, Hong Z, Hong L, Zhou J, Cui L, Yuan
S, Chu X and Yu P: Hydrogen-rich saline promotes the recovery of
renal function after ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats via
anti-apoptosis and anti-inflammation. Front Pharmacol.
7:1062016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang Y, Fu Z, Zhong Z, Wang R, Hu L,
Xiong Y, Wang Y and Ye Q: Hypothermic machine perfusion decreases
renal cell apoptosis during ischemia/reperfusion injury via the
Ezrin/AKT pathway. Artif Organs. 40:129–135. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yu C and Wang J: Neuroprotective effect of
penehyclidine hydrochloride on focal cerebral ischemiareperfusion
injury. Neural Regen Res. 8:622–632. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shen W, Gan J, Xu S, Jiang G and Wu H:
Penehyclidine hydrochloride attenuates LPS-induced acute lung
injury involvement of NF-kappaB pathway. Pharmacol Res. 60:296–302.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhan J, Liu Y, Zhang Z, Chen C, Chen K and
Wang Y: Effect of penehyclidine hydrochloride on expressions of
MAPK in mice with CLP-induced acute lung injury. Mol Biol Rep.
38:1909–1914. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cai DS, Jin BB, Pei L and Jin Z:
Protective effects of penehyclidine hydrochloride on liver injury
in a rat cardiopulmonary bypass model. Eur J Anaesthesiol.
27:824–828. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang Y, Leng YF, Xue X, Zhang Y, Wang T
and Kang YQ: Effects of penehyclidine hydrochloride in small
intestinal damage caused by limb ischemia-reperfusion. World J
Gastroenterol. 17:254–259. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang YP, Li G, Ma LL, Zheng Y, Zhang SD,
Zhang HX, Qiu M and Ma X: Penehyclidine hydrochloride ameliorates
renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. J Surg Res. 186:390–397.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mizushima N and Komatsu M: Autophagy:
Renovation of cells and tissues. Cell. 147:728–741. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Caramés B, Taniguchi N, Otsuki S, Blanco
FJ and Lotz M: Autophagy is a protective mechanism in normal
cartilage, and its aging-related loss is linked with cell death and
osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 62:791–801. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cursio R, Colosetti P and Gugenheim J:
Autophagy and liver ischemia-reperfusion injury. Biomed Res Int.
2015:4175902015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cardinal J, Pan P and Tsung A: Protective
role of cisplatin in ischemic liver injury through induction of
autophagy. Autophagy. 5:1211–1212. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lu Y, Wang WJ, Song YZ and Liang ZQ: The
protective mechanism of schisandrin A in d-galactosamine-induced
acute liver injury through activation of autophagy. Pharm Biol.
52:1302–1307. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang D, Ma Y, Li Z, Kang K, Sun X, Pan S,
Wang J, Pan H, Liu L, Liang D and Jiang H: The role of AKT1 and
autophagy in the protective effect of hydrogen sulphide against
hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Autophagy. 8:954–962.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Guan X, Qian Y, Shen Y, Zhang L, Du Y, Dai
H, Qian J and Yan Y: Autophagy protects renal tubular cells against
ischemia/reperfusion injury in a time-dependent manner. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 36:285–298. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jiang M, Liu K, Luo J and Dong Z:
Autophagy is a renoprotective mechanism during in vitro hypoxia and
in vivo ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Pathol. 176:1181–1192.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Weisman R: Target of rapamycin (TOR)
regulates growth in response to nutritional signals. Microbiol
Spectr. 4:2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang Z and Klionsky DJ: Mammalian
autophagy: Core molecular machinery and signaling regulation. Curr
Opin Cell Biol. 22:124–131. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cao QH, Liu F, Yang ZL, Fu XH, Yang ZH,
Liu Q, Wang L, Wan XB and Fan XJ: Prognostic value of autophagy
related proteins ULK1, Beclin 1, ATG3, ATG5, ATG7, ATG9, ATG10,
ATG12, LC3B and p62/SQSTM1 in gastric cancer. Am J Transl Res.
8:3831–3847. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hamacher-Brady A: Autophagy regulation and
integration with cell signaling. Antioxid Redox Signal. 17:756–765.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Abeliovich H: Guidelines for the use and
interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy. Haematologica.
27:151–175. 2012.
|
|
31
|
Tiwari RV, Parajuli P and Sylvester PW:
Synergistic anticancer effects of combined γ-tocotrienol and
oridonin treatment is associated with the induction of autophagy.
Mol Cell Biochem. 408:123–137. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kang R, Zeh HJ, Lotze MT and Tang D: The
Beclin 1 network regulates autophagy and apoptosis. Cell Death
Differ. 18:571–580. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Moscat J and Diaz-Meco MT: p62 at the
crossroads of autophagy, apoptosis, and cancer. Cell.
137:1001–1004. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals, . Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th.
National Academies Press (US); Washington (DC): 2011
|
|
35
|
Zheng Y, Lu M, Ma L, Zhang S, Qiu M and
Wang Y: Osthole ameliorates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in
rats. J Surg Res. 183:347–354. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shimizu S, Saito M, Kinoshita Y, Ohmasa F,
Dimitriadis F, Shomori K, Hayashi A and Satoh K: Nicorandil
ameliorates ischaemia-reperfusion injury in the rat kidney. Br J
Pharmacol. 163:272–282. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jia X, Zhang L and Mao X: S-propranolol
protected H9C2 cells from ischemia/reperfusion-induced apoptosis
via downregultion of RACK1 gene. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:10335–10344. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Swanlund JM, Kregel KC and Oberley TD:
Investigating autophagy: Quantitative morphometric analysis using
electron microscopy. Autophagy. 6:270–277. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Suzuki C, Isaka Y, Takabatake Y, Tanaka H,
Koike M, Shibata M, Uchiyama Y, Takahara S and Imai E:
Participation of autophagy in renal ischemia/reperfusion injury.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 368:100–106. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wu ZZ, Zhang JJ, Gao CC, Zhao M, Liu SY,
Gao GM and Zheng ZH: Expression of autophagy related genes mTOR,
Becline-1, LC3 and p62 in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells of
systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Clin Exp Immunol. 6:1–8.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cerni S, Shafer D, To K and Venketaraman
V: Investigating the role of everolimus in mTOR inhibition and
autophagy promotion as a potential host-directed therapeutic target
in mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. J Clin Med. 8(pii):
E2322019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Rouschop K and Wouters BG: Regulation of
autophagy through multiple independent hypoxic signaling pathways.
Curr Mol Med. 9:417–424. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ma S, Wang Y, Chen Y and Cao F: The role
of the autophagy in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1852:271–276. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Nuij VJAA, Peppelenbosch MP, van der Woude
CJ and Fuhler GM: Genetic polymorphism in ATG16L1 gene is
associated with adalimumab use in inflammatory bowel disease. J
Transl Med. 15:2482017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cucu MG, Streața I, Riza AL and Lilin A:
Polymorphisms in autophagy genes and active pulmonary tuberculosis
susceptibility in Romania. Rev Romana Med Lab. 25:47–53. 2017.
|
|
46
|
Kabat AM, Harrison OJ, Riffelmacher T,
Moghaddam AE, Pearson CF, Laing A, Abeler-Dörner L, Forman SP,
Grencis RK, Sattentau Q, et al: The autophagy gene Atg16l1
differentially regulates Treg and TH2 cells to control intestinal
inflammation. Elife. 5:e124442016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lin YC, Chang PF, Lin HF, Liu K, Chang MH
and Ni YH: Variants in the autophagy-related gene IRGM confer
susceptibility to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by modulating
lipophagy. J Hepatol. 65:1209–1216. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Mathew R, Karp CM, Beaudoin B, Vuong N,
Chen G, Chen HY, Bray K, Reddy A, Bhanot G, Gelinas C, et al:
Autophagy suppresses tumorigenesis through elimination of p62.
Cell. 137:1062–1075. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Pu D, Lianos EA, Ma J and Lin PH:
Autophagy, innate immunity and tissue repair in acute kidney
injury. Int J Mol Sci. 17(pii): E6622016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Mukhopadhyay P, Eid N, Abdelmegeed MA and
Sen A: Interplay of oxidative stress, inflammation, and autophagy:
Their role in tissue injury of the heart, liver, and kidney. Oxid
Med Cell Longev. 2018:20908132018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Sekiguchi A, Kanno H, Ozawa H, Yamaya S
and Itoi E: Rapamycin promotes autophagy and reduces neural tissue
damage and locomotor impairment after spinal cord injury in mice. J
Neurotrauma. 29:946–956. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Nguan CYC, Guan Q, Gleave ME and Du C:
Promotion of cell proliferation by clusterin in the renal tissue
repair phase after ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Renal
Physiol. 306:F724–F733. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ju-Rong Y, Ke-Hong C, Kun H, Bi-Qiong F,
Li-Rong L, Jian-Guo Z, Kai-Long L and Ya-Ni H: Transcription factor
Trps1 promotes tubular cell proliferation after
ischemia-reperfusion injury through cAMP-specific 3′,5′-cyclic
phosphodiesterase 4D and AKT. J Am Soc Nephrol. 28:532–544. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Peiró G, Diebold J, Baretton GB, Kimmig R
and Löhrs U: Cellular apoptosis susceptibility gene expression in
endometrial carcinoma: Correlation with Bcl-2, Bax, and caspase-3
expression and outcome. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 20:359–367. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Adams JM and Cory S: The Bcl-2 apoptotic
switch in cancer development and therapy. Oncogene. 26:1324–1337.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Guo XL, Li D, Hu F, Song JR, Zhang SS,
Deng WJ, Sun K, Zhao QD, Xie XQ, Song YJ, et al: Targeting
autophagy potentiates chemotherapy-induced apoptosis and
proliferation inhibition in hepatocarcinoma cells. Cancer Lett.
320:171–179. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|