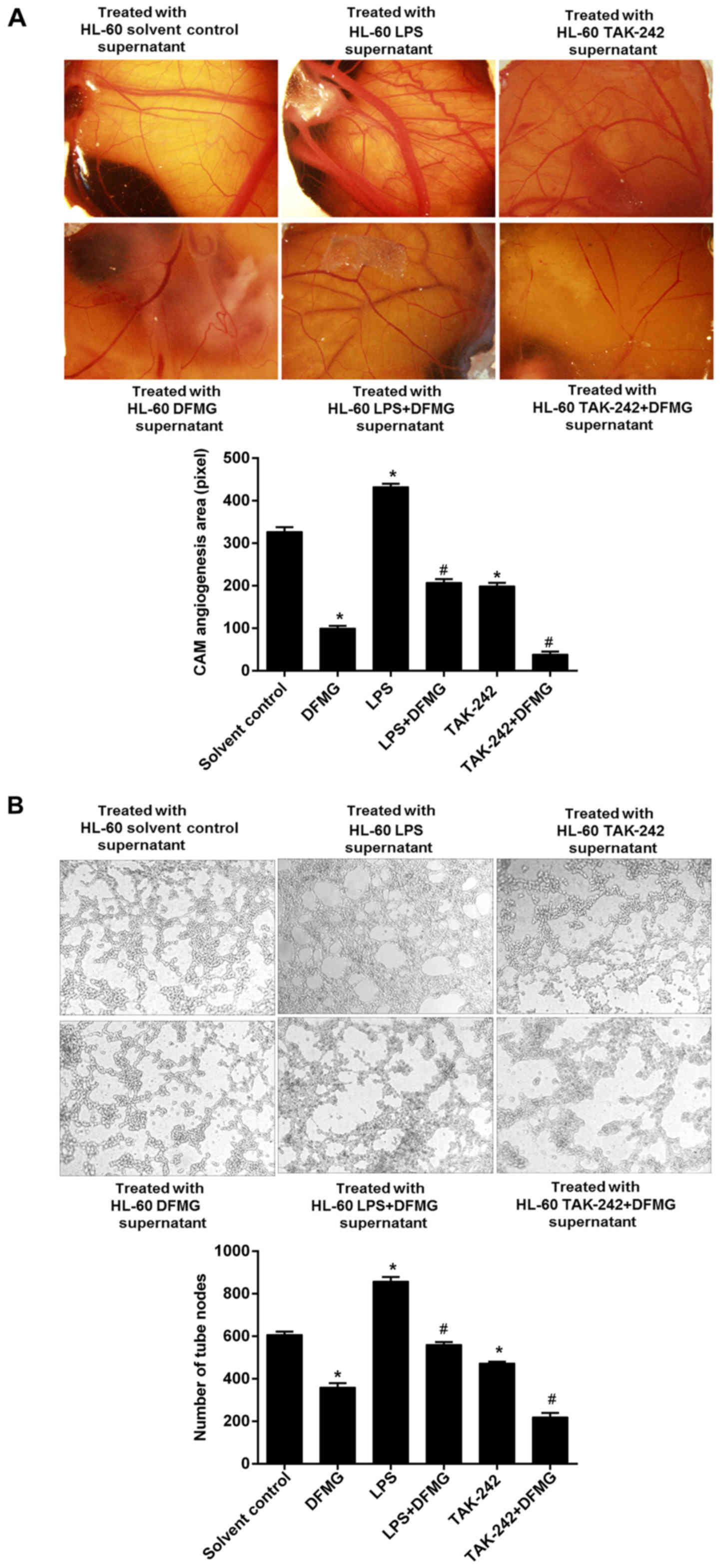
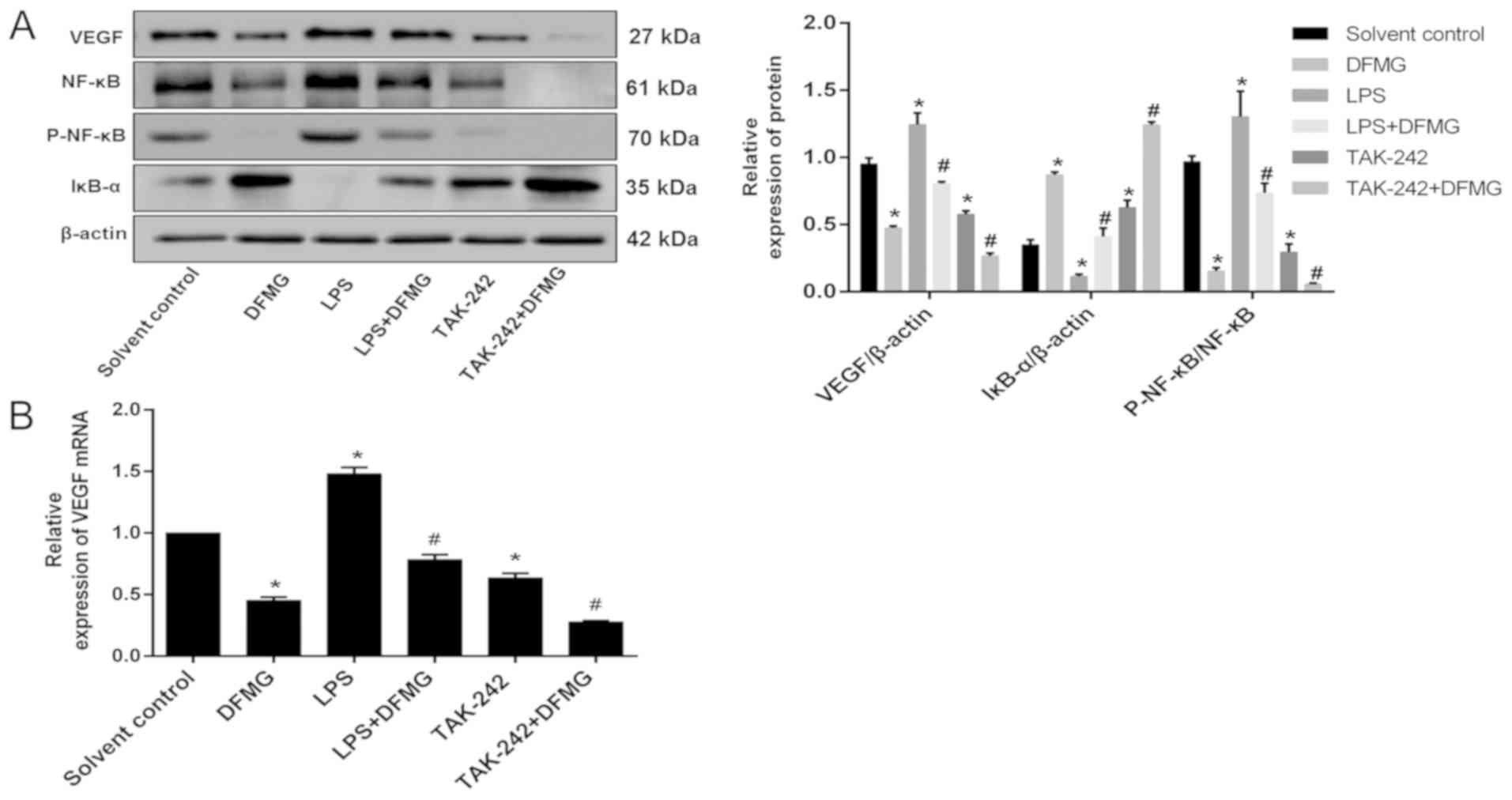
|
1
|
Vardiman J and Reichard K: Acute Myeloid
leukemia with myelodysplasia-related changes. Am J Clin Pathol.
144:29–43. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
De Kouchkovsky I and Abdul-Hay M: ‘Acute
myeloid leukemia: A comprehensive review and 2016 update’. Blood
Cancer J. 6:e4412016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Medinger M and Passweg J: Role of tumour
angiogenesis in haematological malignancies. Swiss Med Wkly.
144:W140502014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee JY and Kim HJ: (Lymph)angiogenic
influences on hematopoietic cells in acute myeloid leukemia. Exp
Mol Med. 46:e1222014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Assis PA, De Figueiredo-Pontes LL, Lima
AS, Leão V, Cândido LA, Pintão CT, Garcia AB, Saggioro FP,
Panepucci RA, Chahud F, et al: Halofuginone inhibits
phosphorylation of SMAD-2 reducing angiogenesis and leukemia burden
in an acute promyelocytic leukemia mouse model. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 34:652015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lin B, Zhao K, Yang D, Bai D, Liao Y, Zhou
Y, Yu Z, Yu X, Guo Q and Lu N: Wogonoside impedes the progression
of acute myeloid leukemia through inhibiting bone marrow
angiogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 234:1913–1924. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lichtenegger FS, Krupka C, Haubner S,
Kohnke T and Subklewe M: Recent developments in immunotherapy of
acute myeloid leukemia. J Hematol Oncol. 10:1422017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Song Y, Tan Y, Liu L, Wang Q, Zhu J and
Liu M: Levels of bone marrow microvessel density are crucial for
evaluating the status of acute myeloid leukemia. Oncol Lett.
10:211–215. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kadia TM, Ravandi F, Cortes J and
Kantarjian H: New drugs in acute myeloid leukemia. Ann Oncol.
27:770–778. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pizzo RJ, Azadniv M, Guo N, Acklin J,
Lacagnina K, Coppage M and Liesveld JL: Phenotypic, genotypic, and
functional characterization of normal and acute myeloid
leukemia-derived marrow endothelial cells. Exp Hematol. 44:378–389.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Drusbosky L, Gars E, Trujillo A, McGee C,
Meacham A, Wise E, Scott EW and Cogle CR: Endothelial cell derived
angiocrine support of acute myeloid leukemia targeted by receptor
tyrosine kinase inhibition. Leuk Res. 39:984–989. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Haouas H: Angiogenesis and acute myeloid
leukemia. Hematology. 19:311–323. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang L, Song K, Zhou L, Xie Z, Zhou P,
Zhao Y, Han Y, Xu X and Li P: Heparan sulfate D-glucosaminyl
3-O-sulfotransferase-3B1 (HS3ST3B1) promotes angiogenesis and
proliferation by induction of VEGF in acute myeloid leukemia cells.
J Cell Biochem. 116:1101–1112. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee SE, Lee JY, Han AR, Hwang HS, Min WS
and Kim HJ: Effect of high VEGF-C mRNA expression on achievement of
complete remission in adult acute myeloid leukemia. Transl Oncol.
11:567–574. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rodriguez-Ariza A, Lopez-Pedrera C, Aranda
E and Barbarroja N: VEGF targeted therapy in acute myeloid
leukemia. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 80:241–256. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zahiragic L, Schliemann C, Bieker R,
Thoennissen NH, Burow K, Kramer C, Zühlsdorf M, Berdel WE and
Mesters RM: Bevacizumab reduces VEGF expression in patients with
relapsed and refractory acute myeloid leukemia without clinical
antileukemic activity. Leukemia. 21:1310–1312. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bose P, Vachhani P and Cortes JE:
Treatment of relapsed/refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Curr Treat
Options Oncol. 18:172017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mohammadi Kian M, Mohammadi S, Tavallaei
M, Chahardouli B, Rostami S, Zahedpanah M, Ghavamzadeh A and
Nikbakht M: Inhibitory effects of arsenic trioxide and thalidomide
on angiogenesis and vascular endothelial growth factor expression
in leukemia cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 19:1127–1134.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Salemi M, Mohammadi S, Ghavamzadeh A and
Nikbakht M: Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor targeting by
curcumin and thalidomide in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Asian Pac
J Cancer Prev. 18:3055–3061. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen C, Yang J and Xu W: Thalidomide in
combination with chemotherapy in treating elderly patients with
acute myeloid leukemia. Oncol Res Treat. 41:461–465. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fu XH, Wang L, Zhao H, Xiang HL and Cao
JG: Synthesis of genistein derivatives and determination of their
protective effects against vascular endothelial cell damages caused
by hydrogen peroxide. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 18:513–517. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang L, Zheng X, Xiang HL, Fu XH and Cao
JG: 7-Difluoromethyl-5,4′-dimethoxygenistein inhibits oxidative
stress induced adhesion between endothelial cells and monocytes via
NF-kappaB. Eur J Pharmacol. 605:31–35. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bo P, Wang R, Zeng F, Xiang L, Xiang X, Fu
X and Zhang Y: The effect of DFMG on the angiogenesis and plaque
stability in the atherosclerosis model of the ApoE-/-. J Third
Military Med Univ. 17:1554–1560. 2018.
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kampen KR, Ter Elst A and de Bont ES:
Vascular endothelial growth factor signaling in acute myeloid
leukemia. Cell Mol Life Sci. 70:1307–1317. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dey G, Bharti R, Ojha PK, Pal I, Rajesh Y,
Banerjee I, Banik P, Parida S, Parekh A, Sen R and Mandal M:
Therapeutic implication of ‘Iturin A’ for targeting MD-2/TLR4
complex to overcome angiogenesis and invasion. Cell Signal.
35:24–36. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pei Z, Li H, Guo Y, Jin Y and Lin D:
Sodium selenite inhibits the expression of VEGF, TGFbeta(1) and
IL-6 induced by LPS in human PC3 cells via TLR4-NF-κB signaling
blockage. Int Immunopharmacol. 10:50–56. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cho JS, Kang JH, Han IH, Um JY and Lee HM:
Activation of TLR4 induces VEGF expression via Akt pathway in nasal
polyps. Clin Exp Allergy. 43:1038–1047. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Folkman J: Role of angiogenesis in tumor
growth and metastasis. Semin Oncol. 29 (6 Suppl 16):S15–S18. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Hida K, Maishi N, Torii C and Hida Y:
Tumor angiogenesis-characteristics of tumor endothelial cells. Int
J Clin Oncol. 21:206–212. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rajabi M and Mousa SA: The role of
angiogenesis in cancer treatment. Biomedicines. 5:E342017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li T, Kang G, Wang T and Huang H: Tumor
angiogenesis and anti-angiogenic gene therapy for cancer. Oncol
Lett. 16:687–702. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mittal K, Ebos J and Rini B: Angiogenesis
and the tumor microenvironment: Vascular endothelial growth factor
and beyond. Semin Oncol. 41:235–251. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Padro T, Ruiz S, Bieker R, Bürger H,
Steins M, Kienast J, Büchner T, Berdel WE and Mesters RM: Increased
angiogenesis in the bone marrow of patients with acute myeloid
leukemia. Blood. 95:2637–2644. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Norén-Nyström U, Roos G, Bergh A and
Forestier E: Prognostic impact of vascular density and fibrosis in
the bone marrow of children with high-risk acute lymphoblastic
leukemia. Leukemia. 19:1998–2001. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hatfield K, Ryningen A, Corbascio M and
Bruserud O: Microvascular endothelial cells increase proliferation
and inhibit apoptosis of native human acute myelogenous leukemia
blasts. Int J Cancer. 119:2313–2321. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fu J, Fu J, Chen X, Zhang Y, Gu H and Bai
Y: CD147 and VEGF co-expression predicts prognosis in patients with
acute myeloid leukemia. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 40:1046–1052. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tino AB, Chitcholtan K, Sykes PH and
Garrill A: Resveratrol and acetyl-resveratrol modulate activity of
VEGF and IL-8 in ovarian cancer cell aggregates via attenuation of
the NF-κB protein. J Ovarian Res. 9:842016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Meshram SN, Paul D, Manne R, Choppara S,
Sankaran G, Agrawal Y and Santra MK: FBXO32 activates NF-κB through
IκBα degradation in inflammatory and genotoxic stress. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 92:134–140. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li Y, Sui H, Jiang C, Li S, Han Y, Huang
P, Du X, Du J and Bai Y: Dihydroartemisinin increases the
sensitivity of photodynamic therapy Via NF-κB/HIF-1α/VEGF pathway
in esophageal cancer cell in vitro and in vivo. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 48:2035–2045. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Webster JA and Pratz KW: Acute myeloid
leukemia in the elderly: Therapeutic options and choice. Leuk
Lymphoma. 59:274–287. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|