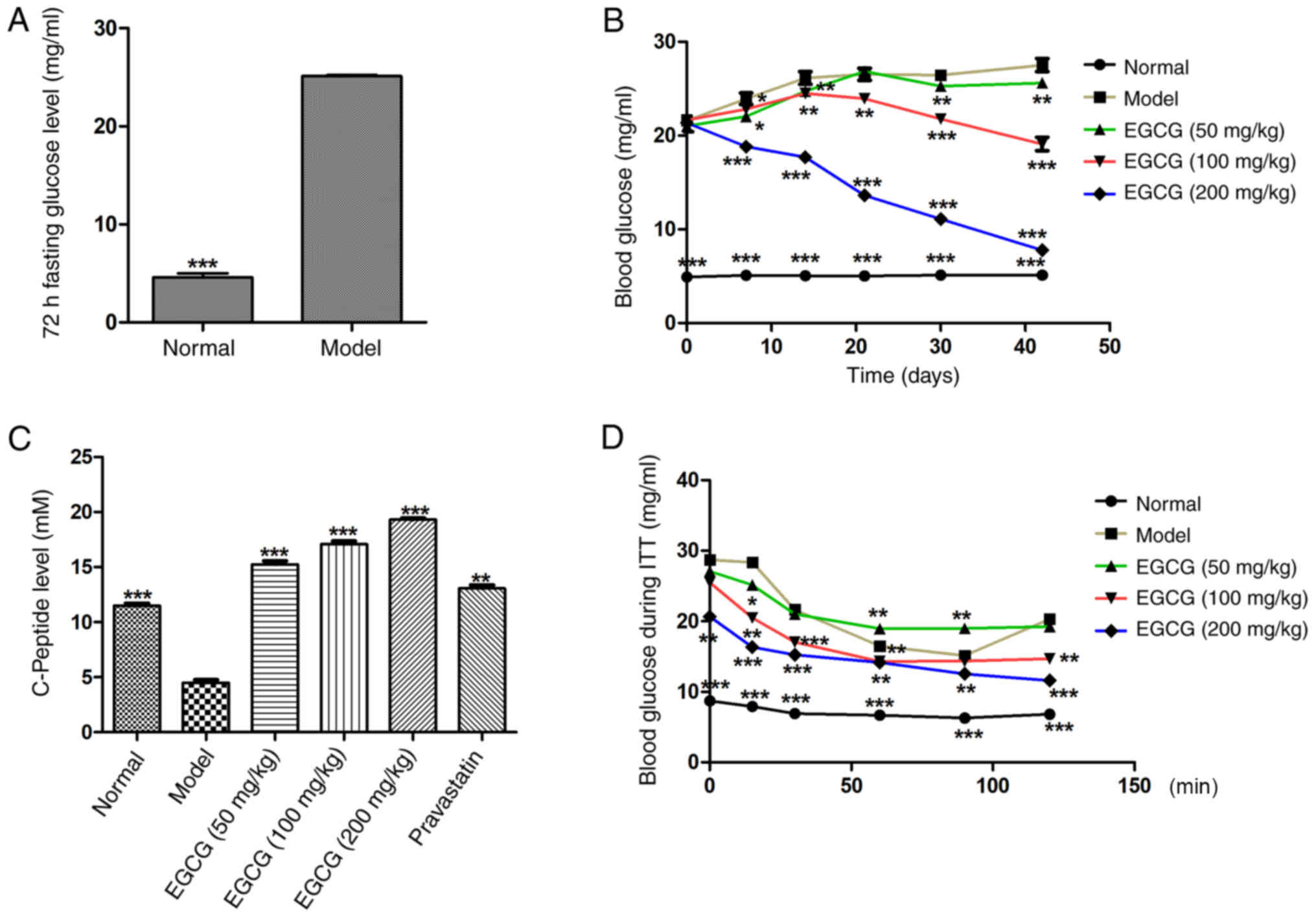
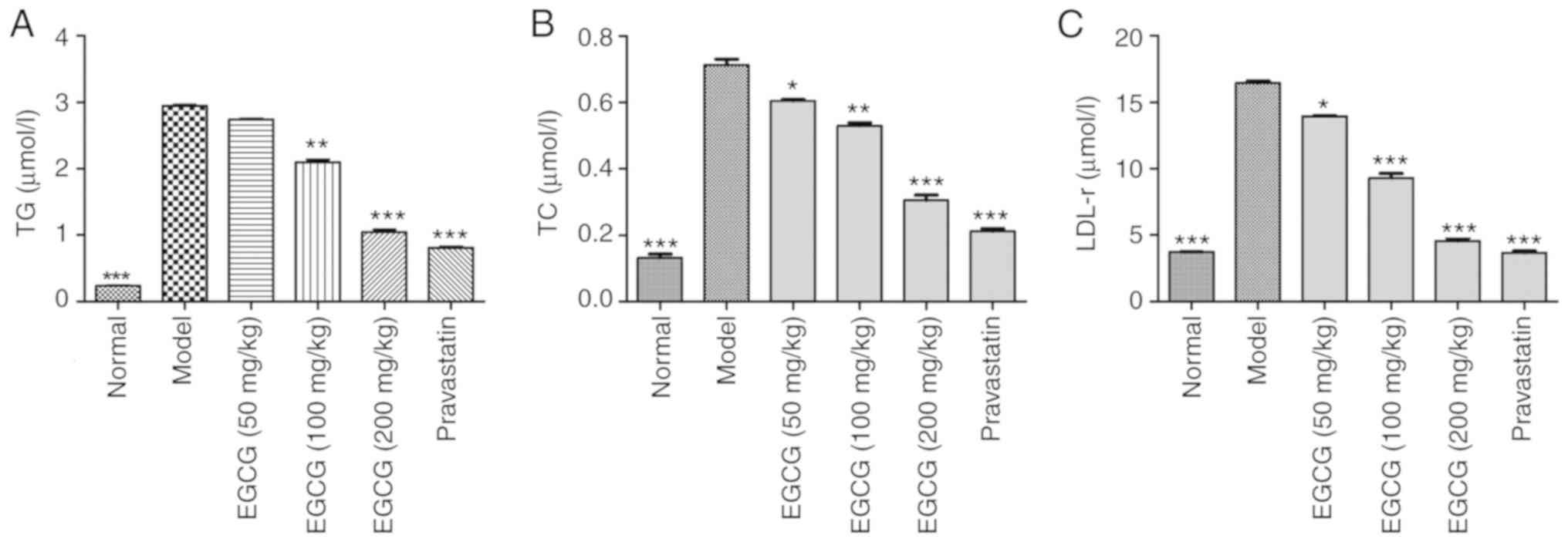
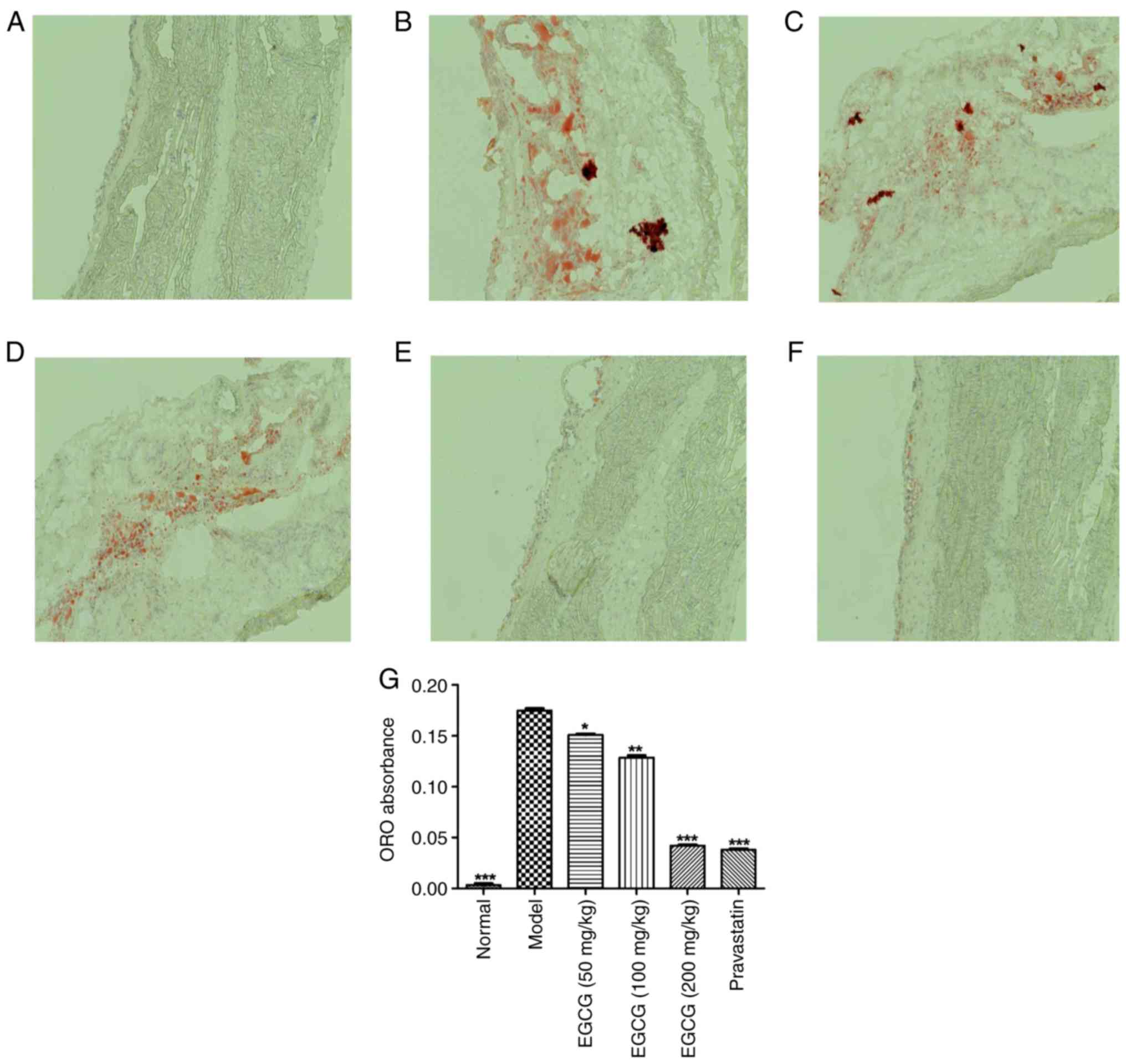
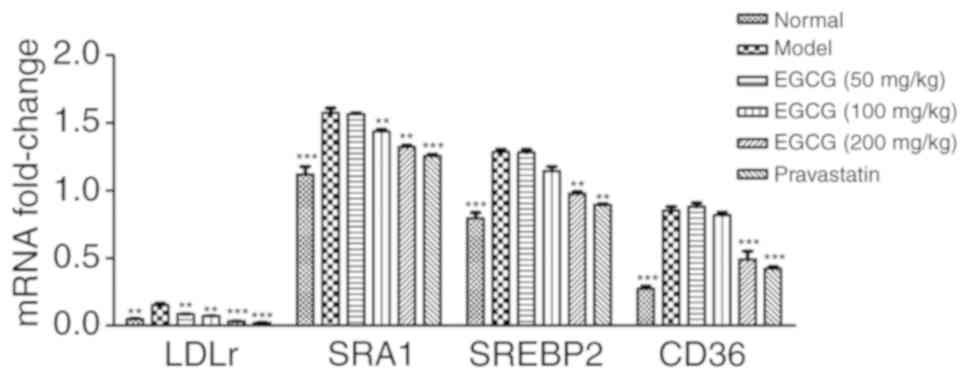
|
1
|
Tanaka S, Tanaka S, Iimuro S, Yamashita H,
Katayama S, Ohashi Y, Akanuma Y, Yamada N and Sone H; Japan
Diabetes Complications Study Group, : Cohort profile: The Japan
diabetes complications study: a long-term follow-up of a randomised
lifestyle intervention study of type 2 diabetes. Int J Epidemiol.
43:1054–1062. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Perry RJ, Samuel VT, Petersen KF and
Shulman GI; RJ P, : The role of hepatic lipids in hepatic insulin
resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature. 510:84–91. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Turner RC, Millns H, Neil HA, Stratton IM,
Manley SE, Matthews DR and Holman RR: Risk factors for coronary
artery disease in non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus: United
Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS: 23). BMJ. 316:823–828.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shin NR, Lee JC, Lee HY, Kim MS, Whon TW,
Lee MS and Bae JW: An increase in the Akkermansia spp. population
induced by metformin treatment improves glucose homeostasis in
diet-induced obese mice. Gut. 63:727–735. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Torimoto K, Okada Y and Tanaka Y: Type 2
diabetes and vascular endothelial dysfunction. J UOEH. 40:65–75.
2018.(In Japanese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Smith SA: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptors and the regulation of mammalian
lipid metabolism. Biochem Soc Trans. 30:1086–1090. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang L, Lin P, Ma A, Zheng H, Wang K, Li
W, Wang C, Zhao R, Liang K, Liu F, et al: C-Peptide is
independently associated with an increased risk of coronary artery
disease in T2DM subjects: A cross-sectional study. PLoS One.
10:e01271122015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cai X, Han X, Zhang S, Luo Y, Chen Y and
Ji L: Age at diagnosis and C-peptide level are associated with
diabetic retinopathy in Chinese. PLoS One. 9:e911742014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Massi-Benedetti M and Orsini-Federici M:
Treatment of type 2 diabetes with combined therapy: what are the
pros and cons? Diabetes Care. 31:S131–135. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Febbraio M, Hajjar DP and Silverstein RL:
CD36: A class B scavenger receptor involved in angiogenesis,
atherosclerosis, inflammation, and lipid metabolism. J Clin Invest.
108:785–791. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Susztak K, Ciccone E, McCue P, Sharma K
and Böttinger EP: Multiple metabolic hits converge on CD36 as novel
mediator of tubular epithelial apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy.
PLoS Med. 2:e452005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gautam S, Pirabu L, Agrawal CG and
Banerjee M: CD36 gene variants and their association with type 2
diabetes in an Indian population. Diabetes Technol Ther.
15:680–687. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pravenec M, Landa V, Zidek V, Musilova A,
Kren V, Kazdova L, Aitman TJ, Glazier AM, Ibrahimi A, Abumrad NA,
et al: Transgenic rescue of defective Cd36 ameliorates insulin
resistance in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Nat Genet.
27:156–158. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Miyaoka K, Kuwasako T, Hirano K, Nozaki S,
Yamashita S and Matsuzawa Y: CD36 deficiency associated with
insulin resistance. Lancet. 357:686–687. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Febbraio M, Abumrad NA, Hajjar DP, Sharma
K, Cheng W, Pearce SF and Silverstein RL: A null mutation in murine
CD36 reveals an important role in fatty acid and lipoprotein
metabolism. J Biol Chem. 274:19055–19062. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Martin CA, Longman E, Wooding C, Hoosdally
SJ, Ali S, Aitman TJ, Gutmann DAP, Freemont PS, Byrne B and Linton
KJ: Cd36, a class B scavenger receptor, functions as a monomer to
bind acetylated and oxidized low-density lipoproteins. Protein Sci.
16:2531–2541. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Park YM: CD36, a scavenger receptor
implicated in atherosclerosis. Exp Mol Med. 46:e992014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Trent CM, Yu S, Hu Y, Skoller N, Huggins
LA, Homma S and Goldberg IJ: Lipoprotein lipase activity is
required for cardiac lipid droplet production. J Lipid Res.
55:645–658. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Moslehi A and Hamidi-zad Z: Role of SREBPs
in liver diseases: A mini-review. J Clin Transl Hepatol.
28:332–338. 2018.
|
|
20
|
Qi Q, Liang L, Doria A, Hu FB and Qi L:
Genetic predisposition to dyslipidemia and type 2 diabetes risk in
two prospective cohorts. Diabetes. 61:745–752. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee EJ, Oh H, Kang BG, Kang MK, Kim DY,
Kim YH, Lee JY, Ji JG, Lim SS and Kang YH: Lipid-lowering effects
of medium-chain triglyceride-enriched coconut oil in combination
with licorice extracts in experimental hyperlipidemic mice. J Agric
Food Chem. 66:10447–10457. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mysliwiec P, Choromanska B, Winnicka MM,
Kaminski K, Mysliwiec H, Dadan J, Supruniuk E and Chabowski A:
Interleukin-6 deficiency modifies the effect of high fat diet on
myocardial expression of fatty acid transporters and myocardial
lipids. J Physiol Pharmacol. 69:692018.
|
|
23
|
Yoon JY, Kwon HH, Min SU, Thiboutot DM and
Suh DH: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate improves acne in humans by
modulating intracellular molecular targets and inhibiting P. acnes.
J Invest Dermatol. 133:429–440. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Song X, Du J, Zhao W and Guo Z:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate(EGCG): Mechanisms and the combined
applications. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen.
doi:10.2174/1386207321666171218115850.
|
|
25
|
Xiao J, Ho CT, Liong EC, Nanji AA, Leung
TM, Lau TY, Fung ML and Tipoe GL: Epigallocatechin gallate
attenuates fibrosis, oxidative stress, and inflammation in
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease rat model through TGF/SMAD, PI3
K/Akt/FoxO1, and NF-kappa B pathways. Eur J Nutr. 53:187–199. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Annaba F, Kumar P, Dudeja AK, Saksena S,
Gill RK and Alrefai WA: Green tea catechin EGCG inhibits ileal
apical sodium bile acid transporter ASBT. Am J Physiol Gastrointest
Liver Physiol. 298:G467–G473. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhou P, Yu JF, Zhao CG, Sui FX, Teng X and
Wu YB: Therapeutic potential of EGCG on acute renal damage in a rat
model of obstructive nephropathy. Mol Med Rep. 7:1096–1102. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Farabegoli F, Papi A and Orlandi M:
(−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate down-regulates EGFR, MMP-2, MMP-9
and EMMPRIN and inhibits the invasion of MCF-7 tamoxifen-resistant
cells. Biosci Rep. 31:99–108. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yan J, Zhao Y, Suo S, Liu Y and Zhao B:
Green tea catechins ameliorate adipose insulin resistance by
improving oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med. 52:1648–1657.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Baselga-Escudero L, Blade C, Ribas-Latre
A, Casanova E, Suárez M, Torres JL, Salvadó MJ, Arola L and
Arola-Arnal A: Resveratrol and EGCG bind directly and distinctively
to miR-33a and miR-122 and modulate divergently their levels in
hepatic cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 42:882–892. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen SJ, Kao YH, Jing L, Chuang YP, Wu WL,
Liu ST, Huang SM, Lai JH, Ho LJ, Tsai MC, et al:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate reduces scavenger receptor A expression
and foam cell formation in human macrophages. J Agric Food Chem.
65:3141–3150. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chang HH, Chien CY, Chen KH, Huang SC and
Chien CT: Catechins blunt the effects of oxLDL and its primary
metabolite phosphatidylcholine hydroperoxide on endothelial
dysfunction through inhibition of oxidative stress and restoration
of eNOS in rats. Kidney Blood Press Res. 42:919–932. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mohan T, Velusamy P, Chakrapani LN,
Srinivasan AK, Singh A, Johnson T and Periandavan K: Impact of EGCG
supplementation on the progression of diabetic nephropathy in rats:
An insight into fibrosis and apoptosis. J Agric Food Chem.
65:8028–8036. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang M, Lv XY, Li J, Xu ZG and Chen L:
The characterization of high-fat diet and multiple low-dose
streptozotocin induced type 2 diabetes rat model. J Diabetes Res.
2008:7040452008.
|
|
35
|
Qian C, Zhu C, Yu W, Jiang X and Zhang F:
High-fat diet/low-dose streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetes in
rats impacts osteogenesis and wnt signaling in bone marrow stromal
cells. PLoS One. 10:e01363902015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Algandaby MM, Alghamdi HA, Ashour OM,
Abdel-Naim AB, Ghareib SA, Abdel-Sattar EA and Hajar AS: Mechanisms
of the antihyperglycemic activity of Retama raetam in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Food Chem Toxicol.
48:2448–2453. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Estil·les E, Téllez N, Nacher M and
Montanya E: A model for human islet transplantation to
immunodeficient streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Cell
Transplant. 27:1684–1691. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
38
|
Grove KA, Sae-tan S, Kennett MJ and
Lambert JD: (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits pancreatic
lipase and reduces body weight gain in high fat-fed obese mice.
Obesity (Silver Spring). 20:2311–2313. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Uchiyama Y, Suzuki T, Mochizuki K and Goda
T: Dietary supplementation with a low dose of
(−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate reduces pro-inflammatory responses
in peripheral leukocytes of non-obese type 2 diabetic GK rats. J
Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 59:541–547. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang YY, Li C, Yao GF, Du LJ, Liu Y,
Zheng XJ, Yan S, Sun JY, Liu Y, Liu MZ, et al: Deletion of
macrophage mineralocorticoid receptor protects hepatic steatosis
and insulin resistance through ERα/HGF/Met pathway. Diabetes.
66:1535–1547. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Δ Δ C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Parhofer KG: The treatment of disorders of
lipid metabolism. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 113:261–268. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Luo J, Yang H and Song BL: Mechanisms and
regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
doi:10.1038/s41580-019-0190-7.
|
|
44
|
Ruiz-Ojeda FJ, Anguita-Ruiz A, Rupérez AI,
Gomez-Llorente C, Olza J, Vázquez-Cobela R, Gil-Campos M, Bueno G,
Leis R, Cañete R, et al: Effects of X-chromosome tenomodulin
genetic variants on obesity in a childrens cohort and implications
of the gene in adipocyte metabolism. Sci Rep. 9:39792019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ahangari N, Ghayour Mobarhan M, Sahebkar A
and Pasdar A: Molecular aspects of hypercholesterolemia treatment:
Current perspectives and hopes. Ann Med. 50:303–311. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hammad RH, El-Madbouly AA, Kotb HG and
Zarad MS: Frequency of circulating B1a and B2 B-cell subsets in
Egyptian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Egypt J Immunol.
25:71–80. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Rajesh M, Mukhopadhyay P, Bátkai S, Patel
V, Saito K, Matsumoto S, Kashiwaya Y, Horváth B, Mukhopadhyay B,
Becker L, et al: Cannabidiol attenuates cardiac dysfunction,
oxidative stress, fibrosis, and inflammatory and cell death
signaling pathways in diabetic cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol.
56:2115–2125. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhang Z, Wang S, Zhou S, Yan X, Wang Y,
Chen J, Mellen N, Kong M, Gu J, Tan Y, et al: Sulforaphane prevents
the development of cardiomyopathy in type 2 diabetic mice probably
by reversing oxidative stress-induced inhibition of LKB1/AMPK
pathway. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 77:42–52. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kurlawalla-Martinez C, Stiles B, Wang Y,
Devaskar SU, Kahn BB and Wu H: Insulin hypersensitivity and
resistance to streptozotocin-induced diabetes in mice lacking PTEN
in adipose tissue. Mol Cell Biol. 25:2498–2510. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Su N, Zhao N, Wang G, Wang L, Zhang Y, Li
R, Liu Y, Yang X, Li C and Hou M: The effects of adiponectin and
adiponectin receptor 1 levels on macrovascular complications among
patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cell Physiol Biochem.
52:225–231. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wang J, He K, Yang C, Lin X, Zhang X, Wang
Y, Liu G and Xian X: Dietary cholesterol is highly associated with
severity of hyperlipidemia and atherosclerotic lesions in
heterozygous LDLR-deficient hamsters. Int J Mol Sci. 20:202019.
|
|
52
|
Walcher D, Marx N, D W and N M: Advanced
glycation end products and C-peptide-modulators in diabetic
vasculopathy and atherogenesis. Semin Immunopathol. 31:103–111.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Chien KL, Hsu HC, Liu PH, Lin HJ and Chen
MF: Common sequence variants in CD36 gene and the levels of
triglyceride and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol among ethnic
Chinese in Taiwan. Lipids Health Dis. 11:1742012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Maréchal L Maximilien Laviolette M,
Rodrigue-Way A, Sow B, Brochu M, Caron V and Tremblay A: The
CD36-PPARγ pathway in metabolic disorders. Int J Mol Sci.
19:15292018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
55
|
Farook VS, Puppala S, Schneider J, Fowler
SP, Chittoor G, Dyer TD, Allayee H, Cole SA, Arya R, Black MH, et
al: Metabolic syndrome is linked to chromosome 7q21 and associated
with genetic variants in CD36 and GNAT3 in Mexican Americans.
Obesity (Silver Spring). 20:2083–2092. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Yang D, Hu C, Deng X, Bai Y, Cao H, Guo J
and Su Z: Therapeutic effect of chitooligosaccharide tablets on
lipids in high-fat diets induced hyperlipidemic rats. Molecules.
24:242019.
|
|
57
|
Kumar NB, Pow-Sang J, Spiess PE, Park J,
Salup R, Williams CR, Parnes H and Schell MJ: Randomized,
placebo-controlled trial evaluating the safety of one-year
administration of green tea catechins. Oncotarget. 7:70794–70802.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Dostal AM, Samavat H, Bedell S, Torkelson
C, Wang R, Swenson K, Le C, Wu AH, Ursin G, Yuan J-M and Kurzer MS:
The safety of green tea extract supplementation in postmenopausal
women at risk for breast cancer: Results of the Minnesota green tea
trial. Food Chem Toxicol. 83:26–35. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Crew KD, Brown P, Greenlee H, Bevers TB,
Arun B, Hudis C, McArthur HL, Chang J, Rimawi M, Vornik L, et al:
Phase IB randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, dose
escalation study of polyphenon E in women with hormone
receptor-negative breast cancer. Cancer Prev Res (Phila).
5:1144–1154. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Zhu W, Jia L, Chen G, Zhao H, Sun X, Meng
X, Zhao X, Xing L, Yu J and Zheng M: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate
ameliorates radiation-induced acute skin damage in breast cancer
patients undergoing adjuvant radiotherapy. Oncotarget.
7:48607–48613. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Zhao H, Zhu W, Xie P, Li H, Zhang X, Sun
X, Yu J and Xing L: A phase I study of concurrent chemotherapy and
thoracic radiotherapy with oral epigallocatechin-3-gallate
protection in patients with locally advanced stage III
non-small-cell lung cancer. Radiother Oncol. 110:132–136. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|