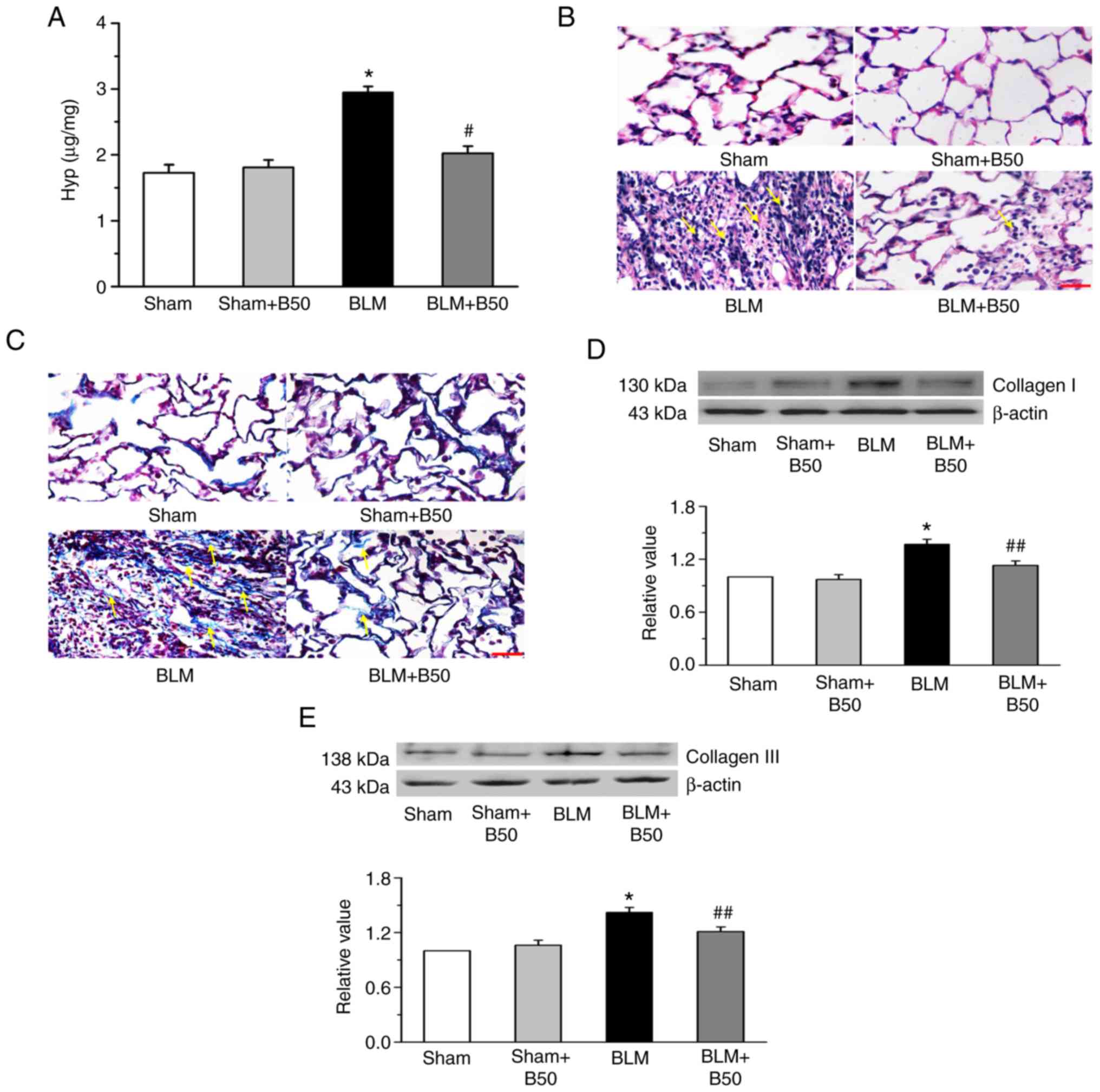
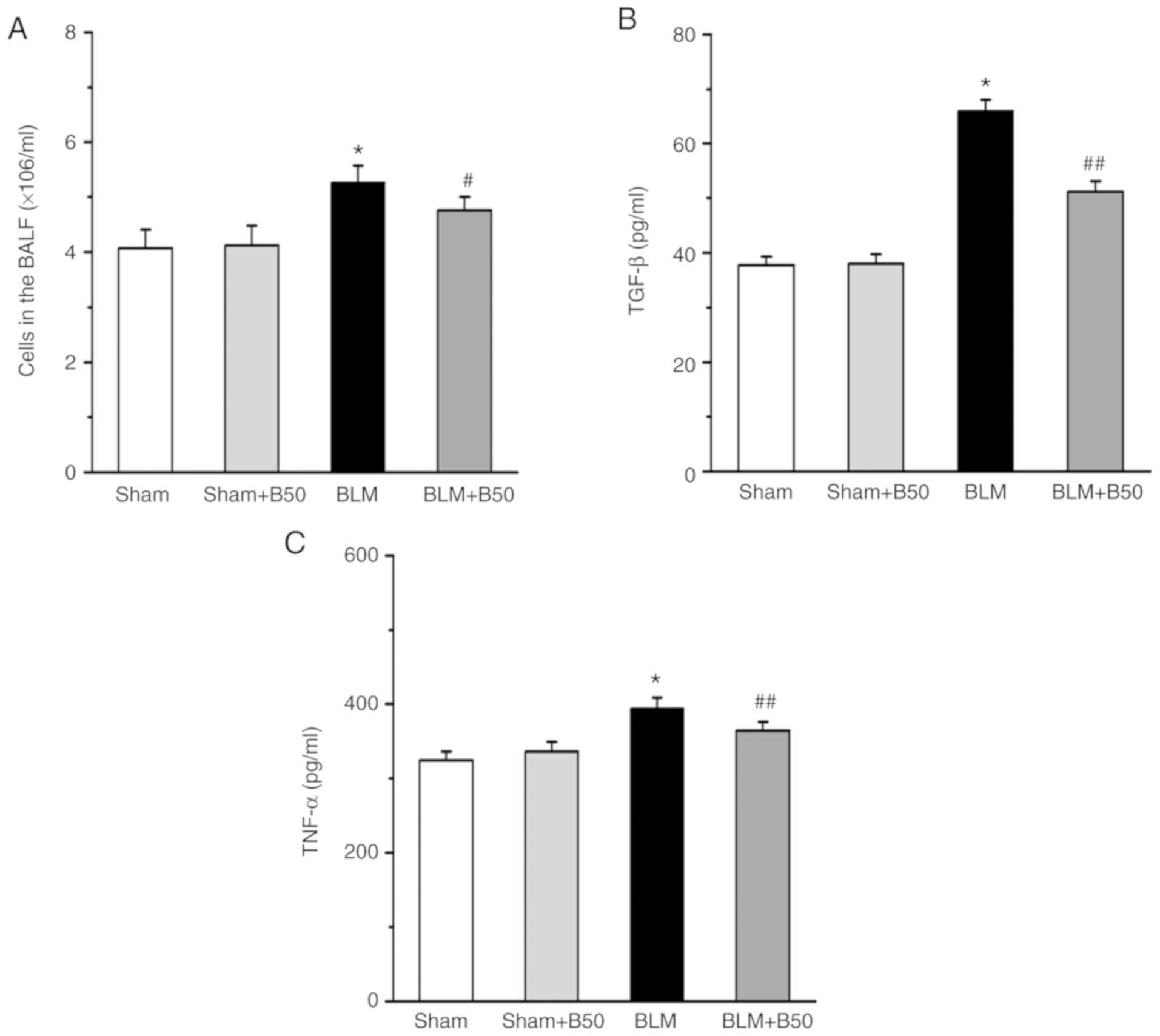
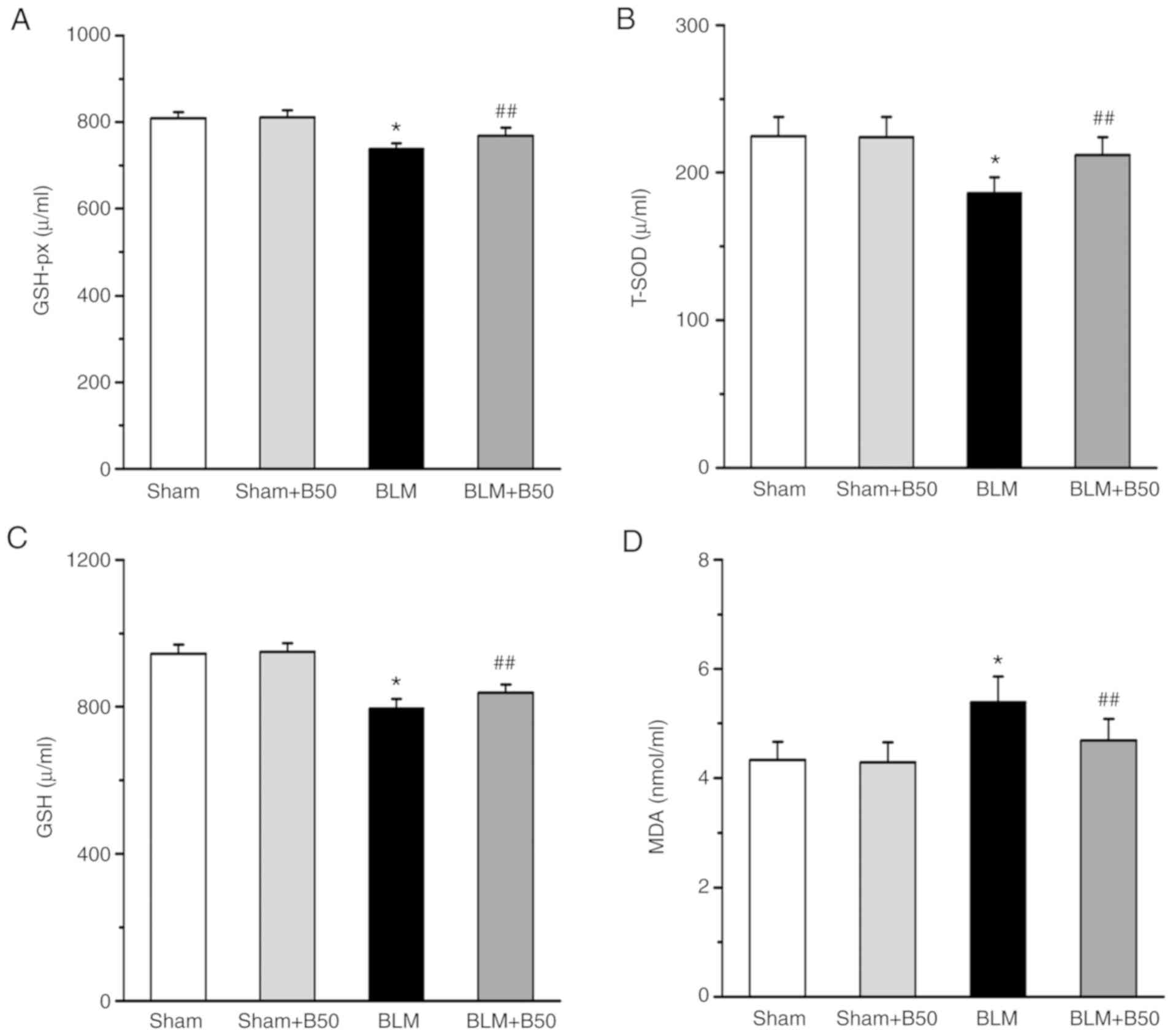
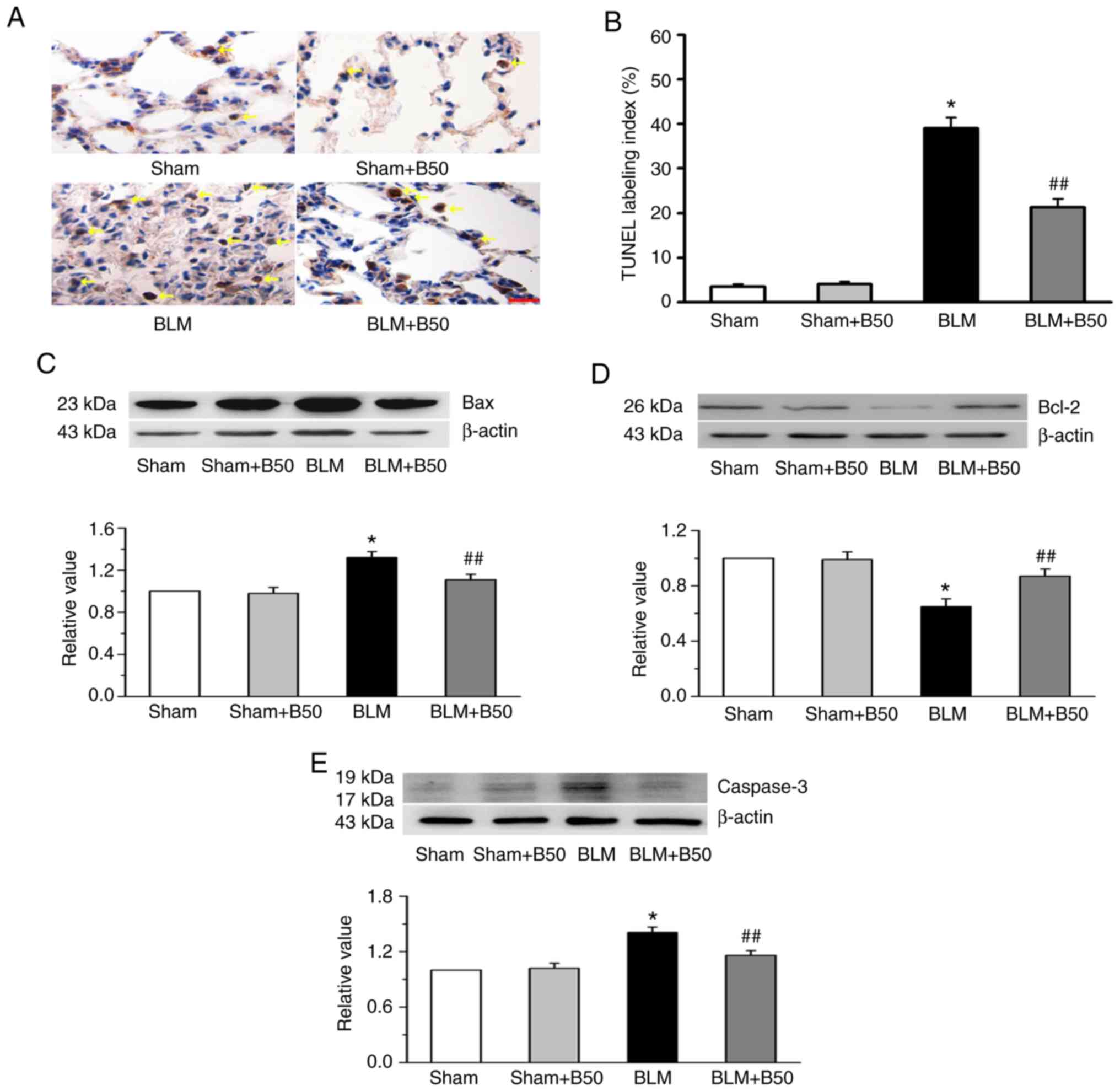
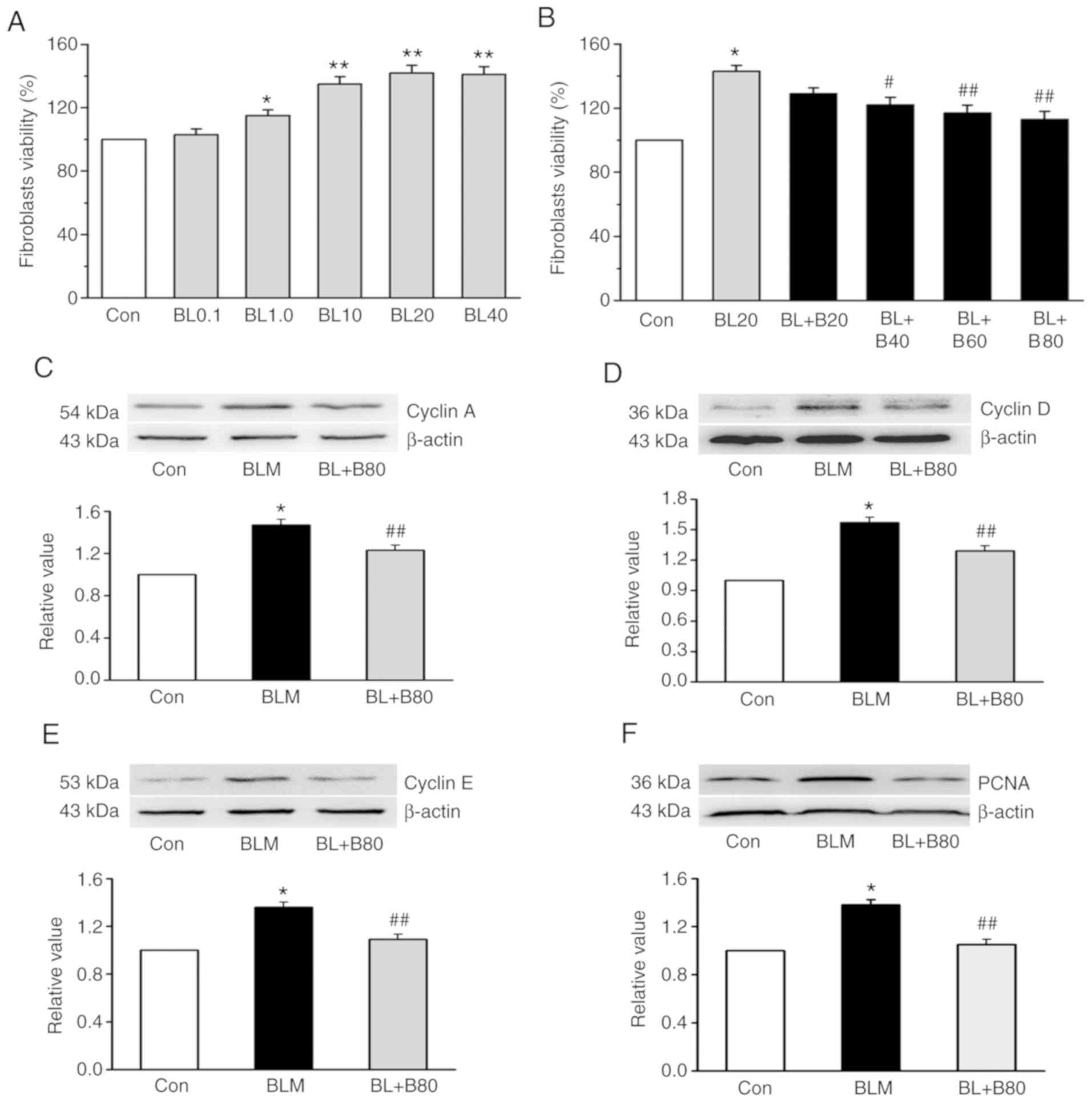
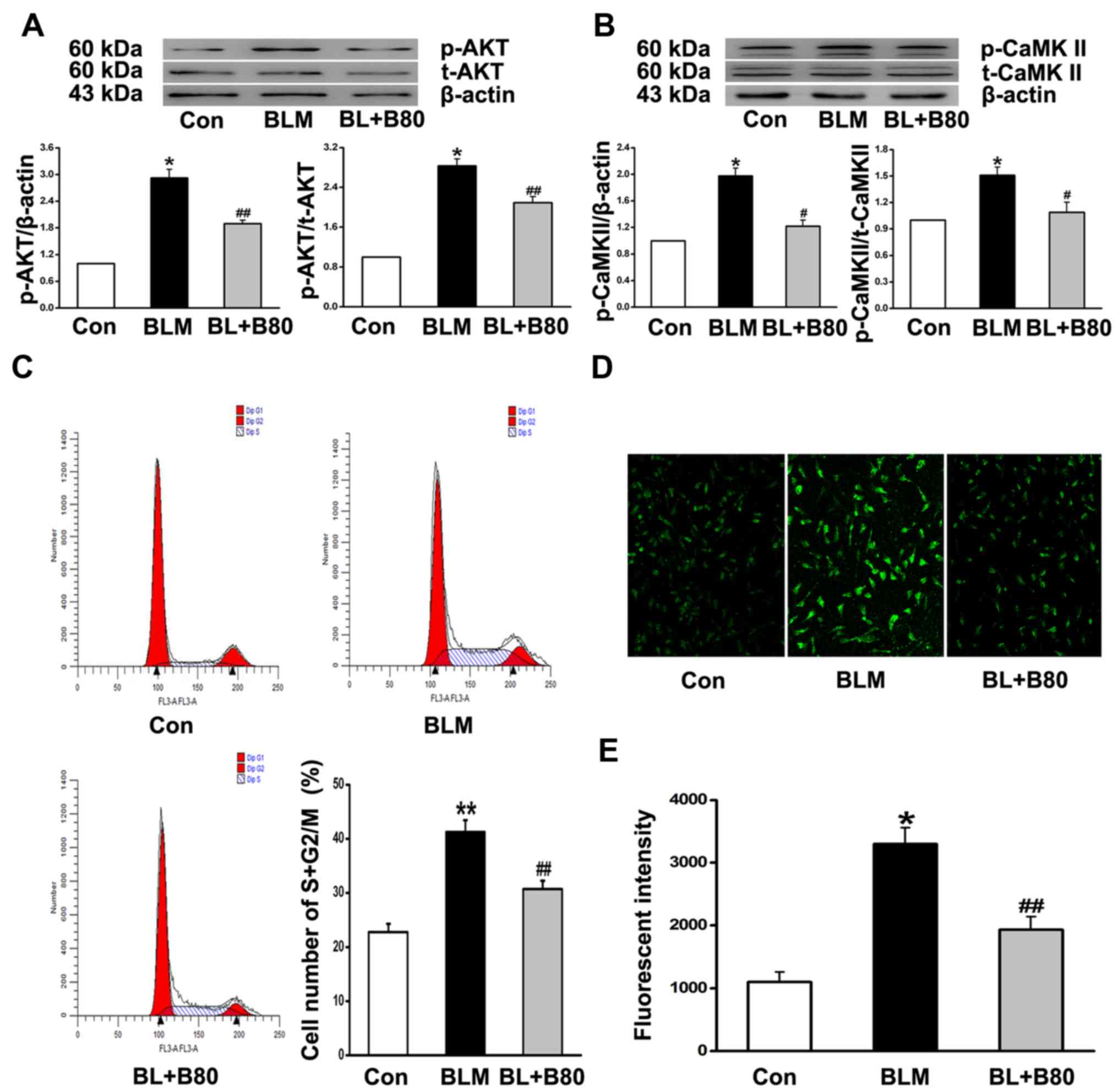
|
1
|
Gross TJ and Hunninghake GW: Idiopathic
pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 345:517–525. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Selman M, Thannickal VJ, Pardo A, Zisman
DA, Martinez FJ and Lynch JP III: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis:
Pathogenesis and therapeutic approaches. Drugs. 64:405–430. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Thannickal VJ, Toews GB, White ES, Lynch
JP III and Martinez FJ: Mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis. Annu Rev
Med. 55:395–417. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Raghu G, Freudenberger TD, Yang S, Curtis
JR, Spada C, Hayes J, Sillery JK, Pope CE II and Pellegrini CA:
High prevalence of abnormal acid gastro-oesophageal reflux in
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir J. 27:136–142. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ask K, Bonniaud P, Maass K, Eickelberg O,
Margetts PJ, Warburton D, Groffen J, Gauldie J and Kolb M:
Progressive pulmonary fibrosis is mediated by TGF-beta isoform 1
but not TGF-beta3. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 40:484–495. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gharaee-Kermani M, Gyetko MR, Hu B and
Phan SH: New insights into the pathogenesis and treatment of
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A potential role for stem cells in
the lung parenchyma and implications for therapy. Pharm Res.
24:819–841. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wilkes DS, Chew T, Flaherty KR, Frye S,
Gibson KF, Kaminski N, Klemsz MJ, Lange W, Noth I and Rothhaar K:
Oral immunotherapy with type V collagen in idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis. Eur Respir J. 45:1393–1402. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
King TE Jr, Pardo A and Selman M:
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet. 378:1949–1961. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kinnula VL, Fattman CL, Tan RJ and Oury
TD: Oxidative stress in pulmonary fibrosis: A possible role for
redox modulatory therapy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 172:417–422.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rydell-Törmänen K, Andréasson K,
Hesselstrand R, Risteli J, Heinegård D, Saxne T and
Westergren-Thorsson G: Extracellular matrix alterations and acute
inflammation; developing in parallel during early induction of
pulmonary fibrosis. Lab Invest. 92:917–925. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jia L, Sun P, Gao H, Shen J, Gao Y, Meng
C, Fu S, Yao H and Zhang G: Mangiferin attenuates bleomycin-induced
pulmonary fibrosis in mice through inhibiting TLR4/p65 and
TGF-β1/Smad2/3 pathway. J Pharm Pharmacol. 71:1017–1028. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hasaneen NA, Cao J, Pulkoski-Gross A,
Zucker S and Foda HD: Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase
inducer (EMMPRIN) promotes lung fibroblast proliferation, survival
and differentiation to myofibroblasts. Respir Res. 17:172016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sergew A and Brown KK: Advances in the
treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Expert Opin Emerg
Drugs. 20:537–552. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu B, Lü W, Ge H, Tang H, Li R and Zhang
C: Protective effect of the traditional chinese patent medicine
Qing-Xuan Granule against bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in
mice. Chem Biodivers. 16:e19004672019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lin CC and Shieh DE: The anti-inflammatory
activity of Scutellaria rivularis extracts and its active
components, baicalin, baicalein and wogonin. Am J Chin Med.
24:31–36. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gao Z, Huang K and Xu H: Protective
effects of flavonoids in the roots of Scutellaria
baicalensis georgi against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative
stress in HS-SY5Y cells. Pharmacol Res. 43:173–178. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huang Y, Tsang SY, Yao X and Chen ZY:
Biological properties of baicalein in cardiovascular system. Curr
Drug Targets Cardiovasc Haematol Disord. 5:177–184. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wu X, Zhi F, Lun W, Deng Q and Zhang W:
Baicalin inhibits PDGF-BB-induced hepatic stellate cell
proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, migration and activation via
the miR-3595/ACSL4 axis. Int J Mol Med. 41:1992–2002.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huang S, Chen P, Shui X, He Y, Wang H,
Zheng J, Zhang L, Li J, Xue Y, Chen C and Lei W: Baicalin
attenuates transforming growth factor-β1-induced human pulmonary
artery smooth muscle cell proliferation and phenotypic switch by
inhibiting hypoxia inducible factor-1α and aryl hydrocarbon
receptor expression. J Pharm Pharmacol. 66:1469–1477. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cheng O, Li Z, Han Y, Jiang Q, Yan Y and
Cheng K: Baicalin improved the spatial learning ability of global
ischemia/reperfusion rats by reducing hippocampal apoptosis. Brain
Res. 1470:111–118. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Orzechowska B, Chaber R, Wiśniewska A,
Pajtasz-Piasecka E, Jatczak B, Siemieniec I, Gulanowski B, Chybicka
A and Błach-Olszewska Z: Baicalin from the extract of
Scutellaria baicalensis affects the innate immunity and
apoptosis in leukocytes of children with acute lymphocytic
leukemia. Int Immunopharmacol. 23:558–567. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang P, Cao Y, Yu J, Liu R, Bai B, Qi H,
Zhang Q, Guo W, Zhu H and Qu L: Baicalin alleviates
ischemia-induced memory impairment by inhibiting the
phosphorylation of CaMKII in hippocampus. Brain Res. 1642:95–103.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wei XL, Fang RT, Yang YH, Bi XY, Ren GX,
Luo AL, Zhao M and Zang WJ: Protective effects of extracts from
Pomegranate peels and seeds on liver fibrosis induced by carbon
tetrachloride in rats. BMC Complement Altern Med. 15:3892015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zheng L, Zhang C, Li L, Hu C, Hu M,
Sidikejiang N, Wang X, Lin M and Rong R: Baicalin ameliorates renal
fibrosis via inhibition of transforming growth factor β1 production
and downstream signal transduction. Mol Med Rep. 15:1702–1712.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu T, Dai W, Li C, Liu F, Chen Y, Weng D
and Chen J: Baicalin alleviates silica-induced lung inflammation
and fibrosis by inhibiting the Th17 response in C57BL/6 mice. J Nat
Prod. 78:3049–3057. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huang X, He Y, Chen Y, Wu P, Gui D, Cai H,
Chen A, Chen M, Dai C, Yao D and Wang L: Baicalin attenuates
bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis via adenosine A2a receptor
related TGF-β1-induced ERK1/2 signaling pathway. BMC Pulm Med.
16:1322016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu XL, Wang LK, Yang DD, Qu M, Yang YJ,
Guo F, Han L and Xue J: Effects of Glut1 gene silencing on
proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis of colorectal cancer
cells by targeting the TGF-β/PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling pathway. J
Cell Biochem. 119:2356–2367. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cantley LC: The phosphoinositide 3-kinase
pathway. Science. 296:1655–1657. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang XQ, Sun P and Paller AS: Inhibition
of integrin-linked kinase/protein kinase B/Akt signaling: Mechanism
for ganglioside-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 276:44504–44511.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li Y, Song YH, Mohler J and Delafontaine
P: ANG II induces apoptosis of human vascular smooth muscle via
extrinsic pathway involving inhibition of Akt phosphorylation and
increased FasL expression. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
290:H2116–H2123. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ma XM and Blenis J: Molecular mechanisms
of mTOR-mediated translational control. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
10:307–318. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gui X, Chen H, Cai H, Sun L and Gu L:
Leptin promotes pulmonary fibrosis development by inhibiting
autophagy via PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
498:660–666. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tsoyi K, Chu SG, Patino-Jaramillo NG,
Wilder J, Villalba J, Doyle-Eisele M, McDonald J, Liu X, El-Chemaly
S, Perrella MA and Rosas IO: Syndecan-2 attenuates
radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis and inhibits fibroblast
activation by regulating PI3K/Akt/ROCK pathway via CD148. Am J
Respir Cell Mol Biol. 58:208–215. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hsu HS, Liu CC, Lin JH, Hsu TW, Hsu JW, Su
K and Hung SC: Involvement of ER stress, PI3K/AKT activation, and
lung fibroblast proliferation in bleomycin-induced pulmonary
fibrosis. Sci Rep. 7:142722017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pitt GS: Calmodulin and CaMKII as
molecular switches for cardiac ion channels. Cardiovasc Res.
73:641–647. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mukherjee S, Sheng W, Sun R and Janssen
LJ: Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IIβ and IIδ
mediate TGFβ-induced transduction of fibronectin and collagen in
human pulmonary fibroblasts. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
312:L510–L519. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Williams CL, Phelps SH and Porter RA:
Expression of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase
types II and IV, and reduced DNA synthesis due to the
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase inhibitor KN-62
(1-[N,O-bis(5-isoquinolinesulfonyl)-N-methyl-L-tyrosyl]-4-phenyl
piperazine) in small cell lung carcinoma. Biochem Pharmacol.
51:707–715. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hwang YP, Kim HG, Hien TT, Jeong MH, Jeong
TC and Jeong HG: Puerarin activates endothelial nitric oxide
synthase through estrogen receptor-dependent PI3-kinase and
calcium-dependent AMP-activated protein kinase. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 257:48–58. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mukherjee S, Sheng W, Michkov A, Sriarm K,
Sun R, Dvorkin-Gheva A, Insel PA and Janssen LJ: Prostaglandin E2
inhibits profibrotic function of human pulmonary fibroblasts by
disrupting Ca2+ signaling. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 316:L810–L821. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Monaco S, Illario M, Rusciano MR,
Gragnaniello G, Di Spigna G, Leggiero E, Pastore L, Fenzi G, Rossi
G and Vitale M: Insulin stimulates fibroblast proliferation through
calcium-calmodulin-dependent kinase II. Cell Cycle. 8:2024–2030.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Choi EJ, Jin GY, Bok SM, Han YM, Lee YS,
Jung MJ and Kwon KS: Serial micro-CT assessment of the therapeutic
effects of rosiglitazone in a bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis mouse
model. Korean J Radiol. 15:448–455. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Meng Y, Li T, Zhou GS, Chen Y, Yu CH, Pang
MX, Li W, Li Y, Zhang WY and Li X: The angiotensin-converting
enzyme 2/angiotensin (1–7)/Mas axis protects against lung
fibroblast migration and lung fibrosis by inhibiting the
NOX4-derived ROS-mediated RhoA/Rho kinase pathway. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 22:241–258. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang Q, Fan K, Wang P, Yu J, Liu R, Qi H,
Sun H and Cao Y: Carvacrol induces the apoptosis of pulmonary
artery smooth muscle cells under hypoxia. Eur J Pharmacol.
770:134–146. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu R, Zhang Q, Luo Q, Qiao H, Wang P, Yu
J, Cao Y, Lu B and Qu L: Norepinephrine stimulation of
alpha1D-adrenoceptor promotes proliferation of pulmonary artery
smooth muscle cells via ERK-1/2 signaling. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
88:100–112. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang P, Luo Q, Qiao H, Ding H, Cao Y, Yu
J, Liu R, Zhang Q, Zhu H and Qu L: The neuroprotective effects of
carvacrol on ethanol-induced hippocampal neurons impairment via the
antioxidative and antiapoptotic pathways. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2017:40794252017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li L, Cai L, Zheng L, Hu Y, Yuan W, Guo Z
and Li W: Gefitinib inhibits bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis
via alleviating the oxidative damage in mice. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2018:82496932018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Cory S, Huang DC and Adams JM: The Bcl-2
family: Roles in cell survival and oncogenesis. Oncogene.
22:8590–8607. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chen M, Guerrero AD, Huang L, Shabier Z,
Pan M, Tan TH and Wang J: Caspase-9-induced mitochondrial
disruption through cleavage of anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family members.
J Biol Chem. 282:33888–33895. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Noble PW, Barkauskas CE and Jiang D:
Pulmonary fibrosis: Patterns and perpetrators. J Clin Invest.
122:2756–2762. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Moeller A, Ask K, Warburton D, Gauldie J
and Kolb M: The bleomycin animal model: A useful tool to
investigate treatment options for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis?
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 40:362–382. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Gao C, Zhou Y, Li H, Cong X, Jiang Z, Wang
X, Cao R and Tian W: Antitumor effects of baicalin on ovarian
cancer cells through induction of cell apoptosis and inhibition of
cell migration in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 16:8729–8734. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Li X, Zou K, Gou J, Du Q, Li D, He X and
Li Z: Effect of baicalin-copper on the induction of apoptosis in
human hepatoblastoma cancer HepG2 cells. Med Oncol. 32:722015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ren X, Zhang Z, Tian J, Wang H, Song G,
Guo Q, Tian J, Han Y, Liao Q, Liu G, et al: The downregulation of
c-Myc and its target gene hTERT is associated with the
antiproliferative effects of baicalin on HL-60 cells. Oncol Lett.
14:6833–6840. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Mouratis MA and Aidinis V: Modeling
pulmonary fibrosis with bleomycin. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 17:355–361.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Chen C, Wang YY, Wang YX, Cheng MQ, Yin
JB, Zhang X and Hong ZP: Gentiopicroside ameliorates
bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice via inhibiting
inflammatory and fibrotic process. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
495:2396–2403. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ji YD, Luo ZL, Chen CX, Li B, Gong J, Wang
YX, Chen L, Yao SL and Shang Y: BML-111 suppresses TGF-β1-induced
lung fibroblast activation in vitro and decreases experimental
pulmonary fibrosis in vivo. Int J Mol Med. 42:3083–3092.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Huang C, Wu X, Wang S, Wang W, Guo F, Chen
Y, Pan B, Zhang M and Fan X: Combination of Salvia miltiorrhiza and
ligustrazine attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in
rats via modulating TNF-α and TGF-β. Chin Med. 13:362018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Jin M, Wang L, Wu Y, Zang BX and Tan L:
Protective effect of hydroxysafflor yellow A on bleomycin-induced
pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis in rats. Chin J Integr Med.
24:32–39. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Akter T, Silver RM and Bogatkevich GS:
Recent advances in understanding the pathogenesis of
scleroderma-interstitial lung disease. Curr Rheumatol Rep.
16:4112014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Schoenfeld SR and Castelino FV:
Interstitial lung disease in scleroderma. Rheum Dis Clin North Am.
41:237–248. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Lu Q, Guo Z, Xie W, Jin W, Zhu D, Chen S
and Ren T: The lncRNA H19 mediates pulmonary fibrosis by regulating
the miR-196a/COL1A1 axis. Inflammation. 41:896–903. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Honda H, Fujimoto M, Serada S, Urushima H,
Mishima T, Lee H, Ohkawara T, Kohno N, Hattori N, Yokoyama A and
Naka T: Leucine-rich α-2 glycoprotein promotes lung fibrosis by
modulating TGF-β signaling in fibroblasts. Physiol Rep.
5:e135562017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Todd NW, Luzina IG and Atamas SP:
Molecular and cellular mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis.
Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 5:112012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Inghilleri S, Morbini P, Oggionni T, Barni
S and Fenoglio C: In situ assessment of oxidant and nitrogenic
stress in bleomycin pulmonary fibrosis. Histochem Cell Biol.
125:661–669. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Kinnula VL and Myllärniemi M:
Oxidant-antioxidant imbalance as a potential contributor to the
progression of human pulmonary fibrosis. Antioxid Redox Signal.
10:727–738. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Fubini B and Hubbard A: Reactive oxygen
species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) generation by
silica in inflammation and fibrosis. Free Radic Biol Med.
34:1507–1516. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Gao F, Kinnula VL, Myllärniemi M and Oury
TD: Extracellular superoxide dismutase in pulmonary fibrosis.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 10:343–354. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Lin CH, Shih CH, Lin YC, Yang YL and Chen
BC: MEKK1, JNK, and SMAD3 mediate CXCL12-stimulated connective
tissue growth factor expression in human lung fibroblasts. J Biomed
Sci. 25:192018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Arezzini B, Vecchio D, Signorini C,
Stringa B and Gardi C: F2-isoprostanes can mediate
bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 115:1–9.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Tian R, Zhu Y, Yao J, Meng X, Wang J, Xie
H and Wang R: NLRP3 participates in the regulation of EMT in
bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Exp Cell Res. 357:328–334.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Chen X, Nishida H and Konishi T: Baicalin
promoted the repair of DNA single strand breakage caused by H2O2 in
cultured NIH3T3 fibroblasts. Biol Pharm Bull. 26:282–284. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Jiang H, Lv P, Li J, Wang H, Zhou T, Liu Y
and Lin W: Baicalin inhibits colistin sulfate-induced apoptosis of
PC12 cells. Neural Regen Res. 8:2597–2604. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Chen WC, Kuo TH, Tzeng YS and Tsai YC:
Baicalin induces apoptosis in SW620 human colorectal carcinoma
cells in vitro and suppresses tumor growth in vivo.
Molecules. 17:3844–3857. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Zhang Q, Cao Y, Luo Q, Wang P, Shi P, Song
C, E M, Ren J, Fu B and Sun H: The transient receptor potential
vanilloid-3 regulates hypoxia-mediated pulmonary artery smooth
muscle cells proliferation via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cell
Prolif. 51:e124362018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Ding L, Huang Y, Dai M, Zhao X, Du Q, Dong
F, Wang L, Huo R, Zhang W, Xu X and Tong D: Transmissible
gastroenteritis virus infection induces cell cycle arrest at S and
G2/M phases via p53-dependent pathway. Virus Res. 178:241–251.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Zhong C, Han Y, Ma J, Zhang X, Sun M, Wang
Y, Chen J, Mi W, Xu X and Qiu J: Viral-mediated expression of c-Myc
and cyclin A2 induces cochlear progenitor cell proliferation.
Neurosci Lett. 591:93–98. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Joshaghani HR, Jafari SM, Aghaei M,
Panjehpour M and Abedi H: A3 adenosine receptor agonist induce G1
cell cycle arrest via Cyclin D and cyclin-dependent kinase 4
pathways in OVCAR-3 and Caov-4 cell lines. J Cancer Res Ther.
13:107–112. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Ventura C, Núñez M, Gaido V, Pontillo C,
Miret N, Randi A and Cocca C: Hexachlorobenzene alters cell cycle
by regulating p27-cyclin E-CDK2 and c-Src-p27 protein complexes.
Toxicol Lett. 270:72–79. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Lu Y, Azad N, Wang L, Iyer AK, Castranova
V, Jiang BH and Rojanasakul Y: Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/akt
regulates bleomycin-induced fibroblast proliferation and collagen
production. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 42:432–441. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Ma SY, Park WS, Lee DS, Choi G, Yim MJ,
Lee JM, Jung WK, Park SG, Seo SK, Park SJ, et al: Fucoxanthin
inhibits profibrotic protein expression in vitro and attenuates
bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol.
811:199–207. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Zhang YP, Li WB, Wang WL, Liu J, Song SX,
Bai LL, Hu YY, Yuan YD and Zhang M: siRNA against plasminogen
activator inhibitor-1 ameliorates bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis
in rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 33:897–908. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Wu X, Li J, Yang X, Bai X, Shi J, Gao J,
Li Y, Han S, Zhang Y, Han F, et al: miR-155 inhibits the formation
of hypertrophic scar fibroblasts by targeting HIF-1α via PI3K/AKT
pathway. J Mol Histol. 49:377–387. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Phosri S, Arieyawong A, Bunrukchai K,
Parichatikanond W, Nishimura A, Nishida M and Mangmool S:
Stimulation of adenosine A2B receptor inhibits
endothelin-1-induced cardiac fibroblast proliferation and α-smooth
muscle actin synthesis through the cAMP/Epac/PI3K/Akt-signaling
pathway. Front Pharmacol. 8:4282017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Yuan J, Li P, Pan H, Li Y, Xu Q, Xu T, Ji
X, Liu Y, Yao W, Han L and Ni C: miR-542-5p attenuates fibroblast
activation by targeting integrin α6 in silica-induced pulmonary
fibrosis. Int J Mol Sci. 19:E37172018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
He Z, Deng Y, Li W, Chen Y, Xing S, Zhao
X, Ding J, Gao Y and Wang X: Overexpression of PTEN suppresses
lipopolysaccharide-induced lung fibroblast proliferation,
differentiation and collagen secretion through inhibition of the
PI3-K-Akt-GSK3beta pathway. Cell Biosci. 4:22014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Hurley RL, Anderson KA, Franzone JM, Kemp
BE, Means AR and Witters LA: The Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein
kinase kinases are AMP-activated protein kinase kinases. J Biol
Chem. 280:29060–29066. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Woods A, Dickerson K, Heath R, Hong SP,
Momcilovic M, Johnstone SR, Carlson M and Carling D:
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase-beta acts upstream
of AMP-activated protein kinase in mammalian cells. Cell Metab.
2:21–33. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Imoto K, Okada M and Yamawaki H:
Characterization of fibroblasts from hypertrophied right ventricle
of pulmonary hypertensive rats. Pflugers Arch. 470:1405–1417. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Sazonova OV, Blishchenko EY, Tolmazova AG,
Khachin DP, Leontiev KV, Karelin AA and Ivanov VT: Stimulation of
fibroblast proliferation by neokyotorphin requires Ca influx and
activation of PKA, CaMK II and MAPK/ERK. FEBS J. 274:474–484. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|