|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 70:7–30. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, .
Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma. Nature.
511:543–550. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Janssen-Heijnen ML, van Erning FN, De
Ruysscher DK, Coebergh JW and Groen HJ: Variation in causes of
death in patients with non-small cell lung cancer according to
stage and time since diagnosis. Ann Oncol. 26:902–907. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, Takada S,
Yamashita Y, Ishikawa S, Fujiwara S, Watanabe H, Kurashina K,
Hatanaka H, et al: Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK
fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 448:561–566.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pan L, Li Y, Jia L, Qin Y, Qi G, Cheng J,
Qi Y, Li H and Du J: Cathepsin S deficiency results in abnormal
accumulation of autophagosomes in macrophages and enhances Ang
II-induced cardiac inflammation. PLoS One. 7:e353152012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dennemärker J, Lohmüller T, Müller S,
Aguilar SV, Tobin DJ, Peters C and Reinheckel T: Impaired turnover
of autophagolysosomes in cathepsin L deficiency. Biol Chem.
391:913–922. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Drake MT, Clarke BL, Oursler MJ and Khosla
S: Cathepsin K inhibitors for osteoporosis: Biology, potential
clinical utility, and lessons learned. Endocr Rev. 38:325–350.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Olson OC and Joyce JA: Cysteine cathepsin
proteases: Regulators of cancer progression and therapeutic
response. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:712–729. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Akkari L, Gocheva V, Quick ML, Kester JC,
Spencer AK, Garfall AL, Bowman RL and Joyce JA: Combined deletion
of cathepsin protease family members reveals compensatory
mechanisms in cancer. Genes Dev. 30:220–232. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kolli N and Garman SC: Proteolytic
activation of human cathepsin A. J Biol Chem. 289:11592–11600.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
You Y, Li WZ, Zhang S, Hu B, Li YX, Li HD,
Tang HH, Li QW, Guan YY, Liu LX, et al: SNX10 mediates
alcohol-induced liver injury and steatosis by regulating the
activation of chaperone-mediated autophagy. J Hepatol. 69:129–141.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Verbovšek U, Van Noorden CJ and Lah TT:
Complexity of cancer protease biology: Cathepsin K expression and
function in cancer progression. Semin Cancer Biol. 35:71–84. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sudhan DR and Siemann DW: Cathepsin L
targeting in cancer treatment. Pharmacol Ther. 155:105–116. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yuan L, Sheng L, He W, Zou C, Hu B, Liu J,
Ge W, Liu Y, Wang J and Ma E: Discovery of novel cathepsin
inhibitors with potent anti-metastatic effects in breast cancer
cells. Bioorg Chem. 81:672–680. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
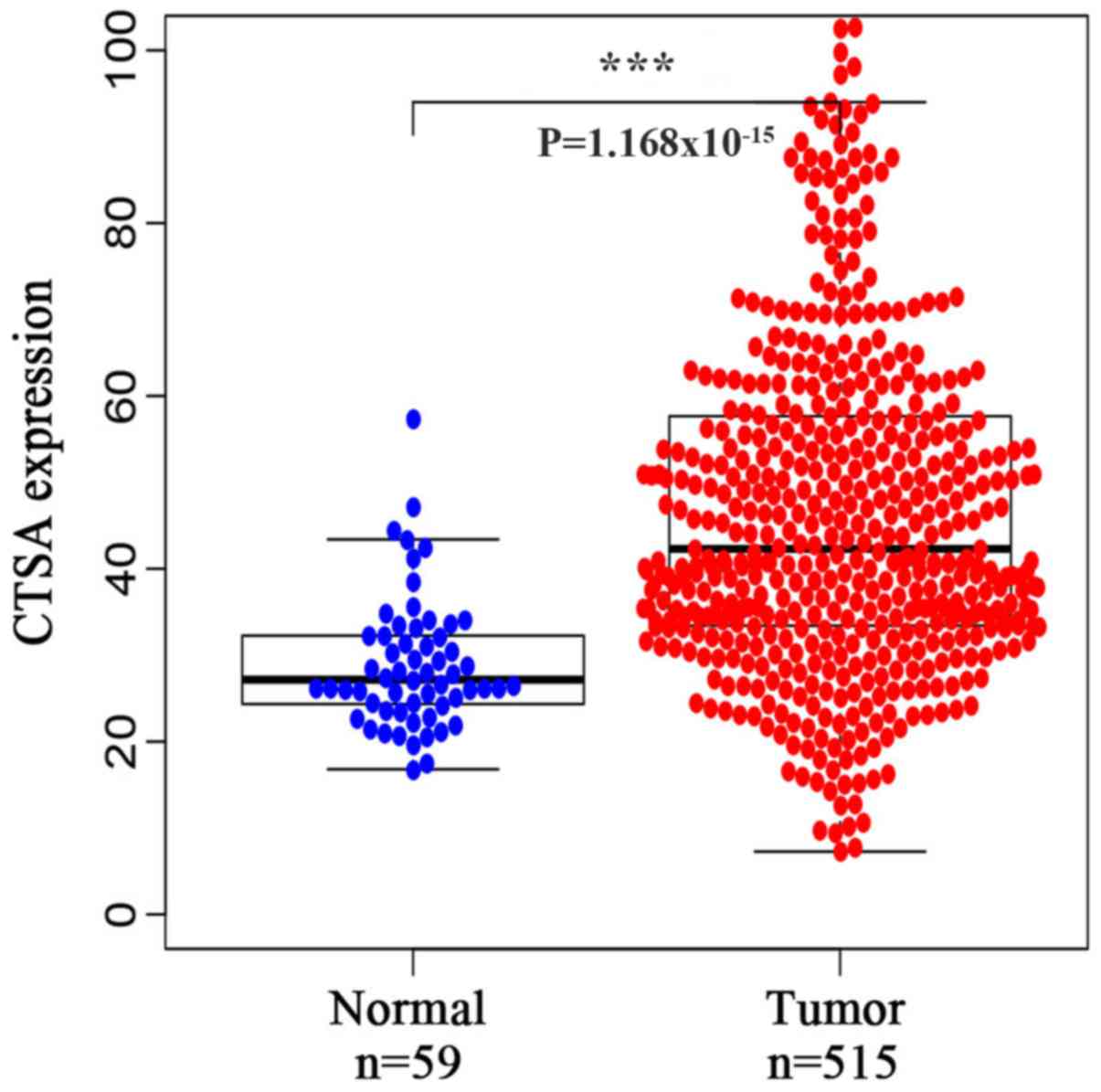
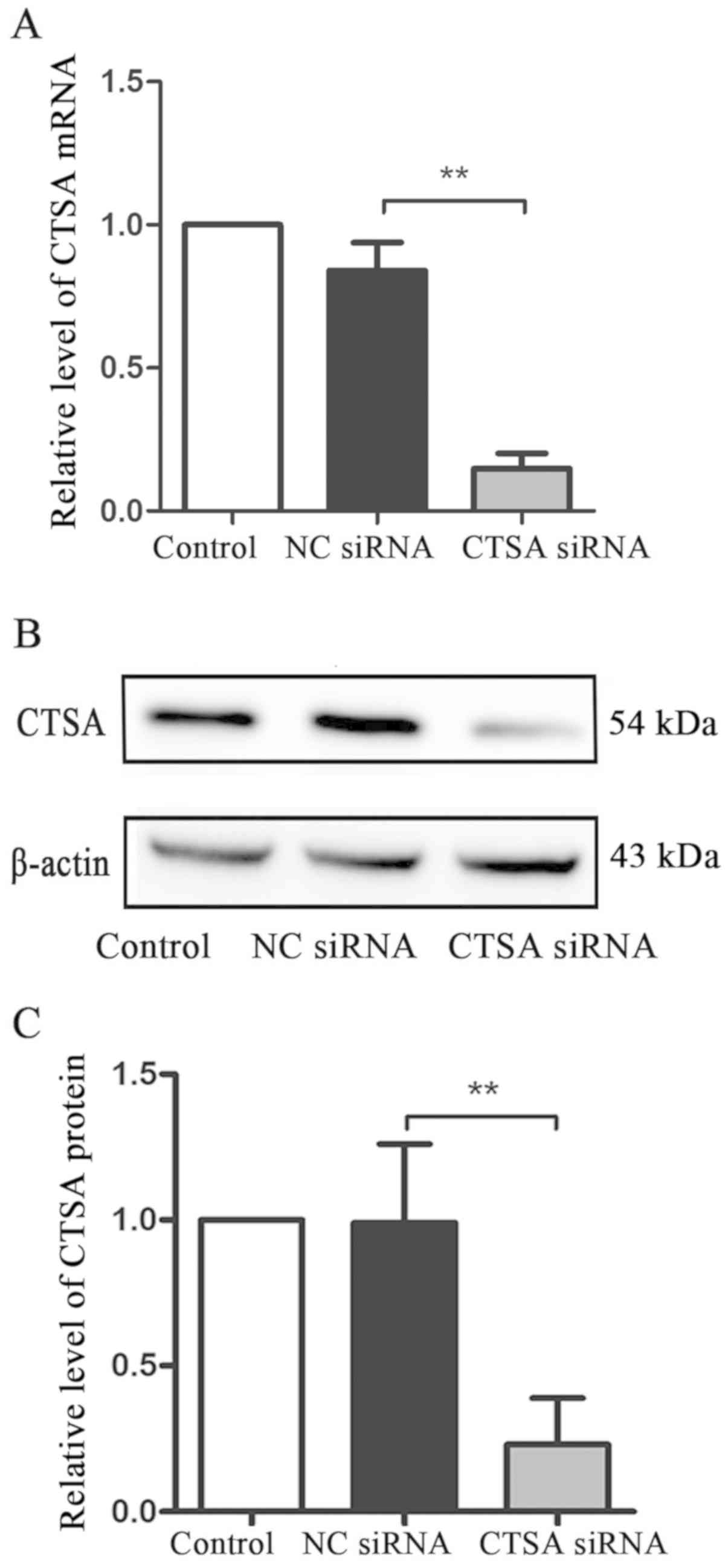
Ni S, Weng W, Xu M, Wang Q, Tan C, Sun H,
Wang L, Huang D, Du X and Sheng W: miR-106b-5p inhibits the
invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer by targeting CTSA.
Onco Targets Ther. 11:3835–3845. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Toss MS, Miligy IM, Haj-Ahmad R, Gorringe
KL, AlKawaz A, Mittal K, Ellis IO, Green AR and Rakha EA: The
prognostic significance of lysosomal protective protein (cathepsin
A) in breast ductal carcinoma in situ. Histopathology.
74:1025–1035. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kozlowski L, Wojtukiewicz MZ and Ostrowska
H: Cathepsin A activity in primary and metastatic human melanocytic
tumors. Arch Dermatol Res. 292:68–71. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, .
Comprehensive genomic characterization of squamous cell lung
cancers. Nature. 489:519–525. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Molina JR, Yang P, Cassivi SD, Schild SE
and Adjei AA: Non-small cell lung cancer: Epidemiology, risk
factors, treatment, and survivorship. Mayo Clin Proc. 83:584–594.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hung JJ, Yeh YC, Jeng WJ, Wu KJ, Huang BS,
Wu YC, Chou TY and Hsu WH: Predictive value of the international
association for the study of lung cancer/American thoracic
society/European respiratory society classification of lung
adenocarcinoma in tumor recurrence and patient survival. J Clin
Oncol. 32:2357–2364. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Reinheckel T, Hagemann S, Dollwet-Mack S,
Martinez E, Lohmuller T, Zlatkovic G, Tobin DJ, Maas-Szabowski N
and Peters C: The lysosomal cysteine protease cathepsin L regulates
keratinocyte proliferation by control of growth factor recycling. J
Cell Sci. 118:3387–3395. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Platt MO and Shockey WA: Endothelial cells
and cathepsins: Biochemical and biomechanical regulation.
Biochimie. 122:314–323. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Brojatsch J, Lima H Jr, Palliser D,
Jacobson LS, Muehlbauer SM, Furtado R, Goldman DL, Lisanti MP and
Chandran K: Distinct cathepsins control necrotic cell death
mediated by pyroptosis inducers and lysosome-destabilizing agents.
Cell Cycle. 14:964–972. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang L, Zhao Y, Xiong Y, Wang W, Fei Y,
Tan C and Liang Z: K-ras mutation promotes ionizing
radiation-induced invasion and migration of lung cancer in part via
the Cathepsin L/CUX1 pathway. Exp Cell Res. 362:424–435. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Willumsen N, Bager CL, Leeming DJ,
Bay-Jensen AC and Karsdal MA: Nidogen-1 degraded by cathepsin S can
be quantified in serum and is associated with non-small cell lung
cancer. Neoplasia. 19:271–278. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tsai JY, Lee MJ, Dah-Tsyr Chang M and
Huang H: The effect of catalase on migration and invasion of lung
cancer cells by regulating the activities of cathepsin S, L, and K.
Exp Cell Res. 323:28–40. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jechorek D, Votapek J, Meyer F, Kandulski
A, Roessner A and Franke S: Characterization of cathepsin X in
colorectal cancer development and progression. Pathol Res Pract.
210:822–829. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang W, Wang S, Wang Q, Yang Z, Pan Z and
Li L: Overexpression of cysteine cathepsin L is a marker of
invasion and metastasis in ovarian cancer. Oncol Rep. 31:1334–1342.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yamashita K, Iwatake M, Okamoto K, Yamada
SI, Umeda M and Tsukuba T: Cathepsin K modulates invasion,
migration and adhesion of oral squamous cell carcinomas in vitro.
Oral Dis. 23:518–525. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Aggarwal N and Sloane BF: Cathepsin B:
Multiple roles in cancer. Proteomics Clin Appl. 8:427–437. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Schweiger A, Staib A, Werle B, Krasovec M,
Lah TT, Ebert W, Turk V and Kos J: Cysteine proteinase cathepsin H
in tumours and sera of lung cancer patients: Relation to prognosis
and cigarette smoking. Br J Cancer. 82:782–788. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ruan J, Zheng H, Fu W, Zhao P, Su N and
Luo R: Increased expression of cathepsin L: A novel independent
prognostic marker of worse outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma
patients. PLoS One. 9:e1121362014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Han ML, Zhao YF, Tan CH, Xiong YJ, Wang
WJ, Wu F, Fei Y, Wang L and Liang ZQ: Cathepsin L
upregulation-induced EMT phenotype is associated with the
acquisition of cisplatin or paclitaxel resistance in A549 cells.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 37:1606–1622. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Turk V, Turk B, Guncar G, Turk D and Kos
J: Lysosomal cathepsins: Structure, role in antigen processing and
presentation, and cancer. Adv Enzyme Regul. 42:285–303. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
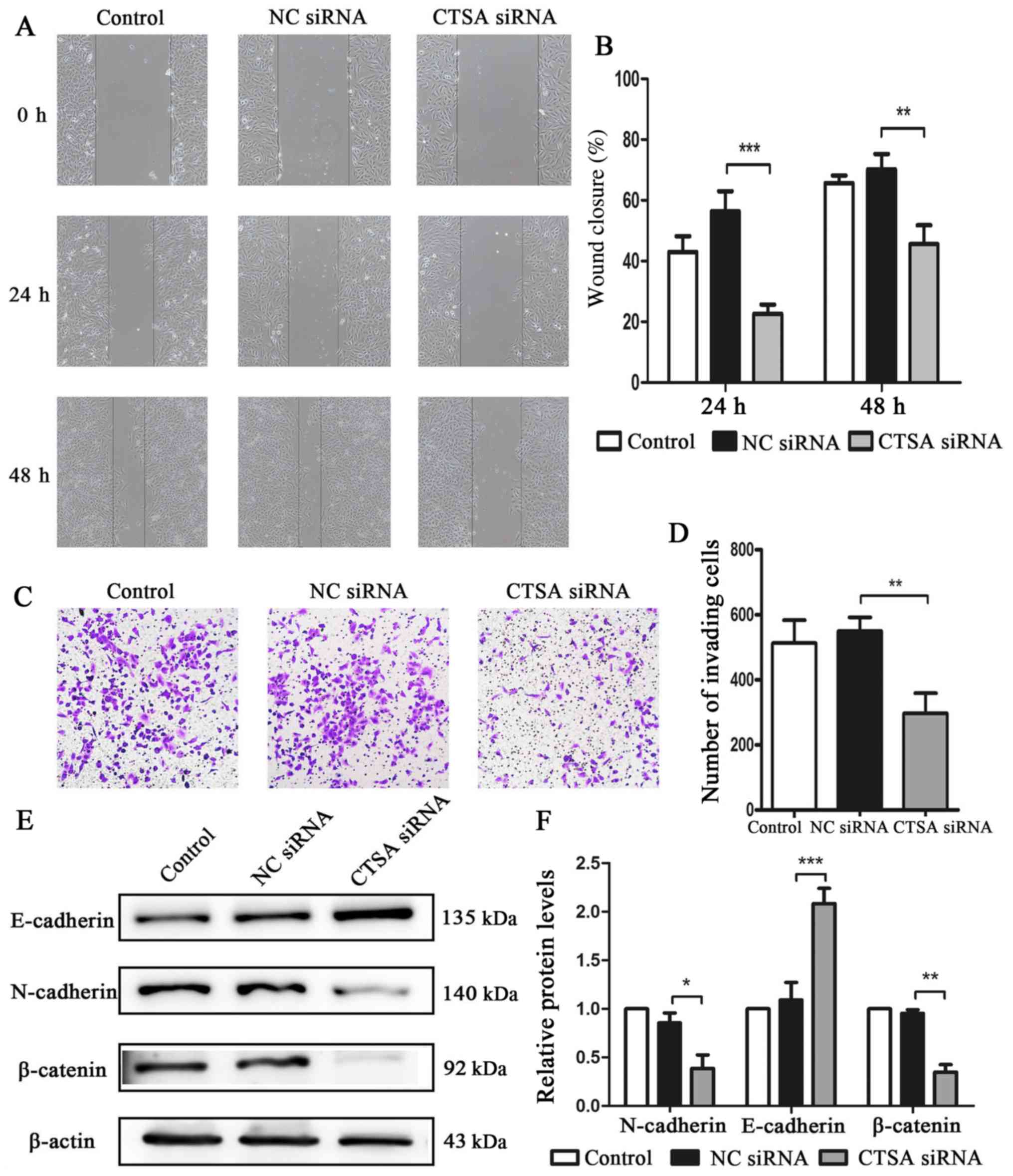
Pastushenko I and Blanpain C: EMT
Transition states during tumor progression and metastasis. Trends
Cell Biol. 29:212–226. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zeisberg M and Neilson EG: Biomarkers for
epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. J Clin Invest. 119:1429–1437.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gocheva V, Zeng W, Ke D, Klimstra D,
Reinheckel T, Peters C, Hanahan D and Joyce JA: Distinct roles for
cysteine cathepsin genes in multistage tumorigenesis. Genes Dev.
20:543–556. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kallunki T, Olsen OD and Jäättelä M:
Cancer-associated lysosomal changes: Friends or foes? Oncogene.
32:1995–2004. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
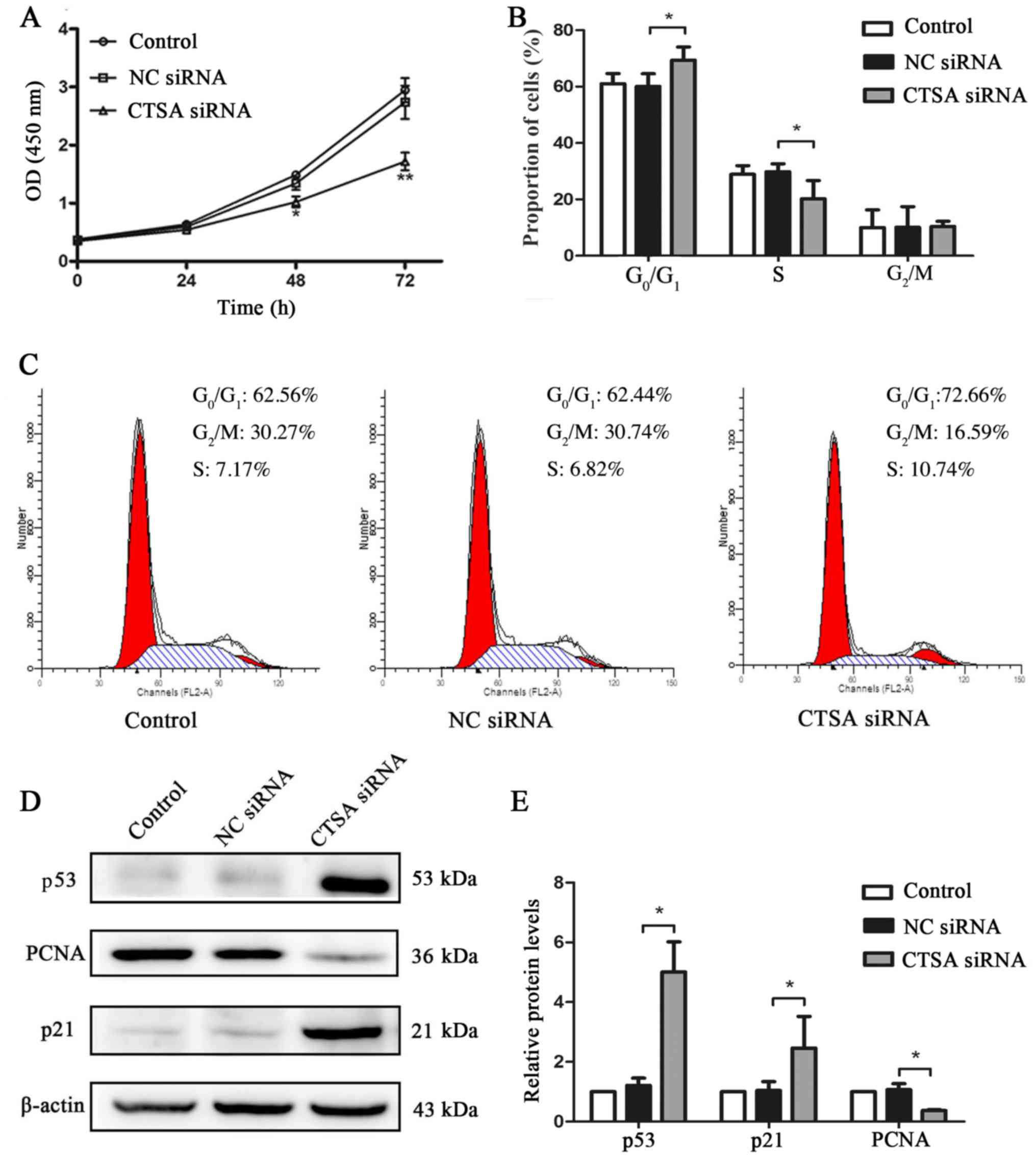
Harris SL and Levine AJ: The p53 pathway:
Positive and negative feedback loops. Oncogene. 24:2899–2908. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|