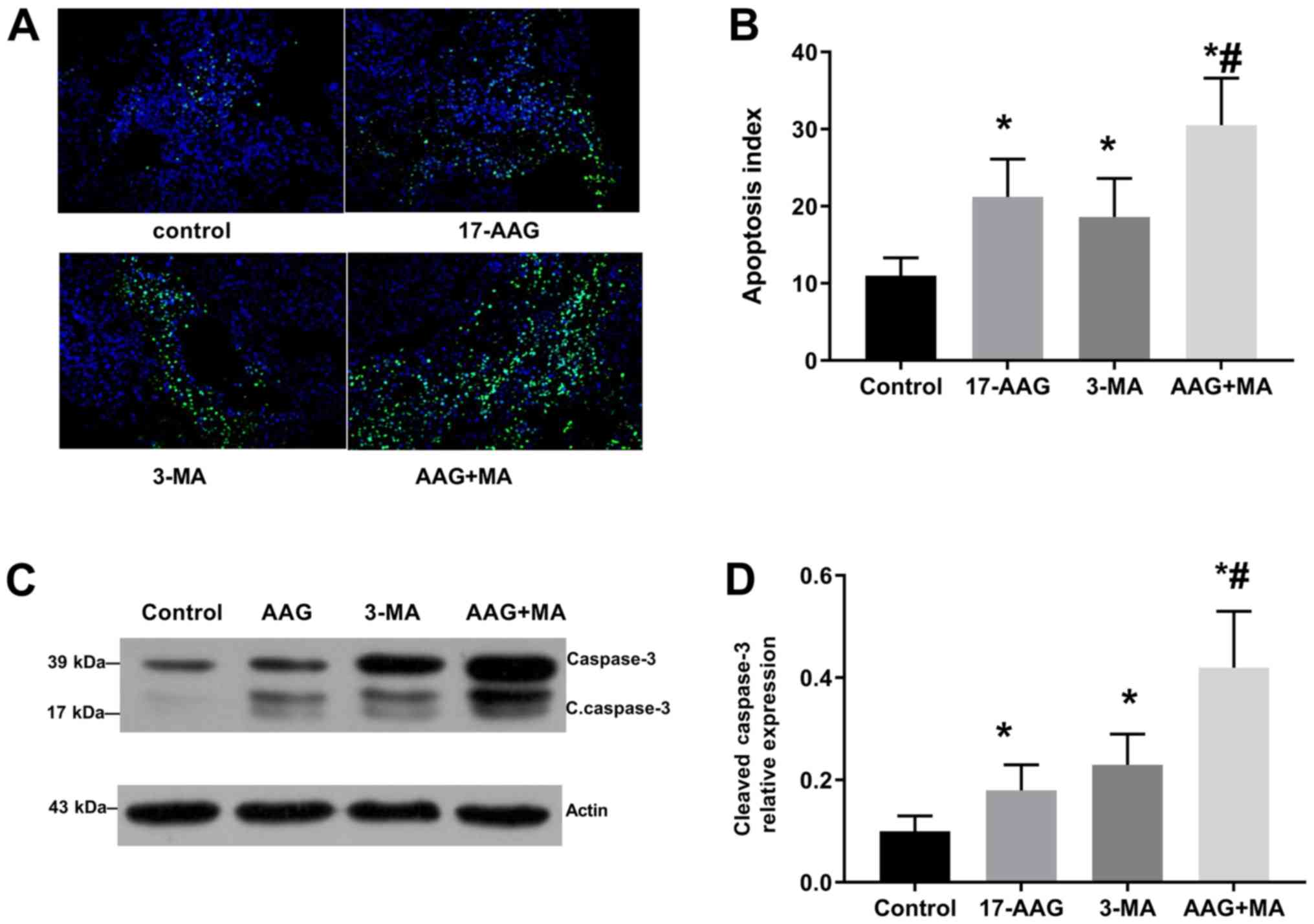
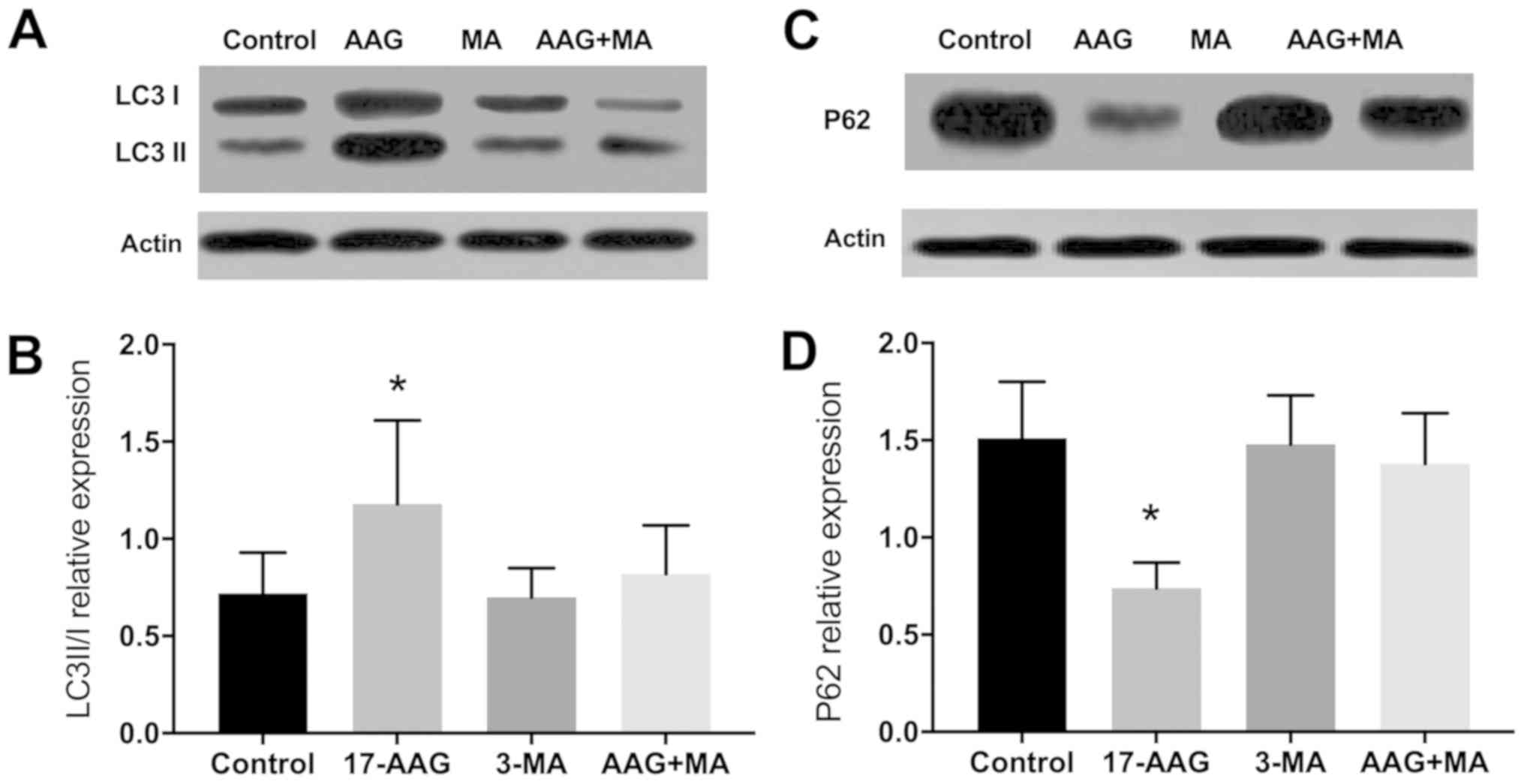
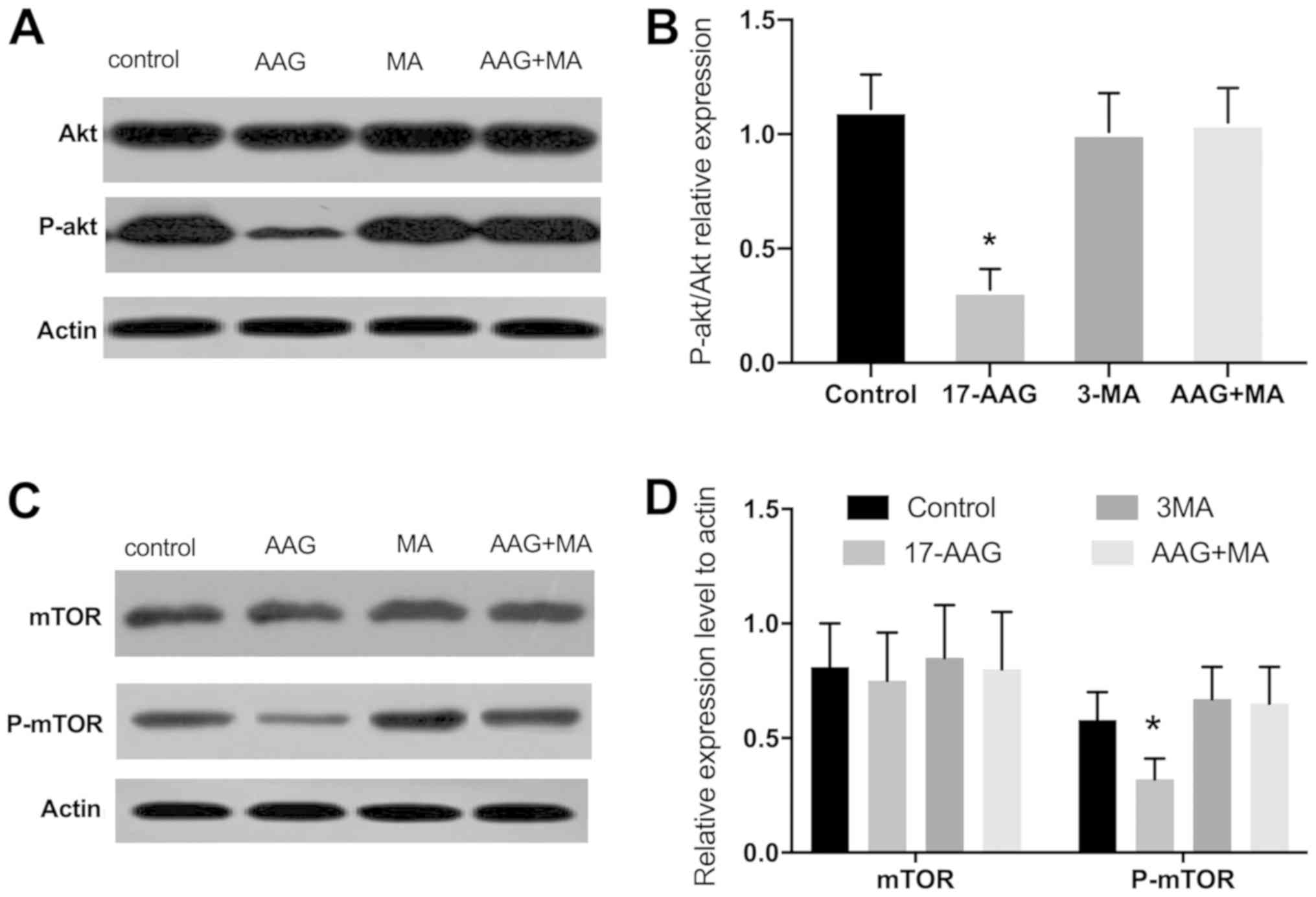
|
1
|
Yun KC, Rhim H and Noh S: Radiofrequency
ablation versus surgical resection as primary treatment of
hepatocellular carcinoma meeting the Milan criteria: A systematic
review. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 26:1354–1360. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hermida M, Cassinotto C, Piron L, Assenat
E, Pageaux GP, Escal L, Pierredon-Foulongne MA, Verzilli D, Jaber S
and Guiu B: Percutaneous thermal ablation of hepatocellular
carcinomas located in the hepatic dome using artificial carbon
dioxide pneumothorax: Retrospective evaluation of safety and
efficacy. Int J Hyperthemia. 35:90–96. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Medhat E, Abdel Aziz A, Nabeel M, Elbaz T,
Zakaria Z, Shousha H, Amer A, Fouad Fathalah W, Maher R and Musa S:
Value of microwave ablation in treatment of large lesions of
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Dig Dis. 16:456–463. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schueller G, Kettenbach J, Sedivy R, Stift
A, Friedl J, Gnant M and Lammer J: Heat shock protein expression
induced by percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular
carcinoma in vivo. Int J Oncol. 24:609–613. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hinz S, Tepel J, Röder C, Kalthoff H and
Becker T: Profile of serum factors and disseminated tumor cells
before and after radiofrequency ablation compared to resection of
colorectal liver metastases-a pilot study. Anticancer Res.
35:2961–2967. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rai R, Richardson C, Flecknell P,
Robertson H, Burt A and Manas DM: Study of apoptosis and heat shock
protein (HSP) expression in hepatocytes following radiofrequency
ablation (RFA). J Surg Res. 129:147–151. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang W, Ahmed M, Tasawwar B, Levchenko T,
Sawant RR, Collins M, Signoretti S, Torchilin V and Goldberg SN:
Radiofrequency ablation combined with liposomal quercetin to
increase tumour destruction by modulation of heat shock protein
production in a small animal model. Int J Hyperthermia. 27:527–538.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schueller G, Kettenbach J, Sedivy R,
Bergmeister H, Stift A, Fried J, Gnant M and Lammer J: Expression
of heat shock proteins in human hepatocellular carcinoma after
radiofrequency ablation in an animal model. Oncol Rep. 12:495–499.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
He W, Ye X, Huang X, Lel W, You L, Wang L,
Chen X and Qian W: Hsp90 inhibitor, BIIB021, induces apoptosis and
autophagy by regulating mTOR-Ulk1 pathway in imatinib-sensitive
and-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Int J Oncol.
48:1710–1720. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Leng AM, Liu T, Yang J, Cui JF, Li XH, Zhu
YN, Xiong T, Zhang G and Chen Y: The apoptotic effect and
associated signalling of HSP90 inhibitor 17-DMAG in hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Cell Biol Int. 36:893–899. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu X, Chen S, Tu J, Cai W and Xu Q: HSP90
inhibits apoptosis and promotes growth by regulating HIF-1α
abundance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Mol Med. 37:825–835.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu X, Ban LL, Luo G, Li ZY, Li YF, Zhou
YC, Wang XC, Jin CG, Ye JG, Ma DD, et al: Acquired resistance to
HSP90 inhibitor 17-AAG and increased metastatic potential are
associated with MUC1 expression in colon carcinoma cells.
Anticancer Drugs. 27:417–426. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen Y, Youn P, Pysher TJ, Scaife CL and
Furgeson DY: Tumour eradication using synchronous thermal ablation
and Hsp90 chemotherapy with protein engineered triblock
biopolymer-geldanamycin conjugates. Int J Hyperthermia. 30:550–564.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lang SA, Moser C, Fichnter-Feigl S,
Schachtschneider P, Hellerbrand C, Schmitz V, Schlitt HJ, Geissler
EK and Stoeltzing O: Targeting heat-shock protein 90 improves
efficacy of rapamycin in a model of hepatocellular carcinoma in
mice. Hepatology. 49:523–532. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Webber PJ, Park C, Qui M, Ramalingam SS,
Khuri FR, Fu H and Du Y: Combination of heat shock protein 90 and
focal adhesion kinase inhibitors synergistically inhibits the
growth of non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncoscience. 2:765–776.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang R, Tang Q, Miao F, An Y, Li M, Han Y,
Wang X, Wang J, Liu P and Chen R: Inhibition of heat-shock protein
90 sensitizes liver cancer stem-like cells to magnetic hyperthermia
and enhances anti-tumor effect on hepatocellular carcinoma-burdened
nude mice. Int J Nanomedicine. 10:7345–7358. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Moussa M, Goldberg SN, Kumar G, Sawant RR,
Levchenko T, Torchilin V and Ahmed M: Radiofrequency
ablation-induced upregulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α can be
suppressed with adjuvant bortezomib or liposomal chemotherapy. J
Vasc Interv Radiol. 25:1972–1982. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen F, Bao H, Xie H, Tian G and Jiang T:
Heat shock protein expression and autophagy after incomplete
thermal ablation and their correlation. Int J Hyperthermia.
36:95–103. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang R, Luo D, Miao R, Bai L, Ge Q, Sessa
WC and Min W: Hsp90-Akt phosphorylates ASK1 and inhibits
ASK1-mediated apoptosis. Oncogene. 24:3954–3963. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sato S, Fujita N and Tsuruo T: Modulation
of Akt kinase activity by binding to Hsp90. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
97:10832–10837. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Oral O, Akkoc Y, Bayraktar O and Gozuacik
D: Physiological and pathological significance of the molecular
cross-talk between autophagy and apoptosis. Histol Histopathol.
31:479–498. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Heras-Sandoval D, Pérez-Rojas JM,
Hernández-Damián J and Pedraza-Chaverri J: The role of
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in the modulation of autophagy and the
clearance of protein aggregates in neurodegeneration. Cell Signal.
26:2694–2701. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nazim UM and Park SY: Attenuation of
autophagy flux by 6-shogaol sensitizes human liver cancer cells to
TRAIL-induced apoptosis via p53 and ROS. Int J Mol Med. 43:701–708.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mukhopadhyay S, Panda PK, Sinha N, Das DN
and Bhutia SK: Autophagy and apoptosis: Where do they meet?
Apoptosis. 19:555–566. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mariño G, Niso-Santano M, Baehrecke EH and
Kroemer G: Self-consumption: The interplay of autophagy and
apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:81–94. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Talaei S, Mellatyar H, Asadi A, Akbarzadeh
A, Sheervalilou R and Zarghami N: Spotlight on 17-AAG as an Hsp90
inhibitor for molecular targeted cancer treatment. Chem Biol Drug
Des. 93:760–786. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Walker AR, Klisovic R, Johnston JS, Jiang
Y, Geyer S, Kefauver C, Binkley P, Byrd JC, Grever MR, Garzon R, et
al: Pharmacokinetics and dose escalation of the heat shock protein
inhibitor 17-allyamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin in combination with
bortezomib in relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk
Lymphoma. 54:1996–2002. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kaufmann SH, Karp JE, Litzow MR, Mesa RA,
Hogan W, Steensma DP, Flatten KS, Loegering DA, Schneider PA,
Peterson KL, et al: Phase I and pharmacological study of cytarabine
and tanespimycin in relapsed and refractory acute leukemia.
Haematologica. 96:1619–1626. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Heath EI, Hillman DW, Vaishampayan U,
Sheng S, Sarkar F, Harper F, Gaskins M, Pitot HC, Tan W, Ivy SP, et
al: A phase II trial of 17-allylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin in
patients with hormone-refractory metastatic prostate cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 14:7940–7946. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Pacey S, Gore M, Chao D, Banerji U, Larkin
J, Sarker S, Owen K, Asad Y, Raynaud F, Walton M, et al: A Phase II
trial of 17-allylamino, 17-demethoxygeldanamycin (17-AAG,
tanespimycin) in patients with metastatic melanoma. Invest New
Drugs. 30:341–349. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Strozyk E and Kulms D: The role of
AKT/mTOR pathway in stress response to UV-irradiation: Implication
in skin carcinogenesis by regulation of apoptosis, autophagy and
senescence. Int J Mol Sci. 14:15260–15285. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Janku F, Mcconkey DJ, Hong DS and Kurzrock
R: Autophagy as a target for anticancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin
Oncol. 8:528–539. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|