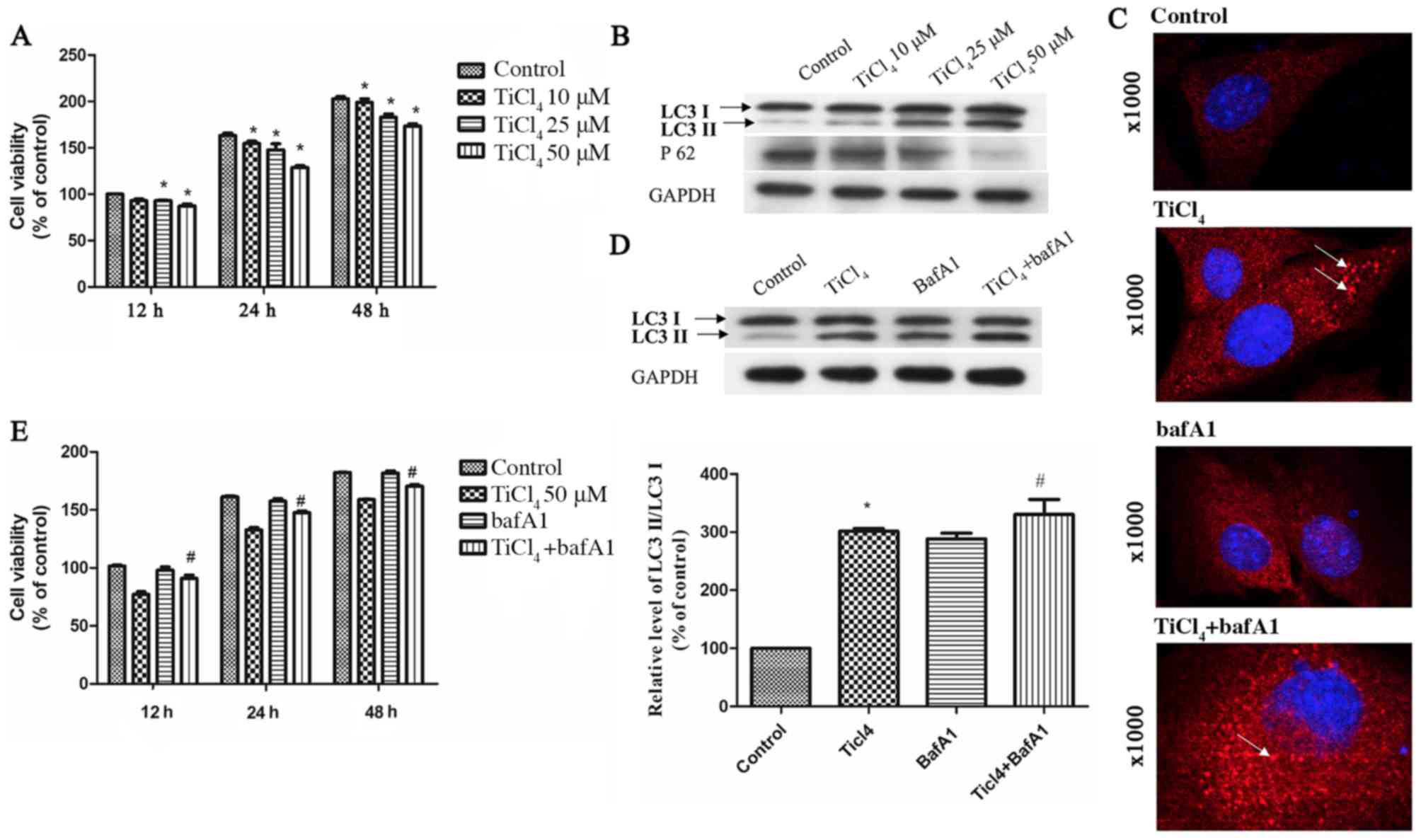
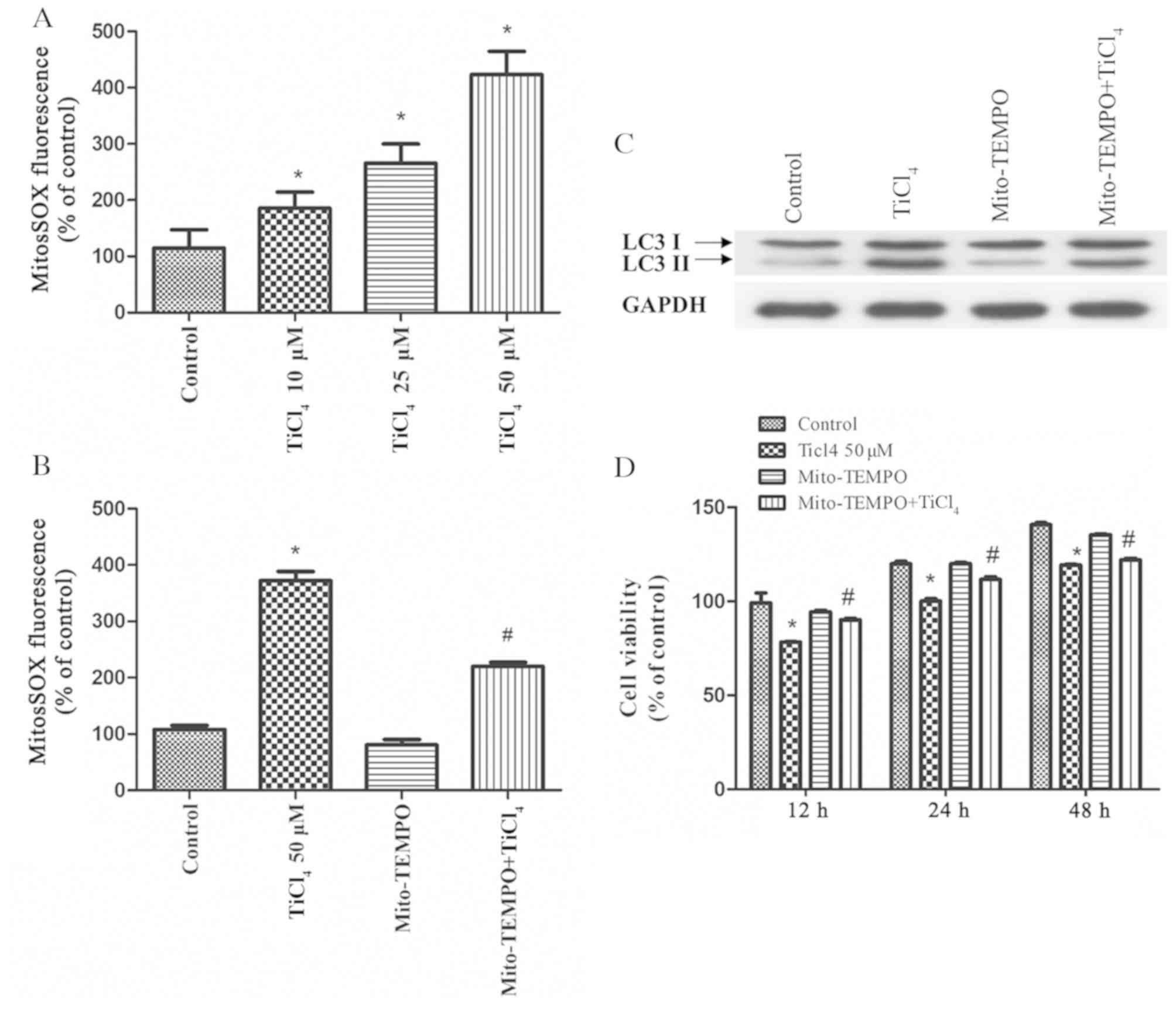
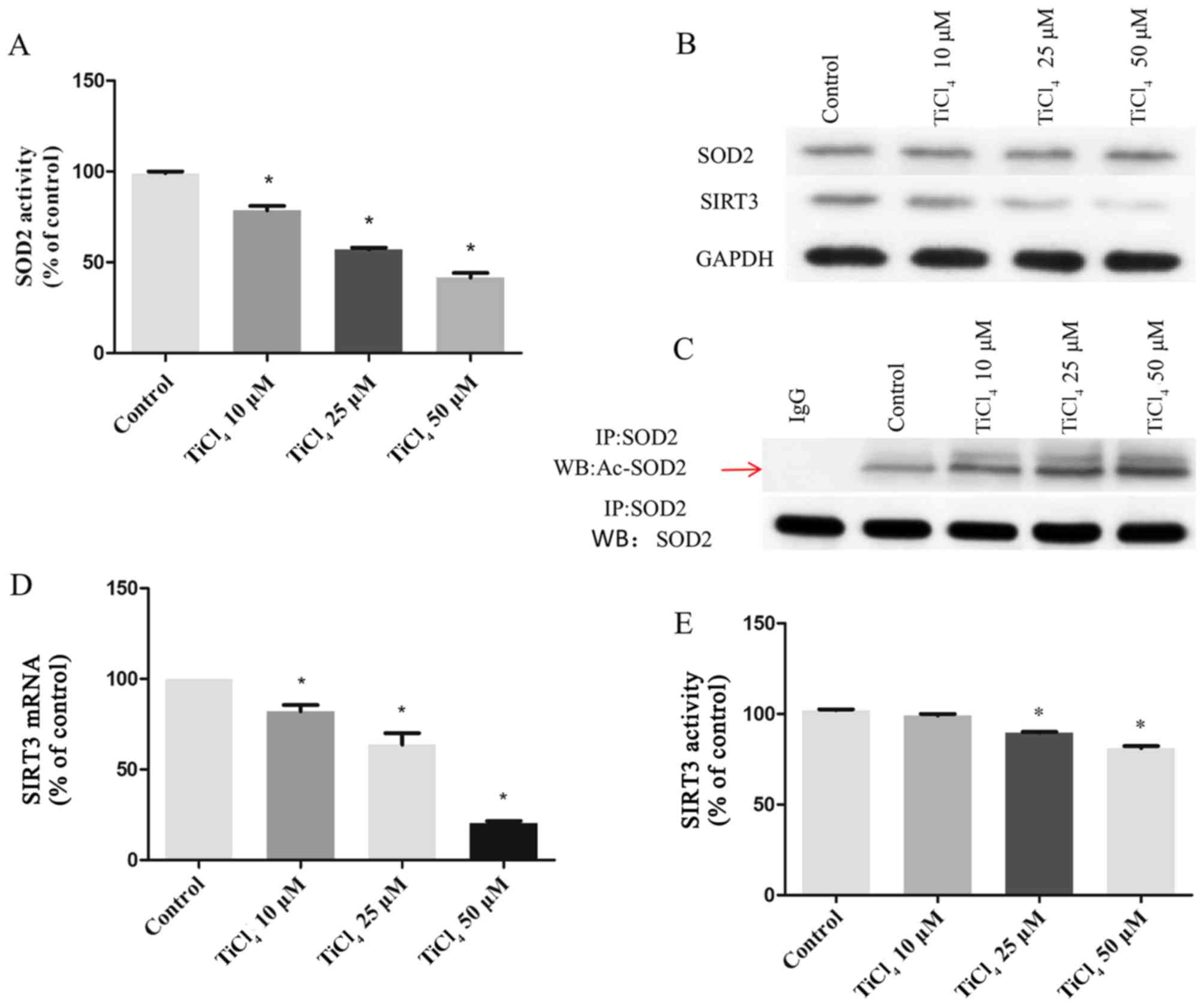
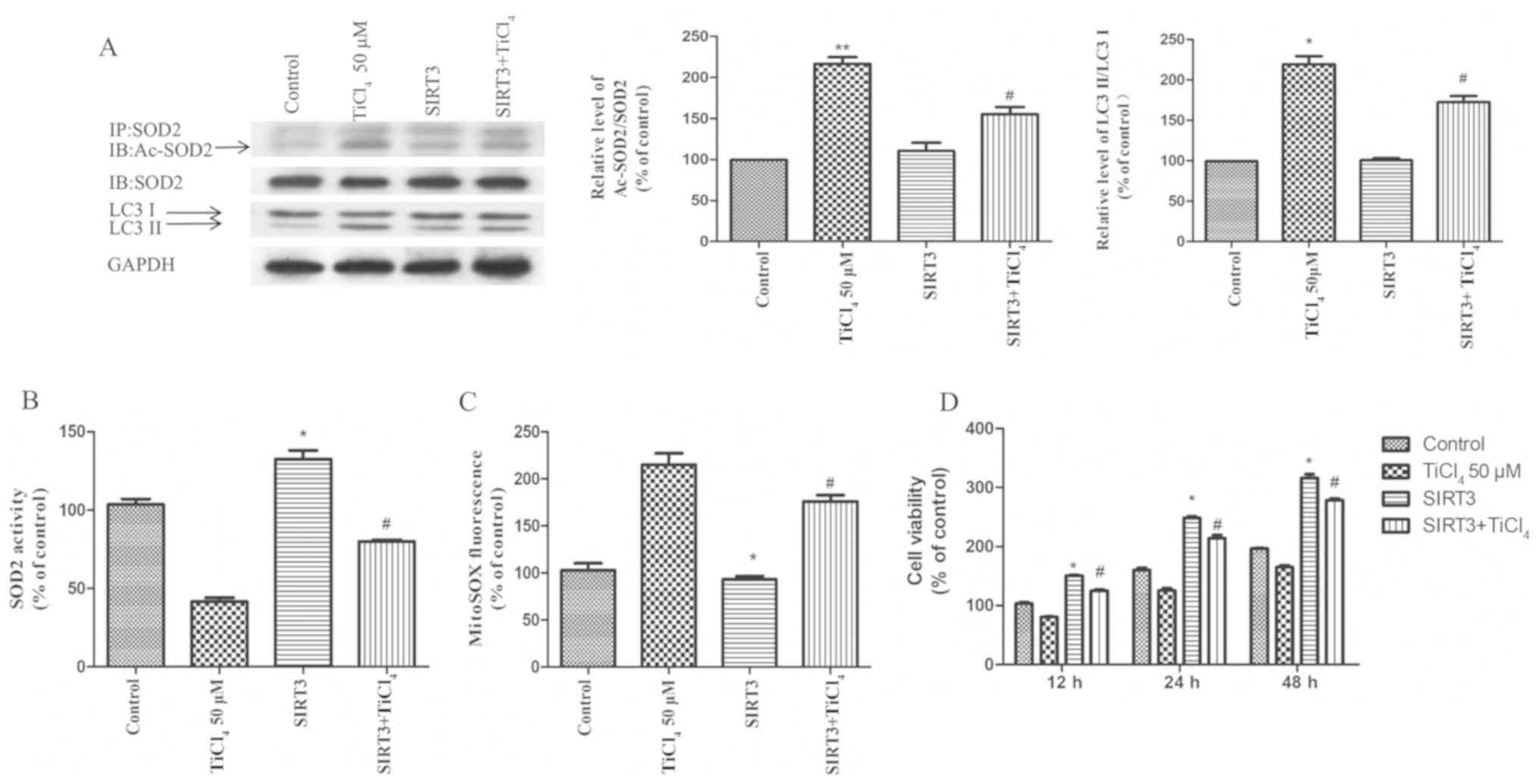
|
1
|
Anselme K: Osteoblast adhesion on
biomaterials. Biomaterials. 21:667–681. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Anselme K: Biomaterials and interface with
bone. Osteoporos Int. 22:2037–2042. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Davies JE: Mechanisms of endosseous
integration. Int J Prosthodont. 11:391–401. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Davies JE: Understanding peri-implant
endosseous healing. J Dent Educ. 67:932–949. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hermann JS, Buser D, Schenk RK,
Schoolfield JD and Cochran DL: Biologic Width around one- and
two-piece titanium implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 12:559–571.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lindhe J and Meyle J; Group D of European
Workshop on Periodontology, : Peri-implant diseases: Consensus
Report of the Sixth European Workshop on Periodontology. J Clin
Periodontol. 35 (Suppl):282–285. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Brånemark PI, Adell R, Albrektsson T,
Lekholm U, Lundkvist S and Rockler B: Osseointegrated titanium
fixtures in the treatment of edentulousness. Biomaterials. 4:25–28.
1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wachi T, Shuto T, Shinohara Y, Matono Y
and Makihira S: Release of titanium ions from an implant surface
and their effect on cytokine production related to alveolar bone
resorption. Toxicology. 327:1–9. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schwarz F, Sahm N, Mihatovic I, Golubovic
V and Becker J: Surgical therapy of advanced ligature-induced
peri-implantitis defects: Cone-beam computed tomographic and
histological analysis. J Clin Periodontol. 38:939–949. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kumazawa R, Watari F, Takashi N, Tanimura
Y, Uo M and Totsuka Y: Effects of Ti ions and particles on
neutrophil function and morphology. Biomaterials. 23:3757–3764.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wennerberg A, Ide-Ektessabi A, Hatkamata
S, Sawase T, Johansson C, Albrektsson T, Martinelli A, Södervall U
and Odelius H: Titanium release from implants prepared with
different surface roughness. Clin Oral Implants Res. 15:505–512.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ellingsen JE, Johansson CB, Wennerberg A
and Holmén A: Improved retention and bone-tolmplant contact with
fluoride-modified titanium implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac
Implants. 19:659–666. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pajarinen J, Kouri VP, Jämsen E, Li TF,
Mandelin J and Konttinen YT: The response of macrophages to
titanium particles is determined by macrophage polarization. Acta
Biomater. 9:9229–9240. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Obando-Pereda GA, Fischer L and
Stach-Machado DR: Titanium and zirconia particle-induced
pro-inflammatory gene expression in cultured macrophages and
osteolysis, inflammatory hyperalgesia and edema in vivo. Life Sci.
97:96–106. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Brettin BT, Grosland NM, Qian F, Southard
KA, Stuntz TD, Morgan TA, Marshall SD and Southard TE: Bicortical
vs monocortical orthodontic skeletal anchorage. Am J Orthod
Dentofacial Orthop. 134:625–635. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bitar D and Parvizi J: Biological response
to prosthetic debris. World J Orthop. 6:172–189. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Grunow M and Schöpp W: [Determination of
the activity of superoxide dismutase in terms of rea substrate
conversion]. Biomed Biochim Acta. 48:185–199. 1989.(In German).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Klionsky DJ, Elazar Z, Seglen PO and
Rubinsztein DC: Does bafilomycin A1 block the fusion of
autophagosomes with lysosomes? Autophagy. 4:849–850. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sena LA and Chandel NS: Physiological
roles of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. Mol Cell.
48:158–167. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lambert AJ and Brand MD: Reactive oxygen
species production by mitochondria. Methods Mol Biol. 554:165–181.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tao R, Vassilopoulos A, Parisiadou L, Yan
Y and Gius D: Regulation of MnSOD enzymatic activity by Sirt3
connects the mitochondrial acetylome signaling networks to aging
and carcinogenesis. Antioxid Redox Signal. 20:1646–1654. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen Y, Zhang J, Lin Y, Lei Q, Guan KL,
Zhao S and Xiong Y: Tumour suppressor SIRT3 deacetylates and
activates manganese superoxide dismutase to scavenge ROS. EMBO Rep.
12:534–541. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tao R, Coleman MC, Pennington JD, Ozden O,
Park SH, Jiang H, Kim HS, Flynn CR, Hill S, Hayes McDonald W, et
al: Sirt3-mediated deacetylation of evolutionarily conserved lysine
122 regulates MnSOD activity in response to stress. Mol Cell.
40:893–904. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Di Tucci AA, Murru R, Alberti D, Rabault
B, Deplano S and Angelucci E: Correction of anemia in a
transfusion-dependent patient with primary myelofibrosis receiving
iron chelation therapy with deferasirox (Exjade, ICL670). Eur J
Haematol. 78:540–542. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Messa E, Cilloni D, Messa F, Arruga F,
Roetto A and Saglio G: Deferasirox treatment improved the
hemoglobin level and decreased transfusion requirements in four
patients with the myelodysplastic syndrome and primary
myelofibrosis. Acta Haematol. 120:70–74. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Angelucci E, Santini V, Di Tucci AA,
Quaresmini G, Finelli C, Volpe A, Quarta G, Rivellini F, Sanpaolo
G, Cilloni D, et al: Deferasirox for transfusion-dependent patients
with myelodysplastic syndromes: Safety, efficacy, and beyond
(GIMEMA MDS0306 Trial). Eur J Haematol. 92:527–536. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jacobs JJ, Gilbert JL and Urban RM:
Corrosion of metal orthopaedic implants. J Bone Joint Surg Am.
80:268–282. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gallo J, Kamínek P, Tichá V, Riháková P
and Ditmar R: Particle disease. A comprehensive theory of
periprosthetic osteolysis: A review. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ
Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 146:21–28. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nakagawa M, Matsuya S and Udoh K: Effects
of fluoride and dissolved oxygen concentrations on the corrosion
behavior of pure titanium and titanium alloys. Dent Mater J.
21:83–92. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Matono Y, Nakagawa M, Matsuya S, Ishikawa
K and Terada Y: Corrosion behavior of pure titanium and titanium
alloys in various concentrations of Acidulated Phosphate Fluoride
(APF) solutions. Dent Mater J. 25:104–112. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Roehlecke C, Witt M, Kasper M, Schulze E,
Wolf C, Hofer A and Funk RW: Synergistic effect of titanium alloy
and collagen type I on cell adhesion, proliferation and
differentiation of osteoblast-like cells. Cells Tissues Organs.
168:178–187. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Terheyden H, Lang NP, Bierbaum S and
Stadlinger B: Osseointegration--communication of cells. Clin Oral
Implants Res. 23:1127–1135. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rajendrakumar SK, Revuri V, Samidurai M,
Mohapatra A, Lee JH, Ganesan P, Jo J, Lee YK and Park IK:
Peroxidase-mimicking nanoassembly mitigates
lipopolysaccharide-induced endotoxemia and cognitive damage in the
brain by impeding inflammatory signaling in macrophages. Nano Lett.
18:6417–6426. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Landgraeber S, Jäger M, Jacobs JJ and
Hallab NJ: The pathology of orthopedic implant failure is mediated
by innate immune system cytokines. Mediators Inflamm.
2014:1851502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li X, Ma XY, Feng YF, Ma ZS, Wang J, Ma
TC, Qi W, Lei W and Wang L: Osseointegration of chitosan coated
porous titanium alloy implant by reactive oxygen species-mediated
activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway under diabetic conditions.
Biomaterials. 36:44–54. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Feng YF, Wang L, Zhang Y, Li X, Ma ZS, Zou
JW, Lei W and Zhang ZY: Effect of reactive oxygen species
overproduction on osteogenesis of porous titanium implant in the
present of diabetes mellitus. Biomaterials. 34:2234–2243. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang L, Zhao X, Wei BY, Liu Y, Ma XY, Wang
J, Cao PC, Zhang Y, Yan YB, Lei W, et al: Insulin improves
osteogenesis of titanium implants under diabetic conditions by
inhibiting reactive oxygen species overproduction via the PI3K-Akt
pathway. Biochimie. 108:85–93. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdelmohsen K, Abe A, Abedin
MDJ, Abeliovich H, Arozena AA, Adachi H, Adams CM, Adams PD, Adeli
K, et al: Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for
monitoring autophagy (3rd edition). Autophagy. 12:1–222. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu Y and Levine B: Autosis and autophagic
cell death: The dark side of autophagy. Cell Death Differ.
22:367–376. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Essick EE and Sam F: Oxidative stress and
autophagy in cardiac disease, neurological disorders, aging and
cancer. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 3:168–177. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang T, Li Y, Park KA, Byun HS, Won M,
Jeon J, Lee Y, Seok JH, Choi SW, Lee SH, et al: Cucurbitacin
induces autophagy through mitochondrial ROS production which
counteracts to limit caspase-dependent apoptosis. Autophagy.
8:559–576. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Shen W, Tian C, Chen H, Yang Y, Zhu D, Gao
P and Liu J: Oxidative stress mediates chemerin-induced autophagy
in endothelial cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 55:73–82. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Dai DF and Rabinovitch P: Mitochondrial
oxidative stress mediates induction of autophagy and hypertrophy in
angiotensin-II treated mouse hearts. Autophagy. 7:917–918. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kim Y, Kim YS, Kim DE, Lee JS, Song JH,
Kim HG, Cho DH, Jeong SY, Jin DH, Jang SJ, et al: BIX-01294 induces
autophagy-associated cell death via EHMT2/G9a dysfunction and
intracellular reactive oxygen species production. Autophagy.
9:2126–2139. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Liang Q, Benavides GA, Vassilopoulos A,
Gius D, Darley-Usmar V and Zhang J: Bioenergetic and autophagic
control by Sirt3 in response to nutrient deprivation in mouse
embryonic fibroblasts. Biochem J. 454:249–257. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Pi H, Xu S, Reiter RJ, Guo P, Zhang L, Li
Y, Li M, Cao Z, Tian L, Xie J, et al: SIRT3-SOD2-mROS-dependent
autophagy in cadmium-induced hepatotoxicity and salvage by
melatonin. Autophagy. 11:1037–1051. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lee J, Giordano S and Zhang J: Autophagy,
mitochondria and oxidative stress: Cross-talk and redox signalling.
Biochem J. 441:523–540. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zorov DB, Juhaszova M and Sollott SJ:
Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and ROS-induced ROS
release. Physiol Rev. 94:909–950. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhu Y, Park SH, Ozden O, Kim HS, Jiang H,
Vassilopoulos A, Spitz DR and Gius D: Exploring the electrostatic
repulsion model in the role of Sirt3 in directing MnSOD acetylation
status and enzymatic activity. Free Radic Biol Med. 53:828–833.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zeng L, Yang Y, Hu Y, Sun Y, Du Z, Xie Z,
Zhou T and Kong W: Age-related decrease in the mitochondrial
sirtuin deacetylase Sirt3 expression associated with ROS
accumulation in the auditory cortex of the mimetic aging rat model.
PLoS One. 9:e880192014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Li M, Chiu JF, Mossman BT and Fukagawa NK:
Down-regulation of manganese-superoxide dismutase through
phosphorylation of FOXO3a by Akt in explanted vascular smooth
muscle cells from old rats. J Biol Chem. 281:40429–40439. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Niska K, Pyszka K, Tukaj C, Wozniak M,
Radomski MW and Inkielewicz-Stepniak I: Titanium dioxide
nanoparticles enhance production of superoxide anion and alter the
antioxidant system in human osteoblast cells. Int J Nanomedicine.
10:1095–1107. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Li Y, Wang W, Wu Q, Li Y, Tang M, Ye B and
Wang D: Molecular control of TiO2-NPs toxicity formation
at predicted environmental relevant concentrations by Mn-SODs
proteins. PLoS One. 7:e446882012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Bánréti A, Sass M and Graba Y: The
emerging role of acetylation in the regulation of autophagy.
Autophagy. 9:819–829. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Papanicolaou KN, O'Rourke B and Foster DB:
Metabolism leaves its mark on the powerhouse: Recent progress in
post-translational modifications of lysine in mitochondria. Front
Physiol. 5:3012014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Hebert AS, Dittenhafer-Reed KE, Yu W,
Bailey DJ, Selen ES, Boersma MD, Carson JJ, Tonelli M, Balloon AJ,
Higbee AJ, et al: Calorie restriction and SIRT3 trigger global
reprogramming of the mitochondrial protein acetylome. Mol Cell.
49:186–199. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Giralt A and Villarroya F: SIRT3, a
pivotal actor in mitochondrial functions: Metabolism, cell death
and aging. Biochem J. 444:1–10. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Kim H, Lee YD, Kim HJ, Lee ZH and Kim HH:
SOD2 and Sirt3 Control Osteoclastogenesis by Regulating
Mitochondrial ROS. J Bone Miner Res. 32:397–406. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|