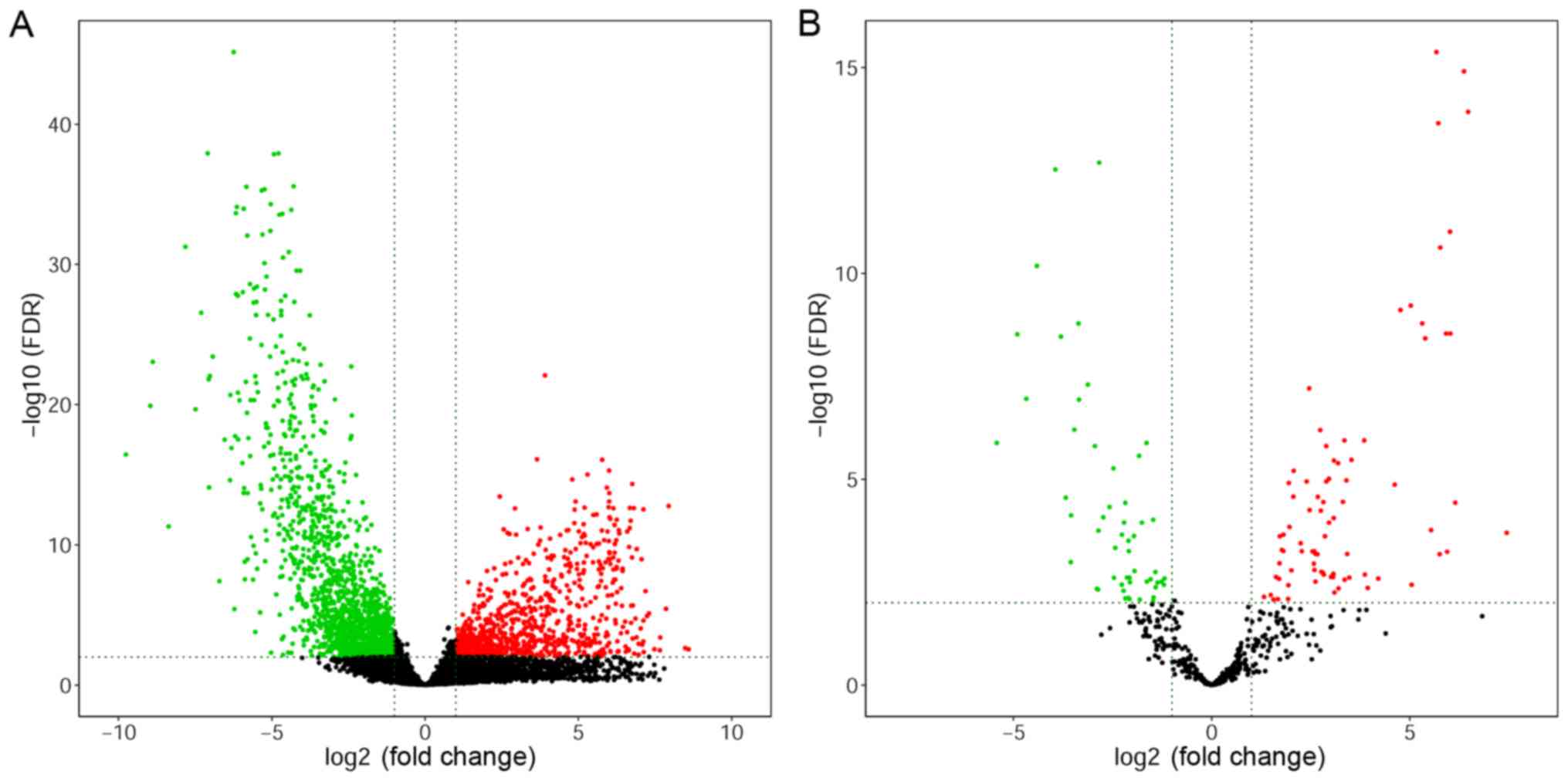
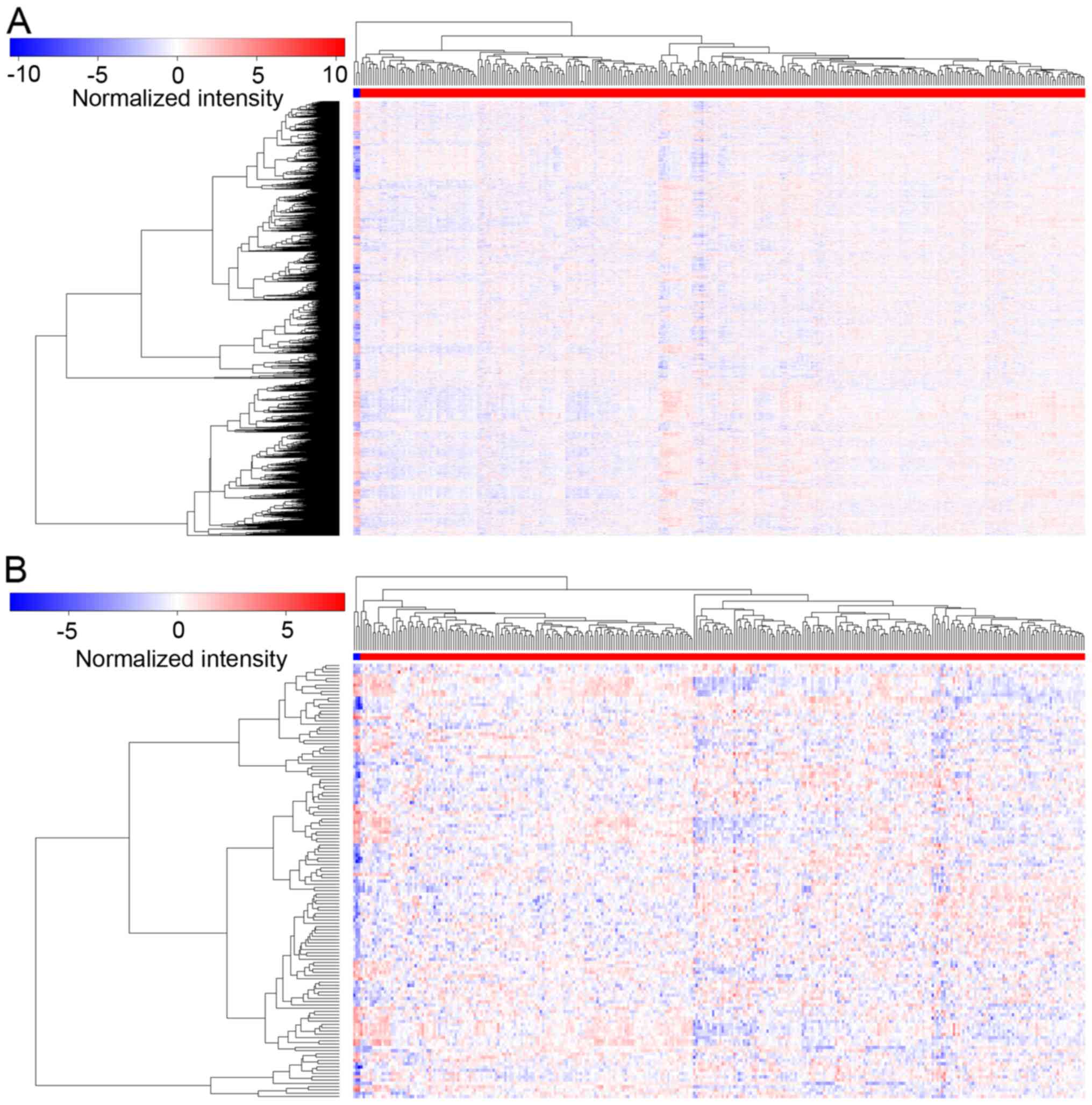
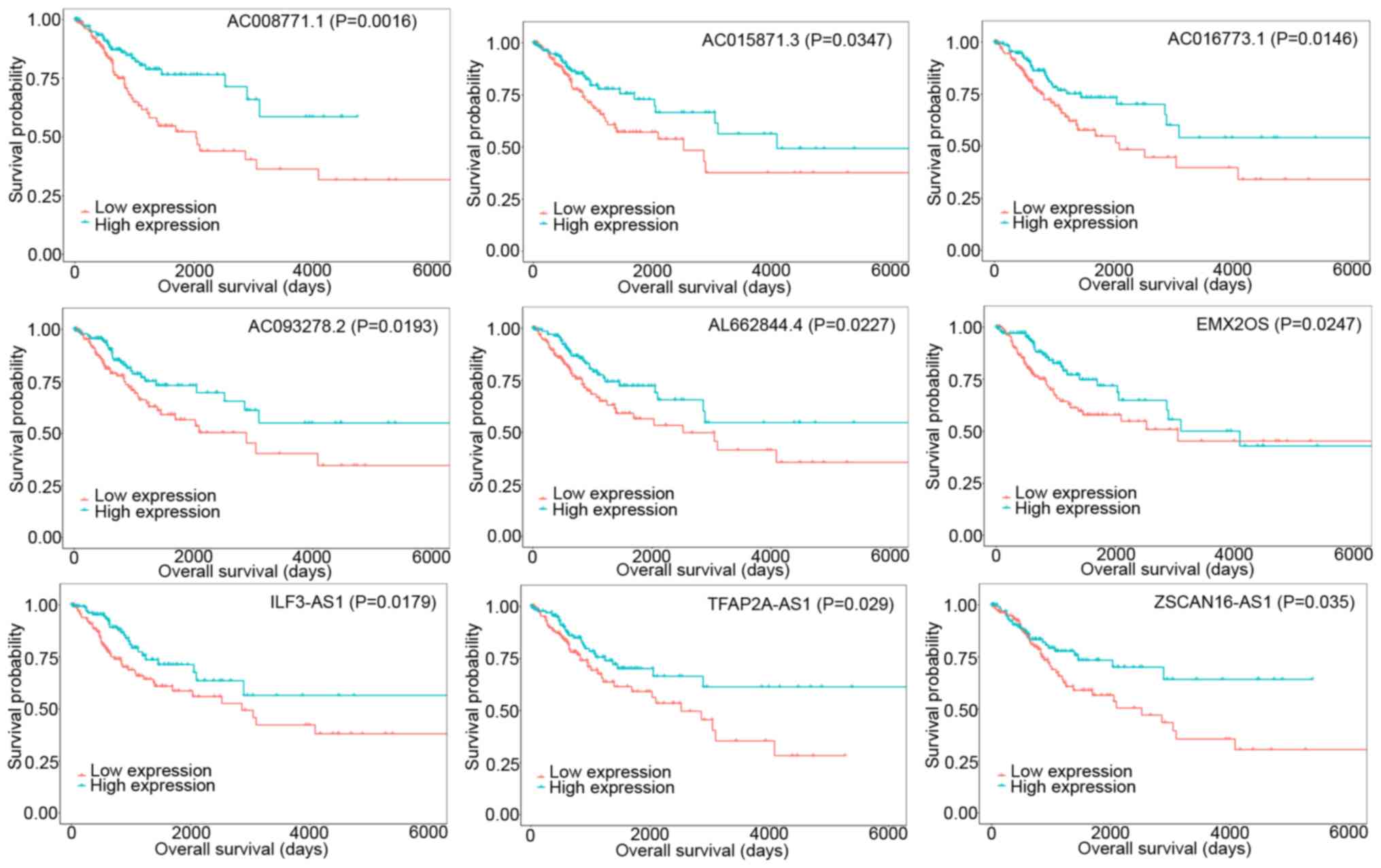
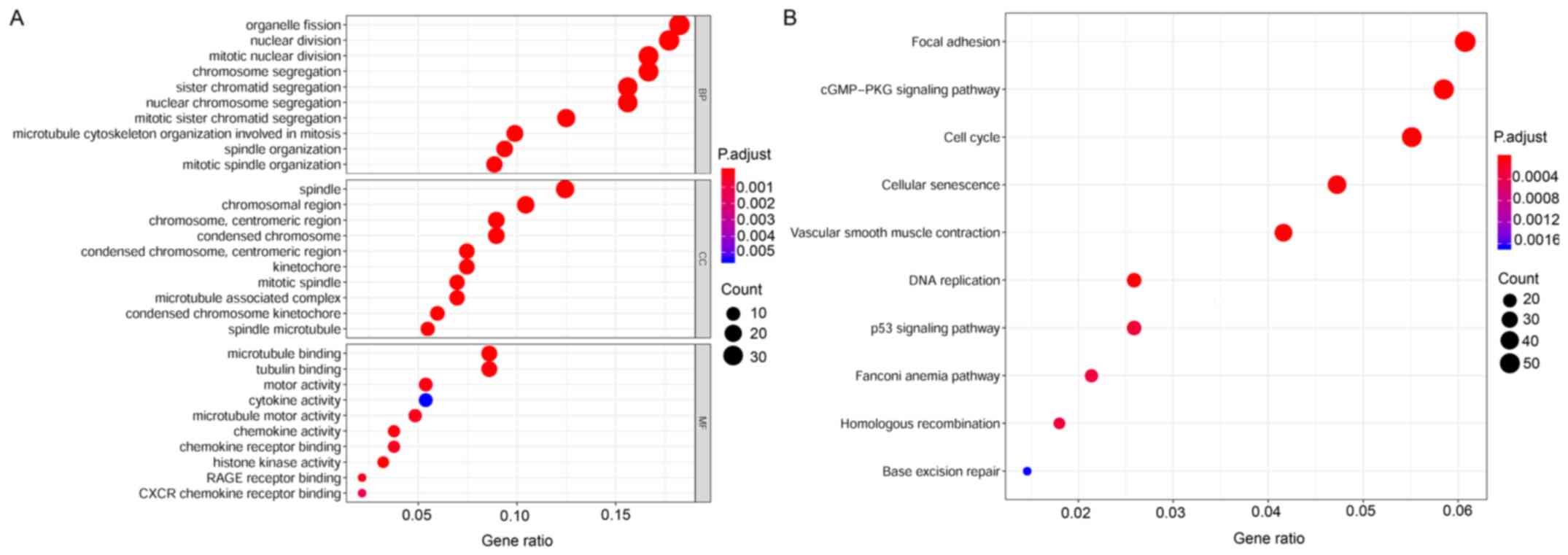
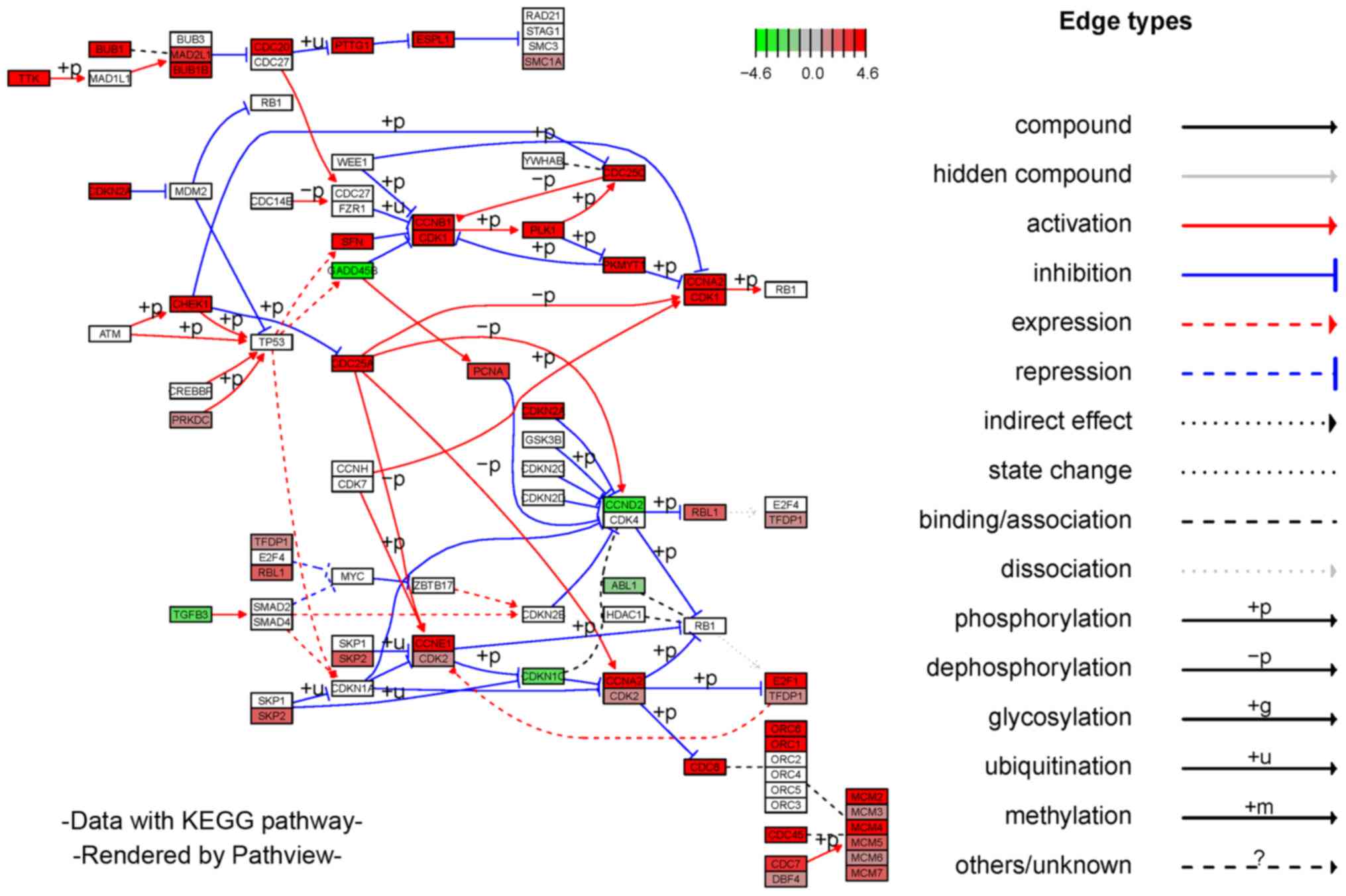
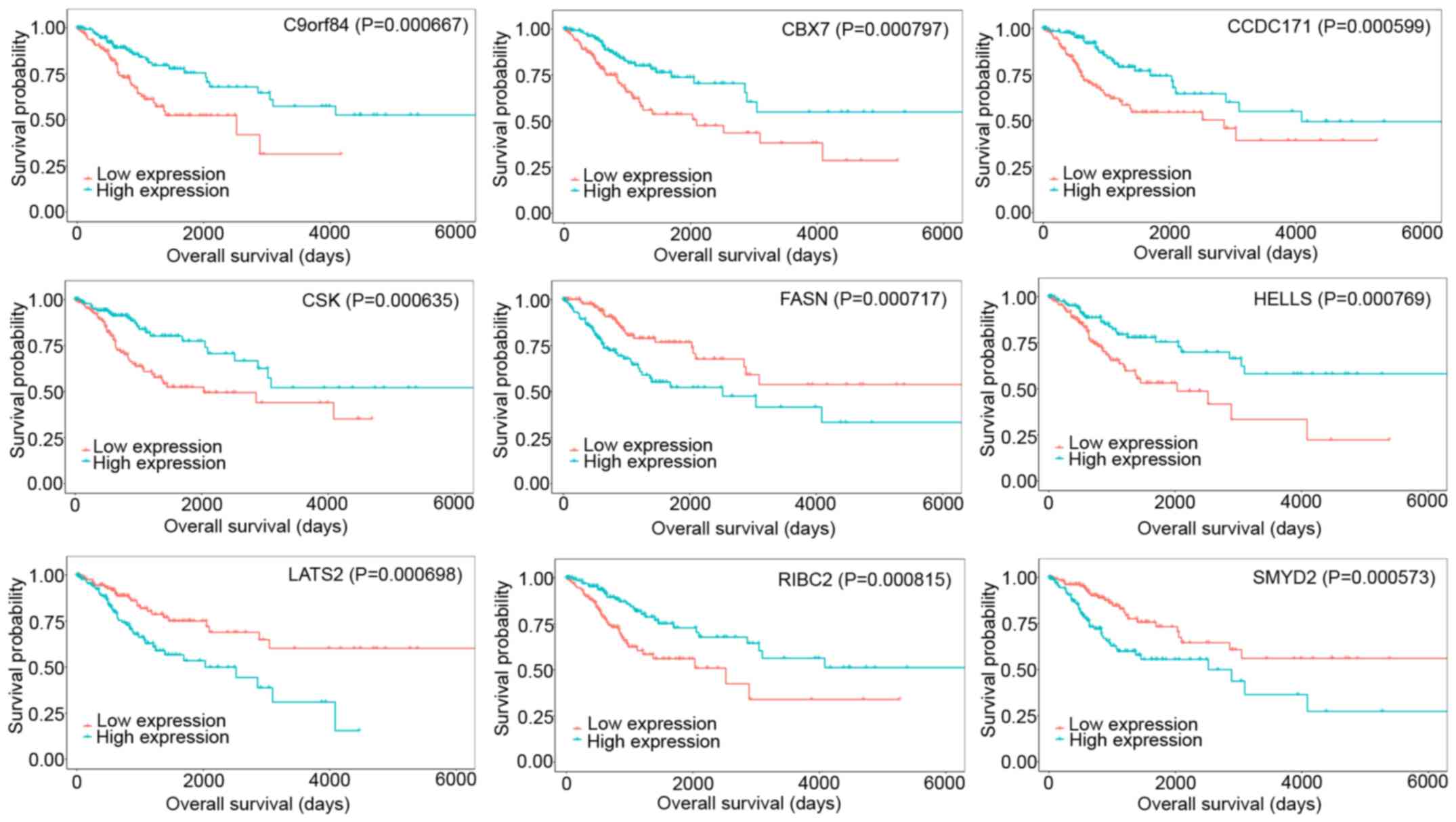
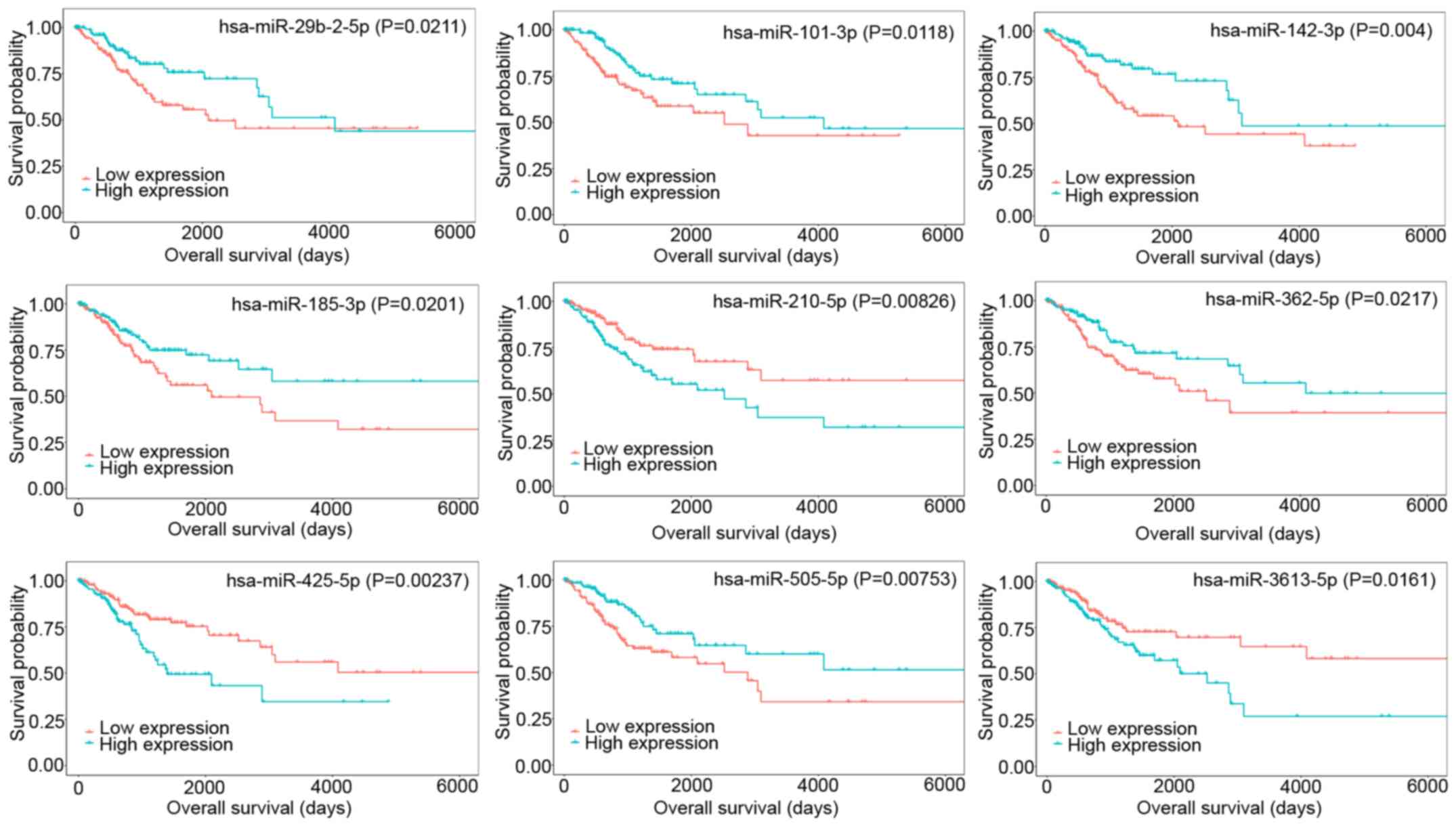
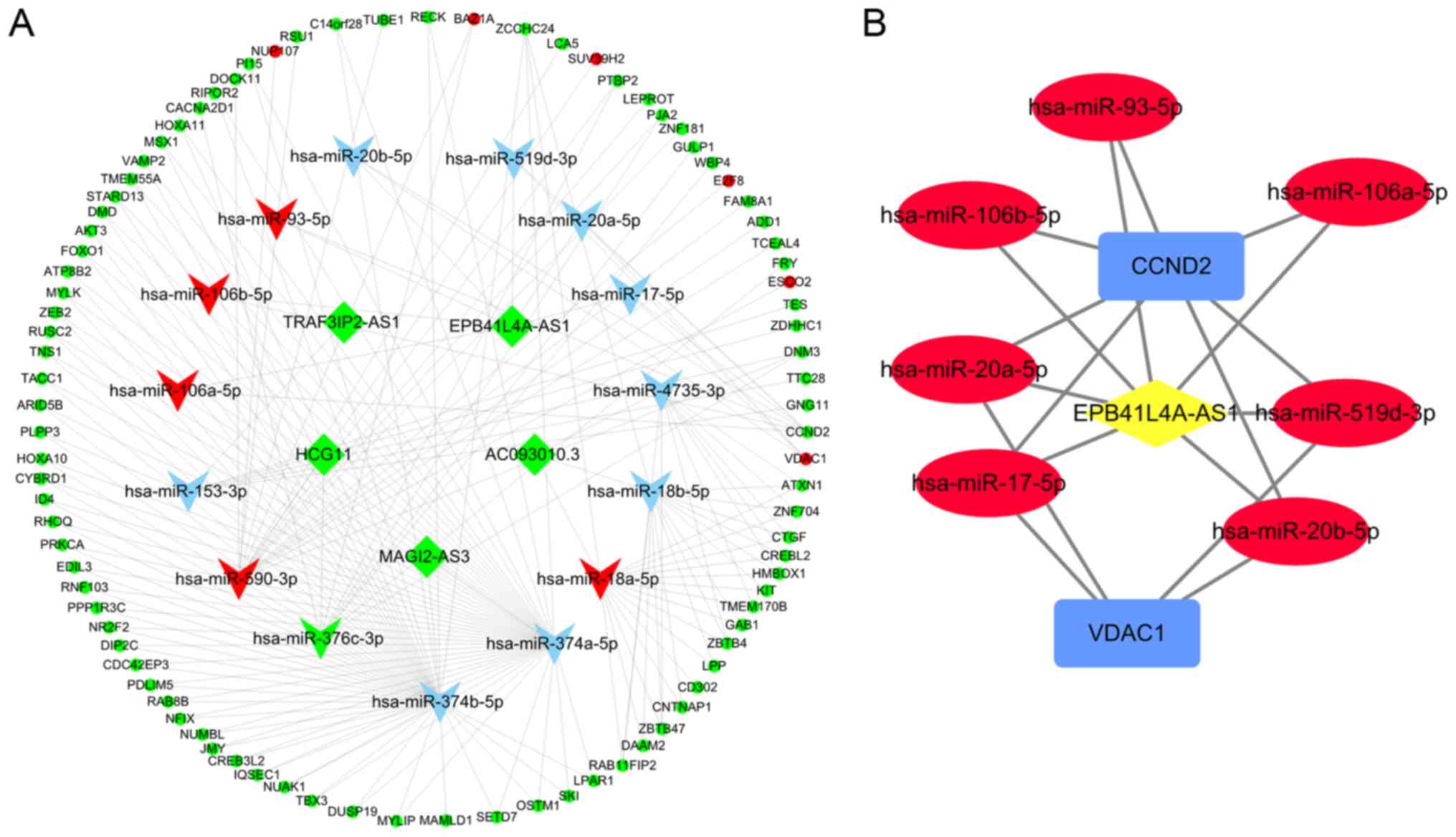
|
1
|
Waggoner SE: Cervical cancer. Lancet.
361:2217–2225. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liu S, Zhang P, Chen Z, Liu M, Li X and
Tang H: MicroRNA-7 downregulates XIAP expression to suppress cell
growth and promote apoptosis in cervical cancer cells. FEBS Lett.
587:2247–2253. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang H, Zhao Y, Chen M and Cui J:
Identification of novel long non-coding and circular RNAs in human
papillomavirus-mediated cervical cancer. Front Microbiol.
8:17202017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li LJ, Zhao W, Tao SS, Leng RX, Fan YG,
Pan HF and Ye DQ: Competitive endogenous RNA network: Potential
implication for systemic lupus erythematosus. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 21:639–648. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Huarte M: The emerging role of lncRNAs in
cancer. Nat Med. 21:1253–1261. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang R, Xing L, Wang M, Chi H, Zhang L and
Chen J: Comprehensive analysis of differentially expressed profiles
of lncRNAs/mRNAs and miRNAs with associated ceRNA networks in
triple-negative breast cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 50:473–488.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tomczak K, Czerwińska P and Wiznerowicz M:
The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA): An immeasurable source of
knowledge. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 19((1A)): A68–A77. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y and He QY:
clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among
gene clusters. OMICS. 16:284–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Furió-Tarí P, Tarazona S, Gabaldón T,
Enright AJ and Conesa A: spongeScan: A web for detecting microRNA
binding elements in lncRNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 44((W1)):
W176–80. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li JH, Liu S, Zhou H, Qu LH and Yang JH:
starBase v2.0: Decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA
interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids
Res. 42(D1): D92–D97. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Paci P, Colombo T and Farina L:
Computational analysis identifies a sponge interaction network
between long non-coding RNAs and messenger RNAs in human breast
cancer. BMC Syst Biol. 8:832014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chin CH, Chen SH, Wu HH, Ho CW, Ko MT and
Lin CY: cytoHubba: Identifying hub objects and sub-networks from
complex interactome. BMC Syst Biol. 8 (Suppl 4):S112014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang H, Chen Z, Wang X, Huang Z, He Z and
Chen Y: Long non-coding RNA: A new player in cancer. J Hematol
Oncol. 6:372013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hu W, Alvarez-Dominguez JR and Lodish HF:
Regulation of mammalian cell differentiation by long non-coding
RNAs. EMBO Rep. 13:971–983. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang L, Li P, Yang W, Ruan X, Kiesewetter
K, Zhu J and Cao H: Integrative transcriptome analyses of metabolic
responses in mice define pivotal LncRNA metabolic regulators. Cell
Metab. 24:627–639. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bolha L, Ravnik-Glavač M and Glavač D:
Long noncoding RNAs as biomarkers in cancer. Dis Markers.
2017:72439682017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang J, Yao T, Wang Y, Yu J, Liu Y and
Lin Z: Long noncoding RNA MEG3 is downregulated in cervical cancer
and affects cell proliferation and apoptosis by regulating miR-21.
Cancer Biol Ther. 17:104–113. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rui X, Xu Y, Jiang X, Ye W, Huang Y and
Jiang J: Long non-coding RNA C5orf66-AS1 promotes cell
proliferation in cervical cancer by targeting miR-637/RING1 axis.
Cell Death Dis. 9:11752018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lu G, Li Y, Ma Y, Lu J, Chen Y, Jiang Q,
Qin Q, Zhao L, Huang Q, Luo Z, et al: Long noncoding RNA LINC00511
contributes to breast cancer tumourigenesis and stemness by
inducing the miR-185-3p/E2F1/Nanog axis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
37:2892018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
He T, Zhang L, Kong Y, Huang Y, Zhang Y,
Zhou D, Zhou X, Yan Y, Zhang L, Lu S, et al: Long non-coding RNA
CASC15 is upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and facilitates
hepatocarcinogenesis. Int J Oncol. 51:1722–1730. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yin H, Wang X, Zhang X, Wang Y, Zeng Y,
Xiong Y, Li T, Lin R, Zhou Q, Ling H, et al: Integrated analysis of
long noncoding RNA associated-competing endogenous RNA as
prognostic biomarkers in clear cell renal carcinoma. Cancer Sci.
109:3336–3349. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Guay C, Kruit JK, Rome S, Menoud V, Mulder
NL, Jurdzinski A, Mancarella F, Sebastiani G, Donda A, Gonzalez BJ,
et al: Lymphocyte-derived exosomal microRNAs promote pancreatic β
cell death and may contribute to type 1 diabetes development. Cell
Metab. 29:348–361.e6. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wüst S, Dröse S, Heidler J, Wittig I,
Klockner I, Franko A, Bonke E, Günther S, Gärtner U, Boettger T, et
al: Metabolic maturation during muscle stem cell differentiation is
achieved by miR-1/133a-mediated inhibition of the Dlk1-Dio3 mega
gene cluster. Cell Metab. 27:1026–1039.e6. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lee H, Li C, Zhang Y, Zhang D, Otterbein
LE and Jin Y: Caveolin-1 selectively regulates microRNA sorting
into microvesicles after noxious stimuli. J Exp Med. 216:2202–2220.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mehta A, Mann M, Zhao JL, Marinov GK,
Majumdar D, Garcia-Flores Y, Du X, Erikci E, Chowdhury K and
Baltimore D: The microRNA-212/132 cluster regulates B cell
development by targeting Sox4. J Exp Med. 212:1679–1692. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Singh PB, Pua HH, Happ HC, Schneider C,
von Moltke J, Locksley RM, Baumjohann D and Ansel KM: MicroRNA
regulation of type 2 innate lymphoid cell homeostasis and function
in allergic inflammation. J Exp Med. 214:3627–3643. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Giza DE, Vasilescu C and Calin GA:
MicroRNAs and ceRNAs: Therapeutic implications of RNA networks.
Expert Opin Biol Ther. 14:1285–1293. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pardini B, De Maria D, Francavilla A, Di
Gaetano C, Ronco G and Naccarati A: MicroRNAs as markers of
progression in cervical cancer: A systematic review. BMC Cancer.
18:6962018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen S, Wang Y, Su Y, Zhang L, Zhang M, Li
X, Wang J and Zhang X: miR-205-5p/PTK7 axis is involved in the
proliferation, migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells.
Mol Med Rep. 17:6253–6260. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Vilming Elgaaen B, Olstad OK, Haug KB,
Brusletto B, Sandvik L, Staff AC, Gautvik KM and Davidson B: Global
miRNA expression analysis of serous and clear cell ovarian
carcinomas identifies differentially expressed miRNAs including
miR-200c-3p as a prognostic marker. BMC Cancer. 14:802014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Qu K, Zhang X, Lin T, Liu T, Wang Z, Liu
S, Zhou L, Wei J, Chang H, Li K, et al: Circulating miRNA-21-5p as
a diagnostic biomarker for pancreatic cancer: Evidence from
comprehensive miRNA expression profiling analysis and clinical
validation. Sci Rep. 7:16922017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhou X, Wu W, Zeng A, Nie E, Jin X, Yu T,
Zhi T, Jiang K, Wang Y, Zhang J, et al: MicroRNA-141-3p promotes
glioma cell growth and temozolomide resistance by directly
targeting p53. Oncotarget. 8:71080–71094. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hang W, Feng Y, Sang Z, Yang Y, Zhu Y,
Huang Q and Xi X: Downregulation of miR-145-5p in cancer cells and
their derived exosomes may contribute to the development of ovarian
cancer by targeting CT. Int J Mol Med. 43:256–266. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ying G, Wu R, Xia M, Fei X, He QE, Zha C
and Wu F: Identification of eight key miRNAs associated with renal
cell carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Oncol Lett. 16:5847–5855.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang Z, Li Y, Fan L, Zhao Q, Tan B, Li Z
and Zang A: microRNA-425-5p is upregulated in human gastric cancer
and contributes to invasion and metastasis in vitro and
in vivo. Exp Ther Med. 9:1617–1622. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xia L, Wang H, Cai S, Su X, Shen J, Meng
Q, Chen Y, Li L, Yan J, Zhang C, et al: Integrated analysis of a
competing endogenous RNA network revealing a prognostic signature
for cervical cancer. Front Oncol. 8:3682018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Teicher BA and Fricker SP: CXCL12
(SDF-1)/CXCR4 pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 16:2927–2931.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Xiong Y, Huang F, Li X, Chen Z, Feng D,
Jiang H, Chen W and Zhang X: CCL21/CCR7 interaction promotes
cellular migration and invasion via modulation of the MEK/ERK1/2
signaling pathway and correlates with lymphatic metastatic spread
and poor prognosis in urinary bladder cancer. Int J Oncol.
51:75–90. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Prasad SB, Yadav SS, Das M, Govardhan HB,
Pandey LK, Singh S, Pradhan S and Narayan G: Down regulation of
FOXO1 promotes cell proliferation in cervical cancer. J Cancer.
5:655–662. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhao L, Zhang Z, Lou H, Liang J, Yan X, Li
W, Xu Y and Ou R: Exploration of the molecular mechanisms of
cervical cancer based on mRNA expression profiles and predicted
microRNA interactions. Oncol Lett. 15:8965–8972. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L and
Pandolfi PP: A ceRNA hypothesis: The Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA
language? Cell. 146:353–358. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li F, Huang C, Li Q and Wu X: Construction
and comprehensive analysis for dysregulated long non-coding RNA
(lncRNA)-associated competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) network in
gastric cancer. Med Sci Monit. 24:37–49. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Song J, Ye A, Jiang E, Yin X, Chen Z, Bai
G, Zhou Y and Liu J: Reconstruction and analysis of the aberrant
lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA network based on competitive endogenous RNA in
CESC. J Cell Biochem. 119:6665–6673. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ni S, Wang H, Zhu X, Wan C, Xu J, Lu C,
Xiao L, He J, Jiang C, Wang W, et al: CBX7 suppresses cell
proliferation, migration, and invasion through the inhibition of
PTEN/Akt signaling in pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget. 8:8010–8021.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Forzati F, Federico A, Pallante P, Abbate
A, Esposito F, Malapelle U, Sepe R, Palma G, Troncone G, Scarfò M,
et al: CBX7 is a tumor suppressor in mice and humans. J Clin
Invest. 122:612–623. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Xu W, Chen F, Fei X, Yang X and Lu X:
Overexpression of SET and MYND domain-containing protein 2 (SMYD2)
is associated with tumor progression and poor prognosis in patients
with papillary thyroid carcinoma. Med Sci Monit. 24:7357–7365.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zuo SR, Zuo XC, He Y, Fang WJ, Wang CJ,
Zou H, Chen P, Huang LF, Huang LH, Xiang H, et al: Positive
expression of SMYD2 is associated with poor prognosis in patients
with primary hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer. 9:321–330. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Luo SY, Sit KY, Sihoe AD, Suen WS, Au WK,
Tang X, Ma ES, Chan WK, Wistuba II, Minna JD, et al: Aberrant large
tumor suppressor 2 (LATS2) gene expression correlates with EGFR
mutation and survival in lung adenocarcinomas. Lung Cancer.
85:282–292. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhan L, Li J and Wei B: Long non-coding
RNAs in ovarian cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37:1202018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Qi DL, Ohhira T, Fujisaki C, Inoue T, Ohta
T, Osaki M, Ohshiro E, Seko T, Aoki S, Oshimura M, et al:
Identification of PITX1 as a TERT suppressor gene located on human
chromosome 5. Mol Cell Biol. 31:1624–1636. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Sastre-Perona A, Hoang-Phou S, Leitner MC,
Okuniewska M, Meehan S and Schober M: De novo PITX1 expression
controls bi-stable transcriptional circuits to govern self-renewal
and differentiation in squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Stem Cell.
24:390–404.e8. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Osei-Amponsa V, Buckwalter JM, Shuman L,
Zheng Z, Yamashita H, Walter V, Wildermuth T, Ellis-Mohl J, Liu C,
Warrick JI, et al: Hypermethylation of FOXA1 and allelic loss of
PTEN drive squamous differentiation and promote heterogeneity in
bladder cancer. Oncogene. 39:1302–1317. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Son DJ, Kumar S, Takabe W, Kim CW, Ni CW,
Alberts-Grill N, Jang IH, Kim S, Kim W, Won Kang S, et al: The
atypical mechanosensitive microRNA-712 derived from pre-ribosomal
RNA induces endothelial inflammation and atherosclerosis. Nat
Commun. 4:30002013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Washietl S, Kellis M and Garber M:
Evolutionary dynamics and tissue specificity of human long
noncoding RNAs in six mammals. Genome Res. 24:616–628. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Kutter C, Watt S, Stefflova K, Wilson MD,
Goncalves A, Ponting CP, Odom DT and Marques AC: Rapid turnover of
long noncoding RNAs and the evolution of gene expression. PLoS
Genet. 8:e10028412012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|