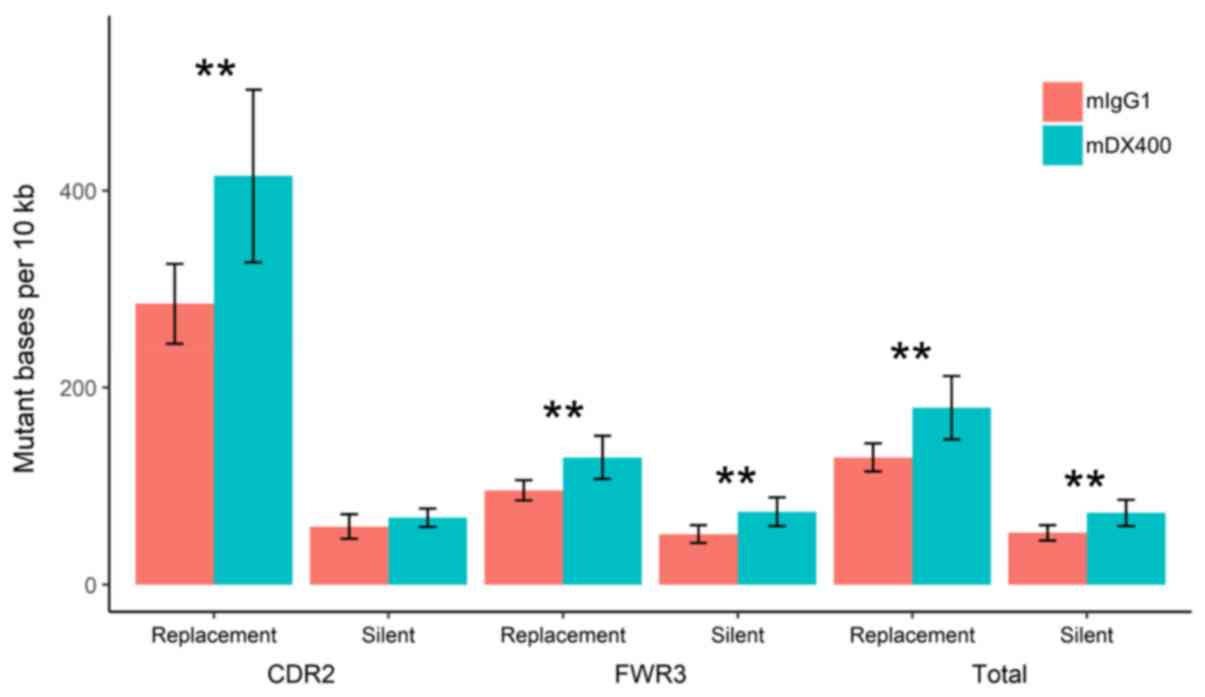
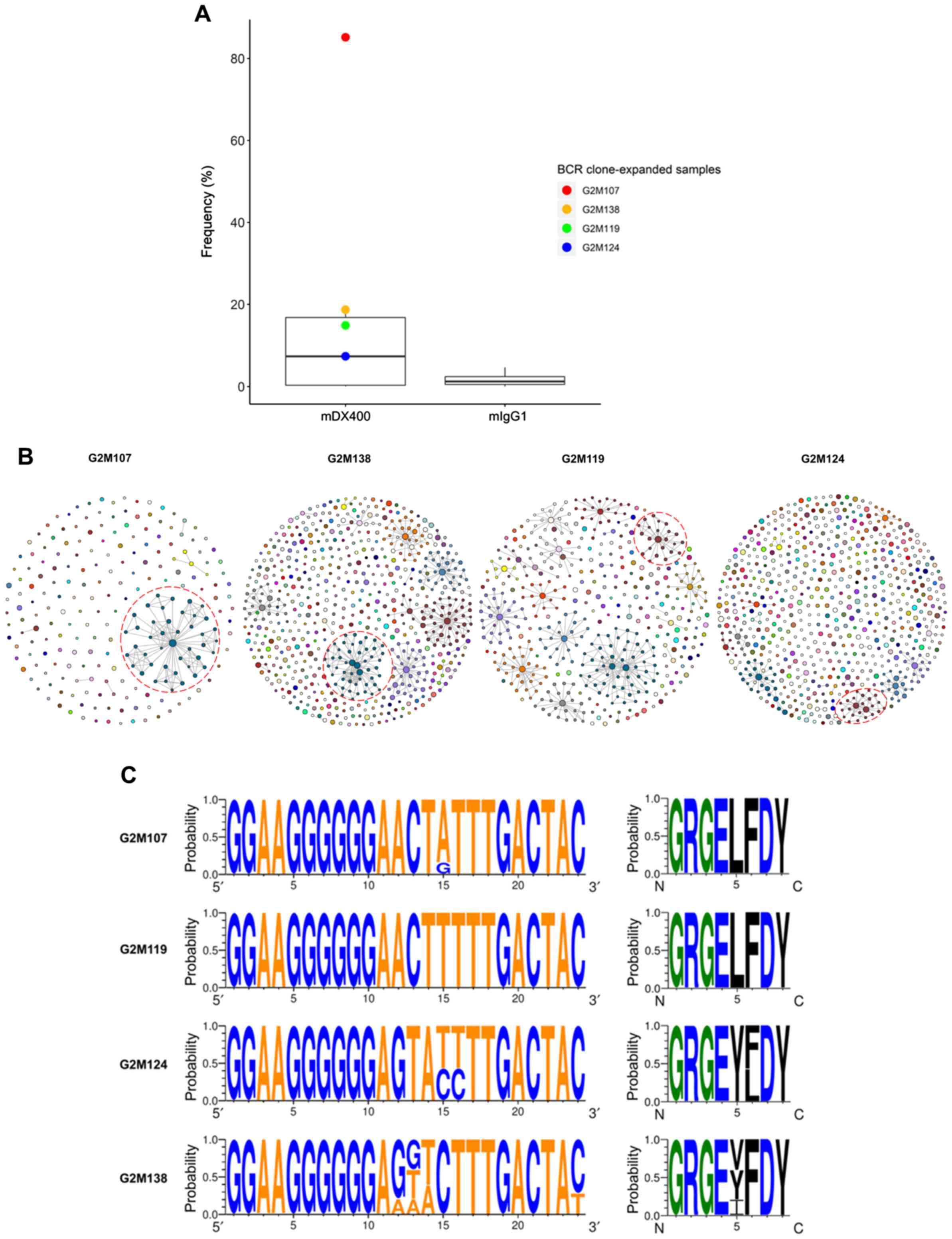
|
1
|
Hamid O, Robert C, Daud A, Hodi FS, Hwu
WJ, Kefford R, Wolchok JD, Hersey P, Joseph R, Weber JS, et al:
Five-year survival outcomes for patients with advanced melanoma
treated with pembrolizumab in KEYNOTE-001. Ann Oncol. 30:582–588.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gandhi L, Rodríguez-Abreu D, Gadgeel S,
Esteban E, Felip E, De Angelis F, Domine M, Clingan P, Hochmair MJ,
Powell SF, et al KEYNOTE-189 Investigators, : Pembrolizumab plus
Chemotherapy in Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N Engl J
Med. 378:2078–2092. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bauml J, Seiwert TY, Pfister DG, Worden F,
Liu SV, Gilbert J, Saba NF, Weiss J, Wirth L, Sukari A, et al:
Pembrolizumab for platinum- and cetuximab-refractory head and neck
cancer: Results from a single-arm, phase II study. J Clin Oncol.
35:1542–1549. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sarfaty M, Hall PS, Chan KKW, Virik K,
Leshno M, Gordon N, Moore A, Neiman V, Rosenbaum E and Goldstein
DA: Cost-effectiveness of Pembrolizumab in Second-line Advanced
Bladder Cancer. Eur Urol. 74:57–62. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Carretero-González A, Lora D, Ghanem I,
Zugazagoitia J, Castellano D, Sepúlveda JM, López-Martin JA,
Paz-Ares L and de Velasco G: Analysis of response rate with ANTI
PD1/PD-L1 monoclonal antibodies in advanced solid tumors: A
meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Oncotarget.
9:8706–8715. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Le DT, Durham JN, Smith KN, Wang H,
Bartlett BR, Aulakh LK, Lu S, Kemberling H, Wilt C, Luber BS, et
al: Mismatch repair deficiency predicts response of solid tumors to
PD-1 blockade. Science. 357:409–413. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yarchoan M, Hopkins A and Jaffee EM: Tumor
Mutational burden and response rate to PD-1 inhibition. N Engl J
Med. 377:2500–2501. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Garon EB, Rizvi NA, Hui R, Leighl N,
Balmanoukian AS, Eder JP, Patnaik A, Aggarwal C, Gubens M, Horn L,
et al KEYNOTE-001 Investigators, : Pembrolizumab for the treatment
of non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 372:2018–2028. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ayers M, Lunceford J, Nebozhyn M, Murphy
E, Loboda A, Kaufman DR, Albright A, Cheng JD, Kang SP, Shankaran
V, et al: IFN-γ-related mRNA profile predicts clinical response to
PD-1 blockade. J Clin Invest. 127:2930–2940. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tumeh PC, Harview CL, Yearley JH, Shintaku
IP, Taylor EJ, Robert L, Chmielowski B, Spasic M, Henry G, Ciobanu
V, et al: PD-1 blockade induces responses by inhibiting adaptive
immune resistance. Nature. 515:568–571. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Roh W, Chen P-L, Reuben A, Spencer CN,
Prieto PA, Miller JP, Gopalakrishnan V, Wang F, Cooper ZA, Reddy
SM, et al: Integrated molecular analysis of tumor biopsies on
sequential CTLA-4 and PD-1 blockade reveals markers of response and
resistance. Sci Transl Med. 9:eaah35602017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Minervina A, Pogorelyy M and Mamedov I:
T-cell receptor and B-cell receptor repertoire profiling in
adaptive immunity. Transpl Int. 32:1111–1123. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Agata Y, Kawasaki A, Nishimura H, Ishida
Y, Tsubata T, Yagita H and Honjo T: Expression of the PD-1 antigen
on the surface of stimulated mouse T and B lymphocytes. Int
Immunol. 8:765–772. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Thibult ML, Mamessier E, Gertner-Dardenne
J, Pastor S, Just-Landi S, Xerri L, Chetaille B and Olive D: PD-1
is a novel regulator of human B-cell activation. Int Immunol.
25:129–137. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hollern DP, Xu N, Thennavan A, Glodowski
C, Garcia-Recio S, Mott KR, He X, Garay JP, Carey-Ewend K, Marron
D, et al: B cells and T follicular helper cells mediate response to
checkpoint inhibitors in high mutation burden mouse models of
breast cancer. Cell. 179:1191–1206.e21. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Selitsky SR, Mose LE, Smith CC, Chai S,
Hoadley KA, Dittmer DP, Moschos SJ, Parker JS and Vincent BG:
Prognostic value of B cells in cutaneous melanoma. Genome Med.
11:362019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Helmink BA, Reddy SM, Gao J, Zhang S,
Basar R, Thakur R, Yizhak K, Sade-Feldman M, Blando J, Han G, et
al: B cells and tertiary lymphoid structures promote immunotherapy
response. Nature. 577:549–555. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Olson B, Li Y, Lin Y, Liu ET and Patnaik
A: Mouse Models for cancer immunotherapy research. Cancer Discov.
8:1358–1365. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hossain DMS, Javaid S, Cai M, Zhang C,
Sawant A, Hinton M, Sathe M, Grein J, Blumenschein W, Pinheiro EM,
et al: Dinaciclib induces immunogenic cell death and enhances
anti-PD1-mediated tumor suppression. J Clin Invest. 128:644–654.
2018. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ngiow SF, Young A, Jacquelot N, Yamazaki
T, Enot D, Zitvogel L and Smyth MJ: A threshold level of intratumor
CD8+ T-cell PD1 expression dictates therapeutic response to
anti-PD1. Cancer Res. 75:3800–3811. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Homet Moreno B, Zaretsky JM, Garcia-Diaz
A, Tsoi J, Parisi G, Robert L, Meeth K, Ndoye A, Bosenberg M,
Weeraratna AT, et al: Response to Programmed cell death-1 blockade
in a murine melanoma syngeneic model requires costimulation, CD4,
and CD8 T Cells. Cancer Immunol Res. 4:845–857. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Grasselly C, Denis M, Bourguignon A, Talhi
N, Mathe D, Tourette A, Serre L, Jordheim LP, Matera EL and
Dumontet C: The Antitumor activity of combinations of cytotoxic
chemotherapy and immune checkpoint inhibitors is model-dependent.
Front Immunol. 9:21002018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Efremova M, Rieder D, Klepsch V,
Charoentong P, Finotello F, Hackl H, Hermann-Kleiter N, Löwer M,
Baier G, Krogsdam A, et al: Targeting immune checkpoints
potentiates immunoediting and changes the dynamics of tumor
evolution. Nat Commun. 9:322018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals, . Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. (8th).
National Academies Press. (Washington, DC). 2011.
|
|
25
|
Masella AP, Bartram AK, Truszkowski JM,
Brown DG and Neufeld JD: PANDAseq: Paired-end assembler for
illumina sequences. BMC Bioinformatics. 13:312012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Giudicelli V, Chaume D and Lefranc MP:
IMGT/GENE-DB: A comprehensive database for human and mouse
immunoglobulin and T cell receptor genes. Nucleic Acids Res.
33:D256–D261. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ye J, Ma N, Madden TL and Ostell JM:
IgBLAST: An immunoglobulin variable domain sequence analysis tool.
Nucleic Acids Res. 41((W1)): W34–40. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gupta NT, Vander Heiden JA, Uduman M,
Gadala-Maria D, Yaari G and Kleinstein SH: Change-O: A toolkit for
analyzing large-scale B cell immunoglobulin repertoire sequencing
data. Bioinformatics. 31:3356–3358. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hill MO: Diversity and Evenness: A
unifying notation and its consequences. Ecology. 54:427–432. 1973.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Shugay M, Bagaev DV, Zvyagin IV, Vroomans
RM, Crawford JC, Dolton G, Komech EA, Sycheva AL, Koneva AE, Egorov
ES, et al: VDJdb: A curated database of T-cell receptor sequences
with known antigen specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 46(D1):
D419–D427. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tickotsky N, Sagiv T, Prilusky J, Shifrut
E and Friedman N: McPAS-TCR: A manually curated catalogue of
pathology-associated T cell receptor sequences. Bioinformatics.
33:2924–2929. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gros A, Robbins PF, Yao X, Li YF, Turcotte
S, Tran E, Wunderlich JR, Mixon A, Farid S, Dudley ME, et al: PD-1
identifies the patient-specific CD8+ tumor-reactive
repertoire infiltrating human tumors. J Clin Invest. 124:2246–2259.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pasetto A, Gros A, Robbins PF, Deniger DC,
Prickett TD, Matus-Nicodemos R, Douek DC, Howie B, Robins H,
Parkhurst MR, et al: Tumor- and Neoantigen-reactive T-cell
receptors can be identified based on their frequency in fresh
tumor. Cancer Immunol Res. 4:734–743. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hosoi A, Takeda K, Nagaoka K, Iino T,
Matsushita H, Ueha S, Aoki S, Matsushima K, Kubo M, Morikawa T, et
al: Increased diversity with reduced “diversity evenness” of tumor
infiltrating T-cells for the successful cancer immunotherapy. Sci
Rep. 8:10582018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lehmann-Horn K, Wang SZ, Sagan SA, Zamvil
SS and von Büdingen HC: B cell repertoire expansion occurs in
meningeal ectopic lymphoid tissue. JCI Insight. 1:e872342016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Katoh H, Komura D, Konishi H, Suzuki R,
Yamamoto A, Kakiuchi M, Sato R, Ushiku T, Yamamoto S, Tatsuno K, et
al: Immunogenetic profiling for gastric cancers identifies sulfated
glycosaminoglycans as major and functional b cell antigens in human
malignancies. Cell Rep. 20:1073–1087. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
DeFalco J, Harbell M, Manning-Bog A, Baia
G, Scholz A, Millare B, Sumi M, Zhang D, Chu F, Dowd C, et al:
Non-progressing cancer patients have persistent B cell responses
expressing shared antibody paratopes that target public tumor
antigens. Clin Immunol. 187:37–45. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Probst P, Stringhini M and Neri D:
Immunotherapy of CT26 murine tumors is characterized by an
oligoclonal response against the AH1 tumor rejection antigen.
bioRxiv. doi.org/10.1101/789784.
|
|
39
|
Rock EP, Sibbald PR, Davis MM and Chien
YH: CDR3 length in antigen-specific immune receptors. J Exp Med.
179:323–328. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
John LB, Devaud C, Duong CP, Yong CS,
Beavis PA, Haynes NM, Chow MT, Smyth MJ, Kershaw MH and Darcy PK:
Anti-PD-1 antibody therapy potently enhances the eradication of
established tumors by gene-modified T cells. Clin Cancer Res.
19:5636–5646. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chung V, Kos FJ, Hardwick N, Yuan Y, Chao
J, Li D, Waisman J, Li M, Zurcher K, Frankel P, et al: Evaluation
of safety and efficacy of p53MVA vaccine combined with
pembrolizumab in patients with advanced solid cancers. Clin Transl
Oncol. 21:363–372. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|