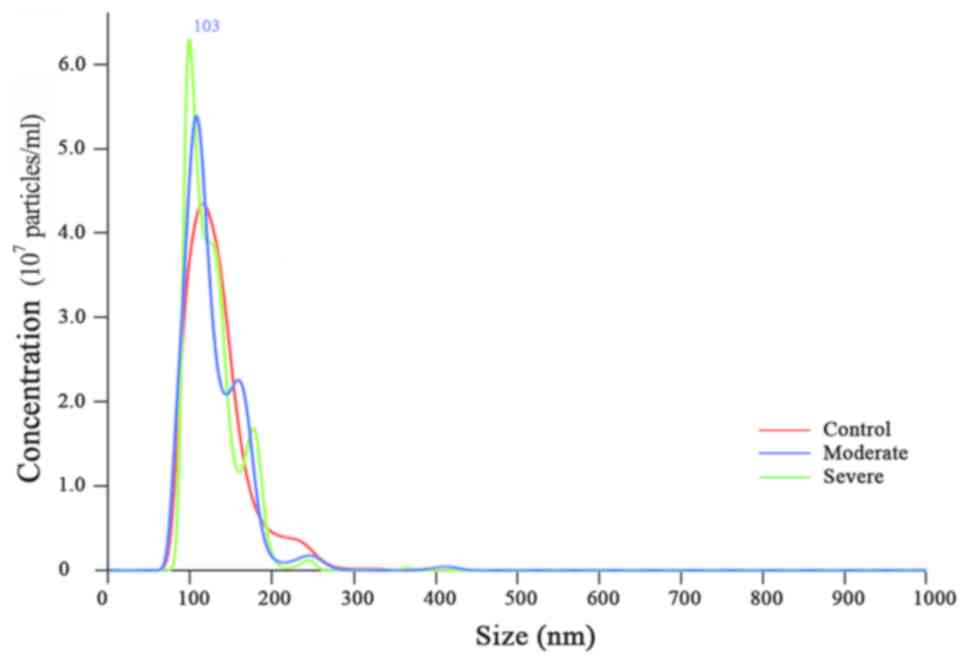
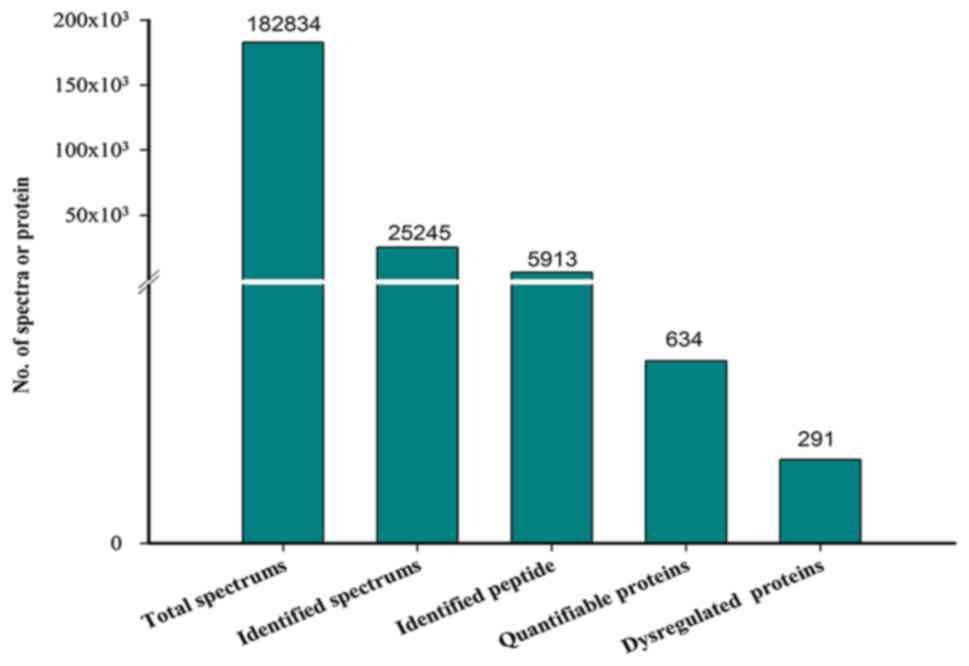
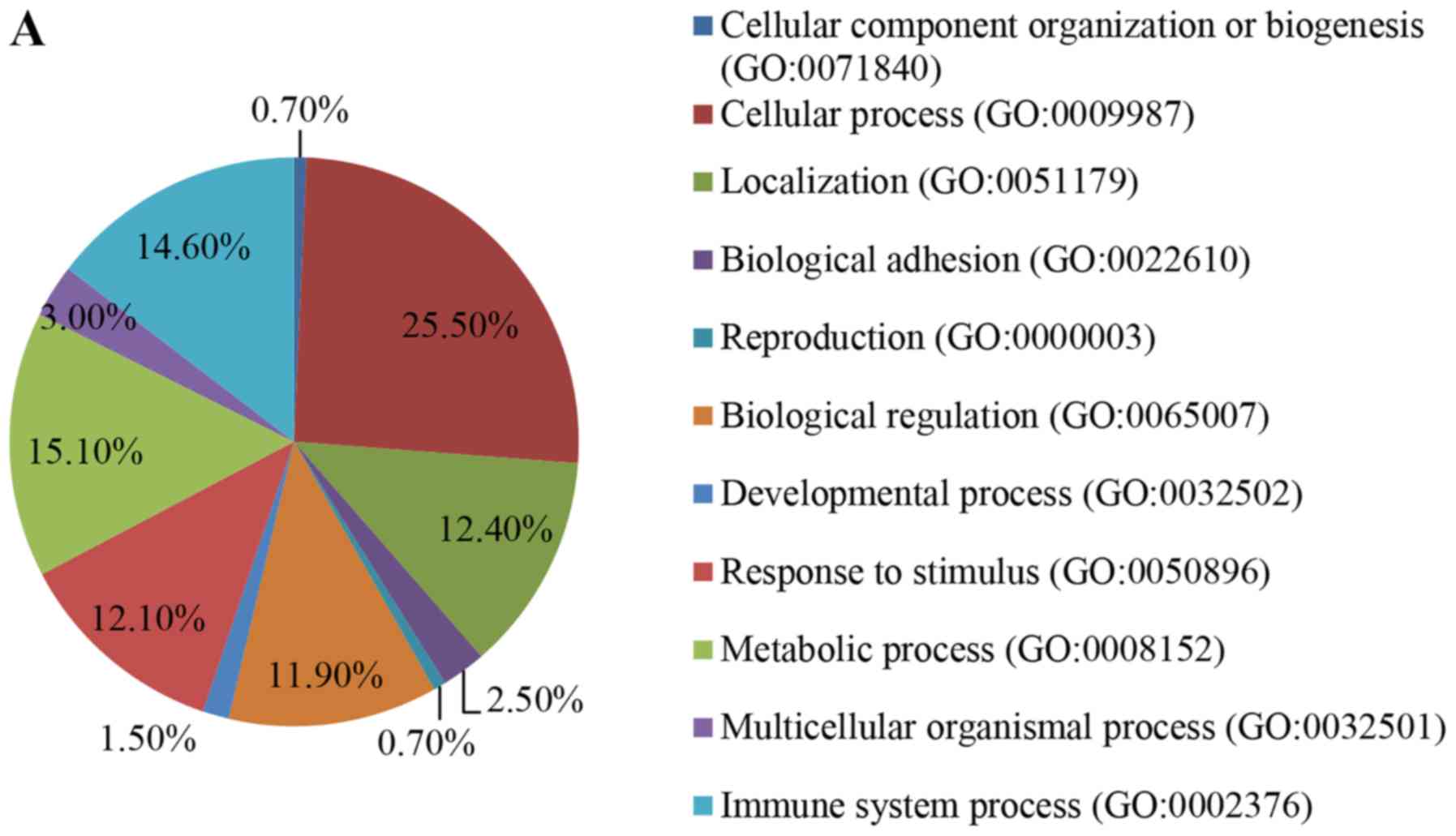
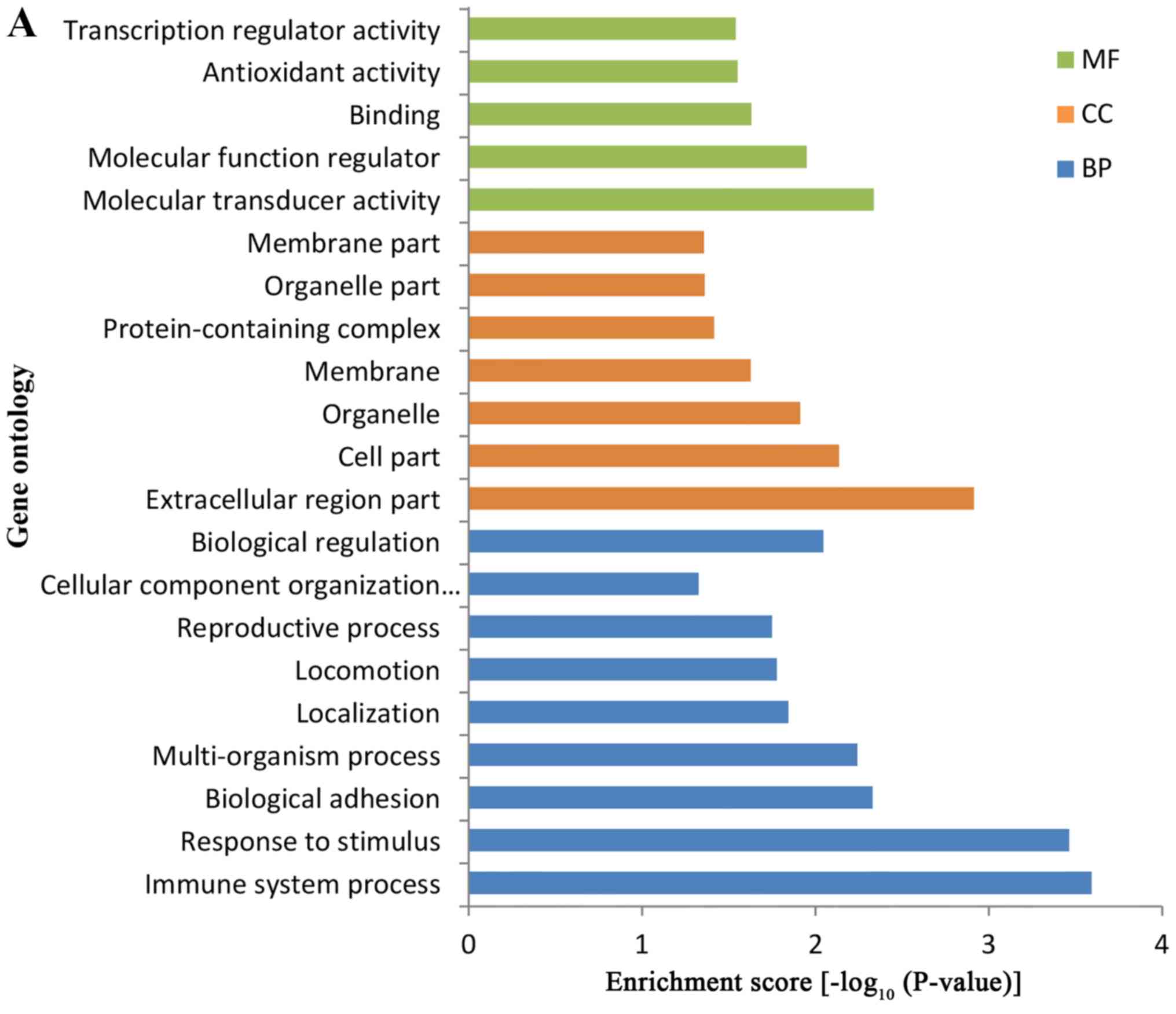
|
1
|
Bhutani VK, Stark AR, Lazzeroni LC, Poland
R, Gourley GR, Kazmierczak S, Meloy L, Burgos AE, Hall JY and
Stevenson DK: Predischarge screening for severe neonatal
hyperbilirubinemia identifies infants who need phototherapy. J
Pediatr. 162:477–482.e1. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bech LF, Donneborg ML, Lund AM and Ebbesen
F: Extreme neonatal hyperbilirubinemia, acute bilirubin
encephalopathy, and kernicterus spectrum disorder in children with
galactosemia. Pediatr Res. 84:228–232. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bahr TM, Christensen RD, Agarwal AM,
George TI and Bhutani VK: The neonatal acute bilirubin
encephalopathy registry (NABER): Background, aims, and protocol.
Neonatology. 115:242–246. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Christensen RD, Agarwal AM, George TI,
Bhutani VK and Yaish HM: Acute neonatal bilirubin encephalopathy in
the state of utah 2009–2018. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 72:10–13. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
McGillivray A and Evans N: Severe neonatal
jaundice: Is it a rare event in Australia? J Paediatr Child Health.
48:801–807. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Olusanya BO, Kaplan M and Hansen TWR:
Neonatal hyperbilirubinaemia: A global perspective. Lancet Child
Adolesc Health. 2:610–620. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Diala UM, Wennberg RP, Abdulkadir I,
Farouk ZL, Zabetta CDC, Omoyibo E, Emokpae A, Aravkin A, Toma B,
Oguche S, et al On behalf of the Stop Kernicterus In Nigeria (SKIN)
study group, : Patterns of acute bilirubin encephalopathy in
Nigeria: A multicenter pre-intervention study. J Perinatol.
38:873–880. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Morioka I, Nakamura H, Koda T, Yokota T,
Okada H, Katayama Y, Kunikata T, Kondo M, Nakamura M, Hosono S, et
al: Current incidence of clinical kernicterus in preterm infants in
Japan. Pediatr Int. 57:494–497. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Radmacher PG, Groves FD, Owa JA, Ofovwe
GE, Amuabunos EA, Olusanya BO and Slusher TM: A modified
Bilirubin-induced neurologic dysfunction (BIND-M) algorithm is
useful in evaluating severity of jaundice in a resource-limited
setting. BMC Pediatr. 15:282015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Morioka I, Iwatani S, Koda T, Iijima K and
Nakamura H: Disorders of bilirubin binding to albumin and
bilirubin-induced neurologic dysfunction. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med.
20:31–36. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Watchko JF: Kernicterus and the molecular
mechanisms of bilirubin-induced CNS injury in newborns.
Neuromolecular Med. 8:513–529. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Deganuto M, Cesaratto L, Bellarosa C,
Calligaris R, Vilotti S, Renzone G, Foti R, Scaloni A, Gustincich
S, Quadrifoglio F, et al: A proteomic approach to the
bilirubin-induced toxicity in neuronal cells reveals a protective
function of DJ-1 protein. Proteomics. 10:1645–1657. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Brites D: The evolving landscape of
neurotoxicity by unconjugated bilirubin: Role of glial cells and
inflammation. Front Pharmacol. 3:882012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Watchko JF and Tiribelli C:
Bilirubin-induced neurologic damage - mechanisms and management
approaches. N Engl J Med. 369:2021–2030. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Silva SL, Vaz AR, Barateiro A, Falcão AS,
Fernandes A, Brito MA, Silva RF and Brites D: Features of
bilirubin-induced reactive microglia: From phagocytosis to
inflammation. Neurobiol Dis. 40:663–675. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Brites D: Bilirubin injury to neurons and
glial cells: New players, novel targets, and newer insights. Semin
Perinatol. 35:114–120. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Daood M, Tsai C, Ahdab-Barmada M and
Watchko JF: ABC transporter (P-gp/ABCB1, MRP1/ABCC1, BCRP/ABCG2)
expression in the developing human CNS. Neuropediatrics.
39:211–218. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Qaisiya M, Brischetto C, Jašprová J, Vitek
L, Tiribelli C and Bellarosa C: Bilirubin-induced ER stress
contributes to the inflammatory response and apoptosis in neuronal
cells. Arch Toxicol. 91:1847–1858. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chivet M, Javalet C, Laulagnier K, Blot B,
Hemming FJ and Sadoul R: Exosomes secreted by cortical neurons upon
glutamatergic synapse activation specifically interact with
neurons. J Extracell Vesicles. 3:247222014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Izadpanah M, Seddigh A, Ebrahimi Barough
S, Fazeli SAS and Ai J: Potential of extracellular vesicles in
neurodegenerative diseases: Diagnostic and therapeutic indications.
J Mol Neurosci. 66:172–179. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Paolicelli RC, Bergamini G and Rajendran
L: Cell-to-cell communication by extracellular vesicles: Focus on
microglia. Neuroscience. 405:148–157. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xiong XG, Liang Q, Zhang C, Wang Y, Huang
W, Peng W, Wang Z and Xia ZA: Serum proteome alterations in
patients with cognitive impairment after traumatic brain injury
revealed by itraq-based quantitative proteomics. BioMed Res Int.
2017:85725092017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Núñez Galindo A, Macron C, Cominetti O and
Dayon L: Analyzing cerebrospinal fluid proteomes to characterize
central nervous system disorders: A highly automated mass
spectrometry-based pipeline for biomarker discovery. Methods Mol
Biol. 1959:89–112. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Adav SS, Park JE and Sze SK: Quantitative
profiling brain proteomes revealed mitochondrial dysfunction in
Alzheimer's disease. Mol Brain. 12:82019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bortolussi G, Codarin E, Antoniali G,
Vascotto C, Vodret S, Arena S, Cesaratto L, Scaloni A, Tell G and
Muro AF: Impairment of enzymatic antioxidant defenses is associated
with bilirubin-induced neuronal cell death in the cerebellum of
Ugt1 KO mice. Cell Death Dis. 6:e17392015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chiasserini D, van Weering JRT, Piersma
SR, Pham TV, Malekzadeh A, Teunissen CE, de Wit H and Jiménez CR:
Proteomic analysis of cerebrospinal fluid extracellular vesicles: A
comprehensive dataset. J Proteomics. 106:191–204. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
World Medical Association: World Medical
Association Declaration of Helsinki, . Ethical Principles for
Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. JAMA. 310:2191–2194.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bhutani VK and Johnson-Hamerman L: The
clinical syndrome of bilirubin-induced neurologic dysfunction.
Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 20:6–13. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gardiner C, Ferreira YJ, Dragovic RA,
Redman CW and Sargent IL: Extracellular vesicle sizing and
enumeration by nanoparticle tracking analysis. J Extracell
Vesicles. 2:22013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Shao H, Im H, Castro CM, Breakefield X,
Weissleder R and Lee H: New technologies for analysis of
extracellular vesicles. Chemical reviews. 118:1917–1950. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Taylor DD and Doellgast GJ: Quantitation
of peroxidase-antibody binding to membrane fragments using column
chromatography. Anal Biochem. 98:53–59. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Osier N, Motamedi V, Edwards K, Puccio A,
Diaz-Arrastia R, Kenney K and Gill J: Exosomes in acquired
neurological disorders: New insights into pathophysiology and
treatment. Mol Neurobiol. 55:9280–9293. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tang BL: Promoting axonal regeneration
through exosomes: An update of recent findings on exosomal PTEN and
mTOR modifiers. Brain Res Bull. 143:123–131. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fernandes A, Barateiro A, Falcão AS, Silva
SL, Vaz AR, Brito MA, Silva RF and Brites D: Astrocyte reactivity
to unconjugated bilirubin requires TNF-α and IL-1β receptor
signaling pathways. Glia. 59:14–25. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li M, Song S, Li S, Feng J and Hua Z: The
blockade of nf-kappab activation by a specific inhibitory peptide
has a strong neuroprotective role in a sprague-dawley rat
kernicterus model. J Biol Chem. 290:30042–30052. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Watchko JF: Bilirubin-induced
neurotoxicity in the preterm neonate. Clin Perinatol. 43:297–311.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Watchko JF and Maisels MJ: The enigma of
low bilirubin kernicterus in premature infants: Why does it still
occur, and is it preventable? Semin Perinatol. 38:397–406. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Vodret S, Bortolussi G, Jašprová J, Vitek
L and Muro AF: Inflammatory signature of cerebellar
neurodegeneration during neonatal hyperbilirubinemia in
Ugt1−/− mouse model. J Neuroinflammation. 14:642017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kitamura M: Control of NF-κB and
inflammation by the unfolded protein response. Int Rev Immunol.
30:4–15. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Feng J, Li M, Wei Q, Li S, Song S and Hua
Z: Unconjugated bilirubin induces pyroptosis in cultured rat
cortical astrocytes. J Neuroinflammation. 15:232018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhu M, Wang X, Schultzberg M and Hjorth E:
Differential regulation of resolution in inflammation induced by
amyloid-β42 and lipopolysaccharides in human microglia. J
Alzheimers Dis. 43:1237–1250. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Davies MG and Hagen PO: Systemic
inflammatory response syndrome. Br J Surg. 84:920–935. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Anada RP, Wong KT, Jayapalan JJ, Hashim OH
and Ganesan D: Panel of serum protein biomarkers to grade the
severity of traumatic brain injury. Electrophoresis. 39:2308–2315.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gasque P, Fontaine M and Morgan BP:
Complement expression in human brain. Biosynthesis of terminal
pathway components and regulators in human glial cells and cell
lines. Immunol. 154:4726–4733. 1995.
|
|
45
|
Nataf S, Levison SW and Barnum SR:
Expression of the anaphylatoxin C5a receptor in the oligodendrocyte
lineage. Brain Res. 894:321–326. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hammad A, Westacott L and Zaben M: The
role of the complement system in traumatic brain injury: A review.
J Neuroinflammation. 15:242018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Brennan FH, Anderson AJ, Taylor SM,
Woodruff TM and Ruitenberg MJ: Complement activation in the injured
central nervous system: Another dual-edged sword? J
Neuroinflammation. 9:1372012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Bellander BM, Olafsson IH, Ghatan PH, Bro
Skejo HP, Hansson LO, Wanecek M and Svensson MA: Secondary insults
following traumatic brain injury enhance complement activation in
the human brain and release of the tissue damage marker S100B. Acta
Neurochir (Wien). 153:90–100. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Stoll BJ, Lee FK, Hale E, Schwartz D,
Holmes R, Ashby R, Czerkinsky C and Nahmias AJ: Immunoglobulin
secretion by the normal and the infected newborn infant. J Pediatr.
122:780–786. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zinn K and Özkan E: Neural immunoglobulin
superfamily interaction networks. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 45:99–105.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Denstaedt SJ, Spencer-Segal JL, Newstead
MW, Laborc K, Zhao AP, Hjelmaas A, Zeng X, Akil H, Standiford TJ
and Singer BH: S100a8/a9 drives neuroinflammatory priming and
protects against anxiety-like behavior after sepsis. J Immunol.
200:3188–3200. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hermani A, De Servi B, Medunjanin S,
Tessier PA and Mayer D: S100A8 and S100A9 activate MAP kinase and
NF-kappaB signaling pathways and trigger translocation of RAGE in
human prostate cancer cells. Exp Cell Res. 312:184–197. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ghavami S, Rashedi I, Dattilo BM, Eshraghi
M, Chazin WJ, Hashemi M, Wesselborg S, Kerkhoff C and Los M:
S100A8/A9 at low concentration promotes tumor cell growth via RAGE
ligation and MAP kinase-dependent pathway. J Leukoc Biol.
83:1484–1492. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Ryu MJ, Liu Y, Zhong X, Du J, Peterson N,
Kong G, Li H, Wang J, Salamat S, Chang Q, et al: Oncogenic Kras
expression in postmitotic neurons leads to S100A8-S100A9 protein
overexpression and gliosis. J Biol Chem. 287:22948–22958. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Wang S, Song R, Wang Z, Jing Z, Wang S and
Ma J: S100A8/A9 in Inflammation. Front Immunol. 9:12982018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Low D, Subramaniam R, Lin L, Aomatsu T,
Mizoguchi A, Ng A, DeGruttola AK, Lee CG, Elias JA, Andoh A, et al:
Chitinase 3-like 1 induces survival and proliferation of intestinal
epithelial cells during chronic inflammation and colitis-associated
cancer by regulating S100A9. Oncotarget. 6:36535–36550. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Donato R, Cannon B, Sorci G, Riuzzi F, Hsu
K, Weber D and Geczy C: Functions of s100 proteins. Curr Mol Med.
13:24–57. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ryckman C, Vandal K, Rouleau P, Talbot M
and Tessier PA: Proinflammatory activities of s100: Proteins
s100a8, s100a9, and s100a8/a9 induce neutrophil chemotaxis and
adhesion. J Immunol. 170:3233–3242. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Pruenster M, Kurz AR, Chung KJ, Cao-Ehlker
X, Bieber S, Nussbaum CF, Bierschenk S, Eggersmann TK, Rohwedder I,
Heinig K, et al: Extracellular MRP8/14 is a regulator of β2
integrin-dependent neutrophil slow rolling and adhesion. Nat
Commun. 6:69152015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Nishikawa Y, Kajiura Y, Lew JH, Kido JI,
Nagata T and Naruishi K: Calprotectin induces il-6 and mcp-1
production via toll-like receptor 4 signaling in human gingival
fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 232:1862–1871. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Ma L, Sun P, Zhang JC, Zhang Q and Yao SL:
Proinflammatory effects of S100A8/A9 via TLR4 and RAGE signaling
pathways in BV-2 microglial cells. Int J Mol Med. 40:31–38. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Horvath I, Jia X, Johansson P, Wang C,
Moskalenko R, Steinau A, Forsgren L, Wågberg T, Svensson J,
Zetterberg H, et al: Pro-inflammatory s100a9 protein as a robust
biomarker differentiating early stages of cognitive impairment in
alzheimer's disease. ACS Chem Neurosci. 7:34–39. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Wache C, Klein M, Ostergaard C, Angele B,
Häcker H, Pfister HW, Pruenster M, Sperandio M, Leanderson T, Roth
J, et al: Myeloid-related protein 14 promotes inflammation and
injury in meningitis. J Infect Dis. 212:247–257. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Meldolesi J: Exosomes and ectosomes in
intercellular communication. Curr Biol. 28:R435–R444. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Fritz G, Botelho HM, Morozova-Roche LA and
Gomes CM: Natural and amyloid self-assembly of S100 proteins:
Structural basis of functional diversity. FEBS J. 277:4578–4590.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Jansen S, Podschun R, Leib SL, Grötzinger
J, Oestern S, Michalek M, Pufe T and Brandenburg LO: Expression and
function of psoriasin (S100A7) and koebnerisin (S100A15) in the
brain. Infect Immun. 81:1788–1797. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Qin W, Ho L, Wang J, Peskind E and
Pasinetti GM: S100A7, a novel Alzheimer's disease biomarker with
non-amyloidogenic alpha-secretase activity acts via selective
promotion of ADAM-10. PLoS One. 4:e41832009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Sharma R, Gowda H, Chavan S, Advani J,
Kelkar D, Kumar GS, Bhattacharjee M, Chaerkady R, Prasad TS, Pandey
A, et al: Proteomic signature of endothelial dysfunction identified
in the serum of acute ischemic stroke patients by the itraq-based
lc-ms approach. J Proteome Res. 14:2466–2479. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Kim C and Kaufmann SH: Defensin: A
multifunctional molecule lives up to its versatile name. Trends
Microbiol. 14:428–431. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Park YG, Jeong JK, Lee JH, Lee YJ, Seol
JW, Kim SJ, Hur TY, Jung YH, Kang SJ and Park SY: Lactoferrin
protects against prion protein-induced cell death in neuronal cells
by preventing mitochondrial dysfunction. Int J Mol Med. 31:325–330.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Semple F and Dorin JR: β-Defensins:
Multifunctional modulators of infection, inflammation and more? J
Innate Immun. 4:337–348. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Tollner TL, Bevins CL and Cherr GN:
Multifunctional glycoprotein DEFB126 - a curious story of
defensin-clad spermatozoa. Nat Rev Urol. 9:365–375. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Kazakos EI, Kountouras J, Polyzos SA and
Deretzi G: Novel aspects of defensins' involvement in virus-induced
autoimmunity in the central nervous system. Med Hypotheses.
102:33–36. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Williams WM, Torres S, Siedlak SL,
Castellani RJ, Perry G, Smith MA and Zhu X: Antimicrobial peptide
β-defensin-1 expression is upregulated in Alzheimer's brain. J
Neuroinflammation. 10:1272013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Rocha-Ferreira E and Hristova M:
Antimicrobial peptides and complement in neonatal hypoxia-ischemia
induced brain damage. Front Immunol. 6:562015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Miles K, Clarke DJ, Lu W, Sibinska Z,
Beaumont PE, Davidson DJ, Barr TA, Campopiano DJ and Gray M: Dying
and necrotic neutrophils are anti-inflammatory secondary to the
release of alpha-defensins. J Immunol. 183:2122–2132. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Zakharova ET, Sokolov AV, Pavlichenko NN,
Kostevich VA, Abdurasulova IN, Chechushkov AV, Voynova IV,
Elizarova AY, Kolmakov NN, Bass MG, et al: Erythropoietin and Nrf2:
Key factors in the neuroprotection provided by apo-lactoferrin.
Biometals. 31:425–443. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Legrand D, Elass E, Carpentier M and
Mazurier J: Lactoferrin: A modulator of immune and inflammatory
responses. Cell Mol Life Sci. 62:2549–2559. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Legrand D: Lactoferrin, a key molecule in
immune and inflammatory processes. Biochem Cell Biol. 90:252–268.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Bennett RM and Kokocinski T: Lactoferrin
content of peripheral blood cells. Br J Haematol. 39:509–521. 1978.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Qaisiya M, Coda Zabetta CD, Bellarosa C
and Tiribelli C: Bilirubin mediated oxidative stress involves
antioxidant response activation via Nrf2 pathway. Cell Signal.
26:512–520. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Ginet V, van de Looij Y, Petrenko V,
Toulotte A, Kiss J, Hüppi PS and Sizonenko SV: Lactoferrin during
lactation reduces lipopolysaccharide-induced brain injury.
Biofactors. 42:323–336. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
van de Looij Y, Ginet V, Chatagner A,
Toulotte A, Somm E, Hüppi PS and Sizonenko SV: Lactoferrin during
lactation protects the immature hypoxic-ischemic rat brain. Ann
Clin Transl Neurol. 1:955–967. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Somm E, Larvaron P, van de Looij Y,
Toulotte A, Chatagner A, Faure M, Métairon S, Mansourian R, Raymond
F, Gruetter R, et al: Protective effects of maternal nutritional
supplementation with lactoferrin on growth and brain metabolism.
Pediatr Res. 75:51–61. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Lee SH, Pyo CW, Hahm DH, Kim J and Choi
SY: Iron-saturated lactoferrin stimulates cell cycle progression
through PI3K/Akt pathway. Mol Cells. 28:37–42. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Thompson AG, Gray E, Heman-Ackah SM, Mäger
I, Talbot K, Andaloussi SE, Wood MJ and Turner MR: Extracellular
vesicles in neurodegenerative disease - pathogenesis to biomarkers.
Nat Rev Neurol. 12:346–357. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|