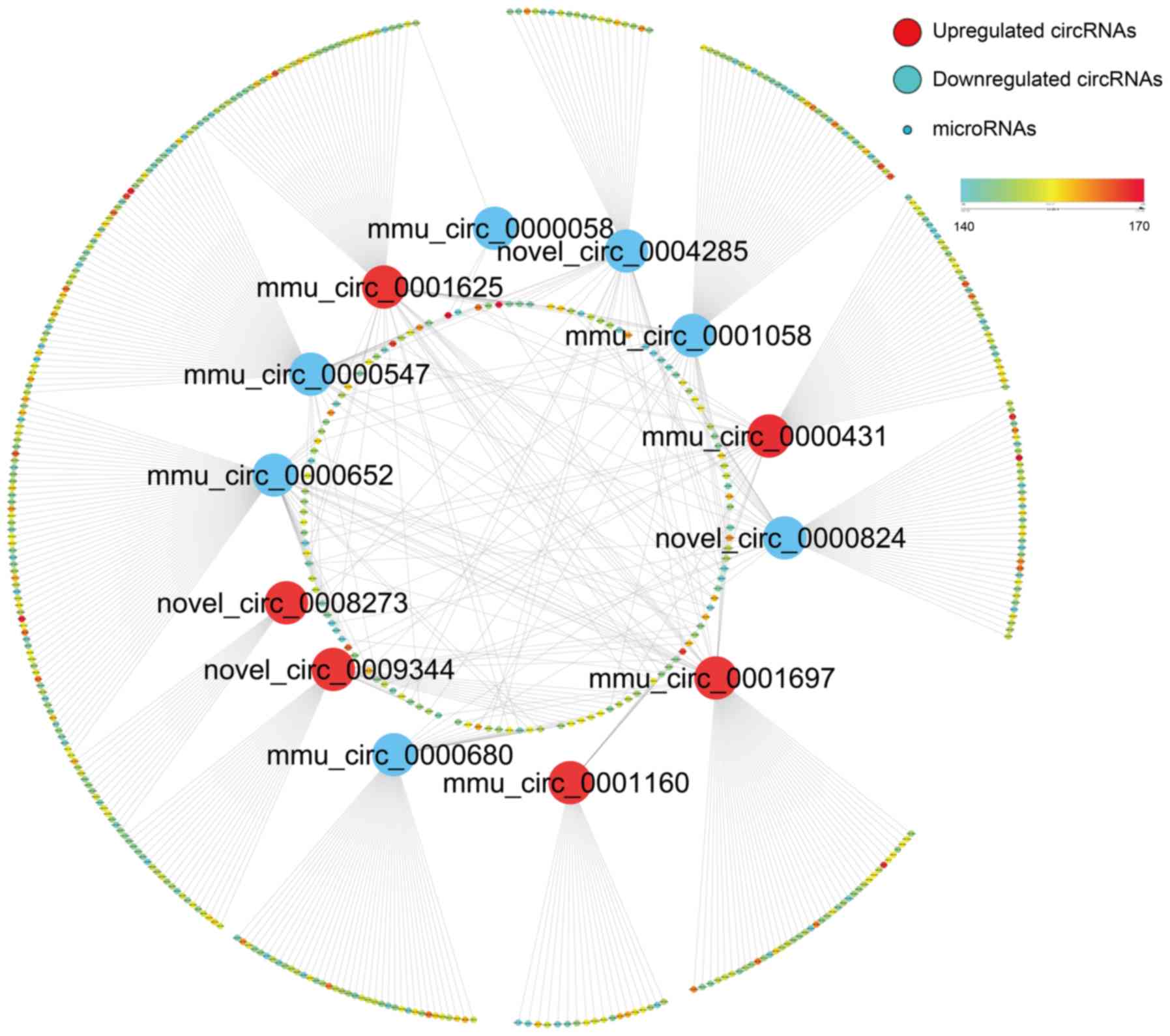
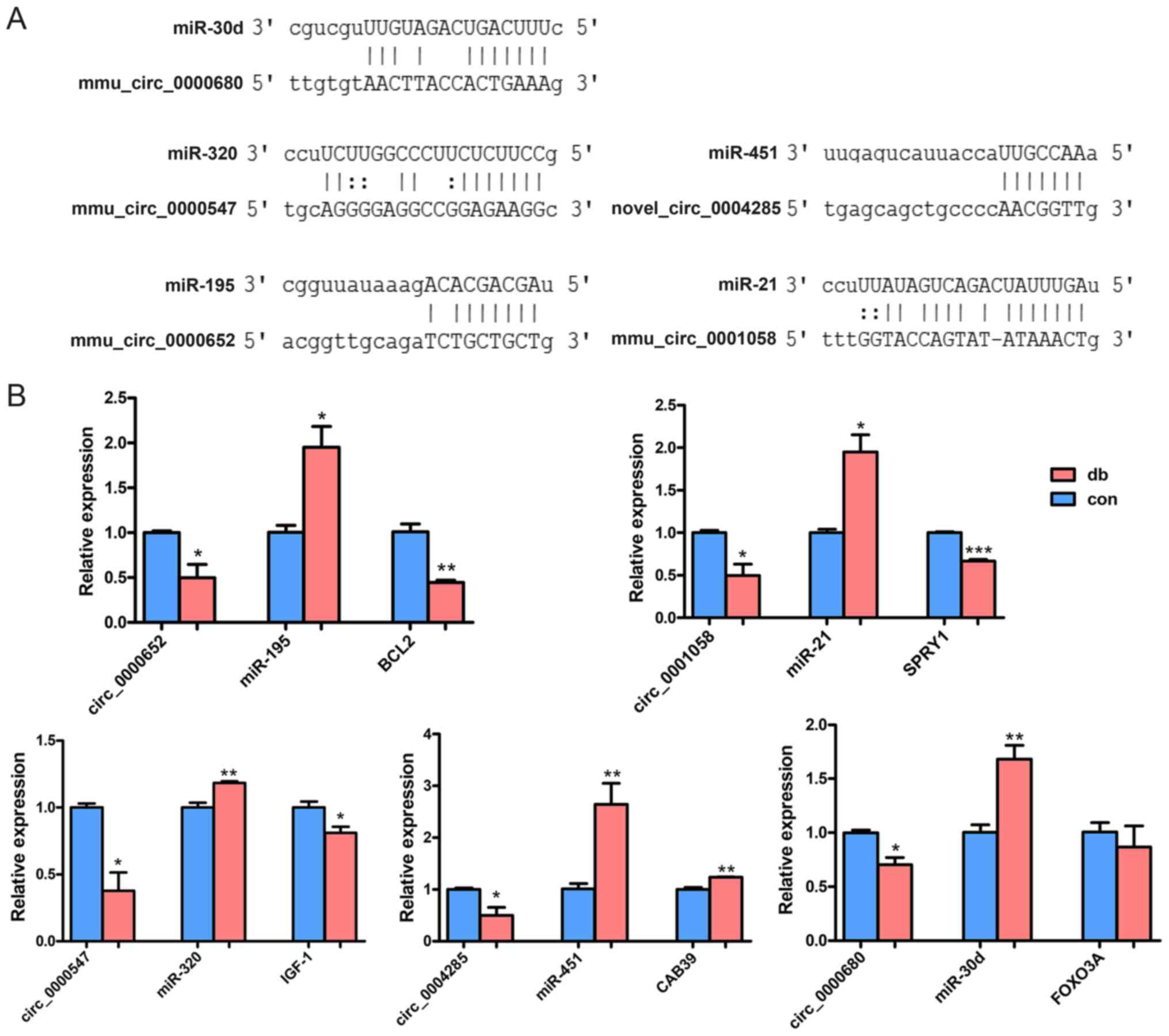
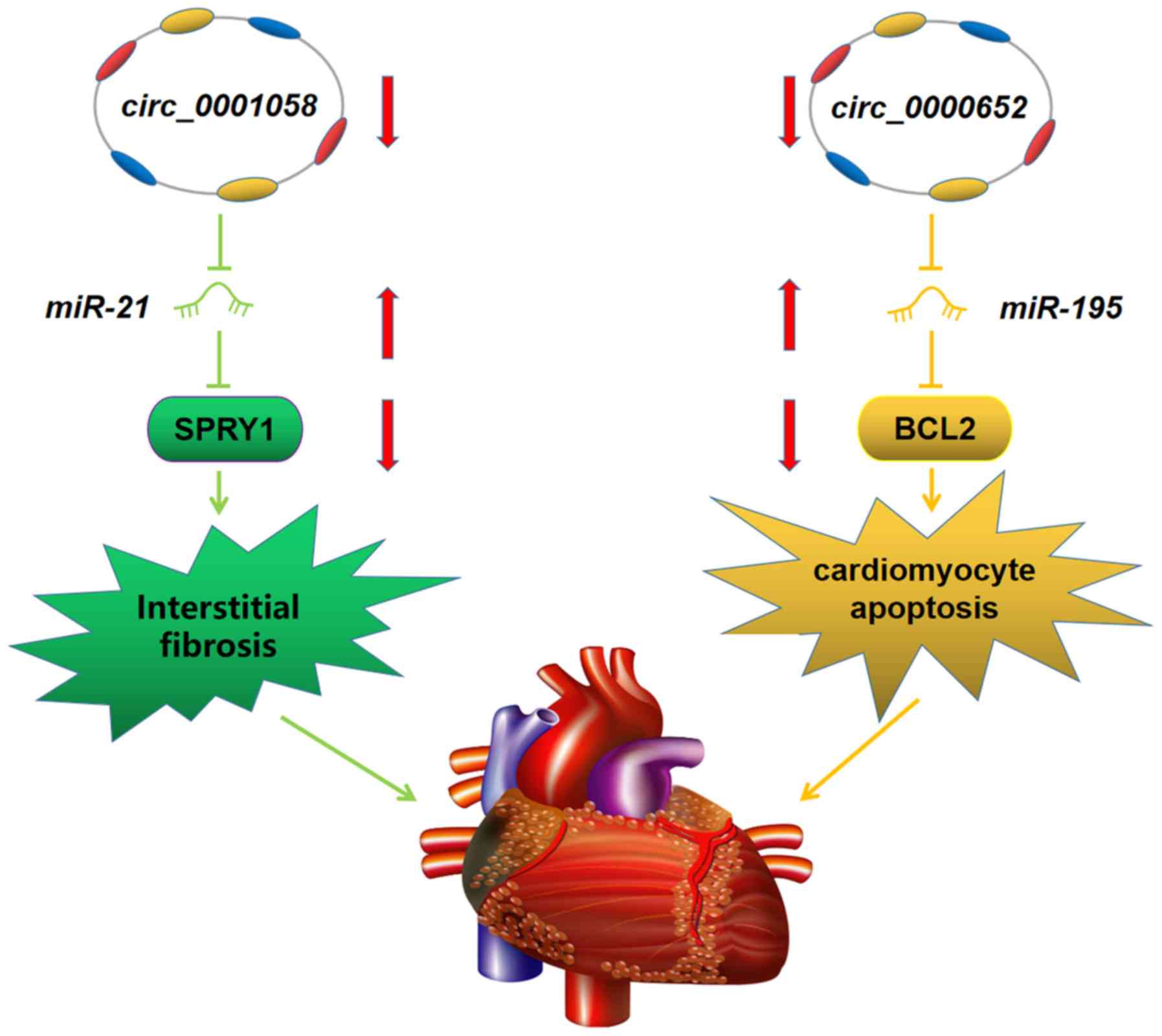
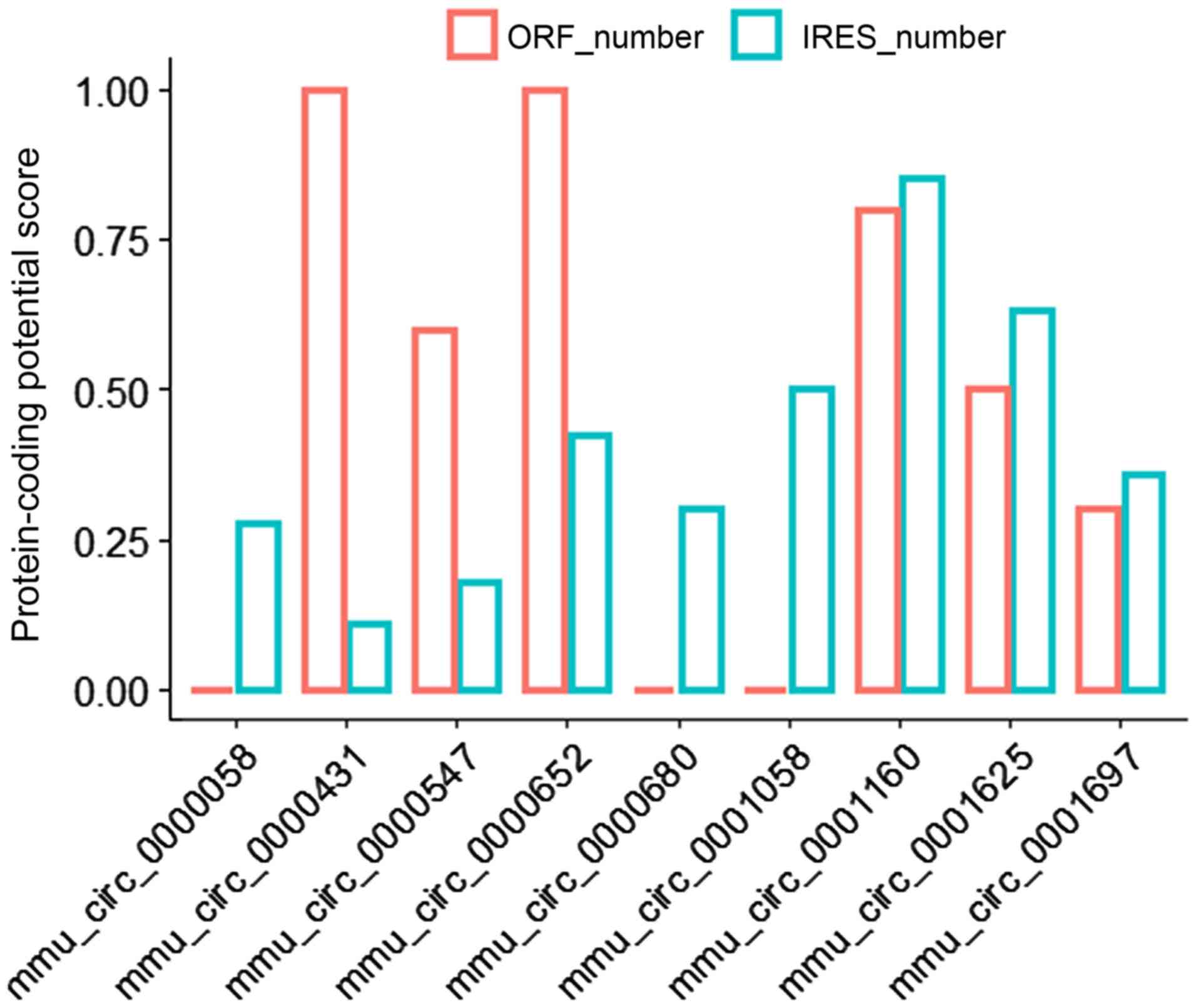
|
1
|
Cho NH, Shaw JE, Karuranga S, Huang Y, da
Rocha Fernandes JD, Ohlrogge AW and Malanda B: IDF diabetes atlas:
Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections
for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 138:271–281. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Marwick TH, Ritchie R, Shaw JE and Kaye D:
Implications of underlying mechanisms for the recognition and
management of diabetic cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol.
71:339–351. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jia G, Hill MA and Sowers JR: Diabetic
cardiomyopathy: An update of mechanisms contributing to this
clinical entity. Circ Res. 122:624–638. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Murtaza G, Virk HUH, Khalid M, Lavie CJ,
Ventura H, Mukherjee D, Ramu V, Bhogal S, Kumar G, Shanmugasundaram
M and Paul TK: Diabetic cardiomyopathy-A comprehensive updated
review. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 62:315–326. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lam CS: Diabetic cardiomyopathy: An
expression of stage B heart failure with preserved ejection
fraction. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 12:234–238. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tadic M, Celic V, Cuspidi C, Ilic S,
Pencic B, Radojkovic J, Ivanovic B, Stanisavljevic D, Kocabay G and
Marjanovic T: Right heart mechanics in untreated normotensive
patients with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A Two- and
three-dimensional echocardiographic study. J Am Soc Echocardiog.
28:317–327. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Shaver A, Nichols A, Thompson E, Mallick
A, Payne K, Jones C, Manne ND, Sundaram S, Shapiro JI and Sodhi K:
Role of serum biomarkers in early detection of diabetic
cardiomyopathy in the west virginian population. Int J Med Sci.
13:161–168. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li X, Yang L and Chen LL: The biogenesis,
functions, and challenges of circular RNAs. Mol Cell. 71:428–442.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang HD, Jiang LH, Sun DW, Hou JC and Ji
ZL: CircRNA: A novel type of biomarker for cancer. Breast Cancer.
25:1–7. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pamudurti NR, Bartok O, Jens M,
Ashwal-Fluss R, Stottmeister C, Ruhe L, Hanan M, Wyler E,
Perez-Hernandez D, Ramberger E, et al: Translation of CircRNAs. Mol
Cell. 66:9–21.e7. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Meng S, Zhou H, Feng Z, Xu Z, Tang Y, Li P
and Wu M: Functions and properties of a novel potential biomarker
for cancer. Mol Cancer. 16:942017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huang C and Shan G: What happens at or
after transcription: Insights into circRNA biogenesis and function.
Transcription. 6:61–64. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhao Z, Li X, Jian D, Hao P, Rao L and Li
M: Hsa_circ_0054633 in peripheral blood can be used as a diagnostic
biomarker of pre-diabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Acta
Diabetol. 54:237–245. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fang Y, Wang X, Li W, Han J, Jin J, Su F,
Zhang J, Huang W, Xiao F, Pan Q and Zou L: Screening of circular
RNAs and validation of circANKRD36 associated with inflammation in
patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Mol Med.
42:1865–1874. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Karkalas J: An improved enzymic method for
the determination of native and modified starch. J Sci Food Agr.
36:1019–1027. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mi H, Muruganujan A, Ebert D, Huang X and
Thomas PD: PANTHER version 14: More genomes, a new PANTHER GO-slim
and improvements in enrichment analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res.
47:D419–D426. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
The Gene Ontology Consortium, . The gene
ontology resource: 20 years and still GOing strong. Nucleic Acids
Res. 47:D330–D338. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene
Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Sato Y, Kawashima M,
Furumichi M and Tanabe M: Data, information, knowledge and
principle: Back to metabolism in KEGG. Nucleic Acids Res 42
(Database Issue). D199–D205. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Jellis CL, Sacre JW, Wright J, Jenkins C,
Haluska B, Jeffriess L, Martin J and Marwick TH: Biomarker and
imaging responses to spironolactone in subclinical diabetic
cardiomyopathy. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 15:776–786. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nunes S, Soares E, Fernandes J, Viana S,
Carvalho E, Pereira FC and Reis F: Early cardiac changes in a rat
model of prediabetes: Brain natriuretic peptide overexpression
seems to be the best marker. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 12:442013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cai J, Chen Z, Wang J, Wang J, Chen X,
Liang L, Huang M, Zhang Z and Zuo X: circHECTD1 facilitates
glutaminolysis to promote gastric cancer progression by targeting
miR-1256 and activating β-catenin/c-Myc signaling. Cell Death Dis.
10:5762019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kuwabara Y, Horie T, Baba O, Watanabe S,
Nishiga M, Usami S, Izuhara M, Nakao T, Nishino T, Otsu K, et al:
MicroRNA-451 exacerbates lipotoxicity in cardiac myocytes and
high-fat diet-induced cardiac hypertrophy in mice through
suppression of the LKB1/AMPK pathway. Circ Res. 116:279–288. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li X, Du N, Zhang Q, Li J, Chen X, Liu X,
Hu Y, Qin W, Shen N, Xu C, et al: MicroRNA-30d regulates
cardiomyocyte pyroptosis by directly targeting foxo3a in diabetic
cardiomyopathy. Cell Death Dis. 5:e14792014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhu H, Yang Y, Wang Y, Li J, Schiller PW
and Peng T: MicroRNA-195 promotes palmitate-induced apoptosis in
cardiomyocytes by down-regulating Sirt1. Cardiovasc Res. 92:75–84.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang XH, Qian RZ, Zhang W, Chen SF, Jin HM
and Hu RM: MicroRNA-320 expression in myocardial microvascular
endothelial cells and its relationship with insulin-like growth
factor-1 in type 2 diabetic rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol.
36:181–188. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Thum T, Gross C, Fiedler J, Fischer T,
Kissler S, Bussen M, Galuppo P, Just S, Rottbauer W, Frantz S, et
al: MicroRNA-21 contributes to myocardial disease by stimulating
MAP kinase signalling in fibroblasts. Nature. 456:980–984. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu J, Liu W, Lu Y, Tian H, Duan C, Lu L,
Gao G, Wu X, Wang X and Yang H: Piperlongumine restores the balance
of autophagy and apoptosis by increasing BCL2 phosphorylation in
rotenone-induced Parkinson disease models. Autophagy. 14:845–861.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chai C, Song LJ, Han SY, Li XQ and Li M:
MicroRNA-21 promotes glioma cell proliferation and inhibits
senescence and apoptosis by targeting SPRY1 via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT
signaling pathway. Cns Neurosci Ther. 24:369–380. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liang WC, Wong CW, Liang PP, Shi M, Cao Y,
Rao ST, Tsui SK, Waye MM, Zhang Q, Fu WM and Zhang JF: Translation
of the circular RNA circβ-catenin promotes liver cancer cell growth
through activation of the Wnt pathway. Genome Biol. 20:842019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang Y, Gao X, Zhang M, Yan S, Sun C, Xiao
F, Huang N, Yang X, Zhao K, Zhou H, et al: Novel role of FBXW7
circular RNA in repressing glioma tumorigenesis. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 110:304–315. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Li LJ, Leng RX, Fan YG, Pan HF and Ye DQ:
Translation of noncoding RNAs: Focus on lncRNAs, pri-miRNAs, and
circRNAs. Exp Cell Res. 361:1–8. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu H, Liu Y, Bian Z, Zhang J, Zhang R,
Chen X, Huang Y, Wang Y and Zhu J: Circular RNA YAP1 inhibits the
proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer cells by regulating
the miR-367-5p/p27Kip1 axis. Mol Cancer. 17:1512019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Altesha MA, Ni T, Khan A, Liu K and Zheng
X: Circular RNA in cardiovascular disease. J Cell Physiol.
234:5588–5600. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lin F, Zhao G, Chen Z, Wang X, Lv F, Zhang
Y, Yang X, Liang W, Cai R, Li J, et al: circRNA-miRNA association
for coronary heart disease. Mol Med Rep. 19:2527–2536.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Patop IL and Kadener S: circRNAs in
cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 48:121–127. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Fischer JW and Leung AK: CircRNAs: A
regulator of cellular stress. Crit Rev Biochem Mol. 52:220–233.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Yang F, Li A, Qin Y, Che H, Wang Y, Lv J,
Li Y, Li H, Yue E, Ding X, et al: A novel circular RNA mediates
pyroptosis of diabetic cardiomyopathy by functioning as a competing
endogenous RNA. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 17:636–643. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu C, Ge HM, Liu BH, Dong R, Shan K, Chen
X, Yao MD, Li XM, Yao J, Zhou RM, et al: Targeting
Pericyte-endothelial cell crosstalk by circular RNA-cPWWP2A
inhibition aggravates diabetes-induced microvascular dysfunction.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 116:7455–7464. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wu H, Wu S, Zhu Y, Ye M, Shen J, Liu Y,
Zhang Y and Bu S: Hsa_circRNA_0054633 is highly expressed in
gestational diabetes mellitus and closely related to glycosylation
index. Clin Epigenetics. 11:222019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Fuentes-Antrás J, Picatoste B, Ramírez E,
Egido J, Tuñón J and Lorenzo Ó: Targeting metabolic disturbance in
the diabetic heart. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 14:172015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Duncan JG: Mitochondrial dysfunction in
diabetic cardiomyopathy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:1351–1359.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Huang P, Qi B, Yao H, Zhang L, Li Y and Li
Q: Circular RNA cSMARCA5 regulates the progression of cervical
cancer by acting as a microRNA-432 sponge. Mol Med Rep.
21:1217–1223. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Salzman J: Circular RNA expression: Its
potential regulation and function. Trends Genet. 32:309–316. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Han D, Li J, Wang H, Su X, Hou J, Gu Y,
Qian C, Lin Y, Liu X, Huang M, et al: Circular RNA circMTO1 acts as
the sponge of microRNA-9 to suppress hepatocellular carcinoma
progression. Hepatology. 66:1151–1164. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zheng D, Ma J, Yu Y, Li M, Ni R, Wang G,
Chen R, Li J, Fan GC, Lacefield JC and Peng T: Silencing of miR-195
reduces diabetic cardiomyopathy in C57BL/6 mice. Diabetologia.
58:1949–1958. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Gu J, Wang S, Guo H, Tan Y, Liang Y, Feng
A, Liu Q, Damodaran C, Zhang Z, Keller BB, et al: Inhibition of p53
prevents diabetic cardiomyopathy by preventing early-stage
apoptosis and cell senescence, reduced glycolysis, and impaired
angiogenesis. Cell Death Dis. 9:822018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Tuncay E and Turan B: Intracellular
Zn2+ increase in cardiomyocytes induces both electrical
and mechanical dysfunction in heart via endogenous generation of
reactive nitrogen species. Biol Trace Elem Res. 169:294–302. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Huang L, Yan M and Kirschke CP:
Over-expression of ZnT7 increases insulin synthesis and secretion
in pancreatic beta-cells by promoting insulin gene transcription.
Exp Cell Res. 316:2630–2643. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Tuncay E, Bitirim CV, Olgar Y, Durak A,
Rutter GA and Turan B: Zn2+-transporters ZIP7 and ZnT7 play
important role in progression of cardiac dysfunction via affecting
Sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum-mitochondria coupling in hyperglycemic
cardiomyocytes. Mitochondrion. 44:41–52. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Jia G, Whaley-Connell A and Sowers JR:
Diabetic cardiomyopathy: A hyperglycaemia- and
insulin-resistance-induced heart disease. Diabetologia. 61:21–28.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lorenzo-Almoros A, Tunon J, Orejas M,
Cortes M, Egido J and Lorenzo O: Diagnostic approaches for diabetic
cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 16:282017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|