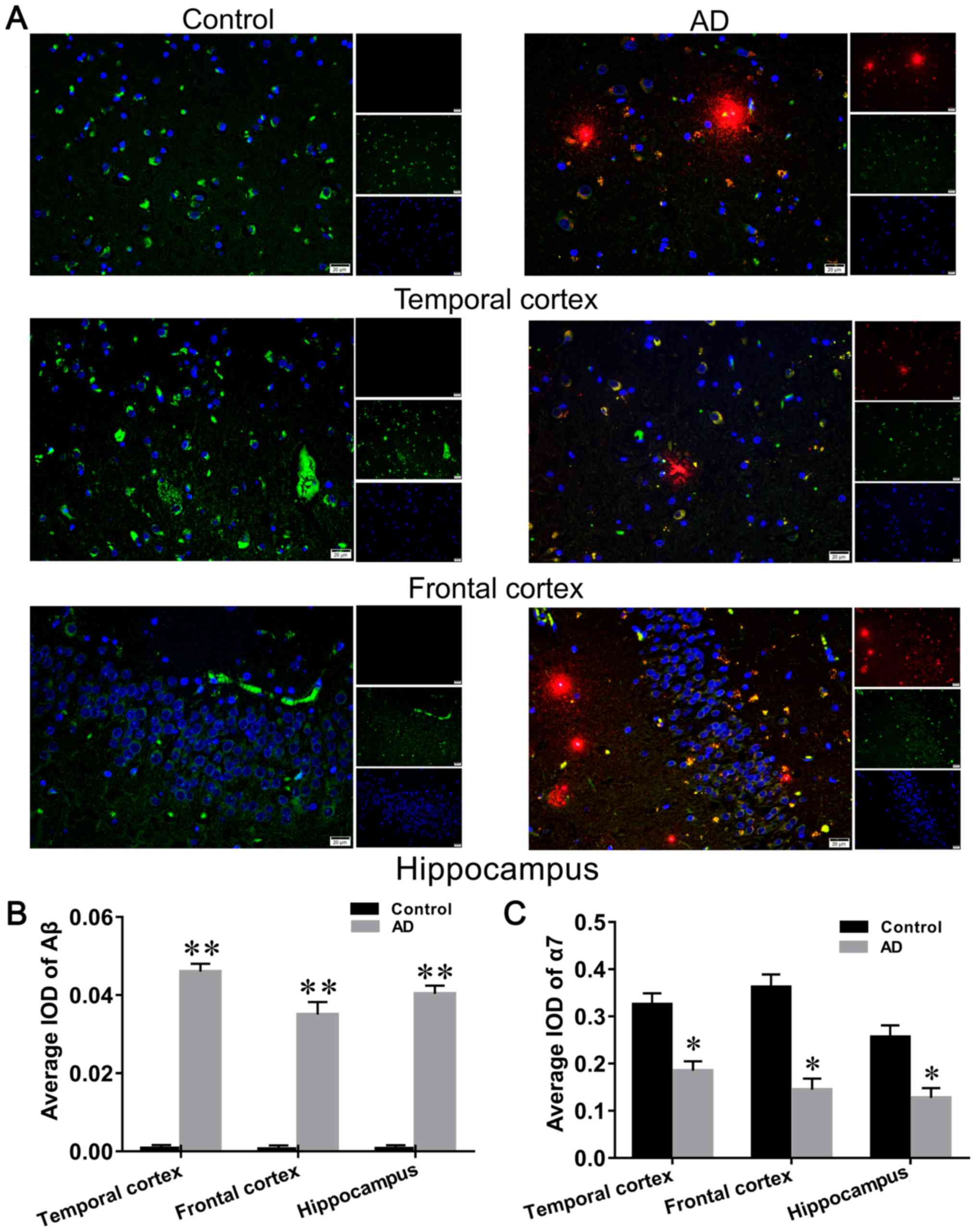
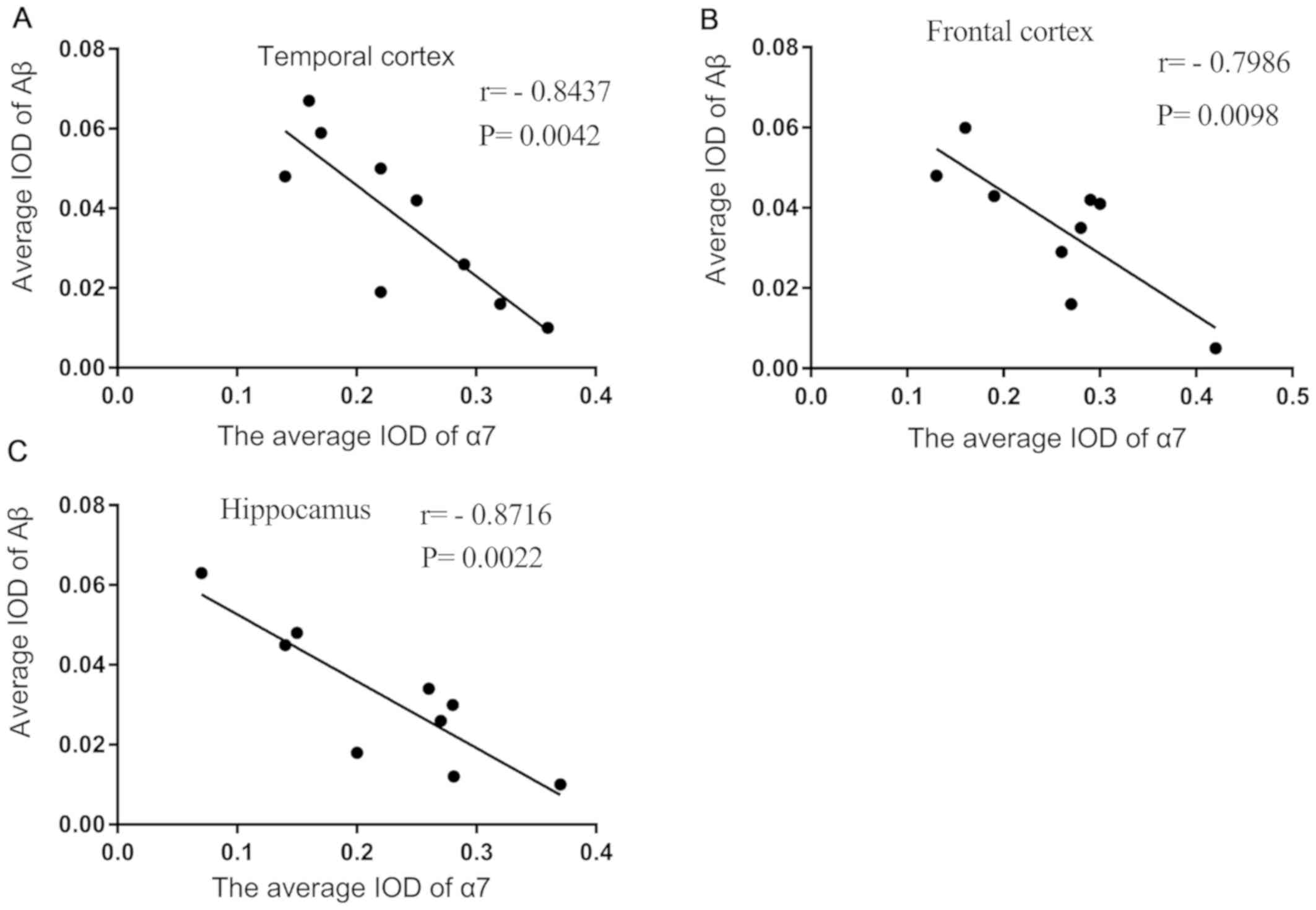
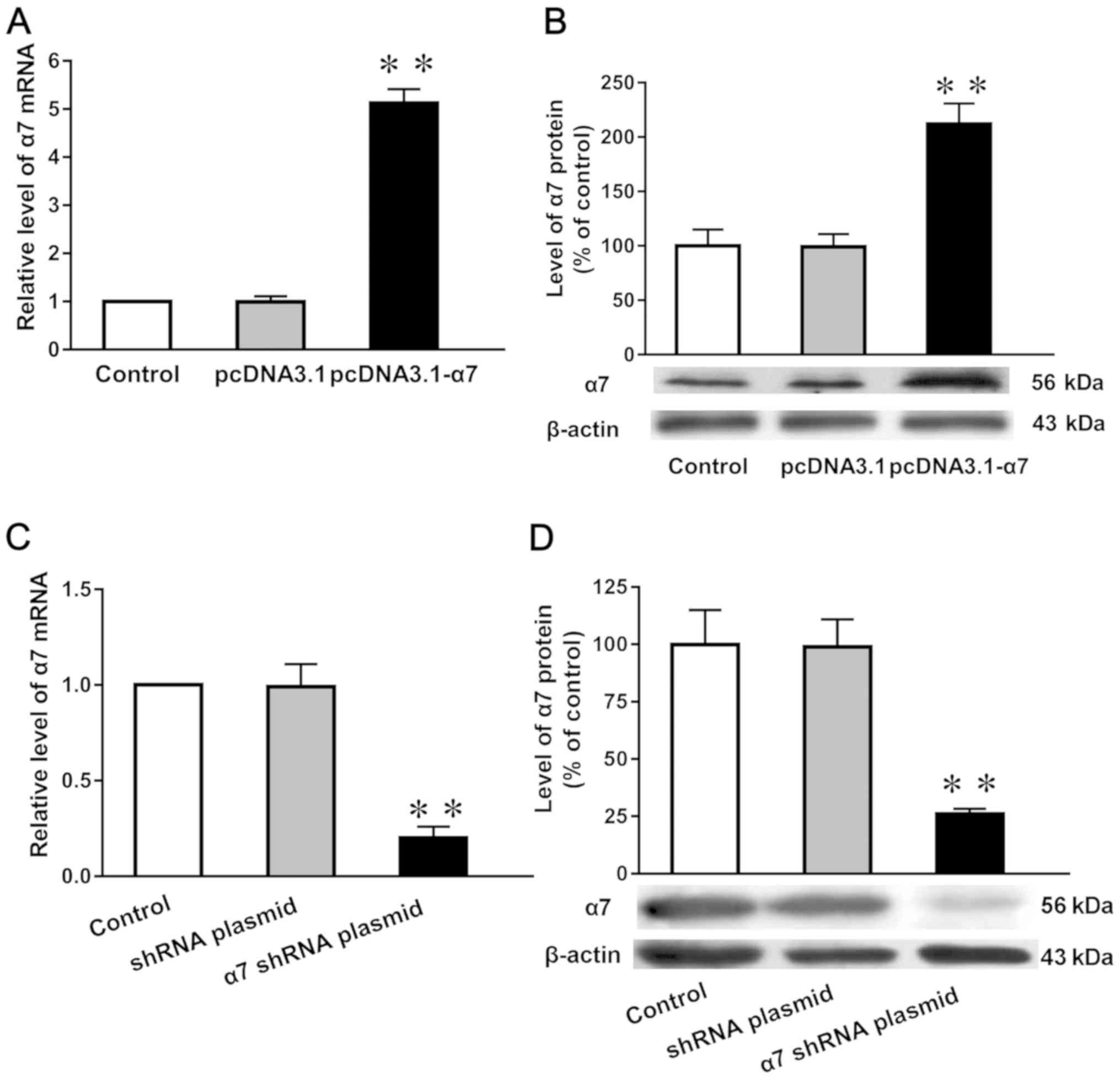
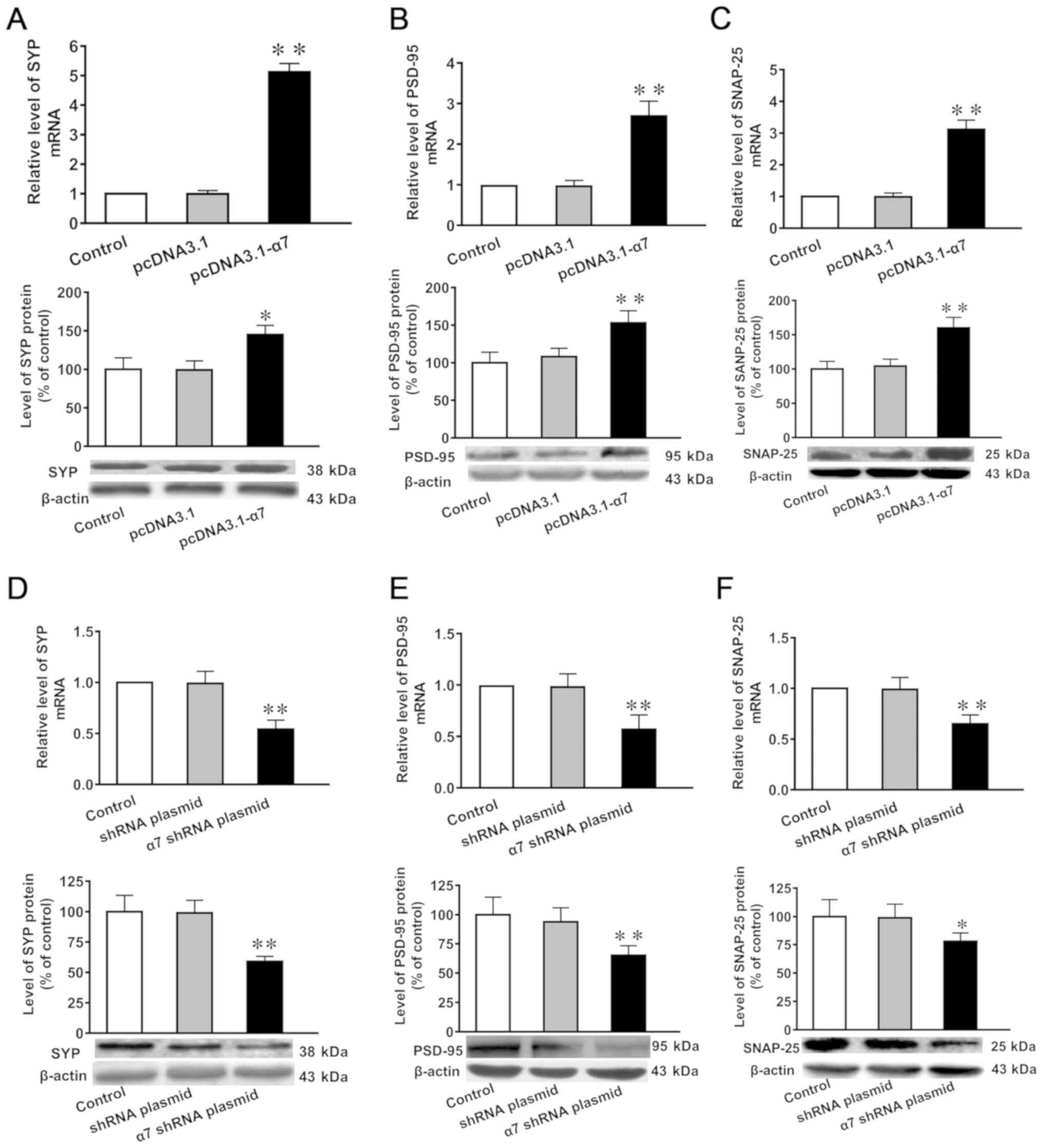
|
1
|
Bloom GS: Amyloid-β and tau: The trigger
and bullet in Alzheimer disease pathogenesis. JAMA Neurol.
71:505–508. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Amemori T, Jendelova P, Ruzicka J,
Urdzikova LM and Sykova E: Alzheimer's disease: Mechanism and
approach to cell therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 16:26417–26451. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ferreira ST, Lourenco MV, Oliveira MM and
De Felice FG: Soluble amyloid-β oligomers as synaptotoxins leading
to cognitive impairment in Alzheimer's disease. Front Cell
Neurosci. 9:1912015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Viola KL and Klein WL: Amyloid β oligomers
in Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis, treatment, and diagnosis. Acta
Neuropathol. 129:183–206. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lesné SE, Sherman MA, Grant M, Kuskowski
M, Schneider JA, Bennett DA and Ashe KH: Brain amyloid-β oligomers
in ageing and Alzheimer's disease. Brain. 136:1383–1398. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Magi S, Castaldo P, Macrì ML, Maiolino M,
Matteucci A, Bastioli G, Gratteri S, Amoroso S and Lariccia V:
Intracellular calcium dysregulation: Implications for Alzheimer's
disease. BioMed Res Int. 2016:67013242016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jagust W: Is amyloid-β harmful to the
brain? Insights from human imaging studies. Brain. 139:23–30. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Overk CR and Masliah E: Pathogenesis of
synaptic degeneration in Alzheimer's disease and Lewy body disease.
Biochem Pharmacol. 88:508–516. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sheng M, Sabatini BL and Südhof TC:
Synapses and Alzheimer's disease. Csh Perspect Biol.
4:doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a005777.
|
|
10
|
Harrill JA, Chen H, Streifel KM, Yang D,
Mundy WR and Lein PJ: Ontogeny of biochemical, morphological and
functional parameters of synaptogenesis in primary cultures of rat
hippocampal and cortical neurons. Mol Brain. 8:102015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
García-Morales V, Montero F,
González-Forero D, Rodríguez-Bey G, Gómez-Pérez L,
Medialdea-Wandossell MJ, Domínguez-Vías G, García-Verdugo JM and
Moreno-López B: Membrane-derived phospholipids control synaptic
neurotransmission and plasticity. PLoS Biol. 13:e10021532015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang DB, Kinoshita Y, Kinoshita C, Uo T,
Sopher BL, Cudaback E, Keene CD, Bilousova T, Gylys K, Case A, et
al: Loss of endophilin-B1 exacerbates Alzheimer's disease
pathology. Brain. 138:2005–2019. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Marcello E, Epis R, Saraceno C and Di Luca
M: Synaptic dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease. Adv Exp Med Biol.
970:573–601. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang DB, Kinoshita Y, Kinoshita C, Uo T,
Sopher BL, Cudaback E, Keene CD, Bilousova T, Gylys K, Case A, et
al: Loss of endophilin-B1 exacerbates Alzheimer's disease
pathology. Brain. 138:2005–2019. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sivanesan S, Tan A and Rajadas J:
Pathogenesis of Abeta oligomers in synaptic failure. Curr Alzheimer
Res. 10:316–323. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Antonucci F, Corradini I, Fossati G,
Tomasoni R, Menna E and Matteoli M: SNAP-25, a known presynaptic
protein with emerging postsynaptic functions. Front Synaptic
Neurosci. 8:72016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang J, Yuan J, Pang J, Ma J, Han B, Geng
Y, Shen L, Wang H, Ma Q, Wang Y and Wang M: Effects of chronic
stress on cognition in male SAMP8 mice. Cell Physiol Biochem.
39:1078–1086. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xi YD, Zhang DD, Ding J, Yu HL, Yuan LH,
Ma WW, Han J and Xiao R: Genistein inhibits Aβ25-35-induced
synaptic toxicity and regulates CaMKII/CREB pathway in SH-SY5Y
cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 36:1151–1159. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ito S, Ménard M, Atkinson T, Brown L,
Whitfield J and Chakravarthy B: Relative expression of the p75
neurotrophin receptor, tyrosine receptor kinase A, and insulin
receptor in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells and hippocampi from
Alzheimer's disease patients. Neurochem Int. 101:22–29. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gray NE, Zweig JA, Kawamoto C, Quinn JF
and Copenhaver PF: STX, a novel membrane estrogen receptor ligand,
protects against amyloid-β toxicity. J Alzheimers Dis. 51:391–403.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ferreira-Vieira TH, Guimaraes IM, Silva FR
and Ribeiro FM: Alzheimer's disease: Targeting the cholinergic
system. Curr Neuropharmacol. 14:101–115. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Park D, Choi EK, Cho TH, Joo SS and Kim
YB: Human neural stem cells encoding ChAT gene restore cognitive
function via acetylcholine synthesis, Aβ elimination, and
neuroregeneration in APPswe/PS1dE9 mice. Int J Mol Sci. 21:212020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Badin AS, Eraifej J and Greenfield S:
High-resolution spatio-temporal bioactivity of a novel peptide
revealed by optical imaging in rat orbitofrontal cortex in vitro:
Possible implications for neurodegenerative diseases.
Neuropharmacology. 73:10–18. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Galimberti D and Scarpini E: Old and new
acetylcholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer's disease. Expert
Opin Investig Drugs. 25:1181–1187. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fukunaga K and Yabuki Y: SAK3-induced
neuroprotection is mediated by nicotinic acetylcholine receptors.
In: Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Signaling in Neuroprotection.
Akaike A, Shimohama S and Yoshimi Misu Y: Springer; Berlin: pp.
159–171. 2018, PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hernandez CM, Kayed R, Zheng H, Sweatt JD
and Dineley KT: Loss of alpha7 nicotinic receptors enhances
beta-amyloid oligomer accumulation, exacerbating early-stage
cognitive decline and septohippocampal pathology in a mouse model
of Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci. 30:2442–2453. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gil SM and Metherate R: Enhanced
sensory-cognitive processing by activation of nicotinic
acetylcholine receptors. Nicotine Tob Res. 21:377–382. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gu Z and Yakel JL: Timing-dependent septal
cholinergic induction of dynamic hippocampal synaptic plasticity.
Neuron. 71:155–165. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lozada AF, Wang X, Gounko NV, Massey KA,
Duan J, Liu Z and Berg DK: Glutamatergic synapse formation is
promoted by α7-containing nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J
Neurosci. 32:7651–7661. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yue Y, Liu R, Cheng W, Hu Y, Li J, Pan X,
Peng J and Zhang P: GTS-21 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced
inflammatory cytokine production in vitro by modulating the Akt and
NF-κB signaling pathway through the α7 nicotinic acetylcholine
receptor. Int Immunopharmacol. 29:504–512. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tyagi E, Agrawal R, Nath C and Shukla R:
Inhibitory role of cholinergic system mediated via alpha7 nicotinic
acetylcholine receptor in LPS-induced neuro-inflammation. Innate
Immun. 16:3–13. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liao Y, Qi XL, Cao Y, Yu WF, Ravid R,
Winblad B, Pei JJ and Guan ZZ: Elevations in the levels of NF-κB
and inflammatory chemotactic factors in the brains with Alzheimer's
disease - One mechanism may involve α3 nicotinic acetylcholine
receptor. Curr Alzheimer Res. 13:1290–1301. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Domínguez-Álvaro M, Montero-Crespo M,
Blazquez-Llorca L, Insausti R, DeFelipe J and Alonso-Nanclares L:
Three-dimensional analysis of synapses in the transentorhinal
cortex of Alzheimer's disease patients. Acta Neuropathol Commun.
6:202018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bauwens M, Mottaghy FM and Bucerius J: PET
imaging of the human nicotinic cholinergic pathway in
atherosclerosis. Curr Cardiol Rep. 17:672015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dubois B, Feldman HH, Jacova C, Dekosky
ST, Barberger-Gateau P, Cummings J, Delacourte A, Galasko D,
Gauthier S, Jicha G, et al: Research criteria for the diagnosis of
Alzheimer's disease: Revising the NINCDS-ADRDA criteria. Lancet
Neurol. 6:734–746. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman
R, Price D and Stadlan EM: Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's
disease: Report of the NINCDS-ADRDA work group under the auspices
of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on
Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 34:939–944. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Reisberg B, Ferris SH, de Leon MJ and
Crook T: The Global Deterioration Scale for assessment of primary
degenerative dementia. Am J Psychiatry. 139:1136–1139. 1982.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang XL, Deng YX, Gao YM, Dong YT, Wang F,
Guan ZZ, Wei H and Qi XL: Activation of α7 nAChR by PNU-282987
improves synaptic and cognitive functions through restoring the
expression of synaptic-associated proteins and the CaM-CaMKII-CREB
signaling pathway. Aging (Albany NY). 12:543–570. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Dunant Y and Gisiger V: Ultrafast and slow
cholinergic transmission. Different involvement of
acetylcholinesterase molecular forms. Molecules. 22:13002017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Dani JA and Bertrand D: Nicotinic
acetylcholine receptors and nicotinic cholinergic mechanisms of the
central nervous system. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 47:699–729.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Albiñana E, Luengo JG, Baraibar AM, Muñoz
MD, Gandía L, Solís JM and Hernández-Guijo JM: Choline induces
opposite changes in pyramidal neuron excitability and synaptic
transmission through a nicotinic receptor-independent process in
hippocampal slices. Pflugers Arch. 469:779–795. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Huang M, Felix AR, Kwon S, Lowe D, Wallace
T, Santarelli L and Meltzer HY: The alpha-7 nicotinic receptor
partial agonist/5-HT3 antagonist RG3487 enhances cortical and
hippocampal dopamine and acetylcholine release. Psychopharmacology
(Berl). 231:2199–2210. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Stoiljkovic M, Kelley C, Nagy D, Hurst R
and Hajós M: Activation of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
facilitates long-term potentiation at the hippocampal-prefrontal
cortex synapses in vivo. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 26:2018–2023.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lagostena L, Trocme-Thibierge C, Morain P
and Cherubini E: The partial alpha7 nicotine acetylcholine receptor
agonist S 24795 enhances long-term potentiation at CA3-CA1 synapses
in the adult mouse hippocampus. Neuropharmacology. 54:676–685.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Inestrosa NC, Godoy JA, Vargas JY,
Arrazola MS, Rios JA, Carvajal FJ, Serrano FG and Farias GG:
Nicotine prevents synaptic impairment induced by amyloid-β
oligomers through α7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor activation.
Neuromolecular Med. 15:549–569. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Counts SE, Nadeem M, Lad SP, Wuu J and
Mufson EJ: Differential expression of synaptic proteins in the
frontal and temporal cortex of elderly subjects with mild cognitive
impairment. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 65:592–601. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Cao Y, Xiao Y, Ravid R and Guan ZZ:
Changed clathrin regulatory proteins in the brains of Alzheimer's
disease patients and animal models. J Alzheimers Dis. 22:329–342.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Carvalho C, Santos MS, Oliveira CR and
Moreira PI: Alzheimer's disease and type 2 diabetes-related
alterations in brain mitochondria, autophagy and synaptic markers.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1852:1665–1675. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ferreira ST and Klein WL: The Aβ oligomer
hypothesis for synapse failure and memory loss in Alzheimer's
disease. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 96:529–543. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Tu S, Okamoto S, Lipton SA and Xu H:
Oligomeric Aβ-induced synaptic dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease.
Mol Neurodegener. 9:482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wang S, Yu L, Yang H, Li C, Hui Z, Xu Y
and Zhu X: Oridonin attenuates synaptic loss and cognitive deficits
in an Aβ1-42-induced mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. PLoS One.
11:e01513972016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Liu SJ, Yang C, Zhang Y, Su RY, Chen JL,
Jiao MM, Chen HF, Zheng N, Luo S, Chen YB, et al: Neuroprotective
effect of β-asarone against Alzheimer's disease: Regulation of
synaptic plasticity by increased expression of SYP and GluR1. Drug
Des Devel Ther. 10:1461–1469. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Chauhan NB, Lichtor T and Siegel GJ: Aging
potentiates Abeta-induced depletion of SNAP-25 in mouse
hippocampus. Brain Res. 982:219–227. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Qi XL, Nordberg A, Xiu J and Guan ZZ: The
consequences of reducing expression of the alpha7 nicotinic
receptor by RNA interference and of stimulating its activity with
an alpha7 agonist in SH-SY5Y cells indicate that this receptor
plays a neuroprotective role in connection with the pathogenesis of
Alzheimer's disease. Neurochem Int. 51:377–383. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|