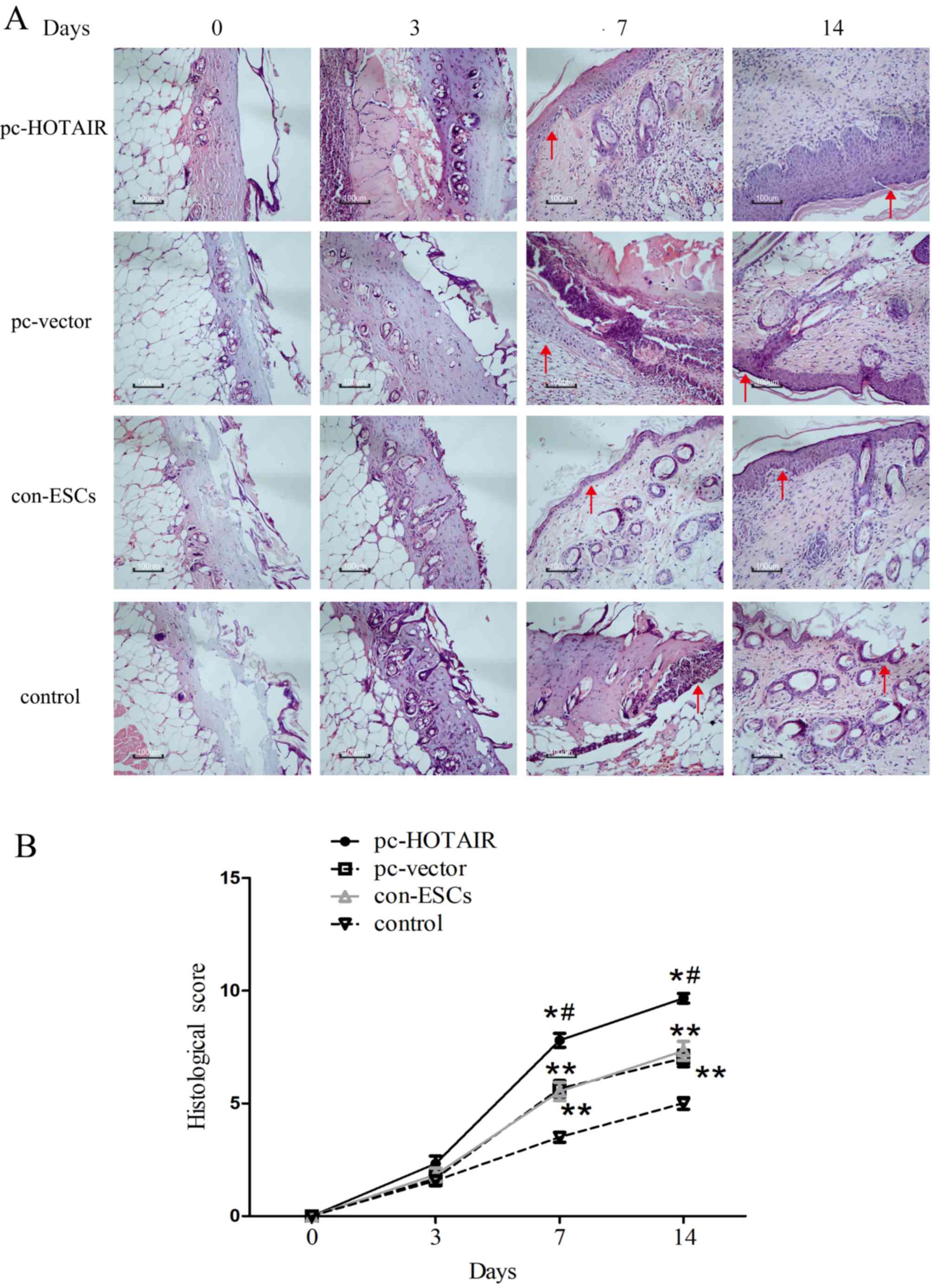
|
1
|
Xiao-Wu W, Herndon DN, Spies M, Sanford AP
and Wolf SE: Effects of delayed wound excision and grafting in
severely burned children. Arch Surg. 137:1049–1054. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kirn DS and Luce EA: Early excision and
grafting versus conservative management of burns in the elderly.
Plast Reconstr Surg. 102:1013–1017. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Saaiq M, Zaib S and Ahmad S: Early
excision and grafting versus delayed excision and grafting of deep
thermal burns up to 40% total body surface area: A comparison of
outcome. Ann Burns Fire Disasters. 25:143–147. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ong YS, Samuel M and Song C: Meta-analysis
of early excision of burns. Burns. 32:145–150. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang P, Hu Z, Cao X, Huang S, Dong Y,
Cheng P, Xu H, Shu B, Xie J, Wu J, et al: Fibronectin precoating
wound bed enhances the therapeutic effects of autologous epidermal
basal cell suspension for full-thickness wounds by improving
epidermal stem cells' utilization. Stem Cell Res Ther. 10:1542019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen L, Tredget EE, Wu PY and Wu Y:
Paracrine factors of mesenchymal stem cells recruit macrophages and
endothelial lineage cells and enhance wound healing. PLoS One.
3:e18862008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Elman JS, Li M, Wang F, Gimble JM and
Parekkadan B: A comparison of adipose and bone marrow-derived
mesenchymal stromal cell secreted factors in the treatment of
systemic inflammation. J Inflamm (Lond). 11:12014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Aberdam D: Derivation of keratinocyte
progenitor cells and skin formation from embryonic stem cells. Int
J Dev Biol. 48:203–206. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang R, Wang J, Zhou Z, Qi S, Ruan S, Lin
Z, Xin Q, Lin Y, Chen X and Xie J: Curcumin promotes burn wound
healing in mice by upregulating caveolin-1 in epidermal stem cells.
Phytother Res. 33:422–430. 2019. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang R, Wang J, Zhou Z, Qi S, Ruan S, Lin
Z, Xin Q, Lin Y, Chen X and Xie J: Role of caveolin-1 in epidermal
stem cells during burn wound healing in rats. Dev Biol.
445:271–279. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang P, Shu B, Xu Y, Zhu J, Liu J, Zhou Z,
Chen L, Zhao J, Liu X, Qi S, et al: Basic fibroblast growth factor
reduces scar by inhibiting the differentiation of epidermal stem
cells to myofibroblasts via the Notch1/Jagged1 pathway. Stem Cell
Res Ther. 8:1142017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu AY, True LD, LaTray L, Nelson PS,
Ellis WJ, Vessella RL, Lange PH, Hood L and van den Engh G:
Cell-cell interaction in prostate gene regulation and
cytodifferentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:10705–10710. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Szabo AZ, Fong S, Yue L, Zhang K, Strachan
LR, Scalapino K, Mancianti ML and Ghadially R: The CD44+ ALDH+
population of human keratinocytes is enriched for epidermal stem
cells with long-term repopulating ability. Stem Cells. 31:786–799.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Barnes L, Ino F, Jaunin F, Saurat JH and
Kaya G: Inhibition of putative hyalurosome platform in
keratinocytes as a mechanism for corticosteroid-induced epidermal
atrophy. J Invest Dermatol. 133:1017–1026. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Barnes L, Saurat JH and Kaya G: Senescent
atrophic epidermis retains Lrig1+ stem cells and loses Wnt
signaling, a phenotype shared with CD44KO mice. PLoS One.
12:e01694522017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang RH, Qi SH, Shu B, Ruan SB, Lin ZP,
Lin Y, Shen R, Zhang FG, Chen XD and Xie JL: Epidermal stem cells
(ESCs) accelerate diabetic wound healing via the Notch signalling
pathway. Biosci Rep. 36:e003642016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhao X, Wang F and Hou M: Expression of
stem cell markers nanog and PSCA in gastric cancer and its
significance. Oncol Lett. 11:442–448. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Da Sacco L, Baldassarre A and Masotti A:
Bioinformatics tools and novel challenges in long non-coding RNAs
(lncRNAs) functional analysis. Int J Mol Sci. 13:97–114. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Flynn RA and Chang HY: Long noncoding RNAs
in cell-fate programming and reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell.
14:752–761. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Si Y, Bai J, Wu J, Li Q, Mo Y, Fang R and
Lai W: lncRNA PlncRNA-1 regulates proliferation and differentiation
of hair follicle stem cells through TGF-β1-mediated Wnt/β-catenin
signal pathway. Mol Med Rep. 17:1191–1197. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tian X, Tian J, Tang X, Ma J and Wang S:
Long non-coding RNAs in the regulation of myeloid cells. J Hematol
Oncol. 9:992016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li J and Sen GL: Post-transcriptional
mechanisms regulating epidermal stem and progenitor cell
self-renewal and differentiation. J Invest Dermatol. 136:746–752.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tanis SEJ, Köksal ES, van Buggenum JAGL
and Mulder KW: BLNCR is a long non-coding RNA adjacent to integrin
beta-1 that is rapidly lost during epidermal progenitor cell
differentiation. Sci Rep. 9:312019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Somarowthu S, Legiewicz M, Chillón I,
Marcia M, Liu F and Pyle AM: HOTAIR forms an intricate and modular
secondary structure. Mol Cell. 58:353–561. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sannigrahi MK, Sharma R, Panda NK and
Khullar M: Role of non-coding RNAs in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma: A narrative review. Oral Dis. 24:1417–1427. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sand M, Bechara FG, Sand D, Gambichler T,
Hahn SA, Bromba M, Stockfleth E and Hessam S: Expression profiles
of long noncoding RNAs in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma.
Epigenomics. 8:501–518. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pádua Alves C, Fonseca AS, Muys BR, de
Barros E Lima Bueno R, Burger MC, de Souza JE, Valente V, Zago MA
and Silva WA Jr: Brief report: The lncRNA Hotair is required for
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stemness maintenance of
cancer cell lines. Stem Cells. 31:2827–2832. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sorensen KP, Thomassen M, Tan Q, Bak M,
Cold S, Burton M, Larsen MJ and Kruse TA: Long non-coding RNA
HOTAIR is an independent prognostic marker of metastasis in
estrogen receptor-positive primary breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 142:529–536. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu T, Zhang H, Zheng J, Lin J, Huang Y,
Chen J, Yu Z, Guo L, Pan W, Xiong Y and Chen C: SPION-mediated
miR-141 promotes the differentiation of HuAESCs into dopaminergic
neuron-like cells via suppressing lncRNA-HOTAIR. J Cell Mol Med.
22:2299–2310. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gao S, Zhou B, Li H, Huang X, Wu Y, Xing
C, Yu X and Ji Y: Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR promotes the
self-renewal of leukemia stem cells through epigenetic silencing of
p15. Exp Hematol. 67:32–40 e3. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu G and Zhang W: Long non-coding RNA
HOTAIR promotes UVB-induced apoptosis and inflammatory injury by
up-regulation of PKR in keratinocytes. Braz J Med Biol Res.
51:e68962018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals. (8th). (Washington, (DC)). National Academies Press (US).
2011.
|
|
33
|
Zhu H, Wei X, Bian K and Murad F: Effects
of nitric oxide on skin burn wound healing. J Burn Care Res.
29:804–814. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Calum H, Høiby N and Moser C: Burn mouse
models. Methods Mol Biol. 1149:793–802. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu Z, Xu Y, Chen L, Xie J, Tang J, Zhao
J, Shu B, Qi S, Chen J, Liang G, et al: Dendritic epidermal T cells
facilitate wound healing in diabetic mice. Am J Transl Res.
8:2375–2384. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shi Y, Shu B, Yang R, Xu Y, Xing B, Liu J,
Chen L, Qi S, Liu X, Wang P, et al: Wnt and Notch signaling pathway
incolved in wound healing by targeting c-Myc and Hes1 separately.
Stem Cell Res Ther. 6:1202015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bendiks L, Geiger F, Gudermann T, Feske S
and Dietrich A: Store-operated Ca2+ entry in primary
murine lung fibroblasts is independent of classical transient
receptor potential (TRPC) channels and contributes to cell
migration. Sci Rep. 10:68122020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li D, Kular L, Vij M, Herter EK, Li X,
Wang A, Chu T, Toma MA, Zhang L, Liapi E, et al: Human skin long
noncoding RNA WAKMAR1 regulates wound healing by enhancing
keratinocyte migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 116:9443–9452.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Herter EK and Xu Landén N: Non-Coding
RNAs: New players in skin wound healing. Adv Wound Care (New
Rochelle). 6:93–107. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wan DC and Wang KC: Long noncoding RNA:
Significance and potential in skin biology. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Med. 4:a0154042014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ge XS, Ma HJ, Zheng XH, Ruan HL, Liao XY,
Xue WQ, Chen YB, Zhang Y and Jia WH: HOTAIR, a prognostic factor in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, inhibits WIF-1 expression and
activates Wnt pathway. Cancer Sci. 104:1675–1682. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lin CM, Liu Y, Huang K, Chen XC, Cai BZ,
Li HH, Yuan YP, Zhang H and Li Y: Long noncoding RNA expression in
dermal papilla cells contributes to hairy gene regulation. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 453:508–514. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Rousselle P, Montmasson M and Garnier C:
Extracellular matrix contribution to skin wound
re-epithelialization. Matrix Biol 75–76. 12–26. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Gurtner GC, Werner S, Barrandon Y and
Longaker MT: Wound repair and regeneration. Nature. 453:314–321.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Jacinto A, Martinez-Arias A and Martin P:
Mechanisms of epithelial fusion and repair. Nat Cell Biol.
3:E117–E123. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Gallico GG III, O'Connor NE, Compton CC,
Kehinde O and Green H: Permanent coverage of large burn wounds with
autologous cultured human epithelium. N Engl J Med. 311:448–451.
1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Carsin H, Ainaud P, Le Bever H, Rives J,
Lakhel A, Stephanazzi J, Lambert F and Perrot J: Cultured
epithelial autografts in extensive burn coverage of severely
traumatized patients: A five year single-center experience with 30
patients. Burns. 26:379–387. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
De Luca M, Pellegrini G and Green H:
Regeneration of squamous epithelia from stem cells of cultured
grafts. Regen Med. 1:45–57. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Tumbar T, Guasch G, Greco V, Blanpain C,
Lowry WE, Rendl M and Fuchs E: Defining the epithelial stem cell
niche in skin. Science. 303:359–363. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Shao T, Hu Y, Tang W, Shen H, Yu Z and Gu
J: The long noncoding RNA HOTAIR serves as a microRNA-34a-5p sponge
to reduce nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis via a NOTCH1-mediated
mechanism. Gene. 715:1440292019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Dong C, Liu S, Lv Y, Zhang C, Gao H, Tan L
and Wang H: Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR regulates proliferation and
invasion via activating Notch signalling pathway in retinoblastoma.
J Biosci. 41:677–687. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lee M, Kim HJ, Kim SW, Park SA, Chun KH,
Cho NH, Song YS and Kim YT: The long non-coding RNA HOTAIR
increases tumour growth and invasion in cervical cancer by
targeting the Notch pathway. Oncotarget. 7:44558–44571. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Luo H, Liu WH, Liang HY, Yan HT, Lin N, Li
DY, Wang T and Tang LJ: Differentiation-inducing therapeutic effect
of Notch inhibition in reversing malignant transformation of liver
normal stem cells via MET. Oncotarget. 9:18885–18895. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Morasso MI and Tomic-Canic M: Epidermal
stem cells: The cradle of epidermal determination, differentiation
and wound healing. Biol Cell. 97:173–183. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ito M and Cotsarelis G: Is the hair
follicle necessary for normal wound healing? J Invest Dermatol.
128:1059–1061. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Garcin CL and Ansell DM: The battle of the
bulge: Re-evaluating hair follicle stem cells in wound repair. Exp
Dermatol. 26:101–104. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Chen M, Przyborowski M and Berthiaume F:
Stem cells for skin tissue engineering and wound healing. Crit Rev
Biomed Eng. 37:399–421. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Kanji S and Das H: Advances of stem cell
therapeutics in cutaneous wound healing and regeneration. Mediators
Inflamm. 2017:52179672017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Pashoutan Sarvar D, Shamsasenjan K and
Akbarzadehlaleh P: Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: New
opportunity in cell-free therapy. Adv Pharm Bull. 6:293–299. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Kaya G, Tran C, Sorg O, Hotz R, Grand D,
Carraux P, Didierjean L, Stamenkovic I and Saurat JH: Hyaluronate
fragments reverse skin atrophy by a CD44-dependent mechanism. PLoS
Med. 3:e4932006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kaya G and Saurat JH: Dermatoporosis: A
chronic cutaneous insufficiency/fragility syndrome.
Clinicopathological features, mechanisms, prevention and potential
treatments. Dermatology. 215:284–294. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Barnes L, Puenchera J, Saurat JH and Kaya
G: Lrig1 and CD44v3 expression in the human folliculosebaceous
unit. Dermatology. 231:116–118. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Pan S, Liu Y, Liu Q, Xiao Y, Liu B, Ren X,
Qi X, Zhou H, Zeng C and Jia L: HOTAIR/miR-326/FUT6 axis
facilitates colorectal cancer progression through regulating
fucosylation of CD44 via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Biochim Biophys
Acta Mol Cell Res. 1866:750–760. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Aragona M, Dekoninck S, Rulands S, Lenglez
S, Mascre G, Simons BD and Blanpain C: Defining stem cell dynamics
and migration during wound healing in mouse skin epidermis. Nat
Commun. 8:146842017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Dekoninck S and Blanpain C: Stem cell
dynamics, migration and plasticity during wound healing. Nat Cell
Biol. 21:18–24. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Kucharzewski M, Rojczyk E,
Wilemska-Kucharzewska K, Wilk R, Hudecki J and Los MJ: Novel trends
in application of stem cells in skin wound healing. Eur J
Pharmacol. 843:307–315. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Yang R, Liu F, Wang J, Chen X, Xie J and
Xiong K: Epidermal stem cells in wound healing and their clinical
applications. Stem Cell Res Ther. 10:2292019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|