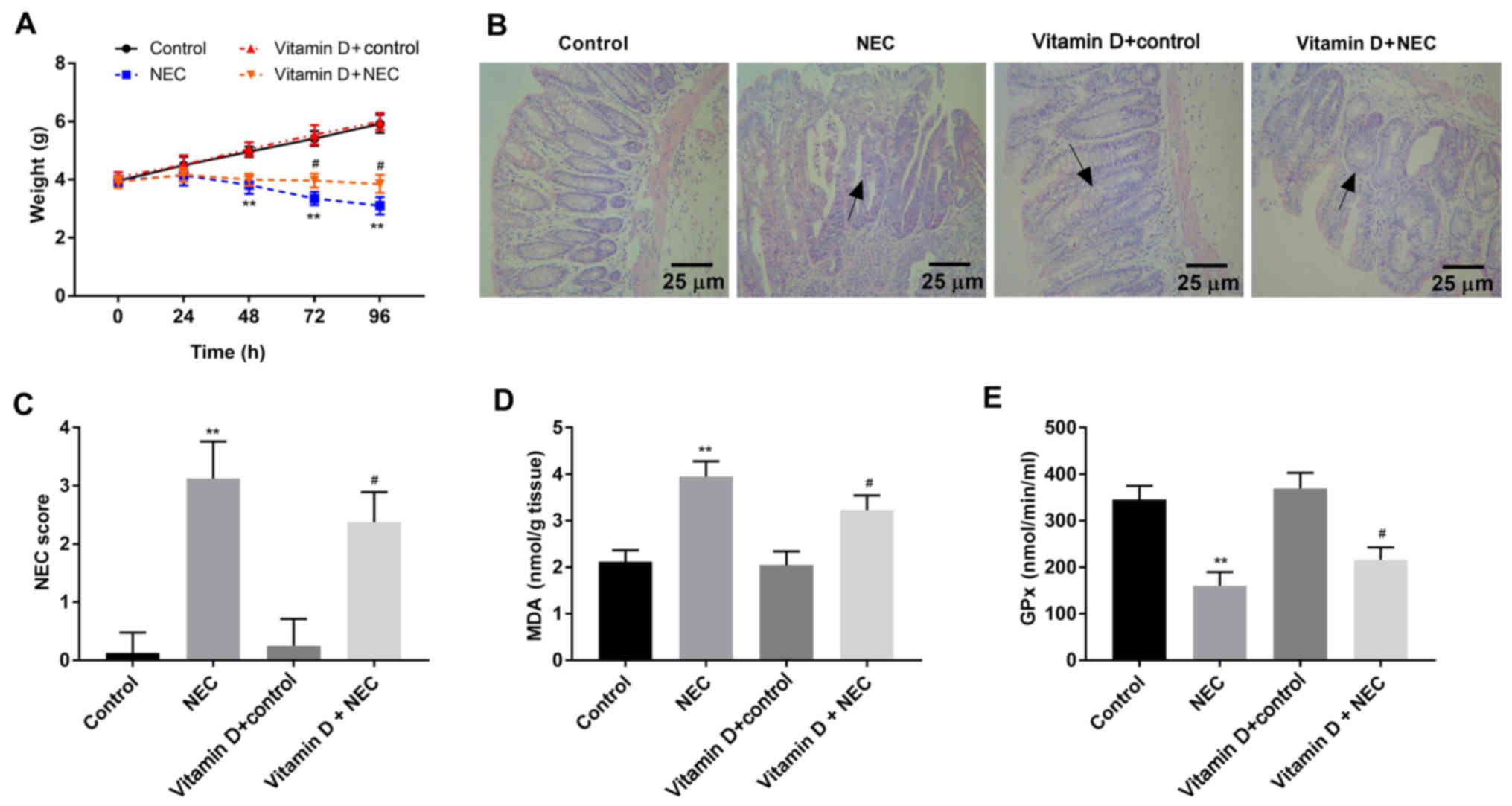
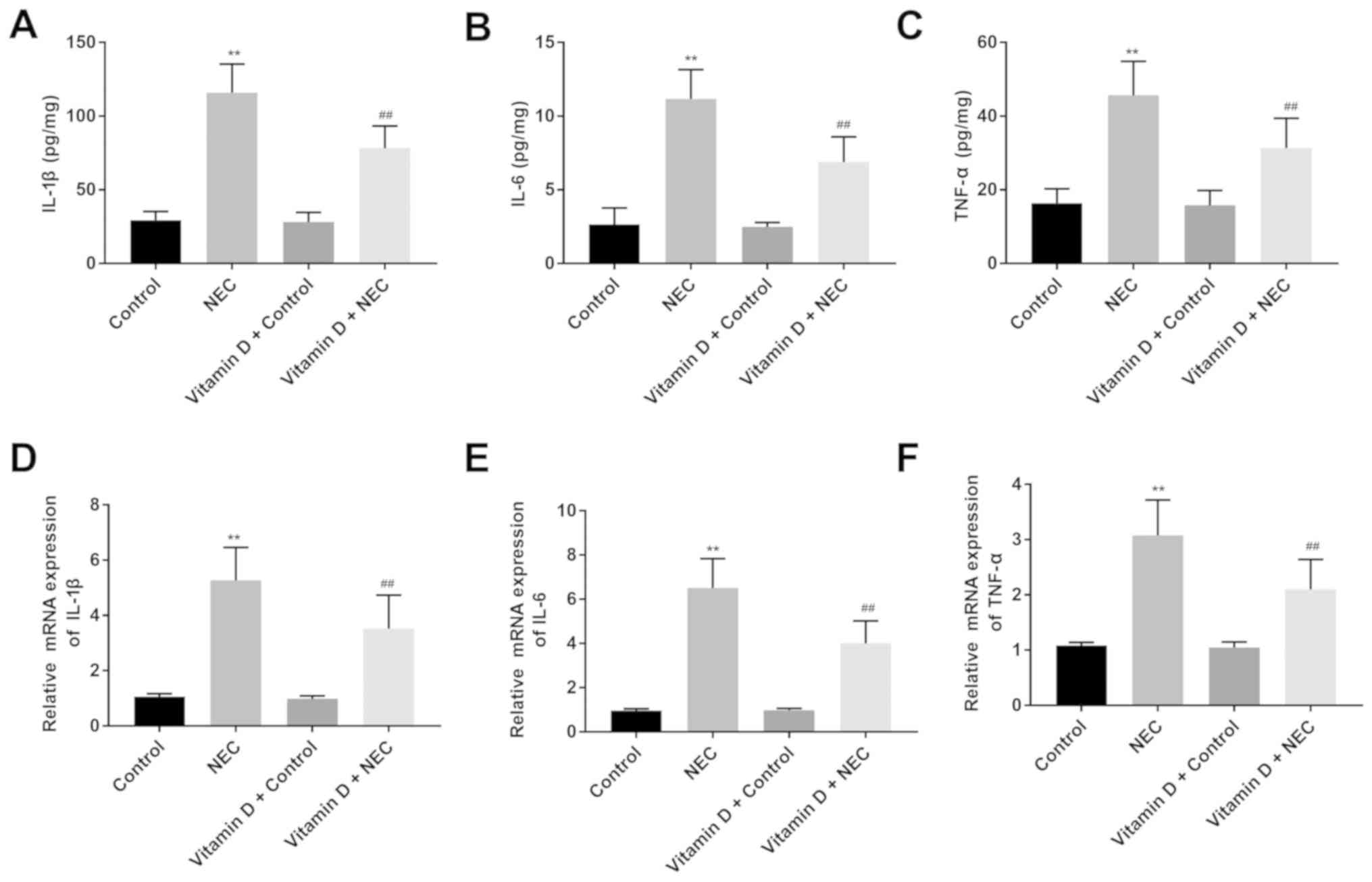
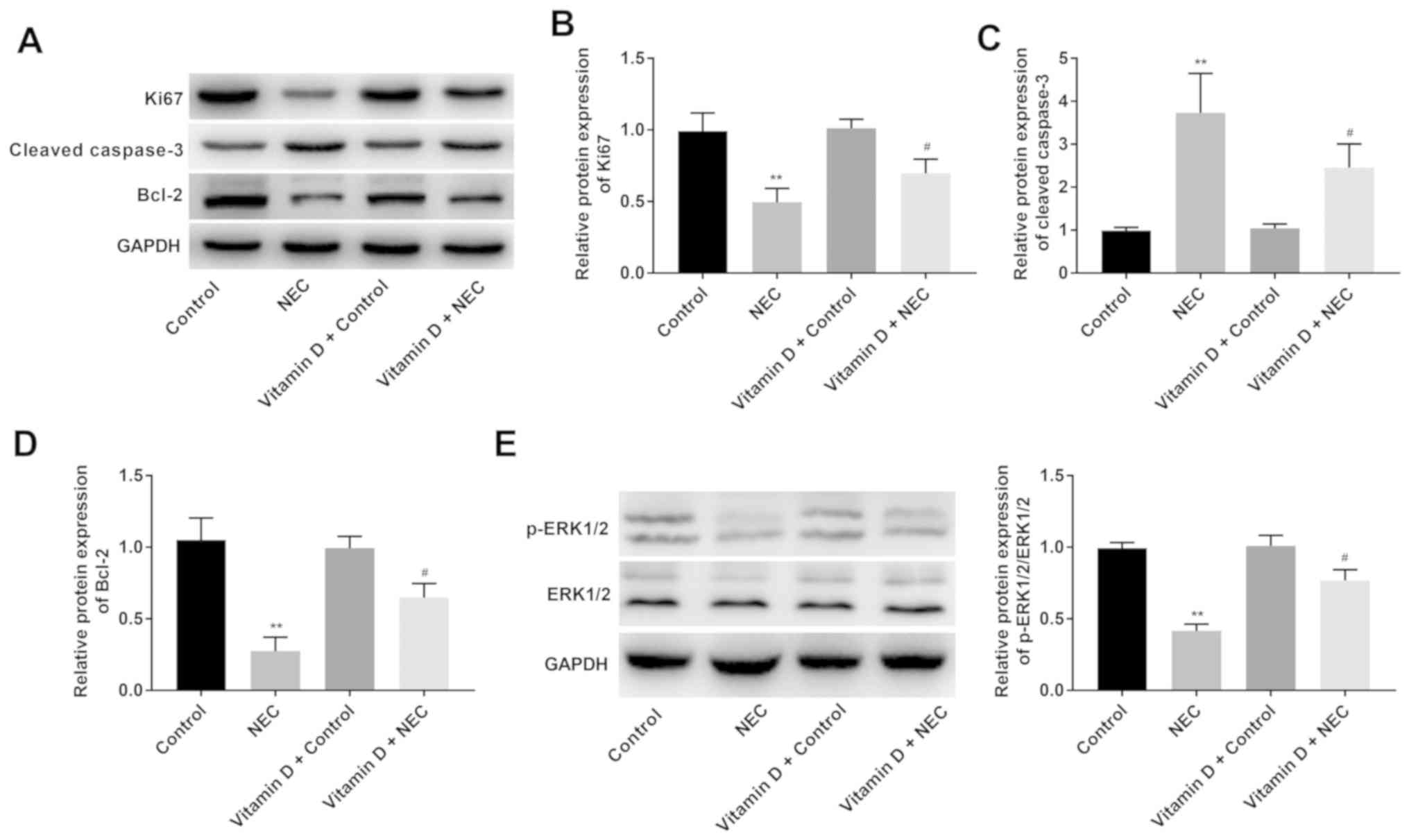
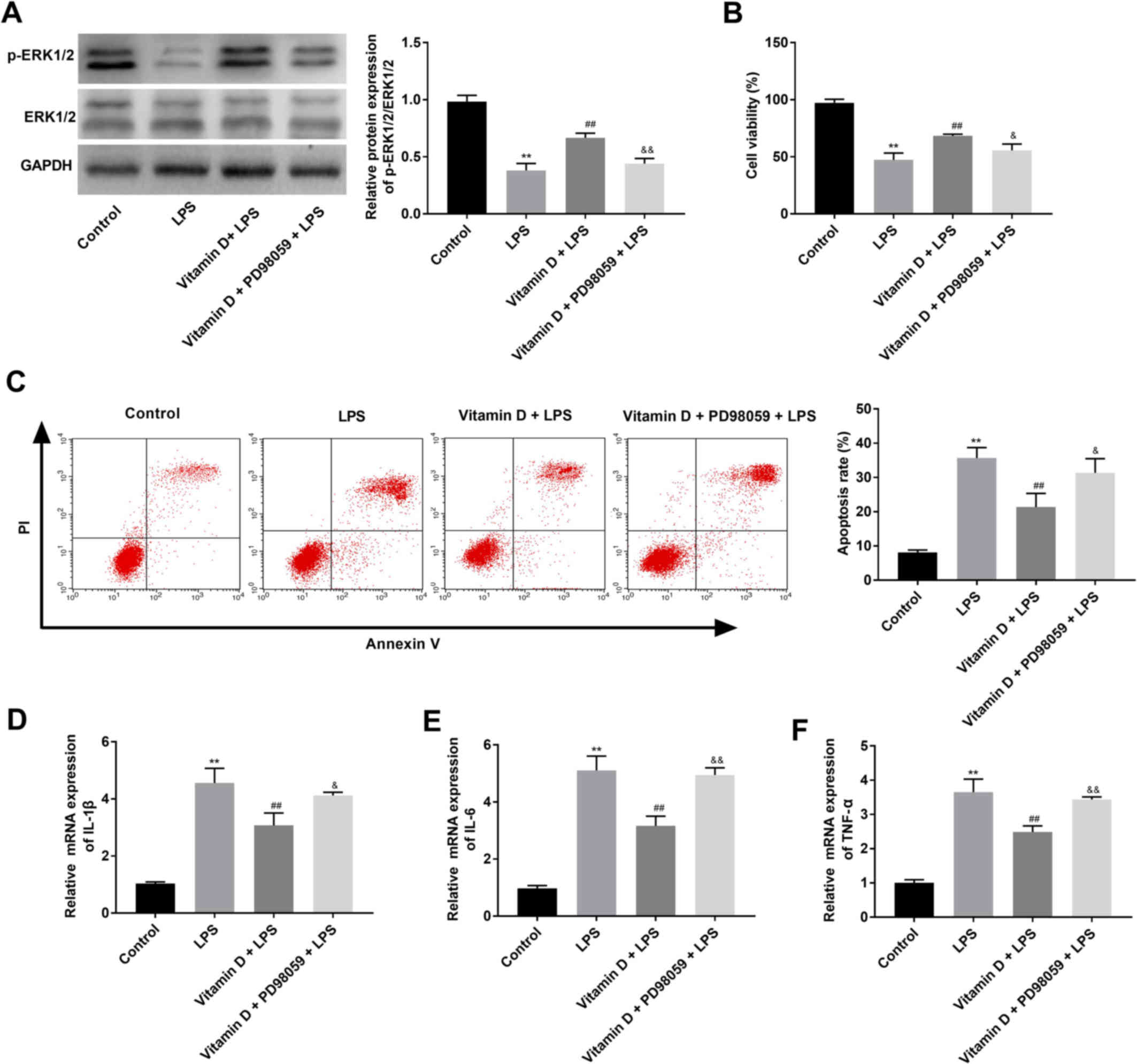
|
1
|
Neu J and Walker WA: Necrotizing
enterocolitis. N Engl J Med. 364:255–264. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Guyot D, Kuo P, Pawlotsky F, Papouin-Rauzy
M and Delbreil JP: Intestinal fistula: An unusual complication of
necrotizing enterocolitis in the preterm infant. Arch Pediatr.
16:435–438. 2009.(In French). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zangari A, Noviello C, Nobile S, Cobellis
G, Gulia C, Piergentili R, Gigli S and Carnielli V: Surgical
management of Necrotizing Enterocolitis in an Incredibly Low Birth
Weight infant and review of the Literature. Clin Ter.
168:e297–e299. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vieten D, Corfield A, Ramani P and Spicer
R: Proliferative response in necrotising enterocolitis is
insufficient to prevent disease progression. Pediatr Surg Int.
22:50–56. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Llanos AR, Moss ME, Pinzòn MC, Dye T,
Sinkin RA and Kendig JW: Epidemiology of neonatal necrotising
enterocolitis: A population-based study. Paediatr Perinat
Epidemiol. 16:342–349. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pittas AG, Harris SS, Stark PC and
Dawson-Hughes B: The effects of calcium and vitamin D
supplementation on blood glucose and markers of inflammation in
nondiabetic adults. Diabetes Care. 30:980–986. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Veldurthy V, Wei R, Oz L, Dhawan P, Jeon
YH and Christakos S: Vitamin D, calcium homeostasis and aging. Bone
Res. 4:160412016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ardesia M, Ferlazzo G and Fries W: Vitamin
D and inflammatory bowel disease. BioMed Res Int. 2015:4708052015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhu T, Liu TJ, Ge X, Kong J, Zhang LJ and
Zhao Q: High prevalence of maternal vitamin D deficiency in preterm
births in northeast China, Shenyang. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:1459–1465. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Du J, Chen Y, Shi Y, Liu T, Cao Y, Tang Y,
Ge X, Nie H, Zheng C and Li YC: 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D protects
intestinal epithelial barrier by regulating the myosin light chain
kinase signaling pathway. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 21:2495–2506. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li Q, Chen M, Liu H, Yang L, Yang T and He
G: The dual role of ERK signaling in the apoptosis of neurons.
Front Biosci. 19:1411–1417. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Wang X, Wang Y, Zhu Y, Yan L and Zhao L:
Neuroprotective effect of S-trans, trans-farnesylthiosalicylic acid
via inhibition of RAS/ERK pathway for the treatment of alzheimer's
Disease. Drug Des Devel Ther. 13:4053–4063. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dziarski R, Jin YP and Gupta D:
Differential activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase
(ERK) 1, ERK2, p38, and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase mitogen-activated
protein kinases by bacterial peptidoglycan. J Infect Dis.
174:777–785. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hu SM, Yao XH, Hao YH, Pan AH and Zhou XW:
8 Gingerol regulates colorectal cancer cell proliferation and
migration through the EGFR/STAT/ERK pathway. Int J Oncol.
56:390–397. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bai X, Gou X, Cai P, Xu C, Cao L, Zhao Z,
Huang M and Jin J: Sesamin enhances Nrf2-mediated protective
defense against oxidative stress and inflammation in colitis via
AKT and ERK activation. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019:24324162019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dai C, Zhao DH and Jiang M: VSL#3
probiotics regulate the intestinal epithelial barrier in vivo and
in vitro via the p38 and ERK signaling pathways. Int J Mol Med.
29:202–208. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bai JA, Xu GF, Yan LJ, Zeng WW, Ji QQ, Wu
JD and Tang QY: SGK1 inhibits cellular apoptosis and promotes
proliferation via the MEK/ERK/p53 pathway in colitis. World J
Gastroenterol. 21:6180–6193. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yuan J, Guo X, Liu Z, Zhao X, Feng Y, Song
S, Cui C and Jiang P: Vitamin D receptor activation influences the
ERK pathway and protects against neurological deficits and neuronal
death. Int J Mol Med. 41:364–372. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ginzel M, Feng X, Kuebler JF, Klemann C,
Yu Y, von Wasielewski R, Park JK, Hornef MW, Vieten G, Ure BM, et
al: Dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) induces necrotizing
enterocolitis-like lesions in neonatal mice. PLoS One.
12:e01827322017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu Y, Tran DQ, Fatheree NY and Marc
Rhoads J: Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 differentially modulates
effector memory T cells and Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in a mouse
model of necrotizing enterocolitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver
Physiol. 307:G177–G186. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ginzel M, Yu Y, Klemann C, Feng X, von
Wasielewski R, Park JK, Hornef MW, Torow N, Vieten G, Ure BM, et
al: The viral dsRNA analogue poly (I:C) induces necrotizing
enterocolitis in neonatal mice. Pediatr Res. 79:596–602. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wu SF, Chiu HY, Chen AC, Lin HY, Lin HC
and Caplan M: Efficacy of different probiotic combinations on death
and necrotizing enterocolitis in a premature rat model. J Pediatr
Gastroenterol Nutr. 57:23–28. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang D, Wen J, Zhou J, Cai W and Qian L:
Milk fat globule membrane ameliorates necrotizing enterocolitis in
neonatal rats and suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced
inflammatory response in IEC-6 enterocytes. JPEN J Parenter Enteral
Nutr. 43:863–873. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Maynard AA, Dvorak K, Khailova L, Dobrenen
H, Arganbright KM, Halpern MD, Kurundkar AR, Maheshwari A and
Dvorak B: Epidermal growth factor reduces autophagy in intestinal
epithelium and in the rat model of necrotizing enterocolitis. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 299:G614–G622. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhou Y, Li Y, Zhou B, Chen K, Lyv Z, Huang
D, Liu B, Xu Z, Xiang B, Jin S, et al: Inflammation and apoptosis:
dual mediator role for toll-like receptor 4 in the development of
necrotizing enterocolitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 23:44–56. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Δ Δ C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Korkut S, Özdemir A, Yay AH, Yalçın B,
Ceylan M, Korkmaz L, Yazıcı C, Güntürk İ and Kurtoğlu S: Obestatin
reduces intestinal damage in experimental necrotizing enterocolitis
in newborn rats. Am J Perinatol. 36:1179–1187. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rolnitsky A, Ng E, Asztalos E, Shama Y,
Karol D, Findlater C, Garsch M and Dunn M: A quality improvement
intervention to reduce necrotizing enterocolitis in premature
infants with probiotic supplementation. Pediatr Qual Saf.
4:e2012019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rose AT and Patel RM: A critical analysis
of risk factors for necrotizing enterocolitis. Semin Fetal Neonatal
Med. 23:374–379. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Aceti A, Beghetti I, Martini S, Faldella G
and Corvaglia L: Oxidative stress and necrotizing enterocolitis:
Pathogenetic mechanisms, opportunities for intervention, and role
of human milk. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018:73976592018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang D, Wen J, Zhou J, Cai W and Qian L:
Milk fat globule membrane ameliorates necrotizing enterocolitis in
neonatal rats and suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced
inflammatory response in IEC-6 enterocytes. JPEN J Parenter Enteral
Nutr. 43:863–873. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Klinke M, Vincent D, Trochimiuk M, Appl B,
Tiemann B, Bergholz R, Reinshagen K and Boettcher M: Degradation of
extracellular DNA significantly ameliorates necrotizing
enterocolitis severity in mice. J Surg Res. 235:513–520. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Amani R, Abbasnezhad A, Hajiani E,
Cheraghian B, Abdoli Z and Choghakhori R: Vitamin D3 induced
decrease in IL-17 and malondialdehyde, and increase in IL-10 and
total antioxidant capacity levels in patients with irritable bowel
syndrome. Iran J Immunol. 15:186–196. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Farhangi MA, Mesgari-Abbasi M, Hajiluian
G, Nameni G and Shahabi P: Adipose tissue inflammation and
oxidative stress: The ameliorative effects of vitamin D.
Inflammation. 40:1688–1697. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kühne H, Hause G, Grundmann SM,
Schutkowski A, Brandsch C and Stangl GI: Vitamin D receptor
knockout mice exhibit elongated intestinal microvilli and increased
ezrin expression. Nutr Res. 36:184–192. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Dauletbaev N, Herscovitch K, Das M, Chen
H, Bernier J, Matouk E, Bérubé J, Rousseau S and Lands LC:
Down-regulation of IL-8 by high-dose vitamin D is specific to
hyperinflammatory macrophages and involves mechanisms beyond
up-regulation of DUSP1. Br J Pharmacol. 172:4757–4771. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Holick MF: Vitamin D deficiency. N Engl J
Med. 357:266–281. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Golan MA, Liu W, Shi Y, Chen L, Wang J,
Liu T and Li YC: Transgenic expression of vitamin D receptor in gut
epithelial cells ameliorates spontaneous colitis caused by
Interleukin-10 deficiency. Dig Dis Sci. 60:1941–1947. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu Y, Chen L, Zhi C, Shen M, Sun W, Miao
D and Yuan X: 1,25(OH)2D3 deficiency induces colon inflammation via
secretion of senescence-associated inflammatory cytokines. PLoS
One. 11:e01464262016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mousavi S, Lobo de Sá FD, Schulzke JD,
Bücker R, Bereswill S and Heimesaat MM: Vitamin D in Acute
Campylobacteriosis-Results From an Intervention Study Applying a
Clinical Campylobacter jejuni Induced Enterocolitis Model. Front
Immunol. 10:20942019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu W, Chen Y, Golan MA, Annunziata ML, Du
J, Dougherty U, Kong J, Musch M, Huang Y, Pekow J, et al:
Intestinal epithelial vitamin D receptor signaling inhibits
experimental colitis. J Clin Invest. 123:3983–3996. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhu T, Liu TJ, Shi YY and Zhao Q: Vitamin
D/VDR signaling pathway ameliorates 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic
acid-induced colitis by inhibiting intestinal epithelial apoptosis.
Int J Mol Med. 35:1213–1218. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
He L, Liu T, Shi Y, Tian F, Hu H, Deb DK,
Chen Y, Bissonnette M and Li YC: Gut epithelial vitamin D receptor
regulates microbiota-dependent mucosal inflammation by suppressing
intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis. Endocrinology. 159:967–979.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ban K, Peng Z and Kozar RA: Inhibition of
ERK1/2 worsens intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury. PLoS One.
8:e767902013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Deng ZH Jr, Yan GT, Wang LH, Zhang JY, Xue
H and Zhang K: Leptin relieves intestinal ischemia/reperfusion
injury by promoting ERK1/2 phosphorylation and the NO signaling
pathway. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 72:143–149. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Jeong SJ, Choi JW, Lee MK, Choi YH and Nam
TJ: Spirulina crude protein promotes the migration and
proliferation in IEC-6 cells by activating EGFR/MAPK signaling
pathway. Mar Drugs. 17:2052019. View Article : Google Scholar
|