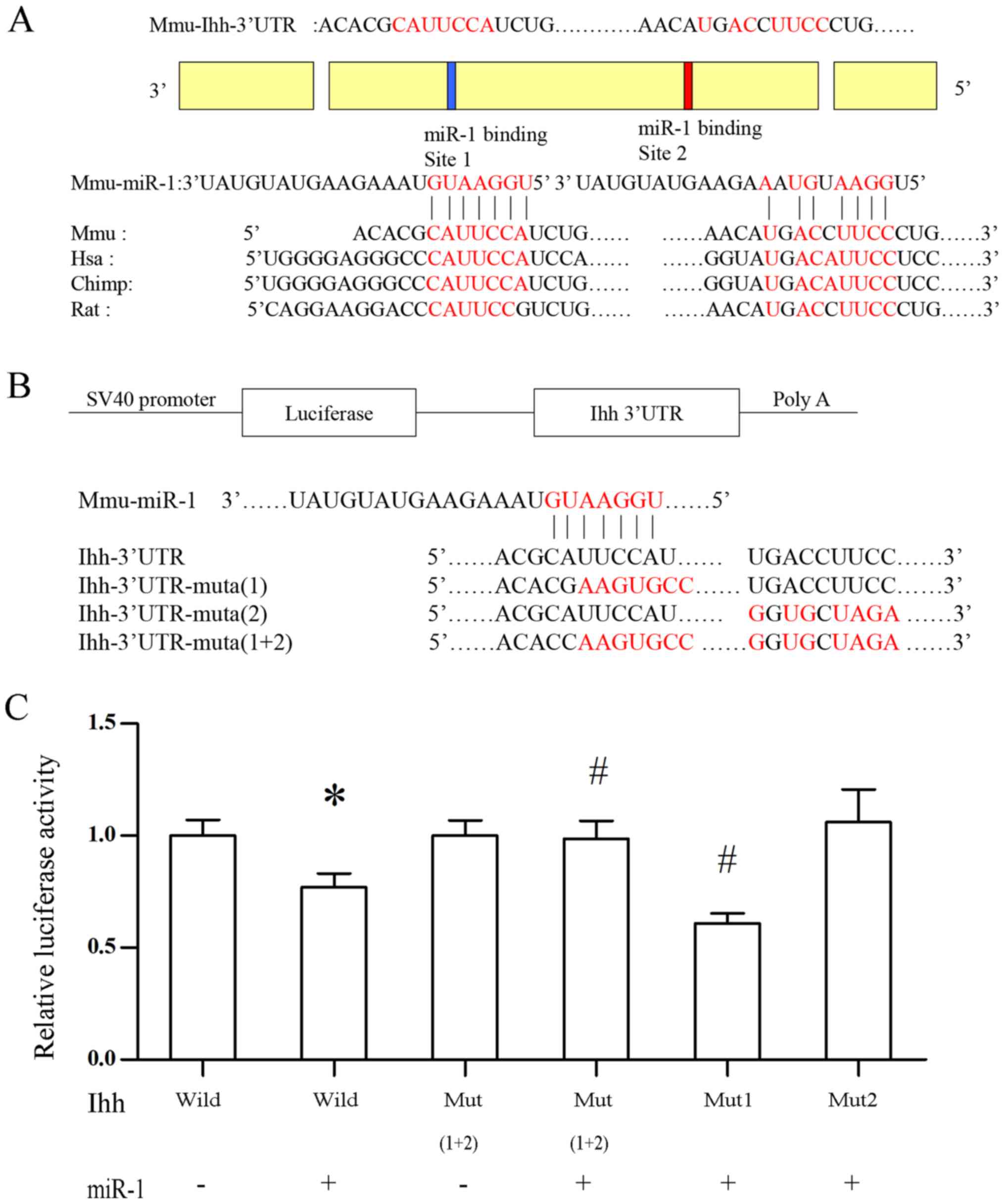
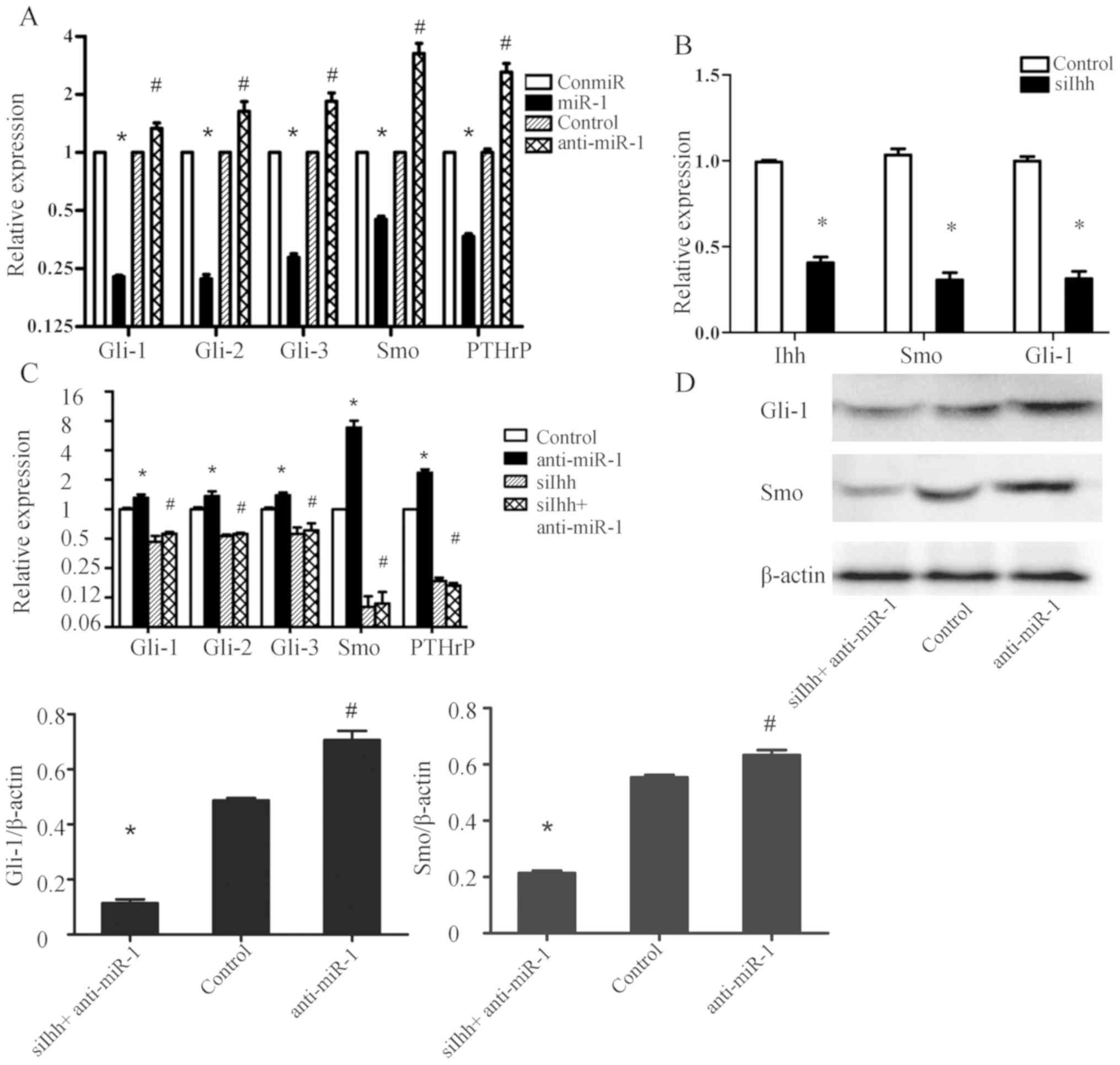
|
1
|
Rupaimoole R and Slack FJ: MicroRNA
therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and
other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 16:203–222. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bagga S, Bracht J, Hunter S, Massirer K,
Holtz J, Eachus R and Pasquinelli AE: Regulation by let-7 and lin-4
miRNAs results in target mRNA degradation. Cell. 122:553–563. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Eulalio A, Rehwinkel J, Stricker M,
Huntzinger E, Yang SF, Doerks T, Dorner S, Bork P, Boutros M and
Izaurralde E: Target-specific requirements for enhancers of
decapping in miRNA-mediated gene silencing. Genes Dev.
21:2558–2570. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Valencia-Sanchez MA, Liu J, Hannon GJ and
Parker R: Control of translation and mRNA degradation by miRNAs and
siRNAs. Genes Dev. 20:515–524. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu X, Xiao J, Zhu H, Wei X, Platt C,
Damilano F, Xiao C, Bezzerides V, Boström P, Che L, et al: miR-222
is necessary for exercise-induced cardiac growth and protects
against pathological cardiac remodeling. Cell Metab. 21:584–595.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mehta A, Mann M, Zhao JL, Marinov GK,
Majumdar D, Garcia-Flores Y, Du X, Erikci E, Chowdhury K and
Baltimore D: The microRNA-212/132 cluster regulates B cell
development by targeting Sox4. J Exp Med. 212:1679–1692. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Guay C, Kruit JK, Rome S, Menoud V, Mulder
NL, Jurdzinski A, Mancarella F, Sebastiani G, Donda A, Gonzalez BJ,
et al: Lymphocyte-derived exosomal microRNAs promote pancreatic β
cell death and may contribute to Type 1 diabetes development. Cell
Metab. 29:348–361.e6. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Singh PB, Pua HH, Happ HC, Schneider C,
von Moltke J, Locksley RM, Baumjohann D and Ansel KM: MicroRNA
regulation of type 2 innate lymphoid cell homeostasis and function
in allergic inflammation. J Exp Med. 214:3627–3643. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Valenti MT, Dalle Carbonare L and Mottes
M: Role of microRNAs in progenitor cell commitment and osteogenic
differentiation in health and disease (Review). Int J Mol Med.
41:2441–2449. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang Y, Liang Y and Lu Q: MicroRNA
epigenetic alterations: Predicting biomarkers and therapeutic
targets in human diseases. Clin Genet. 74:307–315. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Goldring MB and Marcu KB: Epigenomic and
microRNA-mediated regulation in cartilage development, homeostasis,
and osteoarthritis. Trends Mol Med. 18:109–118. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang Y, Huang X and Yuan Y: MicroRNA-410
promotes chondrogenic differentiation of human bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells through down-regulating Wnt3a. Am J Transl
Res. 9:136–145. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhao C, Miao Y, Cao Z, Shi J, Li J, Kang
F, Dou C, Xie Z, Xiang Q and Dong S: MicroRNA-29b regulates
hypertrophy of murine mesenchymal stem cells induced toward
chondrogenesis. J Cell Biochem. 120:8742–8753. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chen S, Xu Z, Shao J, Fu P and Wu H:
MicroRNA-218 promotes early chondrogenesis of mesenchymal stem
cells and inhibits later chondrocyte maturation. BMC Biotechnol.
19:62019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wüst S, Dröse S, Heidler J, Wittig I,
Klockner I, Franko A, Bonke E, Günther S, Gärtner U, Boettger T, et
al: Metabolic maturation during muscle stem cell differentiation is
achieved by miR-1/133a-mediated inhibition of the Dlk1-Dio3 Mega
gene cluster. Cell Metab. 27:1026–1039.e6. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen JF, Mandel EM, Thomson JM, Wu Q,
Callis TE, Hammond SM, Conlon FL and Wang DZ: The role of
microRNA-1 and microRNA-133 in skeletal muscle proliferation and
differentiation. Nat Genet. 38:228–233. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhao Y, Ransom JF, Li A, Vedantham V, von
Drehle M, Muth AN, Tsuchihashi T, McManus MT, Schwartz RJ and
Srivastava D: Dysregulation of cardiogenesis, cardiac conduction,
and cell cycle in mice lacking miRNA-1-2. Cell. 129:303–317. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li P, Wei X, Guan Y, Chen Q, Zhao T, Sun C
and Wei L: MicroRNA-1 regulates chondrocyte phenotype by repressing
histone deacetylase 4 during growth plate development. FASEB J.
28:3930–3941. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
J Mohler: Requirements for Hedgehog, a
segmental polarity gene, in patterning larval and adult cuticle of
drosophila. Genetics. 120:1061–1072. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jahan E, Matsumoto A, Rafiq AM, Hashimoto
R, Inoue T, Udagawa J, Sekine J and Otani H: Fetal jaw movement
affects Ihh signaling in mandibular condylar cartilage development:
The possible role of Ihh as mechanotransduction mediator. Arch Oral
Biol. 59:1108–1118. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhou J, Wei X and Wei L: Indian Hedgehog,
a critical modulator in osteoarthritis, could be a potential
therapeutic target for attenuating cartilage degeneration disease.
Connect Tissue Res. 55:257–261. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wei F, Zhou J, Wei X, Zhang J, Fleming BC,
Terek R, Pei M, Chen Q, Liu T and Wei L: Activation of Indian
hedgehog promotes chondrocyte hypertrophy and upregulation of
MMP-13 in human osteoarthritic cartilage. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
20:755–763. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ma RS, Zhou ZL, Luo JW, Zhang H and Hou
JF: The Ihh signal is essential for regulating proliferation and
hypertrophy of cultured chicken chondrocytes. Comp Biochem Physiol
B Biochem Mol Biol. 166:117–122. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen X, Macica CM, Nasiri A and Broadus
AE: Regulation of articular chondrocyte proliferation and
differentiation by indian hedgehog and parathyroid hormone-related
protein in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 58:3788–3797. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Deng A, Zhang H, Hu M, Liu S, Wang Y, Gao
Q and Guo C: The inhibitory roles of Ihh downregulation on
chondrocyte growth and differentiation. Exp Ther Med. 15:789–794.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kurio N, Saunders C, Bechtold TE, Salhab
I, Nah HD, Sinha S, Billings PC, Pacifici M and Koyama E: Roles of
Ihh signaling in chondroprogenitor function in postnatal condylar
cartilage. Matrix Biol. 67:15–31. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mirando AJ, Dong Y, Kim J and Hilton MJ:
Isolation and culture of murine primary chondrocytes. Methods Mol
Biol. 1130:267–277. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wei L, Fleming BC, Sun X, Teeple E, Wu W,
Jay GD, Elsaid KA, Luo J, Machan JT and Chen Q: Comparison of
differential biomarkers of osteoarthritis with and without
posttraumatic injury in the Hartley guinea pig model. J Orthop Res.
28:900–906. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Guan Y, Chen Q, Yang X, Haines P, Pei M,
Terek R, Wei X, Zhao T and Wei L: Subcellular relocation of histone
deacetylase 4 regulates growth plate chondrocyte differentiation
through Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase IV. Am J
Physiol Cell Physiol. 303:C33–C40. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wei L, Kanbe K, Lee M, Wei X, Pei M, Sun
X, Terek R and Chen Q: Stimulation of chondrocyte hypertrophy by
chemokine stromal cell-derived factor 1 in the chondro-osseous
junction during endochondral bone formation. Dev Biol. 341:236–245.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhou J, Chen Q, Lanske B, Fleming BC,
Terek R, Wei X, Zhang G, Wang S, Li K and Wei L: Disrupting the
Indian hedgehog signaling pathway in vivo attenuates surgically
induced osteoarthritis progression in Col2a1-CreERT2; Ihhfl/fl
mice. Arthritis Res Ther. 16:R112014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sumiyoshi K, Kubota S, Ohgawara T, Kawata
K, Nishida T, Shimo T, Yamashiro T and Takigawa M: Identification
of miR-1 as a micro RNA that supports late-stage differentiation of
growth cartilage cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 402:286–290.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Leung VY, Gao B, Leung KK, Melhado IG,
Wynn SL, Au TY, Dung NW, Lau JY, Mak AC, Chan D, et al: SOX9
governs differentiation stage-specific gene expression in growth
plate chondrocytes via direct concomitant transactivation and
repression. PLoS Genet. 7:e10023562011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|