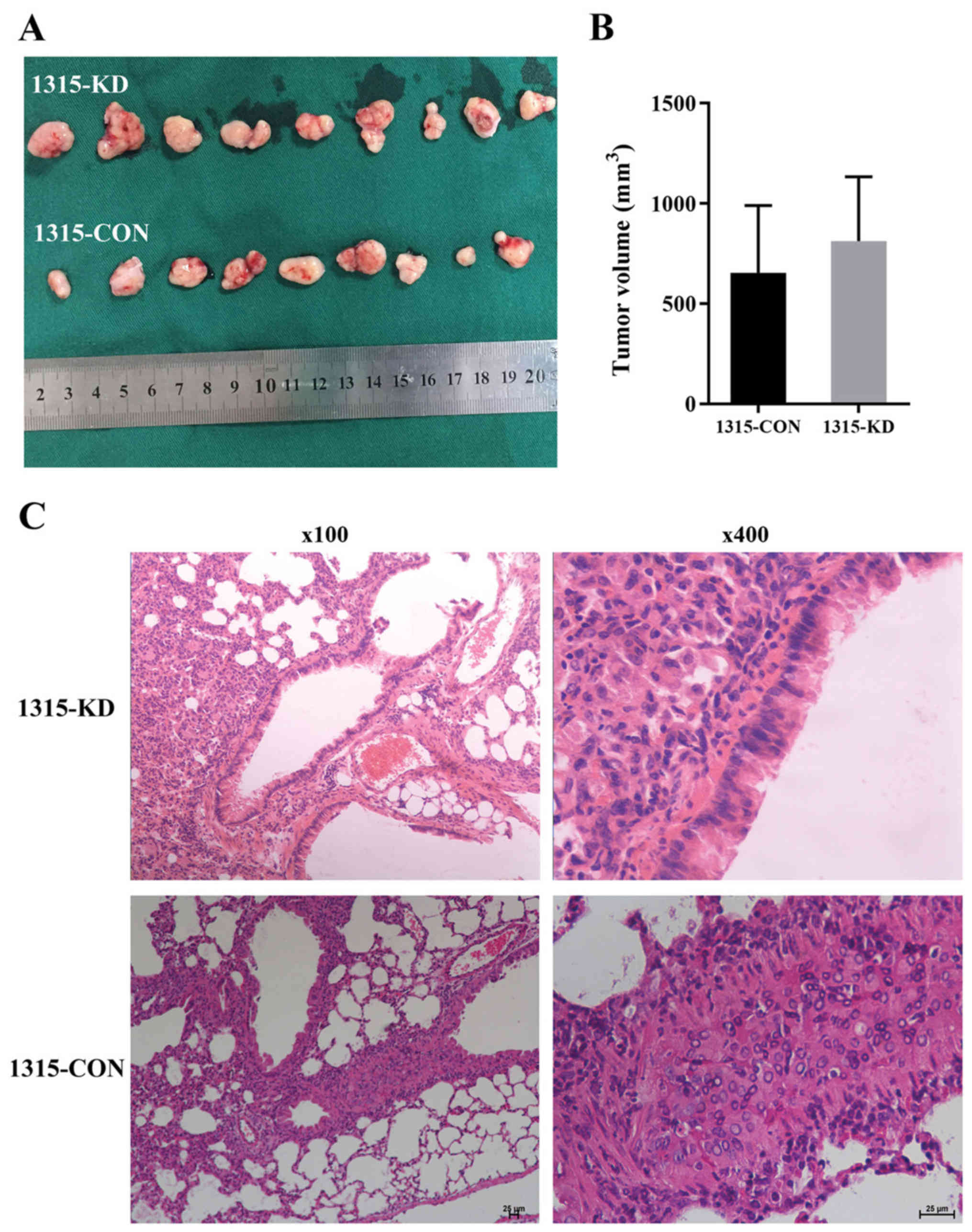
|
1
|
McGuire S: World cancer report 2014.
Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization, International
Agency for Research on cancer, WHO Press, 2015. Adv Nutr.
7:418–419. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Song QK, Li J, Huang R, Fan JH, Zheng RS,
Zhang BN, Zhang B, Tang ZH, Xie XM, Yang HJ, et al: Age of
diagnosis of breast cancer in China: Almost 10 years earlier than
in the United States and the European Union. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 15:10021–10025. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Song QK, Wang XL, Zhou XN, Yang HB, Li YC,
Wu JP, Ren J and Lyerly HK: Breast cancer challenges and screening
in China: Lessons from current registry data and population
screening studies. Oncologist. 20:773–779. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gray J and Druker B: Genomics: The breast
cancer landscape. Nature. 486:328–329. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ban KA and Godellas CV: Epidemiology of
breast cancer. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 23:409–422. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang J, Xia TS, Liu XA, Ding Q, Du Q, Yin
H and Wang S: A novel orthotopic and metastatic mouse model of
breast cancer in human mammary microenvironment. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 120:337–344. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zheng MJ, Wang J, Xu L, Zha XM, Zhao Y,
Ling LJ and Wang S: Human mammary microenvironment better regulates
the biology of human breast cancer in humanized mouse model. Med
Oncol. 32:4272015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zheng M, Wang J, Ling L, Xue D, Wang S and
Zhao Y: Screening and analysis of breast cancer genes regulated by
the human mammary microenvironment in a humanized mouse model.
Oncol Lett. 12:5261–5268. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fatica A and Tollervey D: Making
ribosomes. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 14:313–318. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xue S and Barna M: Specialized ribosomes:
A new frontier in gene regulation and organismal biology. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 13:355–369. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yong WH, Shabihkhani M, Telesca D, Yang S,
Tso JL, Menjivar JC, Wei B, Lucey GM, Mareninov S, Chen Z, et al:
Ribosomal proteins RPS11 and RPS20, two stress-response markers of
glioblastoma stem cells, are novel predictors of poor prognosis in
glioblastoma patients. PLoS One. 10:e01413342015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shi C, Wang Y, Guo Y, Chen Y and Liu N:
Cooperative down-regulation of ribosomal protein L10 and NF-κB
signaling pathway is responsible for the anti-proliferative effects
by DMAPT in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncotarget. 8:35009–35018.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Paquet ÉR, Hovington H, Brisson H, Lacombe
C, Larue H, Têtu B, Lacombe L, Fradet Y and Lebel M: Low level of
the X-linked ribosomal protein S4 in human urothelial carcinomas is
associated with a poor prognosis. Biomark Med. 9:187–197. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jung Y, Lee S, Choi HS, Kim SN, Lee E,
Shin Y, Seo J, Kim B, Jung Y, Kim WK, et al: Clinical validation of
colorectal cancer biomarkers identified from bioinformatics
analysis of public expression data. Clin Cancer Res. 17:700–709.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Russo A, Saide A, Smaldone S, Faraonio R
and Russo G: Role of uL3 in multidrug resistance in p53-mutated
lung cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 18:5472017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Fan H, Li J, Jia Y, Wu J, Yuan L, Li M,
Wei J and Xu B: Silencing of ribosomal protein L34 (RPL34) inhibits
the proliferation and invasion of esophageal cancer cells. Oncol
Res. 25:1061–1068. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sim EU, Chan SL, Ng KL, Lee CW and
Narayanan K: Human ribosomal proteins RPeL27, RPeL43, and RPeL41
are upregulated in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell lines. Dis
Markers. 2016:51795942016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang M, Sun H, Wang H, Zhang S, Yu X and
Zhang L: Down-regulation of ribosomal protein L22 in non-small cell
lung cancer. Med Oncol. 30:6462013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Maruyama Y, Miyazaki T, Ikeda K, Okumura
T, Sato W, Horie-Inoue K, Okamoto K, Takeda S and Inoue S: Short
hairpin RNA library-based functional screening identified ribosomal
protein L31 that modulates prostate cancer cell growth via p53
pathway. PLoS One. 9:e1087432014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen J, Wei Y, Feng Q, Ren L, He G, Chang
W, Zhu D, Yi T, Lin Q, Tang W, et al: Ribosomal protein S15A
promotes malignant transformation and predicts poor outcome in
colorectal cancer through misregulation of p53 signaling pathway.
Int J Oncol. 48:1628–1638. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bisaccia F, De Palma A and Palmieri F:
Identification and purification of the tricarboxylate carrier from
rat liver mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 977:171–176. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hong M, Kim H and Kim I: Ribosomal protein
L19 overexpression activates the unfolded protein response and
sensitizes MCF7 breast cancer cells to endoplasmic reticulum
stress-induced cell death. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 450:673–678.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dmitriev AA, Kashuba VI, Haraldson K,
Senchenko VN, Pavlova TV, Kudryavtseva AV, Anedchenko EA, Krasnov
GS, Pronina IV, Loginov VI, et al: Genetic and epigenetic analysis
of non-small cell lung cancer with NotI-microarrays. Epigenetics.
7:502–513. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Karan D, Kelly DL, Rizzino A, Lin MF and
Batra SK: Expression profile of differentially-regulated genes
during progression of androgen-independent growth in human prostate
cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 23:967–975. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|