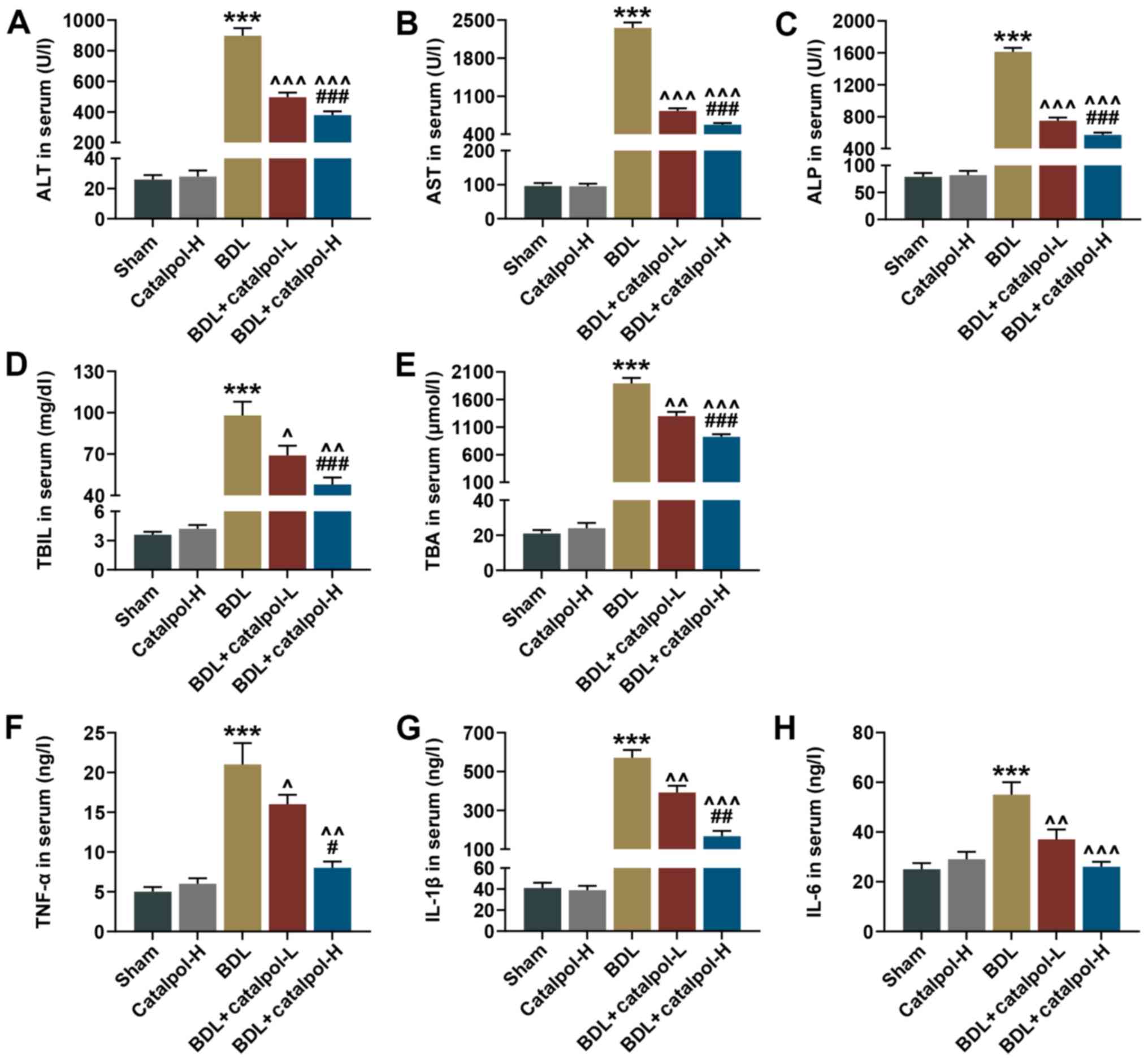
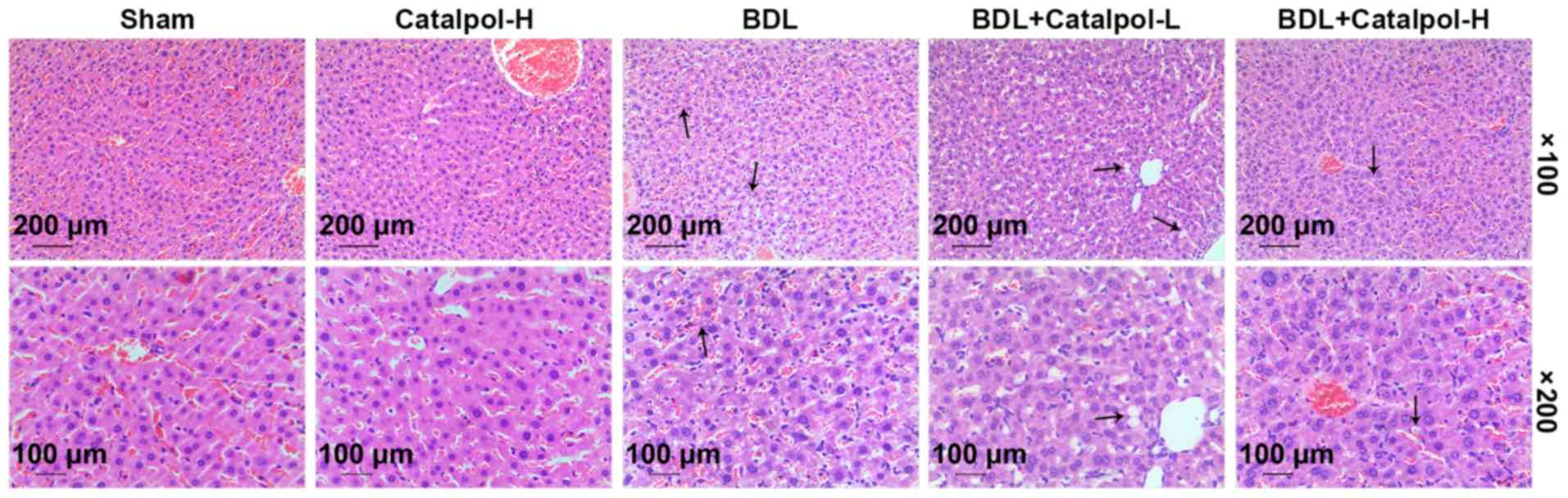
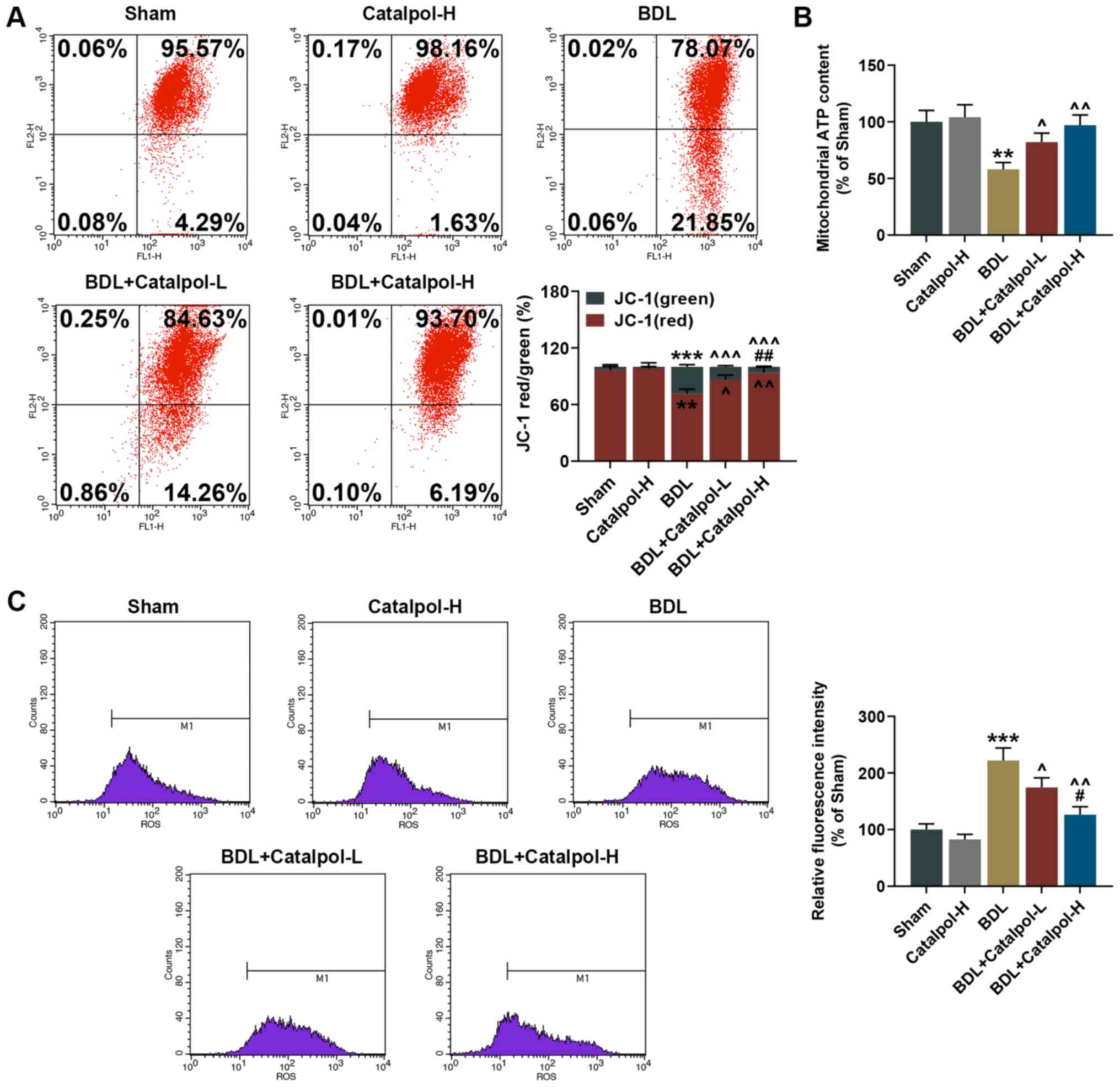
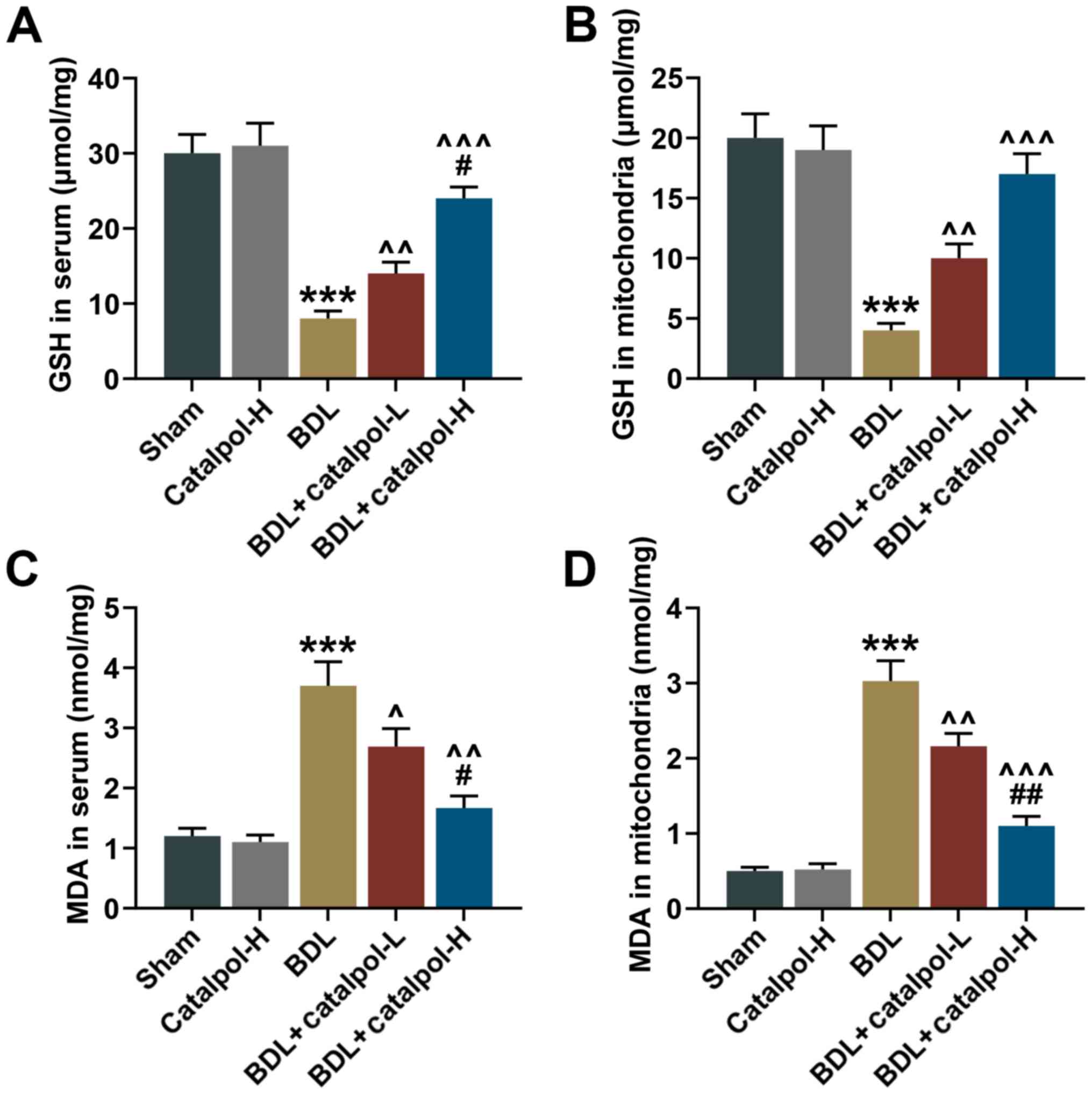
|
1
|
Afonso MB, Rodrigues PM, Simao AL,
Ofengeim D, Carvalho T, Amaral JD, Gaspar MM, Cortez-Pinto H,
Castro RE, Yuan J, et al: Activation of necroptosis in human and
experimental cholestasis. Cell Death Dis. 7:e23902016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vinken M: In vitro prediction of
drug-induced cholestatic liver injury: A challenge for the
toxicologist. Arch Toxicol. 92:1909–1912. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Squires JE and McKiernan P: Molecular
mechanisms in pediatric cholestasis. Gastroenterol Clin North Am.
47:921–937. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gomez-Ospina N, Potter CJ, Xiao R,
Manickam K, Kim MS, Kim KH, Shneider BL, Picarsic JL, Jacobson TA,
Zhang J, et al: Mutations in the nuclear bile acid receptor FXR
cause progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Nat Commun.
7:107132016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ommati MM, Farshad O, Niknahad H,
Arabnezhad MR, Azarpira N, Mohammadi HR, Haghnegahdar M, Mousavi K,
Akrami S, Jamshidzadeh A, et al: Cholestasis-associated
reproductive toxicity in male and female rats: The fundamental role
of mitochondrial impairment and oxidative stress. Toxicol Lett.
316:60–72. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yin F, Yan J, Zhao Y, Guo KJ, Zhang ZL, Li
AP, Meng CY and Guo L: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells repair Cr
(VI)-injured kidney by regulating mitochondria-mediated apoptosis
and mitophagy mediated via the MAPK signaling pathway. Ecotoxicol
Environ Saf. 176:234–241. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rajavel T, Packiyaraj P, Suryanarayanan V,
Singh SK, Ruckmani K and Pandima Devi K: β-sitosterol targets
Trx/Trx1 reductase to induce apoptosis in A549 cells via ROS
mediated mitochondrial dysregulation and p53 activation. Sci Rep.
8:20712018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhao X, Ren X, Zhu R, Luo Z and Ren B:
Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce oxidative DNA damage and
ROS-triggered mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in zebrafish embryos.
Aquat Toxicol. 180:56–70. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang LL, Han L, Ma XL, Yu QL and Zhao SN:
Effect of mitochondrial apoptotic activation through the
mitochondrial membrane permeability transition pore on yak meat
tenderness during postmortem aging. Food Chem. 234:323–331. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xia Z, Wang F, Zhou S, Zhang R, Wang F,
Huang JH, Wu E, Zhang Y and Hu Y: Catalpol protects synaptic
proteins from beta-amyloid induced neuron injury and improves
cognitive functions in aged rats. Oncotarget. 8:69303–69315. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Huang JZ, Wu J, Xiang S, Sheng S, Jiang Y,
Yang Z and Hua F: Catalpol preserves neural function and attenuates
the pathology of Alzheimer's disease in mice. Mol Med Rep.
13:491–496. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gao J, An L, Xu Y and Huang Y: Catalpol
exerts an anti-epilepticus effect, possibly by regulating the
Nrf2-Keap1-ARE signaling pathway. Med Sci Monit. 24:9436–9441.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lin CM, Wang BW, Fang WJ, Pan CM, Shyu KG
and Hou SW: Catalpol ameliorates neointimal hyperplasia in diabetic
rats. Planta Med. 85:406–411. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang H, Jia R, Wang F, Qiu G, Qiao P, Xu
X and Wu D: Catalpol protects mice against
Lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine-induced acute liver injury
through inhibiting inflammatory and oxidative response. Oncotarget.
9:3887–3894. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang Y, Wang C, Jin Y, Yang Q, Meng Q,
Liu Q, Dai Y, Cai L, Liu Z and Liu K; Sun H Activating the
PGC-1α/TERT pathway by catalpol ameliorates atherosclerosis via
modulating ROS production, DNA damage, telomere function, :
Implications on mitochondria and telomere link. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2018:28763502018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Park KS: Catalpol reduces the production
of inflammatory mediators via PPAR-gamma activation in human
intestinal Caco-2 cells. J Natural Med. 70:620–626. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
National Research Council Committee for
the Update of the Guide for the C and use of laboratory A, . The
National Academies Collection: Reports funded by National
Institutes of Health. Guide for the care and use of laboratory
Animals. National Academies Press (US) Copyright © 2011, National
Academy of Sciences. (Washington (DC)). 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cai Q, Ma T, Li C, Tian Y and Li H:
Catalpol protects Pre-myelinating oligodendrocytes against
Ischemia-induced oxidative injury through ERK1/2 signaling pathway.
Int J Biol Sci. 12:1415–1426. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xu D, Wang L, Jiang Z, Zhao G, Hassan HM,
Sun L, Fan S, Zhou Z, Zhang L and Wang T: A new hypoglycemic
mechanism of catalpol revealed by enhancing MyoD/MyoG-mediated
myogenesis. Life Sci. 209:313–323. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zeng YF, Wang R, Bian Y, Chen WS and Peng
L: Catalpol attenuates IL-1β induced matrix catabolism, apoptosis
and inflammation in rat chondrocytes and inhibits cartilage
degeneration. Med Sci Monit. 25:6649–6659. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lin C, Lu Y, Yan X, Wu X, Kuai M, Sun X,
Chen Q, Kong X, Liu Z, Tang Y, et al: Catalpol protects
glucose-deprived rat embryonic cardiac cells by inducing mitophagy
and modulating estrogen receptor. Biomed Pharmacother. 89:973–982.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sun W, Gao Y, Ding Y, Cao Y, Chen J, Lv G,
Lu J, Yu B, Peng M, Xu H, et al: Catalpol ameliorates advanced
glycation end product-induced dysfunction of glomerular endothelial
cells via regulating nitric oxide synthesis by inducible nitric
oxide synthase and endothelial nitric oxide synthase. IUBMB Life.
71:1268–1283. 2019. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ma X, Wen JX, Gao SJ, He X, Li PY, Yang
YX, Wei SZ, Zhao YL and Xiao XH: Paeonia lactiflora Pall. regulates
the NF-κB-NLRP3 inflammasome pathway to alleviate cholestasis in
rats. J Pharm Pharmacol. 70:1675–1687. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang L, Cao F, Zhu LL, Liu P, Shang YR,
Liu WH, Dong X, Bao HD, Gong P and Wang ZY: Andrographolide impairs
alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate-induced cholestatic liver injury in
vivo. J Natural Med. 73:388–396. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wagner M and Trauner M: Recent advances in
understanding and managing cholestasis. F1000Research. 5:F1000
Faculty Rev–705. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Heidari R and Niknahad H: The role and
study of mitochondrial impairment and oxidative stress in
cholestasis. Methods Mol Biol. 1981:117–132. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Baud O, Li J, Zhang Y, Neve RL, Volpe JJ
and Rosenberg PA: Nitric oxide-induced cell death in developing
oligodendrocytes is associated with mitochondrial dysfunction and
apoptosis-inducing factor translocation. Eur J Neurosci.
20:1713–1726. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Javadov S, Karmazyn M and Escobales N:
Mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening as a promising
therapeutic target in cardiac diseases. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
330:670–678. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang XL, Jiang B, Li ZB, Hao S and An LJ:
Catalpol ameliorates cognition deficits and attenuates oxidative
damage in the brain of senescent mice induced by D-galactose.
Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 88:64–72. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bi J, Wang XB, Chen L, Hao S, An LJ, Jiang
B and Guo L: Catalpol protects mesencephalic neurons against MPTP
induced neurotoxicity via attenuation of mitochondrial dysfunction
and MAO-B activity. Toxicol In Vitro. 22:1883–1889. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Riddle A, Luo NL, Manese M, Beardsley DJ,
Green L, Rorvik DA, Kelly KA, Barlow CH, Kelly JJ, Hohimer AR and
Back SA: Spatial heterogeneity in oligodendrocyte lineage
maturation and not cerebral blood flow predicts fetal ovine
periventricular white matter injury. J Neurosc. 26:3045–3055. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Xiong Y, Shi L, Wang L, Zhou Z, Wang C,
Lin Y, Luo D, Qiu J and Chen D: Activation of sirtuin 1 by
catalpol-induced down-regulation of microRNA-132 attenuates
endoplasmic reticulum stress in colitis. Pharmacol Res. 123:73–82.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Antus B: Oxidative stress markers in
sputum. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016:29304342016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shaker RA, Abboud SH, Assad HC and Hadi N:
Enoxaparin attenuates doxorubicin induced cardiotoxicity in rats
via interfering with oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis.
BMC Oharmacol Toxicol. 19:32018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Heidari R, Ghanbarinejad V, Mohammadi H,
Ahmadi A, Ommati MM, Abdoli N, Aghaei F, Esfandiari A, Azarpira N
and Niknahad H: Mitochondria protection as a mechanism underlying
the hepatoprotective effects of glycine in cholestatic mice. Biomed
Pharmacother. 97:1086–1095. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sharanek A, Burban A, Ciriaci N and
Guillouzo A: Pro-inflammatory cytokines enhance dilatation of bile
canaliculi caused by cholestatic antibiotics. Toxicol In Vitro.
58:51–59. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xu YJ, Yu ZQ, Zhang CL, Li XP, Feng CY,
Lei K, He WX and Liu D: Protective effects of ginsenosides on
17[Formula: See text]-Ethynyelstradiol-Induced intrahepatic
cholestasis via anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory mechanisms in
rats. Am J Chin Med. 45:1613–1629. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|