|
1
|
Lara-Castro C and Garvey WT: Intracellular
lipid accumulation in liver and muscle and the insulin resistance
syndrome. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 37:2932–856. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Samuel VT and Shulman GI: Mechanisms for
insulin resistance: Common threads and missing links. Cell.
148:852–871. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Di Meo S, Iossa S and Venditti P:
Improvement of obesity-linked skeletal muscle insulin resistance by
strength and endurance training. J Endocrinol. 234:R159–R181. 2017.
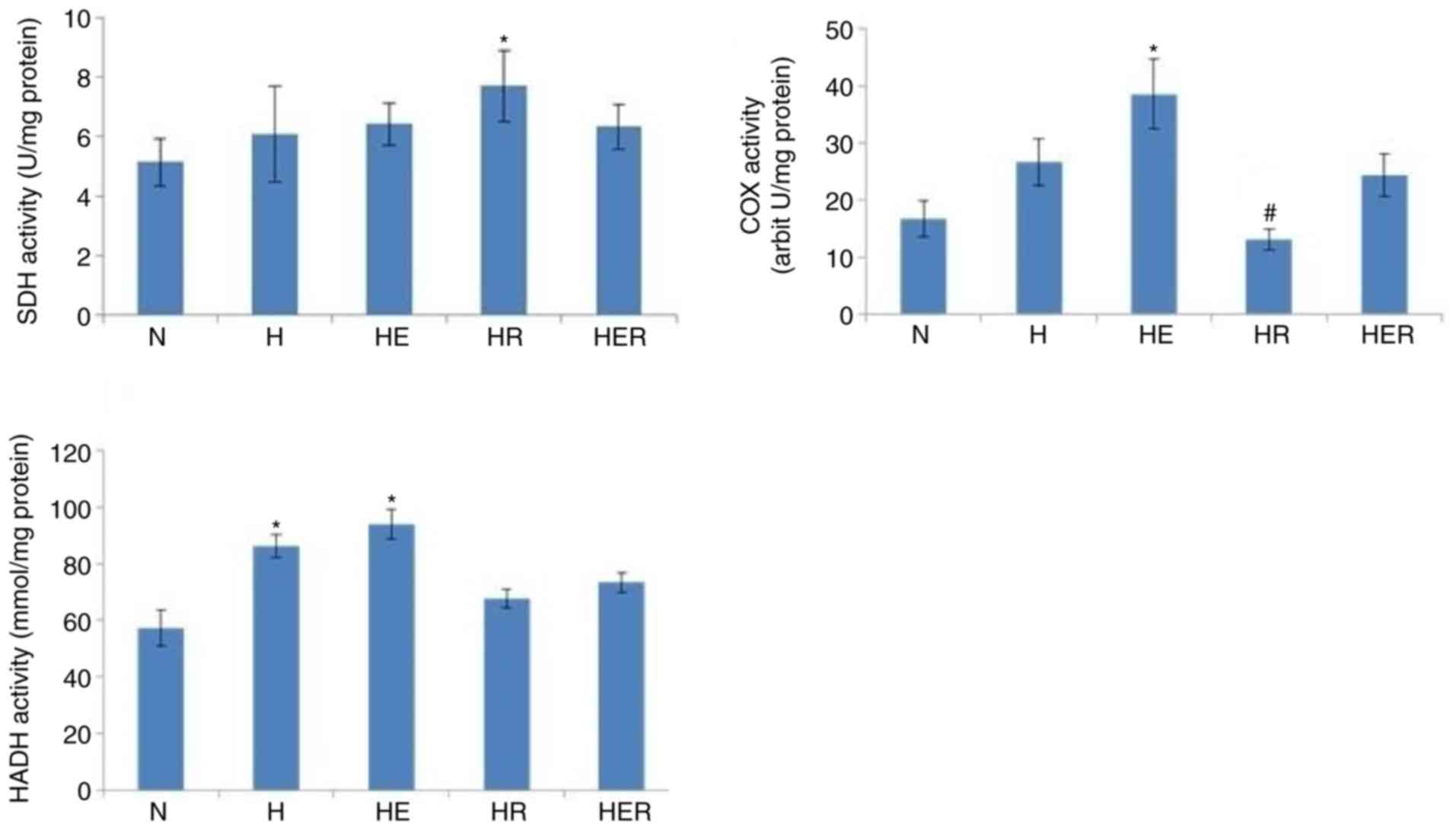
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Golabi P, Locklear CT, Austin P, Afdhal S,
Byrns M, Gerber L and Younossi ZM: Effectiveness of exercise in
hepatic fat mobilization in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease:
Systematic review. World J Gastroenterol. 22:6318–6327. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
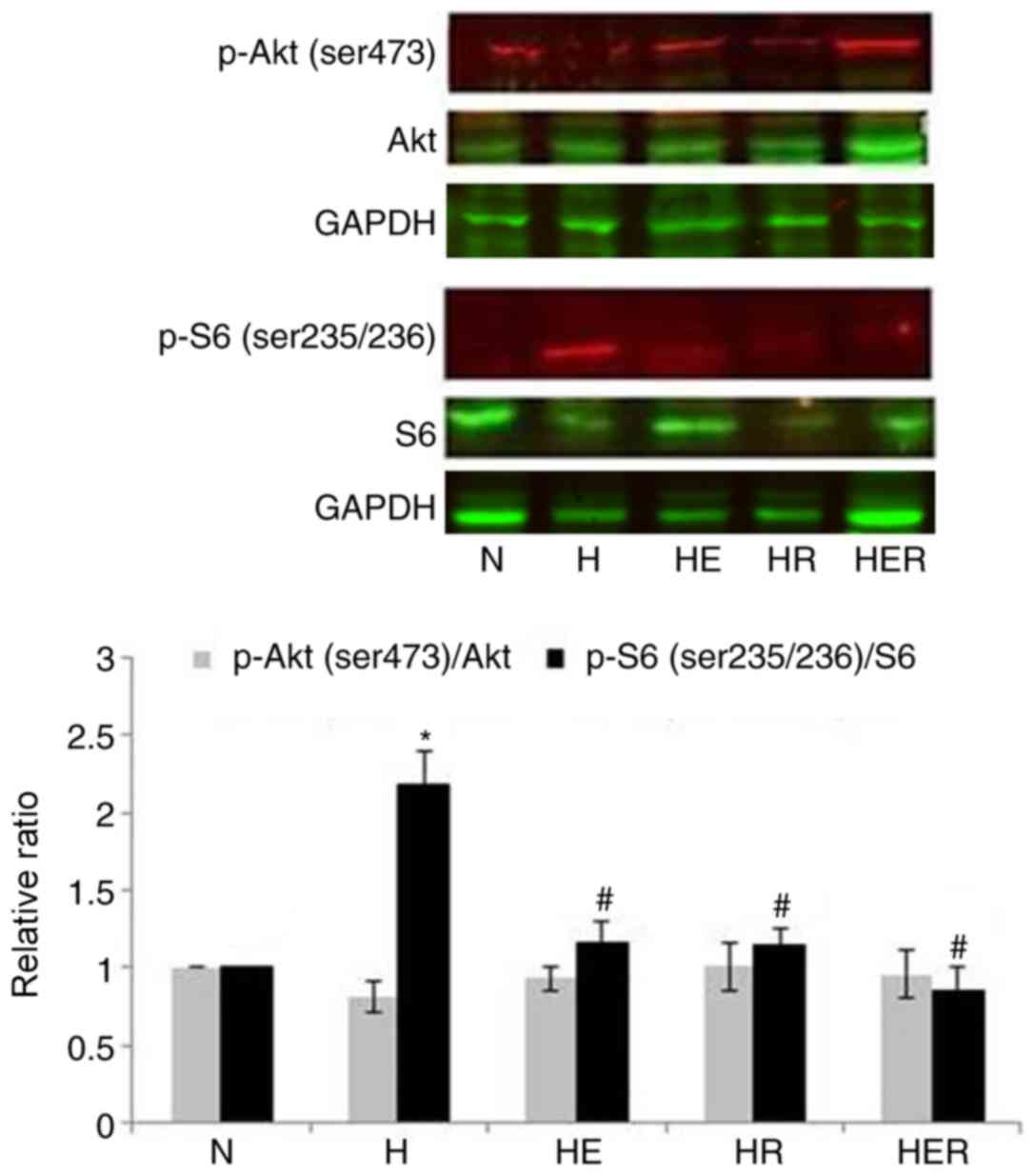
Laplante M and Sabatini DM: mTOR signaling
in growth control and disease. Cell. 149:274–293. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Guillén C and Benito M: mTORC1
overactivation as a key aging factor in the progression to type 2
diabetes mellitus. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 9:6212018.
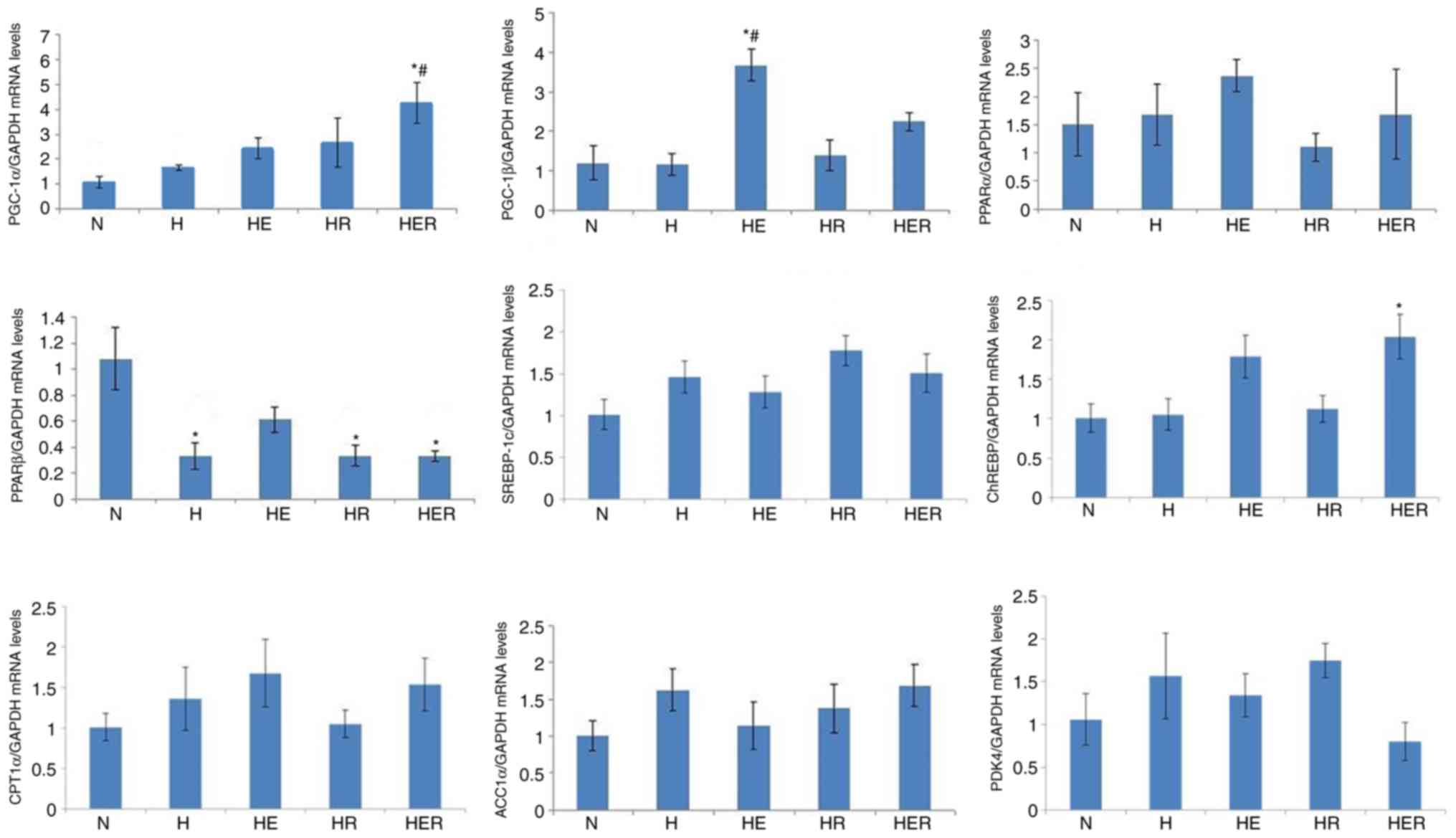
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lushchak O, Strilbytska O, Piskovatska V,
Storey KB, Koliada A and Vaiserman A: The role of the TOR pathway
in mediating the link between nutrition and longevity. Mech Ageing
Dev. 164:127–138. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kimball SR: Integration of signals
generated by nutrients, hormones, and exercise in skeletal muscle.
Am J Clin Nutr. 99:237S–242S. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li J, Kim SG and Blenis J: Rapamycin: One
drug, many effects. Cell Metab. 19:373–379. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sabatini DM: Twenty-five years of mTOR:
Uncovering the link from nutrients to growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 114:11818–11825. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
El Ouarrat D, Isaac R, Lee YS, Oh DY,
Wollam J, Lackey D, Riopel M, Bandyopadhyay G, Seo JB,
Sampath-Kumar R and Olefsky JM: TAZ Is a negative regulator of
PPARgamma activity in adipocytes and TAZ deletion improves insulin
sensitivity and glucose tolerance. Cell Metab. 31:162–173 e165.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Peterson TR, Sengupta SS, Harris TE,
Carmack AE, Kang SA, Balderas E, Guertin DA, Madden KL, Carpenter
AE, Finck BN and Sabatini DM: mTOR complex 1 regulates lipin 1
localization to control the SREBP pathway. Cell. 146:408–420. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sengupta S, Peterson TR, Laplante M, Oh S
and Sabatini DM: mTORC1 controls fasting-induced ketogenesis and
its modulation by ageing. Nature. 468:1100–1104. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li S, Brown MS and Goldstein JL:
Bifurcation of insulin signaling pathway in rat liver: mTORC1
required for stimulation of lipogenesis, but not inhibition of
gluconeogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:3441–3446. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fletcher JA, Meers GM, Linden MA, Kearney
ML, Morris EM, Thyfault JP and Rector RS: Impact of various
exercise modalities on hepatic mitochondrial function. Med Sci
Sports Exerc. 46:1089–1097. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Houde VP, Brûlé S, Festuccia WT, Blanchard
PG, Bellmann K, Deshaies Y and Marette A: Chronic rapamycin
treatment causes glucose intolerance and hyperlipidemia by
upregulating hepatic gluconeogenesis and impairing lipid deposition
in adipose tissue. Diabetes. 59:1338–1348. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Caron A, Mouchiroud M, Gautier N, Labbé
SM, Villot R, Turcotte L, Secco B, Lamoureux G, Shum M, Gélinas Y,
et al: Loss of hepatic DEPTOR alters the metabolic transition to
fasting. Mol Metab. 6:447–458. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kucejova B, Duarte J, Satapati S, Fu X,
Ilkayeva O, Newgard CB, Brugarolas J and Burgess SC: Hepatic mTORC1
opposes impaired insulin action to control mitochondrial metabolism
in obesity. Cell Rep. 16:508–519. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kenerson HL, Subramanian S, McIntyre R,
Kazami M and Yeung RS: Livers with constitutive mTORC1 activity
resist steatosis independent of feedback suppression of Akt. PLoS
One. 10:e01170002015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liao B and Xu Y: Exercise improves
skeletal muscle insulin resistance without reduced basal mTOR/S6K1
signaling in rats fed a high-fat diet. Eur J Appl Physiol.
111:2743–2752. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bass A, Brdiczka D, Eyer P, Hofer S and
Pette D: Metabolic differentiation of distinct muscle types at the
level of enzymatic organization. Eur J Biochem. 10:198–206. 1969.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Osumi T and Hashimoto T: Occurrence of two
3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenases in rat liver. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 574:258–267. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Leontieva OV, Paszkiewicz GM and
Blagosklonny MV: Comparison of rapamycin schedules in mice on
high-fat diet. Cell Cycle. 13:3350–3356. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lamming DW, Ye L, Katajisto P, Goncalves
MD, Saitoh M, Stevens DM, Davis JG, Salmon AB, Richardson A, Ahima
RS, et al: Rapamycin-induced insulin resistance is mediated by
mTORC2 loss and uncoupled from longevity. Science. 335:1638–1643.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Khamzina L, Veilleux A, Bergeron S and
Marette A: Increased activation of the mammalian target of
rapamycin pathway in liver and skeletal muscle of obese rats:
Possible involvement in obesity-linked insulin resistance.
Endocrinology. 146:1473–1481. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Volkers M, Doroudgar S, Nguyen N,
Konstandin MH, Quijada P, Din S, Ornelas L, Thuerauf DJ, Gude N,
Friedrich K, et al: PRAS40 prevents development of diabetic
cardiomyopathy and improves hepatic insulin sensitivity in obesity.
EMBO Mol Med. 6:57–65. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Makki K, Taront S, Molendi-Coste O,
Bouchaert E, Neve B, Eury E, Lobbens S, Labalette M, Duez H, Staels
B, et al: Beneficial metabolic effects of rapamycin are associated
with enhanced regulatory cells in diet-induced obese mice. PLoS
One. 9:e926842014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Salmon AB: About-face on the metabolic
side effects of rapamycin. Oncotarget. 6:2585–2586. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu Y, Diaz V, Fernandez E, Strong R, Ye
L, Baur JA, Lamming DW, Richardson A and Salmon AB:
Rapamycin-induced metabolic defects are reversible in both lean and
obese mice. Aging (Albany NY). 6:742–754. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fang Y, Westbrook R, Hill C, Boparai RK,
Arum O, Spong A, Wang F, Javors MA, Chen J, Sun LY and Bartke A:
Duration of rapamycin treatment has differential effects on
metabolism in mice. Cell Metab. 17:456–462. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Reifsnyder PC, Flurkey K, Te A and
Harrison DE: Rapamycin treatment benefits glucose metabolism in
mouse models of type 2 diabetes. Aging (Albany NY). 8:3120–3130.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kenerson HL, Yeh MM and Yeung RS: Tuberous
sclerosis complex-1 deficiency attenuates diet-induced hepatic
lipid accumulation. PLoS One. 6:e180752011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Binsch C, Jelenik T, Pfitzer A, Dille M,
Müller-Lühlhoff S, Hartwig S, Karpinski S, Lehr S, Kabra DG, Chadt
A, et al: Absence of the kinase S6k1 mimics the effect of chronic
endurance exercise on glucose tolerance and muscle oxidative
stress. Mol Metab. 6:1443–1453. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim JA, Wei Y and Sowers JR: Role of
mitochondrial dysfunction in insulin resistance. Circ Res.
102:401–414. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Softic S, Meyer JG, Wang GX, Gupta MK,
Batista TM, Lauritzen HPMM, Fujisaka S, Serra D, Herrero L,
Willoughby J, et al: Dietary sugars alter hepatic fatty acid
oxidation via transcriptional and post-translational modifications
of mitochondrial proteins. Cell Metab. 30:735–753 e734. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ramanathan A and Schreiber SL: Direct
control of mitochondrial function by mTOR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
106:22229–22232. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Schieke SM, Phillips D, McCoy JP Jr,
Aponte AM, Shen RF, Balaban RS and Finkel T: The mammalian target
of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway regulates mitochondrial oxygen
consumption and oxidative capacity. J Biol Chem. 281:27643–27652.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Han L, Shen WJ, Bittner S, Kraemer FB and
Azhar S: PPARs: Regulators of metabolism and as therapeutic targets
in cardiovascular disease. Part II: PPAR-b/δ and PPAR-g. Future
Cardiol. 13:279–296. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Villena JA: New insights into PGC-1
coactivators: Redefining their role in the regulation of
mitochondrial function and beyond. FEBS J. 282:647–672. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Souza-Mello V: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptors as targets to treat non-alcoholic
fatty liver disease. World J Hepatol. 7:1012–1019. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Shimano H and Sato R: SREBP-regulated
lipid metabolism: Convergent physiology-divergent pathophysiology.
Nat Rev Endocrinol. 13:710–730. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang Y, Viscarra J, Kim SJ and Sul HS:
Transcriptional regulation of hepatic lipogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 16:678–689. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chambers KT, Chen Z, Crawford PA, Fu X,
Burgess SC, Lai L, Leone TC, Kelly DP and Finck BN: Liver-specific
PGC-1beta deficiency leads to impaired mitochondrial function and
lipogenic response to fasting-refeeding. PLoS One. 7:e526452012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chau GC, Im DU, Kang TM, Bae JM, Kim W,
Pyo S, Moon EY and Um SH: mTOR controls ChREBP transcriptional
activity and pancreatic β cell survival under diabetic stress. J
Cell Biol. 216:2091–2105. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Iizuka K: Recent progress on the role of
ChREBP in glucose and lipid metabolism. Endocrine J. 60:543–555.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Iso T, Sunaga H, Matsui H, Kasama S,
Oshima N, Haruyama Furukawa N, Nakajima K, Machida T, Murakami M,
et al: Serum levels of fatty acid binding protein 4 and fat
metabolic markers in relation to catecholamines following exercise.
Clin Biochem. 50:896–902. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Aye IL, Rosario FJ, Powell TL and Jansson
T: Adiponectin supplementation in pregnant mice prevents the
adverse effects of maternal obesity on placental function and fetal
growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:12858–12863. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|