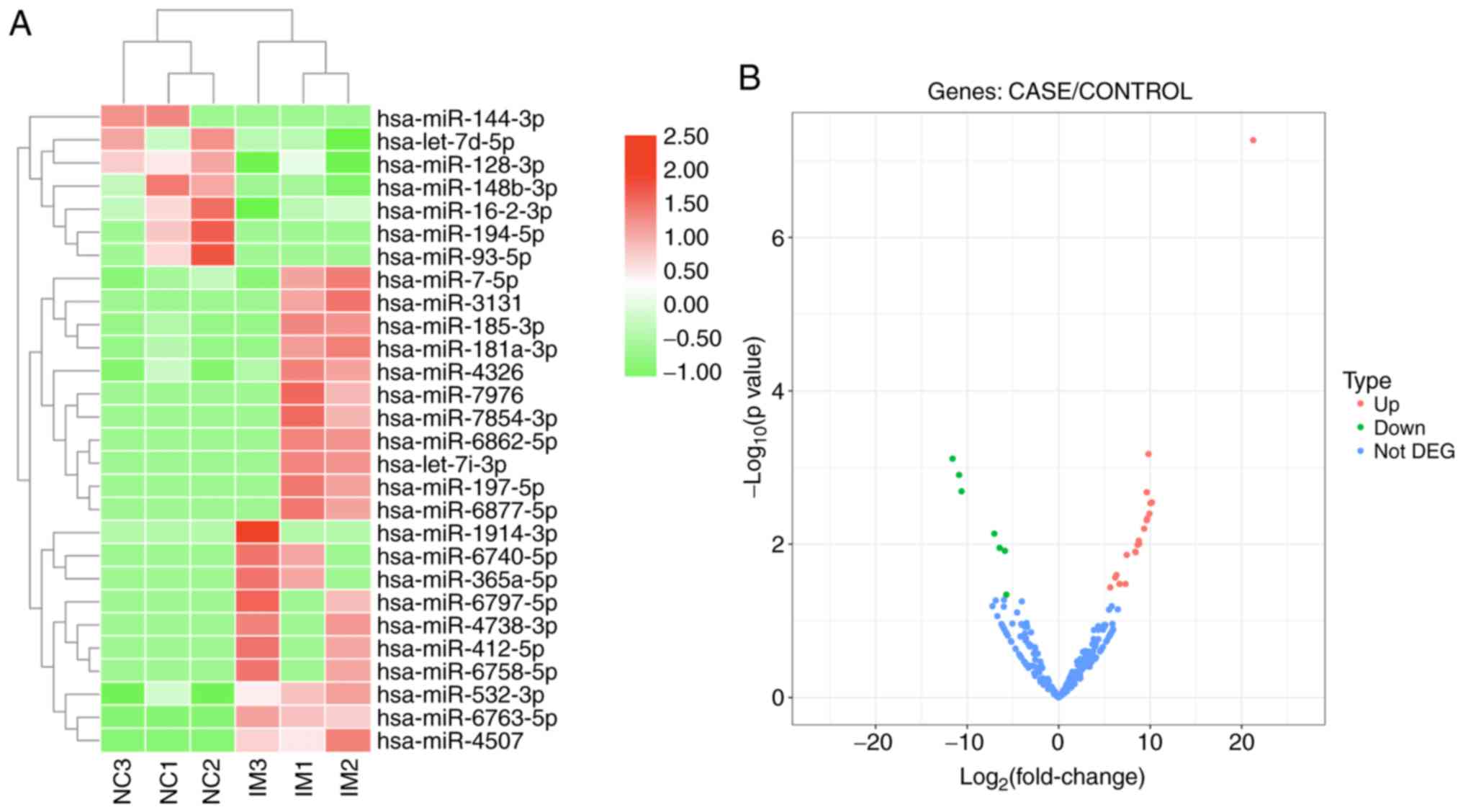
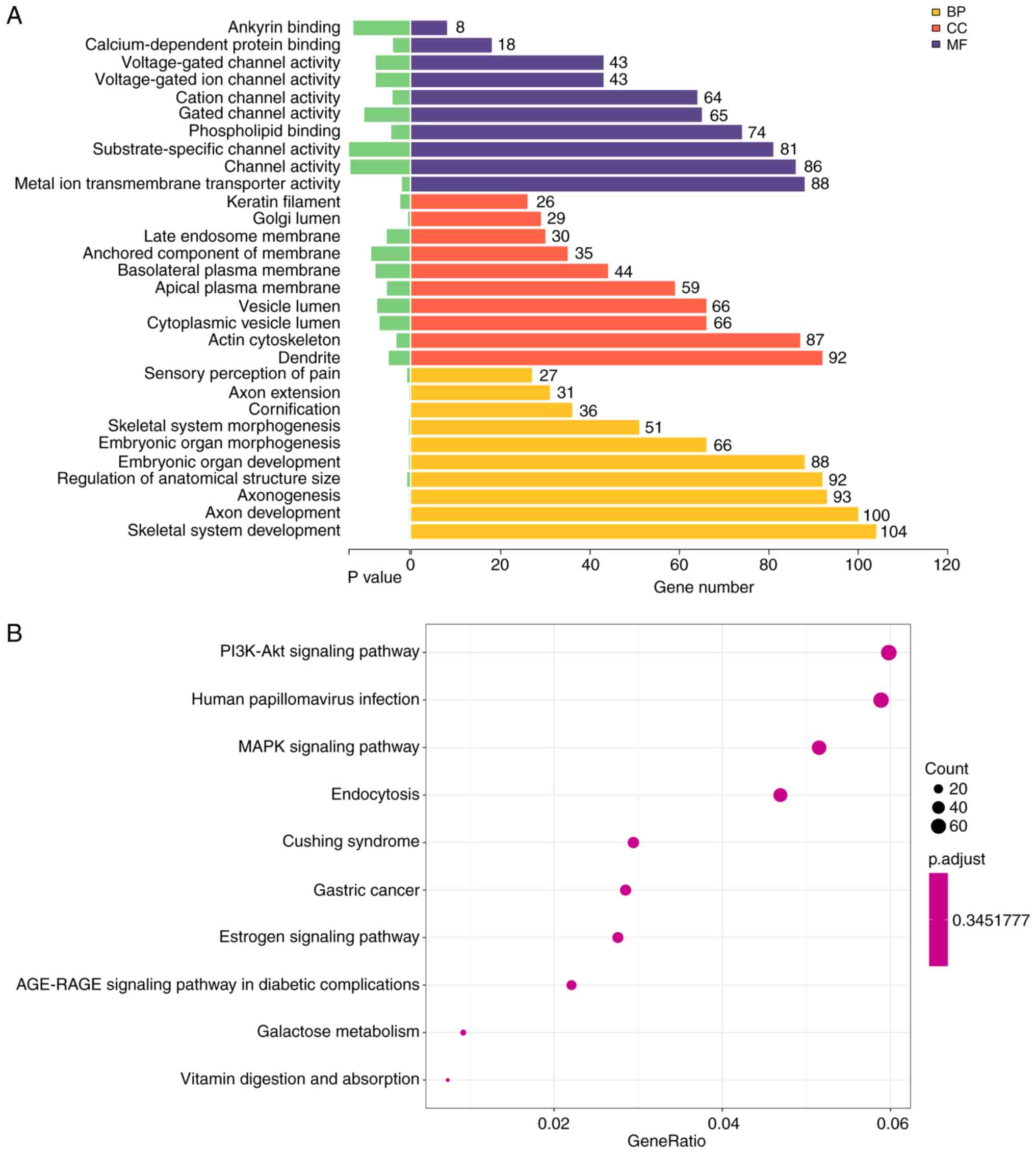
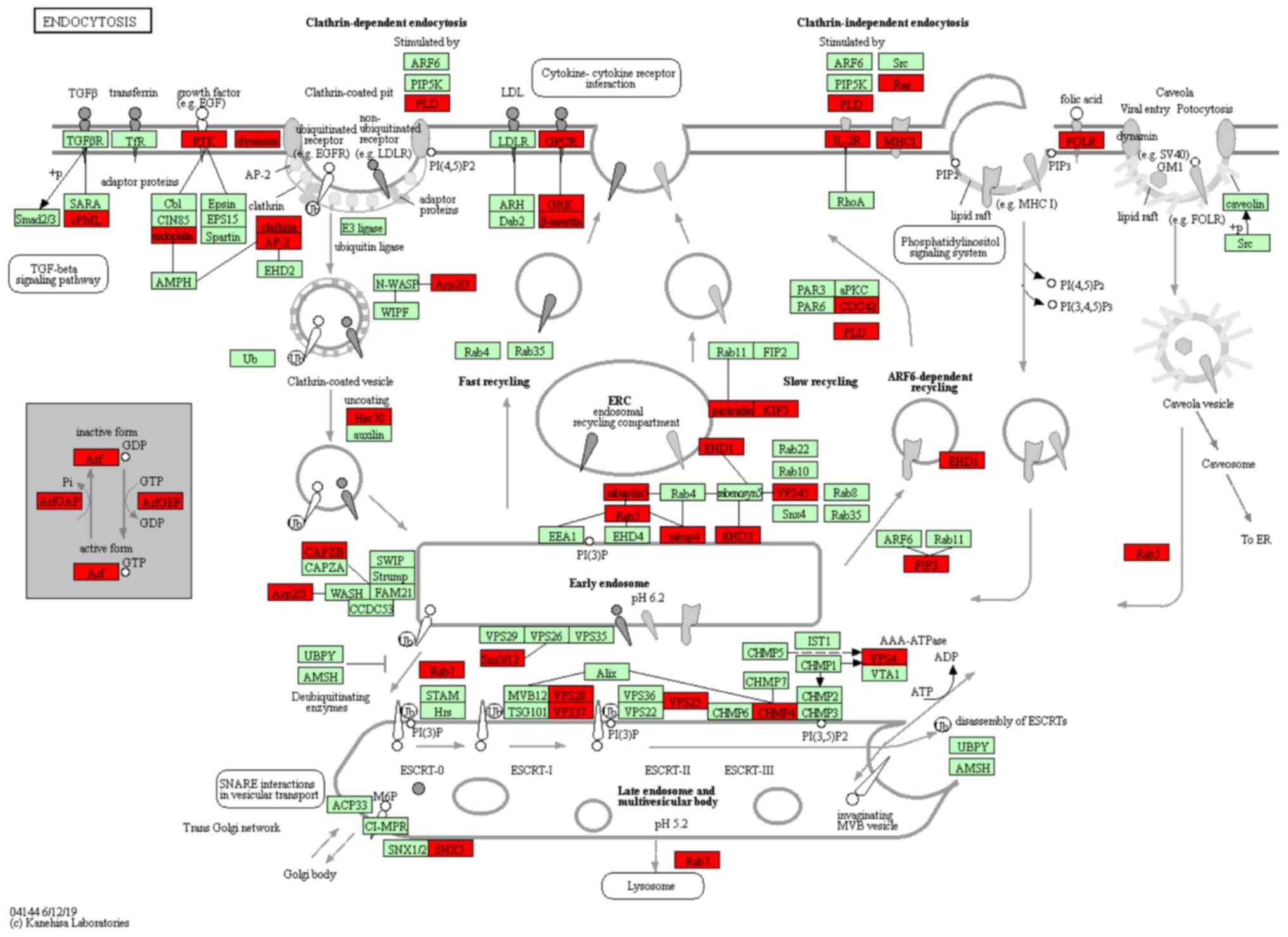
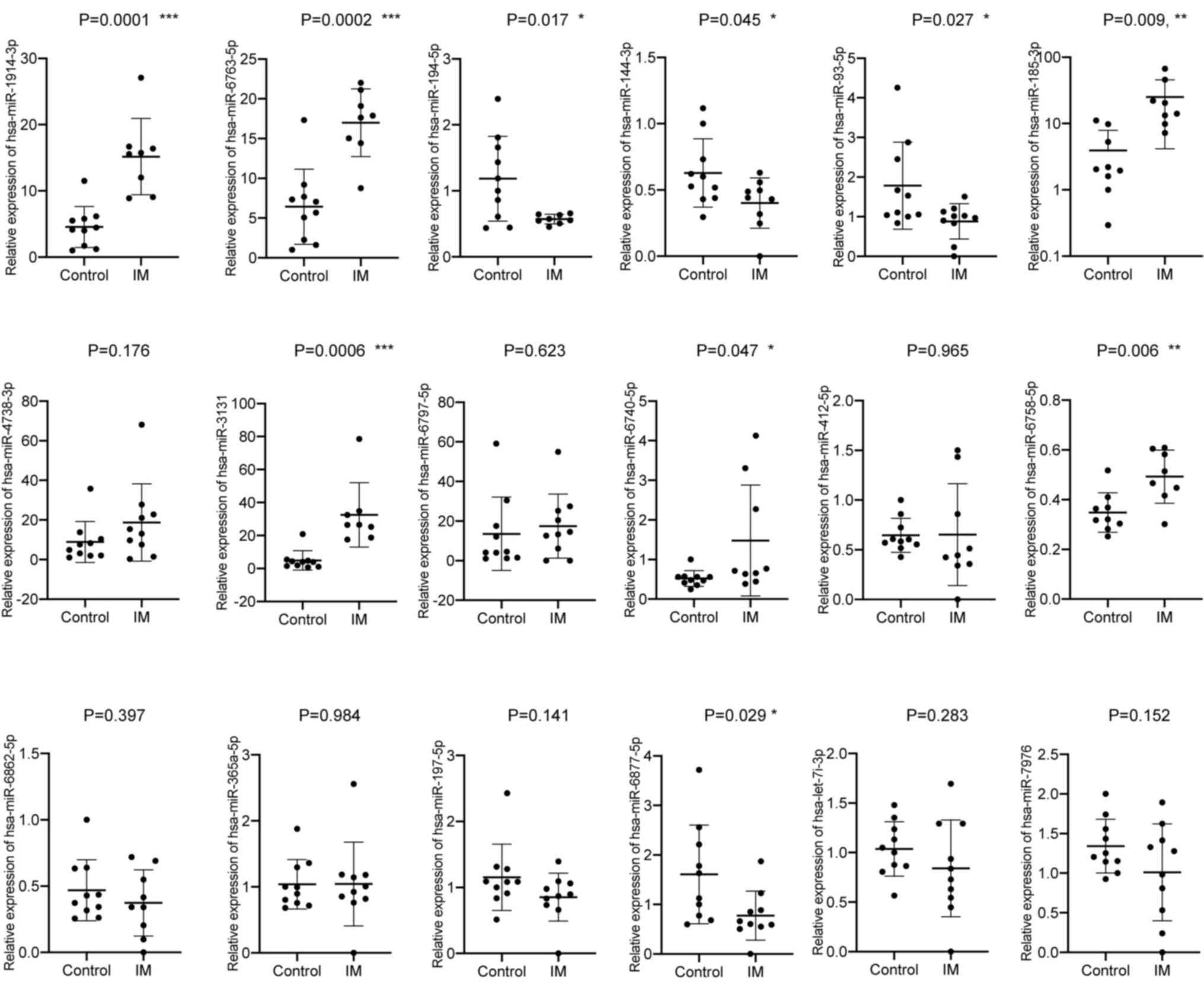
|
1
|
Applegate KE, Anderson JM and Klatte EC:
Intestinal malrotation in children: A problem-solving approach to
the upper gastrointestinal series. Radiographics. 26:3289–1500.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Blumberg K: Intestinal malrotation.
Radiology. 202:5841997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Coste AH, Waheed A and Ahmad H: Midgut
Volvulus. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL: 2019
|
|
4
|
Adams SD and Stanton MP: Malrotation and
intestinal atresias. Early Hum Dev. 90:921–925. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Morris G, Kennedy A Jr and Cochran W:
Small bowel congenital anomalies: A review and update. Curr
Gastroenterol Rep. 18:162016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Graziano K, Islam S, Dasgupta R, Lopez ME,
Austin M, Chen LE, Goldin A, Downard CD, Renaud E and Abdullah F:
Asymptomatic malrotation: Diagnosis and surgical management: An
American Pediatric Surgical Association outcomes and evidence based
practice committee systematic review. J Pediatr Surg. 50:1783–1790.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dilley AV, Pereira J, Shi EC, Adams S,
Kern IB, Currie B and Henry GM: The radiologist says malrotation:
Does the surgeon operate? Pediatr Surg Int. 16:45–49. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Long FR, Kramer SS, Markowitz RI, Taylor
GE and Liacouras CA: Intestinal malrotation in children: Tutorial
on radiographic diagnosis in difficult cases. Radiology.
198:775–780. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Strouse PJ: Malrotation. Semin Roentgenol.
43:7–14. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Taylor GA: CT appearance of the duodenum
and mesenteric vessels in children with normal and abnormal bowel
rotation. Pediatr Radiol. 41:1378–1383. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tackett JJ, Muise ED and Cowles RA:
Malrotation: Current strategies navigating the radiologic diagnosis
of a surgical emergency. World J Radiol. 6:730–736. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dekonenko C, Sujka JA, Weaver K, Sharp SW,
Gonzalez K and St Peter SD: The identification and treatment of
intestinal malrotation in older children. Pediatr Surg Int.
35:665–671. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kroh EM, Parkin RK, Mitchell PS and Tewari
M: Analysis of circulating microRNA biomarkers in plasma and serum
using quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR). Methods.
50:298–301. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Patel M, Verma A, Aslam I, Pringle H and
Singh B: Novel plasma microRNA biomarkers for the identification of
colitis-associated carcinoma. Lancet. 385 (Suppl 1):S782015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
van de Vrie M, Deegens JK, Eikmans M, van
der Vlag J and Hilbrands LB: Urinary MicroRNA as biomarker in renal
transplantation. Am J Transplant. 17:1160–1166. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Panico C and Condorelli G: microRNA-132: A
new biomarker of heart failure at last? Eur J Heart Fail. 20:86–88.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu R, Chen X, Du Y, Yao W, Shen L, Wang
C, Hu Z, Zhuang R, Ning G, Zhang C, et al: Serum microRNA
expression profile as a biomarker in the diagnosis and prognosis of
pancreatic cancer. Clin Chem. 58:610–618. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
McGuire A, Brown JA and Kerin MJ:
Metastatic breast cancer: The potential of miRNA for diagnosis and
treatment monitoring. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 34:145–155. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fabris L, Ceder Y, Chinnaiyan AM, Jenster
GW, Sorensen KD, Tomlins S, Visakorpi T and Calin GA: The potential
of microRNAs as prostate cancer biomarkers. Eur Urol. 70:312–322.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zampetaki A, Willeit P, Tilling L, Drozdov
I, Prokopi M, Renard JM, Mayr A, Weger S, Schett G, Shah A, et al:
Prospective study on circulating microRNAs and risk of myocardial
infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 60:290–299. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Barwari T, Joshi A and Mayr M: MicroRNAs
in cardiovascular disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 68:2577–2584. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lu TX and Rothenberg ME: MicroRNA. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 141:1202–1207. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kumar S, Vijayan M, Bhatti JS and Reddy
PH: MicroRNAs as peripheral biomarkers in aging and age-related
diseases. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 146:47–94. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Backes C, Meese E and Keller A: Specific
miRNA disease biomarkers in blood, serum and plasma: Challenges and
prospects. Mol Diagn Ther. 20:509–518. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Miranda J, Rocha G, Soares P, Morgado H,
Baptista MJ, Azevedo I, Fernandes S, Brandão O, Sen P and Guimarães
H: A novel mutation in FOXF1 gene associated with alveolar
capillary dysplasia with misalignment of pulmonary veins,
intestinal malrotation and annular pancreas. Neonatology.
103:241–245. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Martin V and Shaw-Smith C: Review of
genetic factors in intestinal malrotation. Pediatr Surg Int.
26:769–781. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sohn W, Kim J, Kang SH, Yang SR, Cho JY,
Cho HC, Shim SG and Paik YH: Serum exosomal microRNAs as novel
biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Exp Mol Med. 47:e1842015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Powell DM, Othersen HB and Smith CD:
Malrotation of the intestines in children: The effect of age on
presentation and therapy. J Pediatr Surg. 24:777–780. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gross E, Chen MK and Lobe TE: Laparoscopic
evaluation and treatment of intestinal malrotation in infants. Surg
Endosc. 10:936–937. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Durkin ET, Lund DP, Shaaban AF, Schurr MJ
and Weber SM: Age-related differences in diagnosis and morbidity of
intestinal malrotation. J Am Coll Surg. 206:658–663. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lin JN, Lou CC and Wang KL: Intestinal
malrotation and midgut volvulus: A 15-year review. J Formos Med
Assoc. 94:178–181. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hwang SM, Na YS, Cho Y, You DG and Lee JJ:
Midgut volvulus as a complication of intestinal malrotation in a
term pregnancy. Korean J Anesthesiol. 67 (Suppl):S98–S99. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Beasley SW and de Campo JF: Pitfalls in
the radiological diagnosis of malrotation. Australas Radiol.
31:376–383. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Prasil P, Flageole H, Shaw KS, Nguyen LT,
Youssef S and Laberge JM: Should malrotation in children be treated
differently according to age? J Pediatr Surg. 35:756–758. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Torres AM and Ziegler MM: Malrotation of
the intestine. World J Surg. 17:326–331. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Burgess AM and Vere DW: Teratogenic
effects of some calcium channel blocking agents in Xenopus embryos.
Pharmacol Toxicol. 64:78–82. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Botvin'ev OK, Eremeeva AV, Razumovskaia IN
and Kondrikova EV: Intestinal malrotation: Genetics features and
other congenital malformations in children. Arkh Patol. 73:29–32.
2011.(In Russian).
|
|
39
|
Haq S, Grondin J, Banskota S and Khan WI:
Autophagy: Roles in intestinal mucosal homeostasis and
inflammation. J Biomed Sci. 26:192019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bujko A, Atlasy N, Landsverk OJB, Richter
L, Yaqub S, Horneland R, Øyen O, Aandahl EM, Aabakken L,
Stunnenberg HG, et al: Transcriptional and functional profiling
defines human small intestinal macrophage subsets. J Exp Med.
215:441–458. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yoshikawa T, Wu J, Otsuka M, Kishikawa T,
Suzuki N, Takata A, Ohno M, Ishibashi R, Yamagami M, Nakagawa R, et
al: Repression of microRNA function mediates
inflammation-associated colon tumorigenesis. Gastroenterology.
152:631–643. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xiao L, Wu J and Wang JY, Chung HK,
Kalakonda S, Rao JN, Gorospe M and Wang JY: Long noncoding RNA
uc.173 promotes renewal of the intestinal mucosa by inducing
degradation of microRNA 195. Gastroenterology. 154:599–611. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cao B, Zhou X, Ma J, Zhou W, Yang W, Fan D
and Hong L: Role of miRNAs in inflammatory bowel disease. Dig Dis
Sci. 62:1426–1438. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|