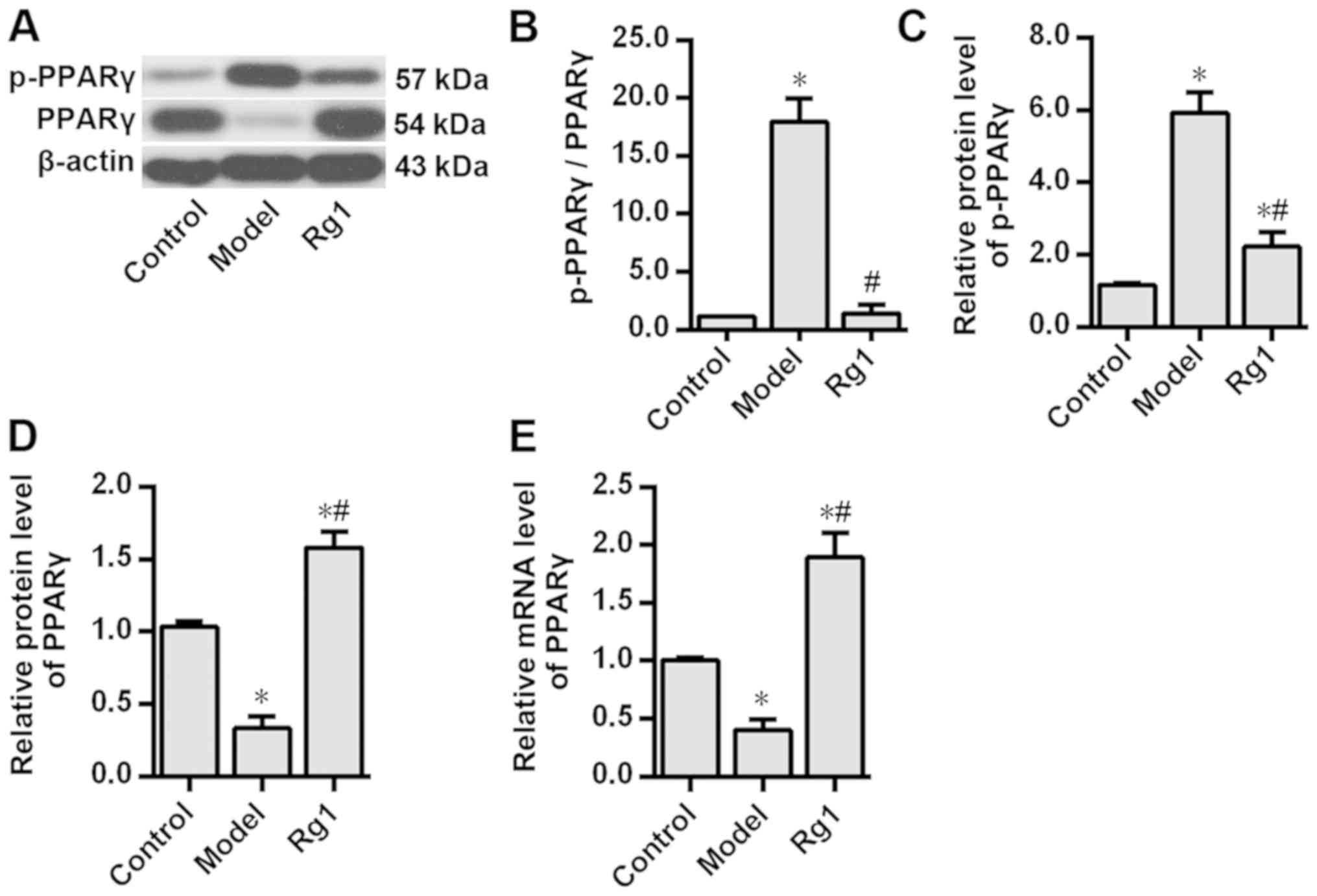
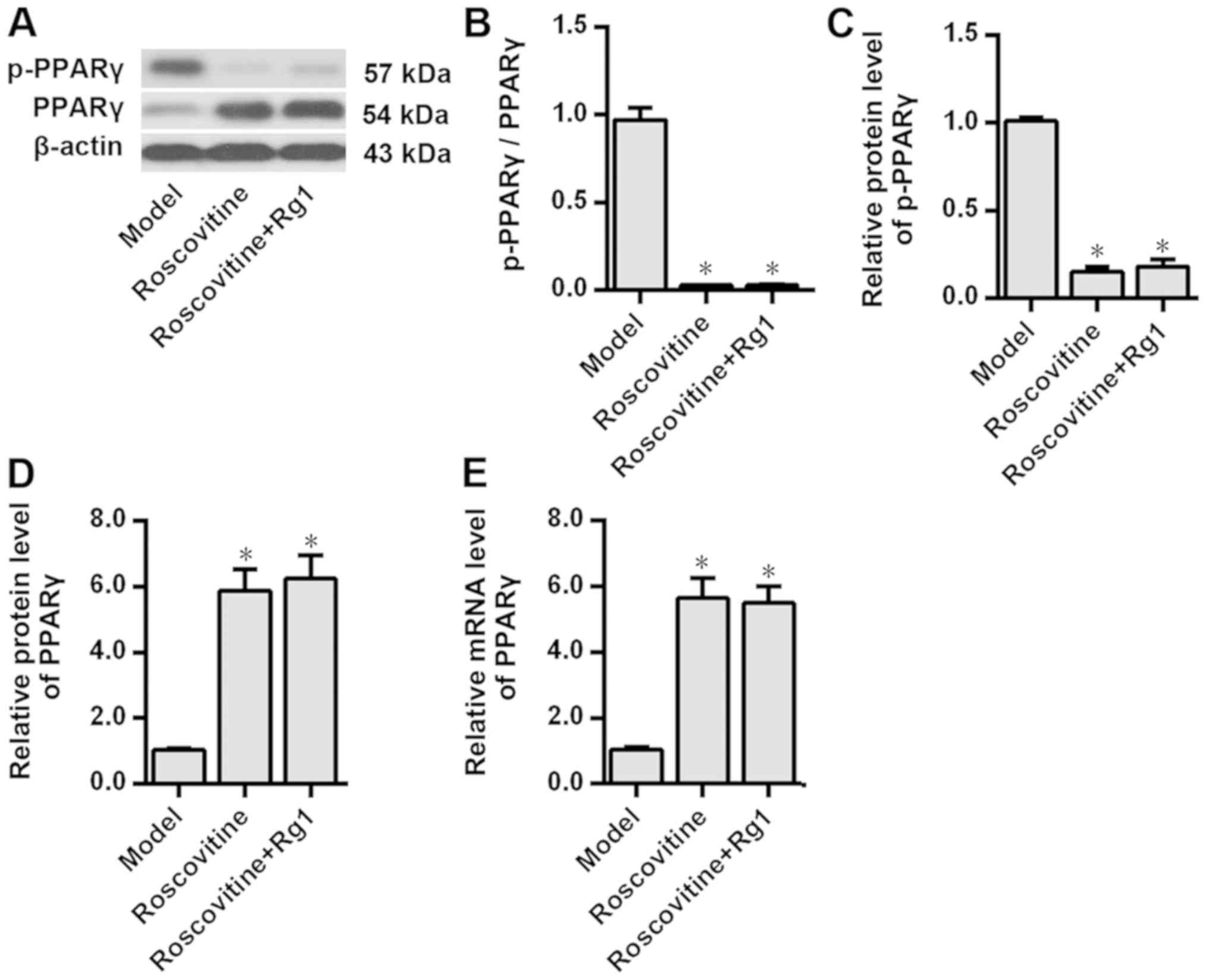
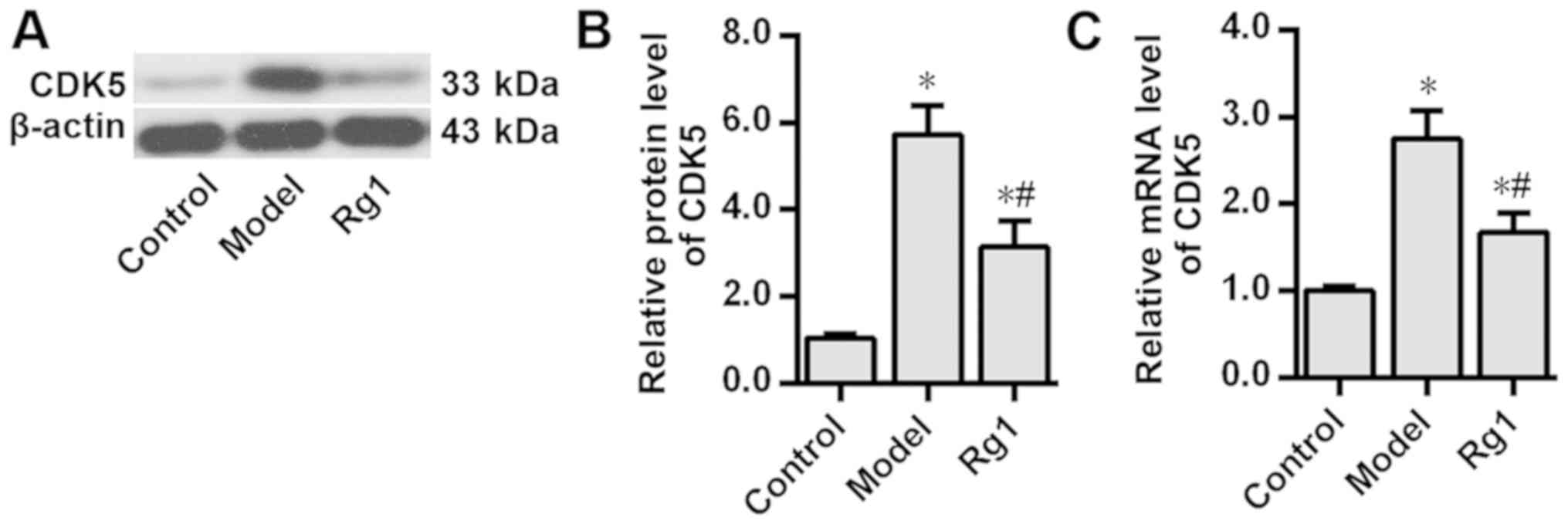
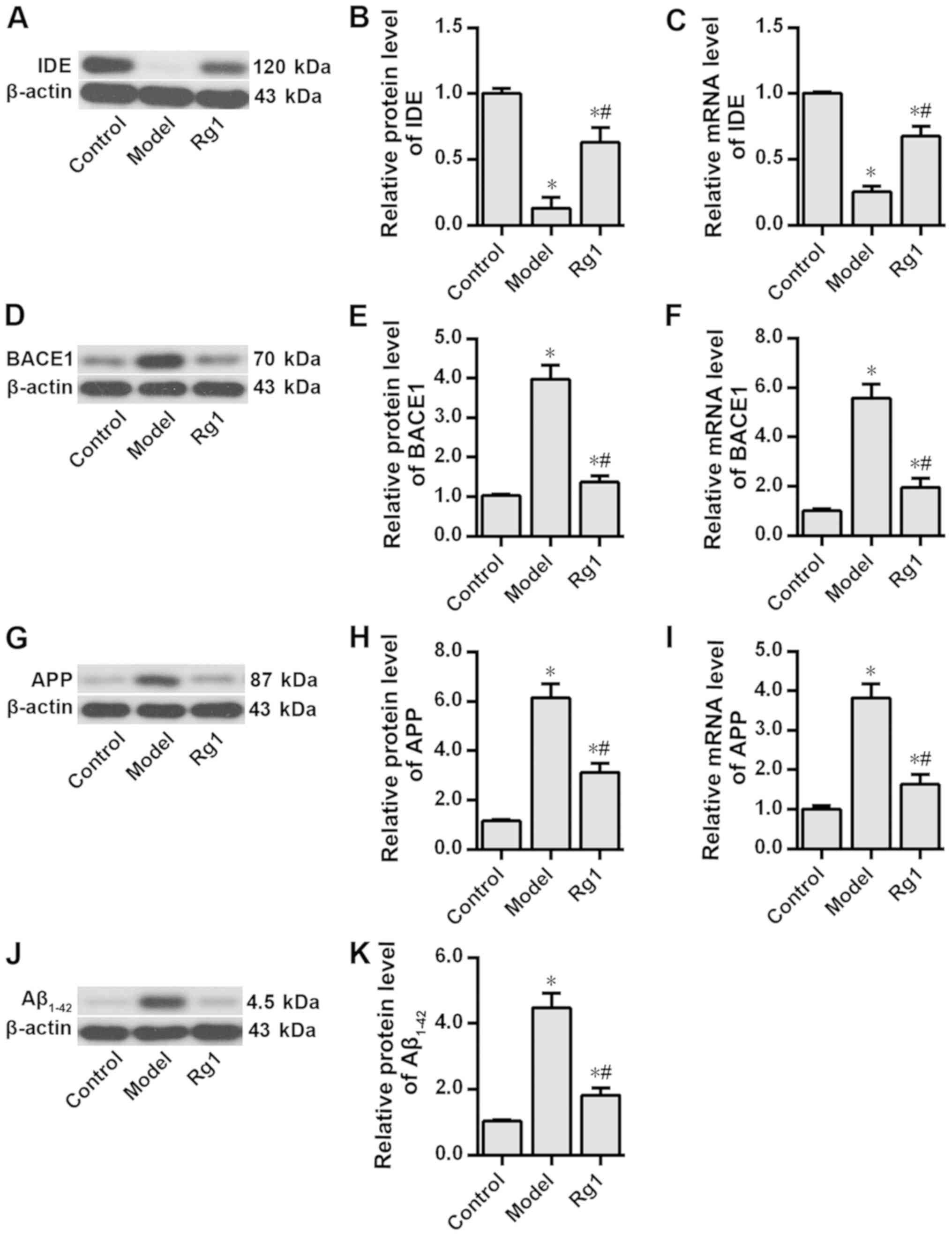
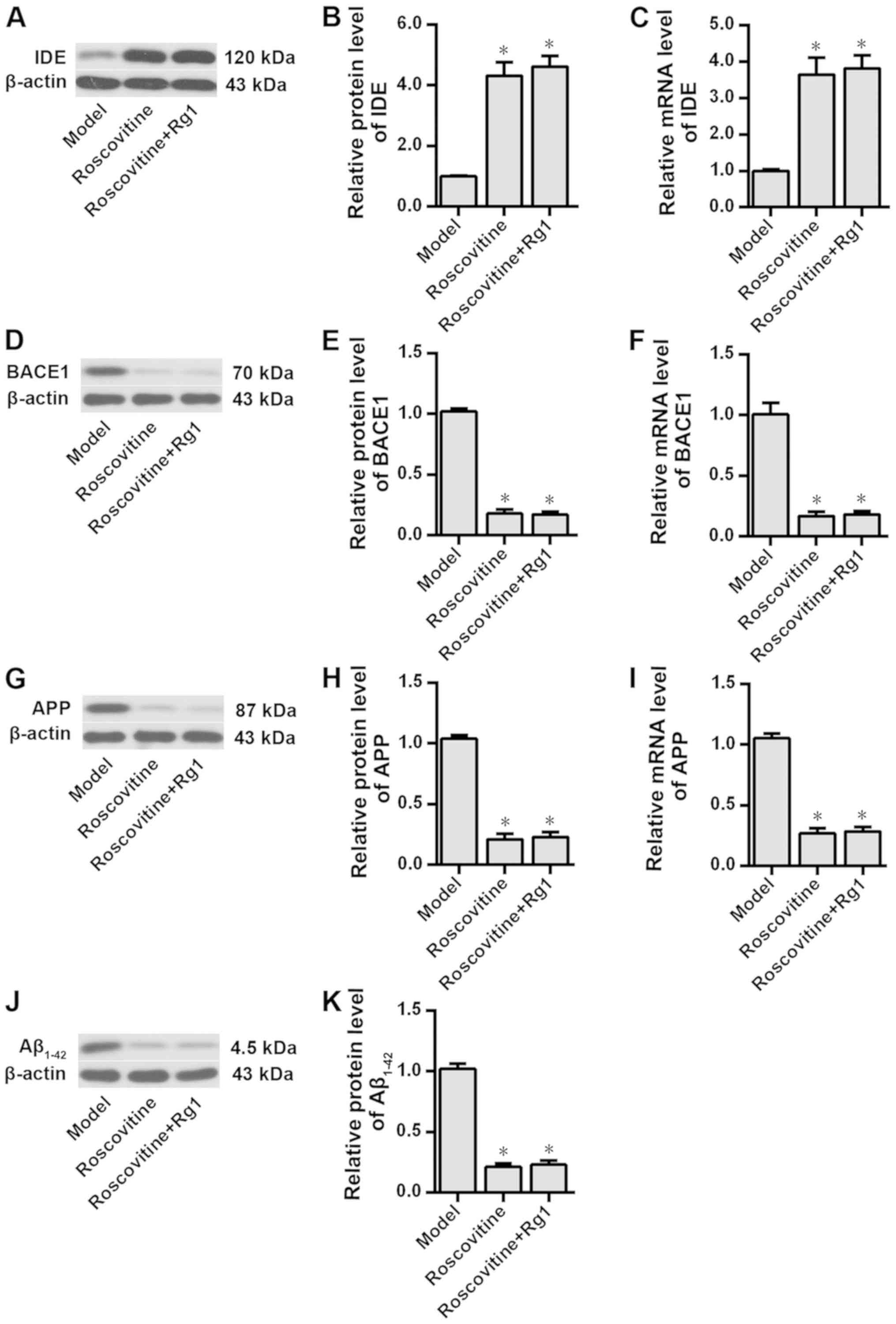
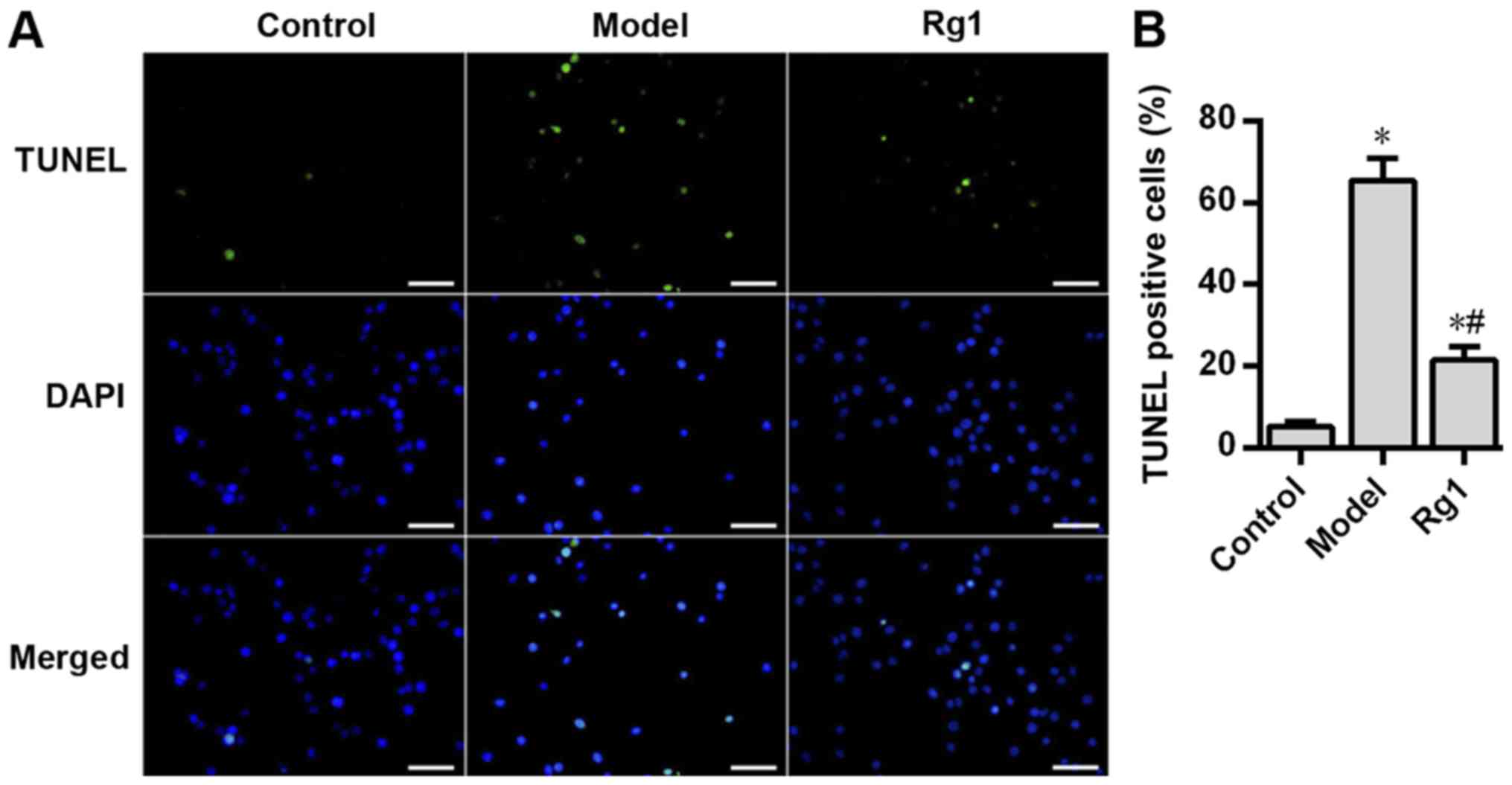
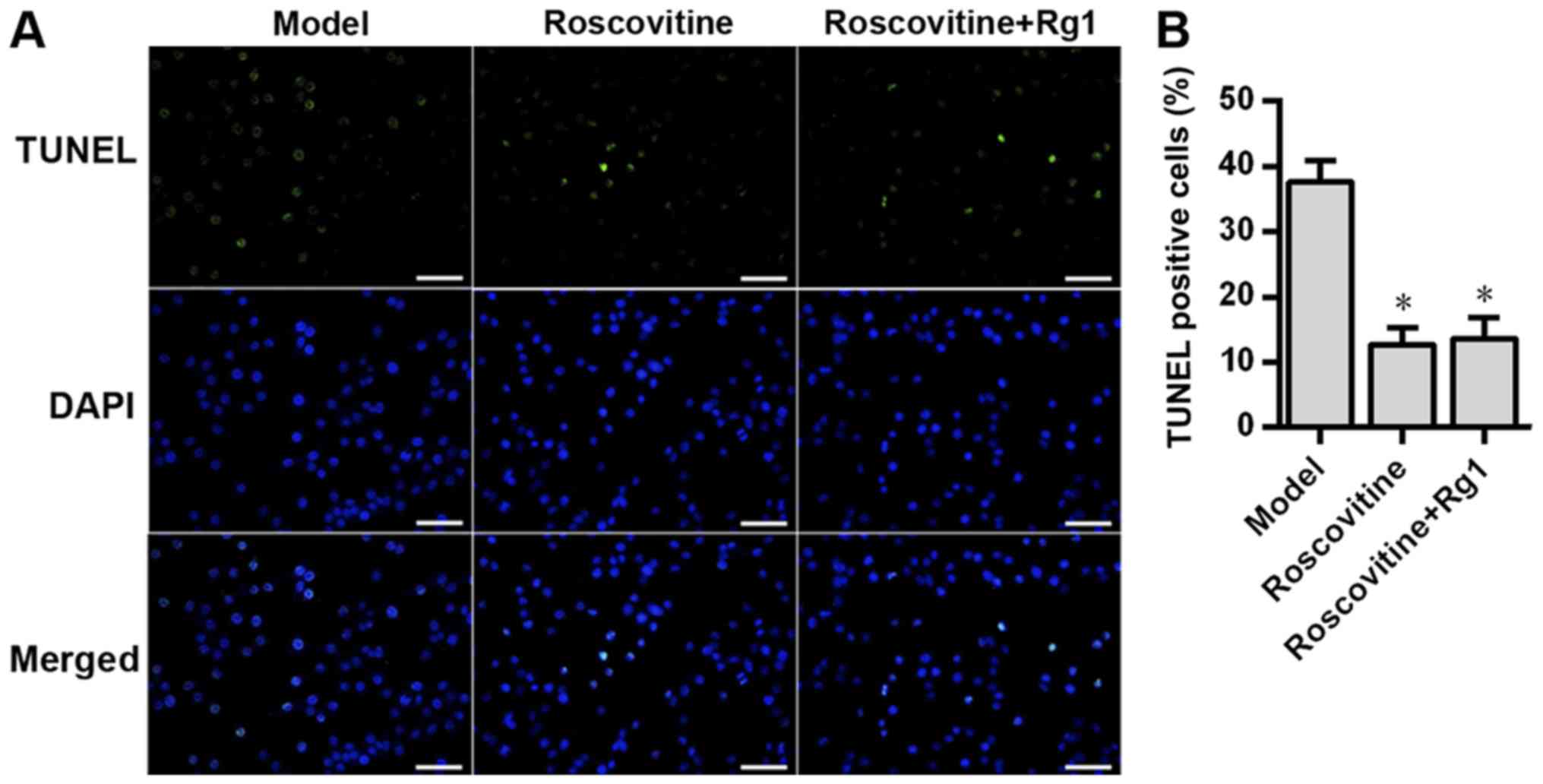
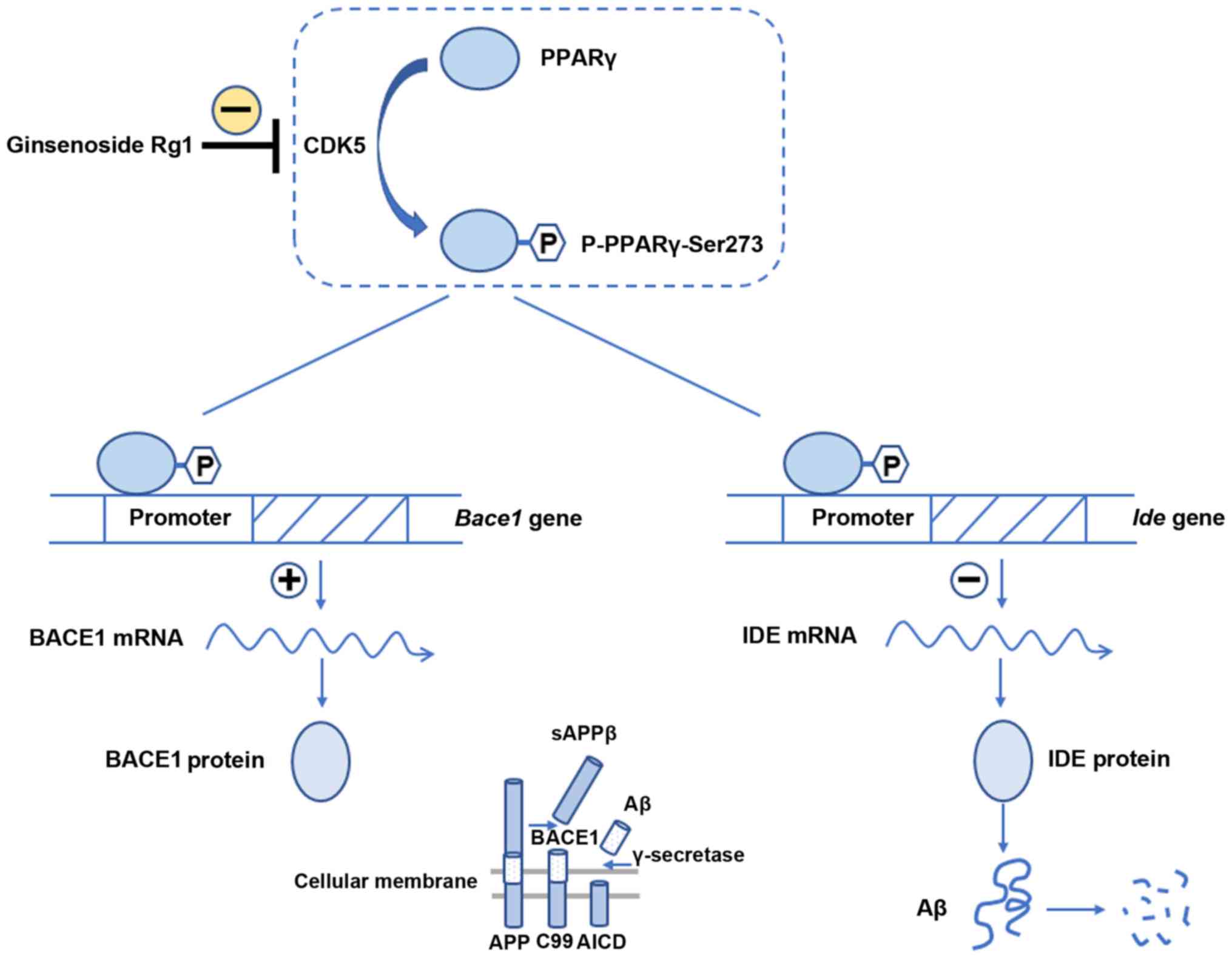
|
1
|
Chen CF, Chiou WF and Zhang JT: Comparison
of the pharmacological effects of Panax ginseng and Panax
quinquefolium. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 29:3277–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Nie L, Xia J, Li H, Zhang Z, Yang Y, Huang
X, He Z, Liu J and Yang X: Ginsenoside Rg1 ameliorates behavioral
abnormalities and modulates the hippocampal proteomic change in
triple transgenic mice of Alzheimer's disease. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2017:64735062017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mu JS, Lin H, Ye JX, Lin M and Cui XP: Rg1
exhibits neuroprotective effects by inhibiting the endoplasmic
reticulum stress-mediated c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase apoptotic
pathway in a rat model of Alzheimer's disease. Mol Med Rep.
12:3862–3868. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu QA, Kou JP and Yu BY: Ginsenoside Rg1
protects against hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death in PC12 cells
via inhibiting NF-κB activation. Neurochem Int. 58:119–125. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Huang T, Fang F, Chen L, Zhu Y, Zhang J,
Chen X and Yan SS: Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates oligomeric
Aβ(1–42)-induced mitochondrial dysfunction. Curr Alzheimer Res.
9:388–395. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tanzi RE, Moir RD and Wagner SL: Clearance
of Alzheimer's Abeta peptide: The many roads to perdition. Neuron.
43:605–608. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Álvarez-Arellano L, Pedraza-Escalona M,
Blanco-Ayala T, Camacho-Concha N, Cortés-Mendoza J, Pérez-Martínez
L and Pedraza-Alva G: Autophagy impairment by caspase-1-dependent
inflammation mediates memory loss in response to β-amyloid peptide
accumulation. J Neurosci Res. 96:234–246. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Seino Y, Kawarabayashi T, Wakasaya Y,
Watanabe M, Takamura A, Yamamoto-Watanabe Y, Kurata T, Abe K, Ikeda
M, Westaway D, et al: Amyloid β accelerates phosphorylation of tau
and neurofibrillary tangle formation in an amyloid precursor
protein and tau double-transgenic mouse model. J Neurosci Res.
88:3547–3554. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vargas LM, Leal N, Estrada LD, González A,
Serrano F, Araya K, Gysling K, Inestrosa NC, Pasquale EB and
Alvarez AR: EphA4 activation of c-Abl mediates synaptic loss and
LTP blockade caused by amyloid-β oligomers. PLoS One. 9:e923092014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ibi D, Tsuchihashi A, Nomura T and
Hiramatsu M: Involvement of GAT2/BGT-1 in the preventive effects of
betaine on cognitive impairment and brain oxidative stress in
amyloid β peptide-injected mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 842:57–63. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hooshmandi E, Ghasemi R, Iloun P and
Moosavi M: The neuroprotective effect of agmatine against amyloid
β-induced apoptosis in primary cultured hippocampal cells involving
ERK, Akt/GSK-3β, and TNF-α. Mol Biol Rep. 46:489–496. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Schirinzi T, Di Lorenzo F, Sancesario GM,
Di Lazzaro G, Ponzo V, Pisani A, Mercuri NB, Koch G and Martorana
A: Amyloid-mediated cholinergic dysfunction in motor impairment
related to Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 64:525–532. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ali T, Yoon GH, Shah SA, Lee HY and Kim
MO: Osmotin attenuates amyloid beta-induced memory impairment, tau
phosphorylation and neurodegeneration in the mouse hippocampus. Sci
Rep. 5:117082015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen LM, Lin ZY, Zhu YG, Lin N, Zhang J,
Pan XD and Chen XC: Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates β-amyloid generation
via suppressing PPARγ-regulated BACE1 activity in N2a-APP695 cells.
Eur J Pharmacol. 675:15–21. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Quan Q, Wang J, Li X and Wang Y:
Ginsenoside Rg1 decreases Aβ1-42 level by upregulating
PPARγ and IDE expression in the hippocampus of a rat model of
Alzheimer's disease. PLoS One. 8:e591552013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu C, Zhai X, Zhao B, Wang Y and Xu Z:
Cyclin I-like (CCNI2) is a Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK5)
activator and is involved in cell cycle regulation. Sci Rep.
7:409792017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Su SC and Tsai LH: Cyclin-dependent
kinases in brain development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
27:465–491. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lopes JP and Agostinho P: Cdk5:
Multitasking between physiological and pathological conditions.
Prog Neurobiol. 94:49–63. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wilkaniec A, Czapski GA and Adamczyk A:
Cdk5 at crossroads of protein oligomerization in neurodegenerative
diseases: Facts and hypotheses. J Neurochem. 136:222–233. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Choi JH, Banks AS, Estall JL, Kajimura S,
Boström P, Laznik D, Ruas JL, Chalmers MJ, Kamenecka TM, Blüher M,
et al: Anti-diabetic drugs inhibit obesity-linked phosphorylation
of PPARγ by Cdk5. Nature. 466:451–456. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Quan Q, Qian Y, Li X and Li M: CDK5
participates in amyloid-β production by regulating PPARγ
phosphorylation in primary rat hippocampal neurons. J Alzheimers
Dis. 71:443–460. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Vadukul DM, Gbajumo O, Marshall KE and
Serpell LC: Amyloidogenicity and toxicity of the reverse and
scrambled variants of amyloid-β 1-42. FEBS Lett. 591:822–830. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang EJ, Ahn S, Ryu J, Choi MS, Choi S,
Chong YH, Hyun JW, Chang MJ and Kim HS: Phloroglucinol attenuates
the cognitive deficits of the 5XFAD mouse model of Alzheimer's
sisease. PLoS One. 10:e01356862015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li Y, Guan Y, Wang Y, Yu CL, Zhai FG and
Guan LX: Neuroprotective effect of the ginsenoside Rg1 on cerebral
ischemic injury in vivo and in vitro is mediated by PPARγ-regulated
antioxidative and anti-inflammatory pathways. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2017:78420822017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Manser C, Vagnoni A, Guillot F, Davies J
and Miller CC: Cdk5/p35 phosphorylates lemur tyrosine kinase-2 to
regulate protein phosphatase-1C phosphorylation and activity. J
Neurochem. 121:343–348. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mandrekar-Colucci S, Karlo JC and Landreth
GE: Mechanisms underlying the rapid peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-γ-mediated amyloid clearance and
reversal of cognitive deficits in a murine model of Alzheimer's
disease. J Neurosci. 32:10117–10128. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Houseknecht KL, Cole BM and Steele PJ:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) and
its ligands: A review. Domest Anim Endocrinol. 22:1–23. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Echeverría F, Valenzuela R, Catalina
Hernandez-Rodas M and Valenzuela A: Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), a
fundamental fatty acid for the brain: New dietary sources.
Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 124:1–10. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Echeverría F, Ortiz M, Valenzuela R and
Videla LA: Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids regulation of
PPARs, signaling: Relationship to tissue development and aging.
Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 114:28–34. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lin N, Chen LM, Pan XD, Zhu YG, Zhang J,
Shi YQ and Chen XC: Tripchlorolide attenuates β-amyloid generation
via suppressing PPARγ-regulated BACE1 activity in N2a/APP695 cells.
Mol Neurobiol. 53:6397–6406. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sadleir KR, Eimer WA, Cole SL and Vassar
R: Aβ reduction in BACE1 heterozygous null 5XFAD mice is associated
with transgenic APP level. Mol Neurodegener. 10:12015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Du J, Zhang L, Liu SB, Zhang C, Huang XQ,
Li J, Zhao NM and Wang Z: PPARgamma transcriptionally regulates the
expression of insulin-degrading enzyme in primary neurons. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 383:485–490. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Vingtdeux V, Chandakkar P, Zhao H, Blanc
L, Ruiz S and Marambaud P: CALHM1 ion channel elicits amyloid-β
clearance by insulin-degrading enzyme in cell lines and in vivo in
the mouse brain. J Cell Sci. 128:2330–2338. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Delerive P, Fruchart JC and Staels B:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors in inflammation
control. J Endocrinol. 169:453–459. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Decourt B, Lahiri DK and Sabbagh MN:
Targeting tumor necrosis factor alpha for Alzheimer's disease. Curr
Alzheimer Res. 14:412–425. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mendiola AS and Cardona AE: The IL-1β
phenomena in neuroinflammatory diseases. J Neural Transm (Vienna).
125:781–795. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Haddick PC, Larson JL, Rathore N, Bhangale
TR, Phung QT, Srinivasan K, Hansen DV, Lill JR; Alzheimer's Disease
Genetic Consortium (ADGC); Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging
Initiative (ADNI), ; et al: A common variant of IL-6R is associated
with elevated IL-6 pathway activity in Alzheimer's disease brains.
J Alzheimers Dis. 56:1037–1054. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cifuentes D, Poittevin M, Bonnin P, Ngkelo
A, Kubis N, Merkulova-Rainon T and Lévy BI: Inactivation of nitric
oxide synthesis exacerbates the development of Alzheimer disease
pathology in APPPS1 mice (Amyloid Precursor Protein/Presenilin-1).
Hypertension. 70:613–623. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Moussa C, Hebron M, Huang X, Ahn J,
Rissman RA, Aisen PS and Turner RS: Resveratrol regulates
Neuro-inflammation and induces adaptive immunity in Alzheimer's
disease. J Neuroinflammation. 14:12017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Spitzer P, Weinbeer J, Herrmann M,
Oberstein TJ, Condic M, Lewczuk P, Kornhuber J and Maler JM:
Analysis of surface levels of IL-1 receptors and macrophage
scavenger receptor I in peripheral immune cells of patients with
Alzheimer's disease. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol. 32:211–220. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
de la Monte SM and Wands JR: Molecular
indices of oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction occur
early and often progress with severity of Alzheimer's disease. J
Alzheimers Dis. 9:167–181. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang ZX, Li YB and Zhao RP:
Epigallocatechin gallate attenuates β-Amyloid generation and
oxidative stress involvement of PPARγ in N2a/APP695 cells.
Neurochem Res. 42:468–480. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Silva-Abreu M, Calpena AC, Andrés-Benito
P, Aso E, Romero IA, Roig-Carles D, Gromnicova R, Espina M, Ferrer
I, García ML and Male D: PPARγ agonist-loaded PLGA-PEG nanocarriers
as a potential treatment for Alzheimer's disease: In vitro and in
vivo studies. Int J Nanomedicine. 13:5577–5590. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Searcy JL, Phelps JT, Pancani T, Kadish I,
Popovic J, Anderson KL, Beckett TL, Murphy MP, Chen KC, Blalock EM,
et al: Long-term pioglitazone treatment improves learning and
attenuates pathological markers in a mouse model of Alzheimer's
disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 30:943–961. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hamano T, Shirafuji N, Makino C, Yen SH,
Kanaan NM, Ueno A, Suzuki J, Ikawa M, Matsunaga A, Yamamura O, et
al: Pioglitazone prevents tau oligomerization. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 478:1035–1042. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Dehghani L, Meamar R, Askari G, Khorvash
F, Shaygannejad V, Pour AF and Javanmard SH: The effect of
pioglitazone on the Alzheimer's disease-induced apoptosis in human
umbilical vein endothelial cells. Int J Prev Med. 4 (Suppl
2):S205–S210. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Escribano L, Simón AM, Gimeno E,
Cuadrado-Tejedor M, de Maturana RL, García-Osta A, Ricobaraza A,
Pérez-Mediavilla A, Del Río J and Frechilla D: Rosiglitazone
rescues memory impairment in Alzheimer's transgenic mice:
Mechanisms involving a reduced amyloid and tau pathology.
Neuropsychopharmacology. 35:1593–1604. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chiang MC, Nicol CJ, Cheng YC, Lin KH, Yen
CH and Lin CH: Rosiglitazone activation of PPARγ-dependent pathways
is neuroprotective in human neural stem cells against
amyloid-beta-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative
stress. Neurobiol Aging. 40:181–190. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Toledo EM and Inestrosa NC: Activation of
Wnt signaling by lithium and rosiglitazone reduced spatial memory
impairment and neurodegeneration in brains of an APPswe/PSEN1ΔE9
mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Mol Psychiatry. 15:272–285,
228. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Strum JC, Shehee R, Virley D, Richardson
J, Mattie M, Selley P, Ghosh S, Nock C, Saunders A and Roses A:
Rosiglitazone induces mitochondrial biogenesis in mouse brain. J
Alzheimers Dis. 11:45–51. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Risner ME, Saunders AM, Altman JF, Ormandy
GC, Craft S, Foley IM, Zvartau-Hind ME and Hosford DA;
Rosiglitazone in Alzheimer's disease study group, : Efficacy of
rosiglitazone in a genetically defined population with
mild-to-moderate Alzheimer's disease. Pharmacogenomics J.
6:246–254. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Combs CK, Johnson DE, Karlo JC, Cannady SB
and Landreth GE: Inflammatory mechanisms in Alzheimer's disease:
Inhibition of β-amyloid-stimulated proinflammatory responses and
neurotoxicity by PPARγ agonists. J Neurosci. 20:558–567. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Quan Q, Qian Y, Li X and Li M:
Pioglitazone reduces β amyloid levels via inhibition of PPARγ
phosphorylation in a neuronal model of Alzheimer's disease. Front
Aging Neurosci. 11:1782019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Aubert RE, Herrera V, Chen W, Haffner SM
and Pendergrass M: Rosiglitazone and pioglitazone increase fracture
risk in women and men with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab.
12:716–721. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Home PD, Pocock SJ, Beck-Nielsen H, Gomis
R, Hanefeld M, Jones NP, Komajda M and McMurray JJ; RECORD study
group, : Rosiglitazone evaluated for cardiovascular outcomes-an
interim analysis. New Engl J Med. 357:28–38. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wang AT and Smith SA: ACP Journal Club. In
older patients, rosiglitazone was associated with increased risk
for stroke, heart failure, and mortality compared with
pioglitazone. Ann Intern Med. 153:JC6–JC11. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Lewis JD, Ferrara A, Peng T, Hedderson M,
Bilker WB, Quesenberry CP, Vaughn DJ, Nessel L, Selby J and Strom
BL: Risk of bladder cancer among diabetic patients treated with
pioglitazone interim report of a longitudinal cohort study.
Diabetes Care. 34:916–922. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Toyota T and Ueno Y: Clinical effect and
side effect of troglitazone. Nihon Rinsho. 58:376–382.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Kim HJ, Kim P and Shin CY: A comprehensive
review of the therapeutic and pharmacological effects of ginseng
and ginsenosides in central nervous system. J Ginseng Res. 37:8–29.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Zhang S, Sun H, Wang C, Zheng X, Jia X,
Cai E and Zhao Y: Comparative analysis of active ingredients and
effects of the combination of Panax ginseng and Ophiopogon
japonicus at different proportions on chemotherapy-induced
myelosuppression mouse. Food Funct. 10:1563–1570. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Kim MH, Kim SH and Yang WM: Mechanisms of
action of phytochemicals from medicinal herbs in the treatment of
Alzheimer's disease. Planta Med. 80:1249–1258. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
LaFerla FM, Green KN and Oddo S:
Intracellular amyloid-beta in Alzheimer's disease. Nat Rev
Neurosci. 8:499–509. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Vassar R, Bennett BD, Babu-Khan S, Kahn S,
Mendiaz EA, Denis P, Teplow DB, Ross S, Amarante P, Loeloff R, et
al: Beta-secretase cleavage of Alzheimer's amyloid precursor
protein by the transmembrane aspartic protease BACE. Science.
286:735–741. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Yu G, Nishimura M, Arawaka S, Levitan D,
Zhang L, Tandon A, Song YQ, Rogaeva E, Chen F, Kawarai T, et al:
Nicastrin modulates presenilin-mediated notch/glp-1 signal
transduction and betaAPP processing. Nature. 407:48–54. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Xu H, Sweeney D, Wang R, Thinakaran G, Lo
AC, Sisodia SS, Greengard P and Gandy S: Generation of Alzheimer
β-amyloid protein in the trans-Golgi network in the apparent
absence of vesicle formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:3748–3752.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Gouras GK, Tsai J, Naslund J, Vincent B,
Edgar M, Checler F, Greenfield JP, Haroutunian V, Buxbaum JD, Xu H,
et al: Intraneuronal Abeta42 accumulation in human brain. Am J
Pathol. 156:15–20. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Pérez A, Morelli L, Cresto JC and Castano
EM: Degradation of soluble amyloid β-peptides 1–40, 1–42, and the
Dutch variant 1–40Q by insulin degrading enzyme from Alzheimer
disease and control brains. Neurochem Res. 25:247–255. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Helenius K, Yang Y, Alasaari J and Mäkelä
TP: Mat1 inhibits peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
γ-mediated adipocyte differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 29:315–323.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Iankova I, Petersen RK, Annicotte JS,
Chavey C, Hansen JB, Kratchmarova I, Sarruf D, Benkirane M,
Kristiansen K and Fajas L: Peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor gamma recruits the positive transcription elongation
factor b complex to activate transcription and promote
adipogenesis. Mol Endocrinol. 20:1494–1505. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|