|
1
|
Baena R and Salinas P: Diet and colorectal
cancer. Maturitas. 80:3245–264. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang XC, Du LQ, Tian LL, Wu HL, Jiang XY,
Zhang H, Li DG, Wang YY, Wu HY, She Y, et al: Expression and
function of miRNA in postoperative radiotherapy sensitive and
resistant patients of non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer.
72:92–99. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
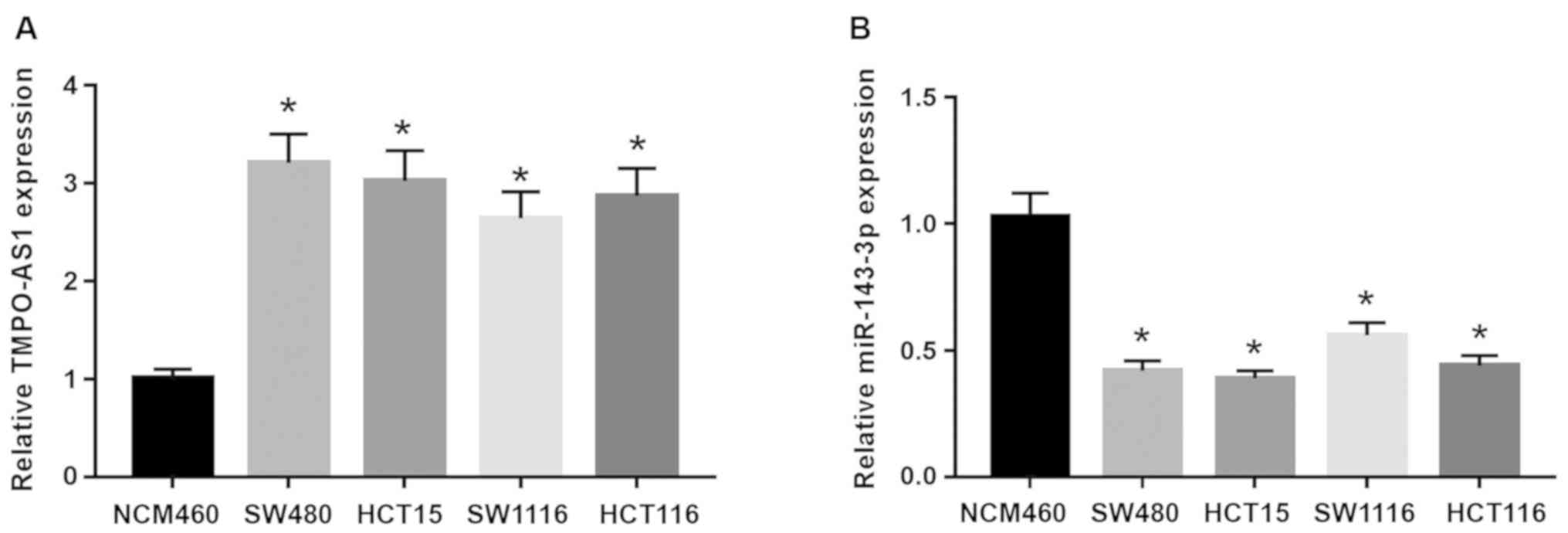
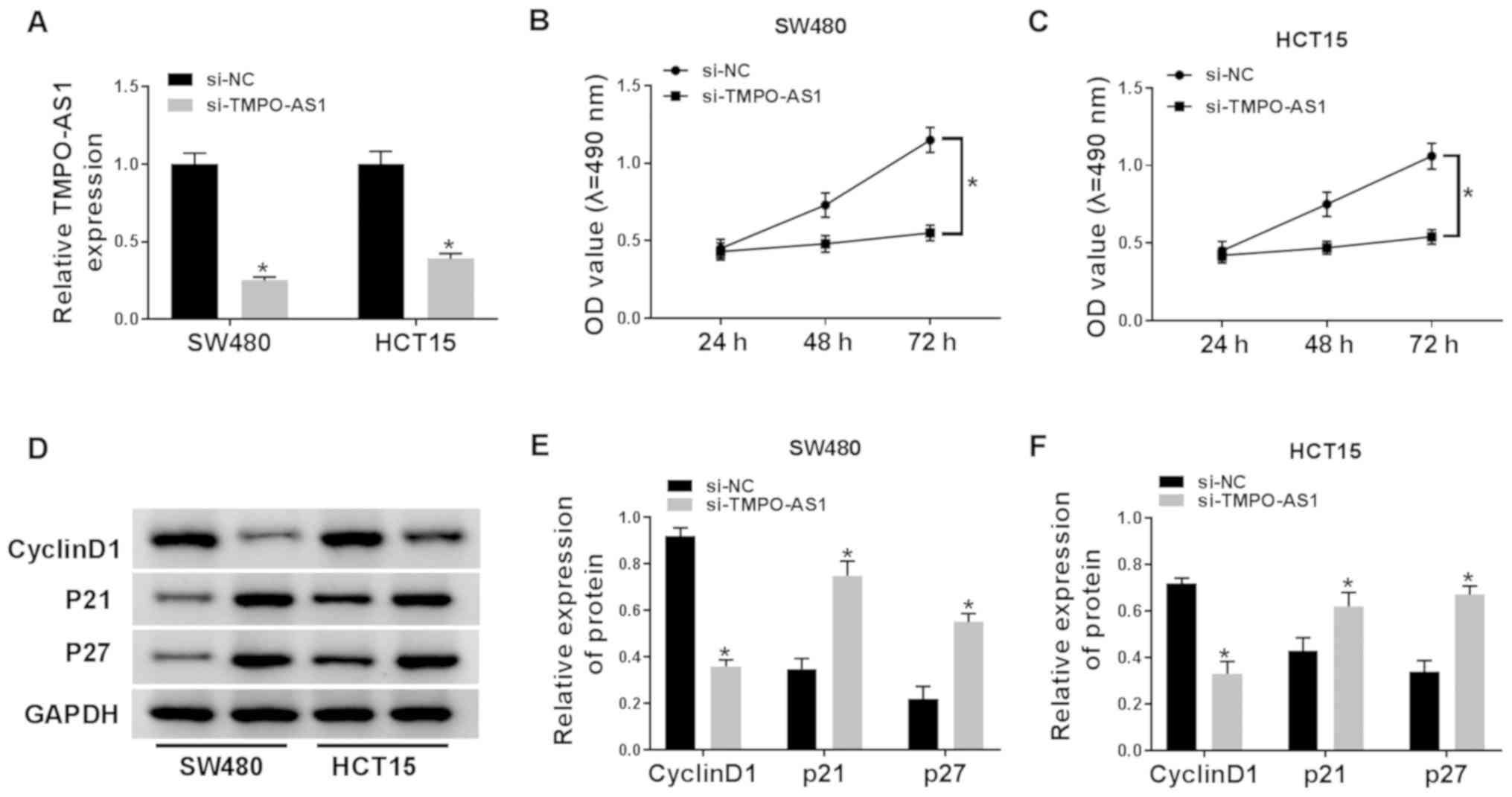
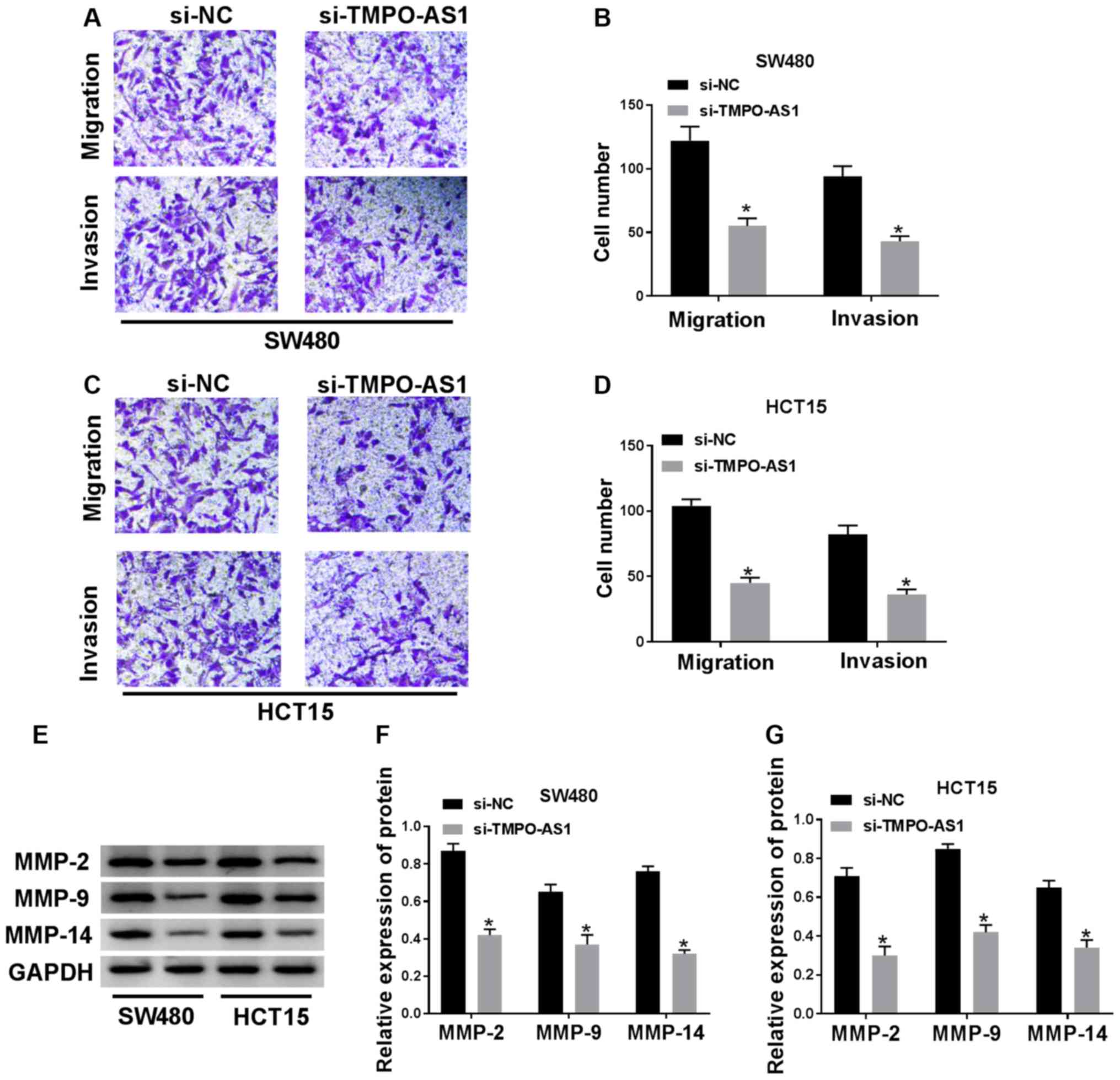
|
4
|
Qi W, Liang W, Jiang H and Waye MM: The
function of miRNA in hepatic cancer stem cell. Biomed Res Int.
2013:3589022013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bao AD, Liu CQ, Hong-Mei WU, Liu S, Guan
WJ and Yue-Hui MA: Association analysis between function of miRNA
and formation of cancer. Chin Anim Husbandry Veterinary Medicine.
2008.
|
|
6
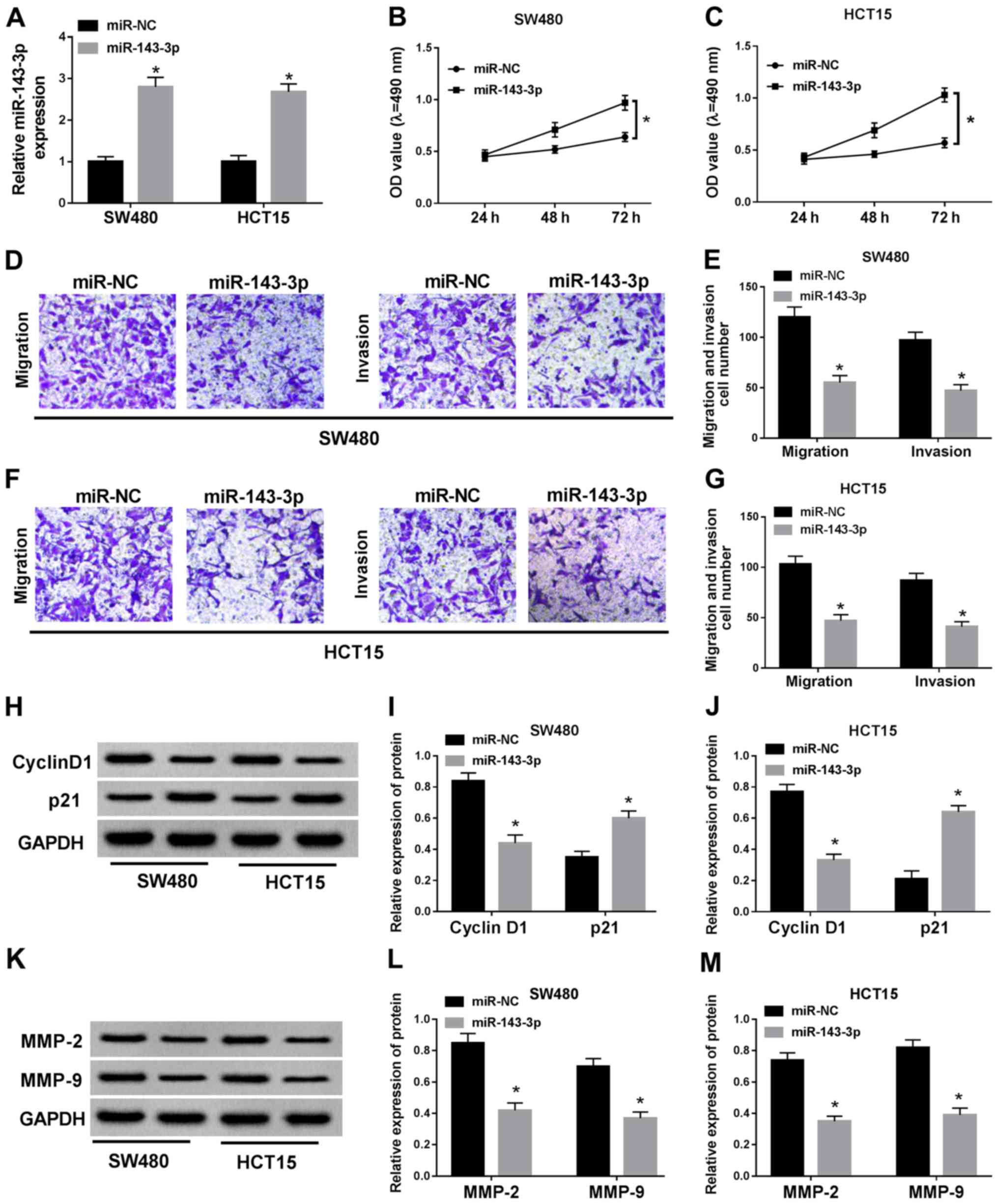
|
Dhamija S and Diederichs S: From junk to
master regulators of invasion: LncRNA functions in migration, EMT
and metastasis. Int J Cancer. 139:269–280. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lian Y, Xia-Yu LI, Tang YY, Yang LT,
Xiao-Ling LI, Xiong W, Gui-Yuan LI and Zeng ZY: Long non-coding
RNAs function as competing endogenous RNAs to regulate cancer
progression. Prog Biochem Biophys. 2016.
|
|
8
|
Fang Q, Chen XY and Zhi XT: Long
non-coding RNA (LncRNA) urothelial carcinoma associated 1 (UCA1)
increases multi-drug resistance of gastric cancer via
downregulating miR-27b. Med Sci Monit. 22:3506–3513. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu H, Yang Z, Ma J and Fan D: Function of
miRNA in controlling drug resistance of human cancers. Curr Drug
Targets. 14:1118–1127. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dou J, Ni Y, He X, Wu D, Li M, Wu S, Zhang
R, Guo M and Zhao F: Decreasing lncRNA HOTAIR expression inhibits
human colorectal cancer stem cells. Am J Transl Res. 8:98–108.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Han P, Li JW, Zhang BM, Lv JC, Li YM, Gu
XY, Yu ZW, Jia YH, Bai XF, Li L, et al: The lncRNA CRNDE promotes
colorectal cancer cell proliferation and chemoresistance via
miR-181a-5p-mediated regulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Mol
Cancer. 16:92017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Peng W, Wang Z and Fan H: LncRNA NEAT1
impacts cell proliferation and apoptosis of colorectal cancer via
regulation of Akt signaling. Pathol Oncol Res. 23:651–656. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang W, Yuan W, Song J, Wang S and Gu X:
LncRna CPS1-IT1 suppresses cell proliferation, invasion and
metastasis in colorectal cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 44:567–580.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen Y, Han X, Yin X, Zhou Y and Wu T:
Decreased expression of miR-132 in CRC tissues and its inhibitory
function on tumor progression. Open Life Sci. 11:130–135. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Guo H, Hu X, Ge S, Qian G and Zhang J:
Regulation of RAP1B by miR-139 suppresses human colorectal
carcinoma cell proliferation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
44:1465–1472. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ma K, Pan X, Fan P, He Y, Gu J, Wang W,
Zhang T, Li Z and Luo X: Loss of miR-638 in vitro promotes cell
invasion and a mesenchymal-like transition by influencing SOX2
expression in colorectal carcinoma cells. Mol Cancer. 13:1182014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Luo H, Zou J, Dong Z, Zeng Q, Wu D and Liu
L: Up-regulated miR-17 promotes cell proliferation, tumour growth
and cell cycle progression by targeting the RND3 tumour suppressor
gene in colorectal carcinoma. Biochem J. 442:311–321. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gao Y, Meng H, Liu S, Hu J, Zhang Y, Jiao
T, Liu Y, Ou J, Wang D, Yao L, et al: LncRNA-HOST2 regulates cell
biological behaviors in epithelial ovarian cancer through a
mechanism involving microRNA let-7b. Hum Mol Genet. 24:841–852.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Paraskevopoulou MD and Hatzigeorgiou AG:
Analyzing MiRNA-LncRNA interactions. Methods Mol Biol.
1402:271–286. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jalali S, Bhartiya D, Lalwani MK,
Sivasubbu S and Scaria V: Systematic transcriptome wide analysis of
lncRNA-miRNA interactions. PLoS One. 8:e538232013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ye S, Yang L, Zhao X, Song W, Wang W and
Zheng S: Bioinformatics method to predict two regulation mechanism:
TF-miRNA-mRNA and lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA in pancreatic cancer. Cell
Biochem Biophys. 70:1849–1858. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhao L, Kong H, Sun H, Chen Z, Chen B and
Zhou M: LncRNA-PVT1 promotes pancreatic cancer cells proliferation
and migration through acting as a molecular sponge to regulate
miR-448. J Cell Physiol. 233:4044–4055. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mohammadrezakhani H, Baradaran B,
Shanehbandi D, Asadi M, Hashemzadeh S, Hajiasgharzadeh K and
Safaralizadeh R: Overexpression and clinicopathological correlation
of long noncoding RNA TMPO-AS1 in colorectal cancer patients. J
Gastrointest Cancer. Nov 25–2019.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
24
|
Cui H and Zhao J: LncRNA TMPO-AS1 serves
as a ceRNA to promote osteosarcoma tumorigenesis by regulating
miR-199a-5p/WNT7B axis. J Cell Biochem. 121:2284–2293. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Saluzzo J, Hallman KM, Aleck K, Dwyer B,
Quigley M, Mladenovik V, Siebert AE and Dinda S: The regulation of
tumor suppressor protein, p53, and estrogen receptor (ERα) by
resveratrol in breast cancer cells. Genes Cancer. 7:414–425.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen R, Li WX, Sun Y, Duan Y, Li Q, Zhang
AX, Hu JL, Wang YM and Gao YD: Comprehensive analysis of lncRNA and
mRNA expression profiles in lung cancer. Clin Lab. 63:313–320.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang X, Hu Y, Cui J, Zhou Y and Chen L:
Coordinated targeting of MMP-2/MMP-9 by miR-296-3p/FOXCUT exerts
tumor-suppressing effects in choroidal malignant melanoma. Mol Cell
Biochem. 445:25–33. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bhan A, Soleimani M and Mandal SS: Long
noncoding RNA and cancer: A new paradigm. Cancer Res. 77:3965–3981.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cui Y, Zhang F, Zhu C, Geng L, Tian T and
Liu H: Upregulated lncRNA SNHG1 contributes to progression of
non-small cell lung cancer through inhibition of miR-101-3p and
activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncotarget.
8:17785–17794. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang G, Li S, Lu J, Ge Y, Wang Q, Ma G,
Zhao Q, Wu D, Gong W, Du M, et al: LncRNA MT1JP functions as a
ceRNA in regulating FBXW7 through competitively binding to
miR-92a-3p in gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 17:872018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang J, Li XY, Hu P and Ding YS: LncRNA
NORAD contributes to colorectal cancer progression by inhibition of
miR-202-5p. Oncol Res. Feb 22–2018 (Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhang M, Wu WB, Wang ZW and Wang XH:
LncRNA NEAT1 is closely related with progression of breast cancer
via promoting proliferation and EMT. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
21:1020–1026. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
An Y, Chen XM, Yang Y, Mo F, Jiang Y, Sun
DL and Cai HH: LncRNA DLX6-AS1 promoted cancer cell proliferation
and invasion by attenuating the endogenous function of miR-181b in
pancreatic cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 18:1432018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Iguchi T, Uchi R, Nambara S, Saito T,
Komatsu H, Hirata H, Ueda M, Sakimura S, Takano Y, Kurashige J, et
al: A long noncoding RNA, lncRNA-ATB, is involved in the
progression and prognosis of colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res.
35:1385–1388. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Peng Q, Lei D, Lin W, Zhou X and Xiang D:
Abstract B42: A two-lncRNA signature in serous exosomes serves as a
new biomarker for colorectal cancer diagnosis. Cancer Res. 76 (6
Suppl):B422016.
|
|
37
|
Shi D, Zheng H, Zhuo C, Peng J, Li D, Xu
Y, Li X, Cai G and Cai S: Low expression of novel lncRNA
RP11-462C24.1 suggests a biomarker of poor prognosis in colorectal
cancer. Med Oncol. 31:312014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zheng HT, Shi DB, Wang YW, Li XX, Xu Y,
Tripathi P, Gu WL, Cai GX and Cai SJ: High expression of lncRNA
MALAT1 suggests a biomarker of poor prognosis in colorectal cancer.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:3174–3181. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Huang W, Su X, Yan W, Kong Z, Wang D,
Huang Y, Zhai Q, Zhang X, Wu H, Li Y, et al: Overexpression of
AR-regulated lncRNA TMPO-AS1 correlates with tumor progression and
poor prognosis in prostate cancer. Prostate. 78:1248–1261. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li D, Hu J, Song H, Xu H, Wu C, Zhao B,
Xie D, Wu T, Zhao J and Fang L: miR-143-3p targeting LIM domain
kinase 1 suppresses the progression of triple-negative breast
cancer cells. Am J Transl Res. 9:2276–2285. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen L, Yao H, Wang K and Liu X: Long
non-coding RNA MALAT1 regulates ZEB1 expression by sponging
miR-143-3p and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression. J
Cell Biochem. 118:4836–4843. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
He Z, Yi J, Liu X, Chen J, Han S, Jin L,
Chen L and Song H: MiR-143-3p functions as a tumor suppressor by
regulating cell proliferation, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition by targeting QKI-5 in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 15:512016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu M, Jia J, Wang X, Liu Y, Wang C and
Fan R: Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes cervical cancer
progression through regulating BCL2 via targeting miR-143-3p.
Cancer Biol Ther. 19:391–399. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ding X, Du J, Mao K, Wang X, Ding Y and
Wang F: MicroRNA-143-3p suppresses tumorigenesis by targeting
catenin-δ1 in colorectal cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 12:3255–3265.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|