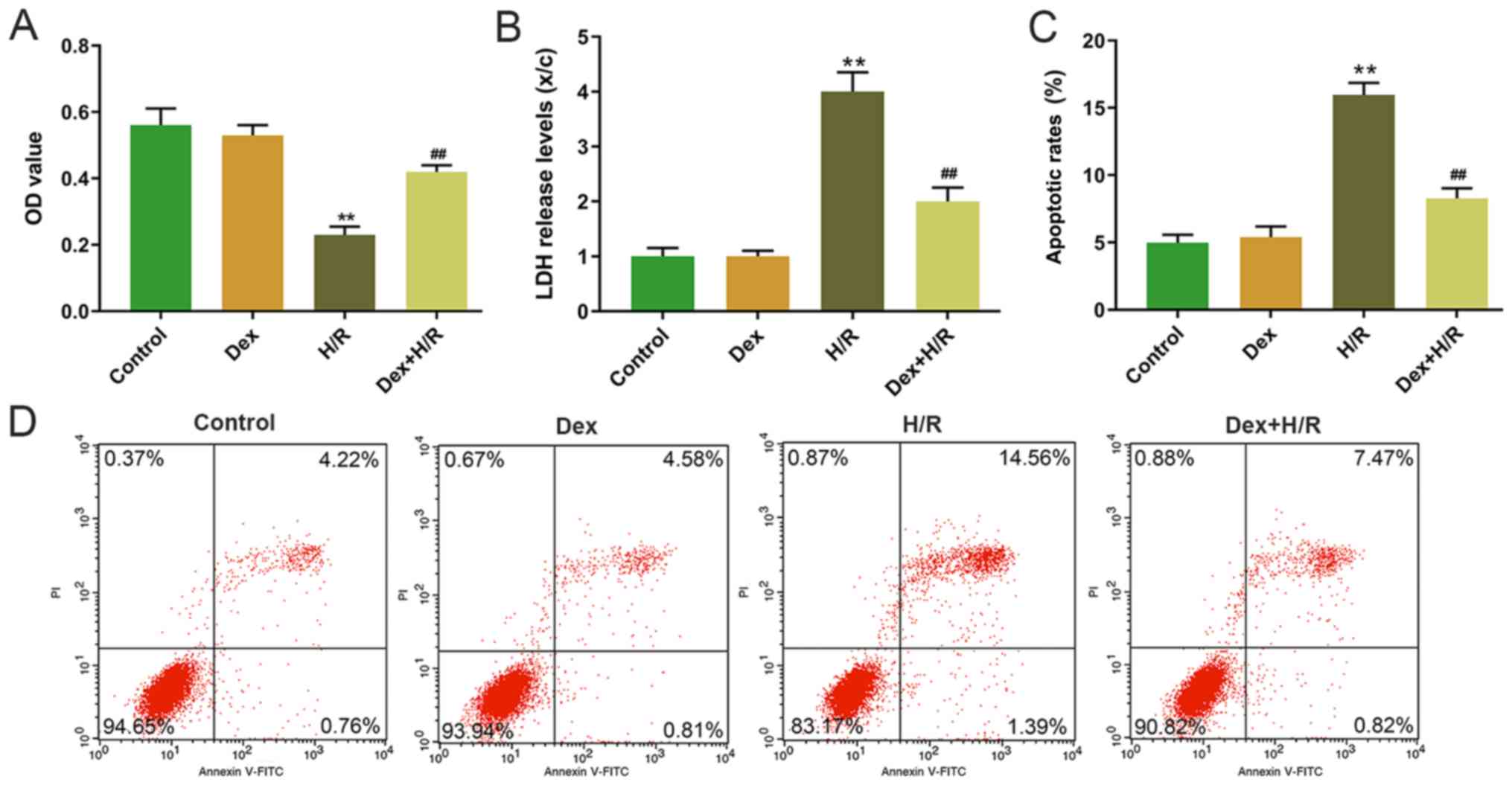
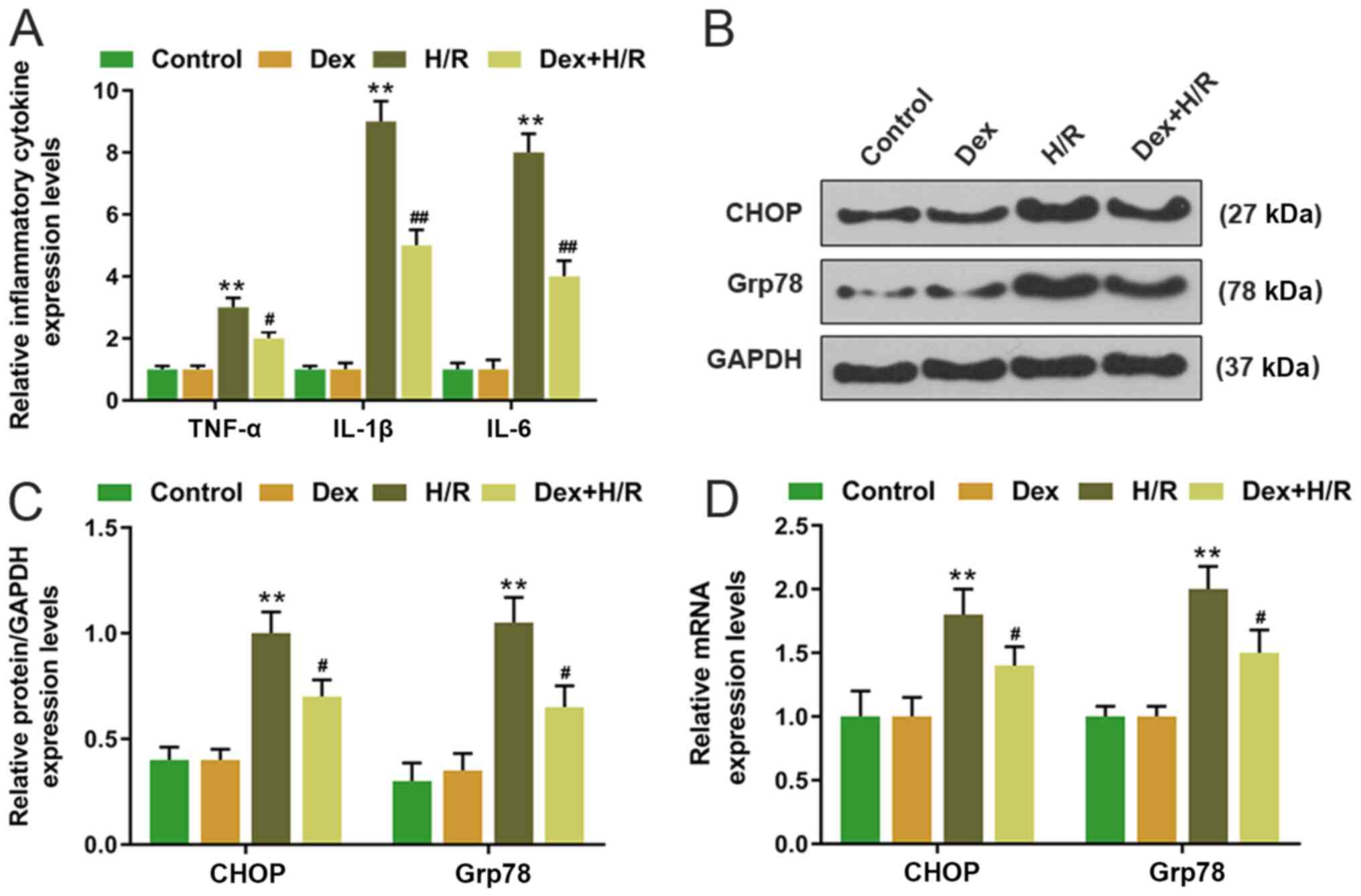
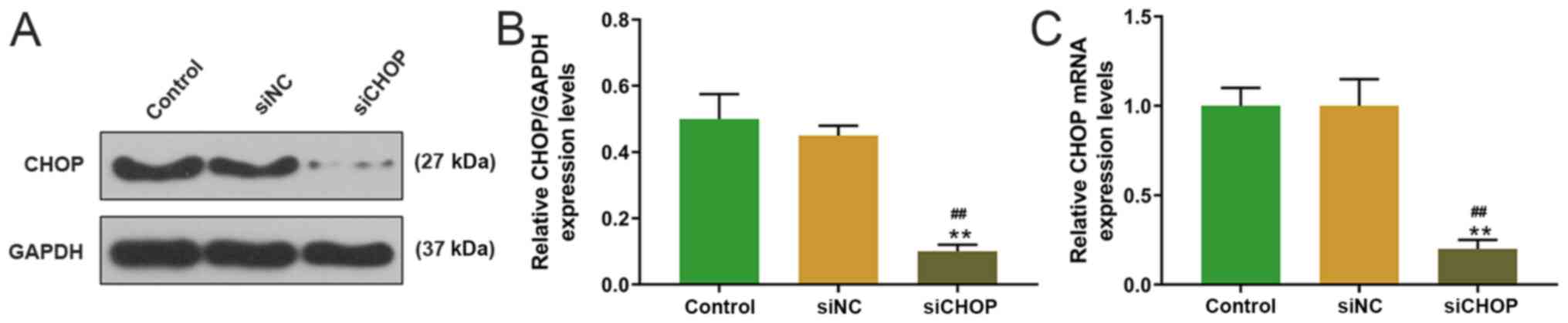
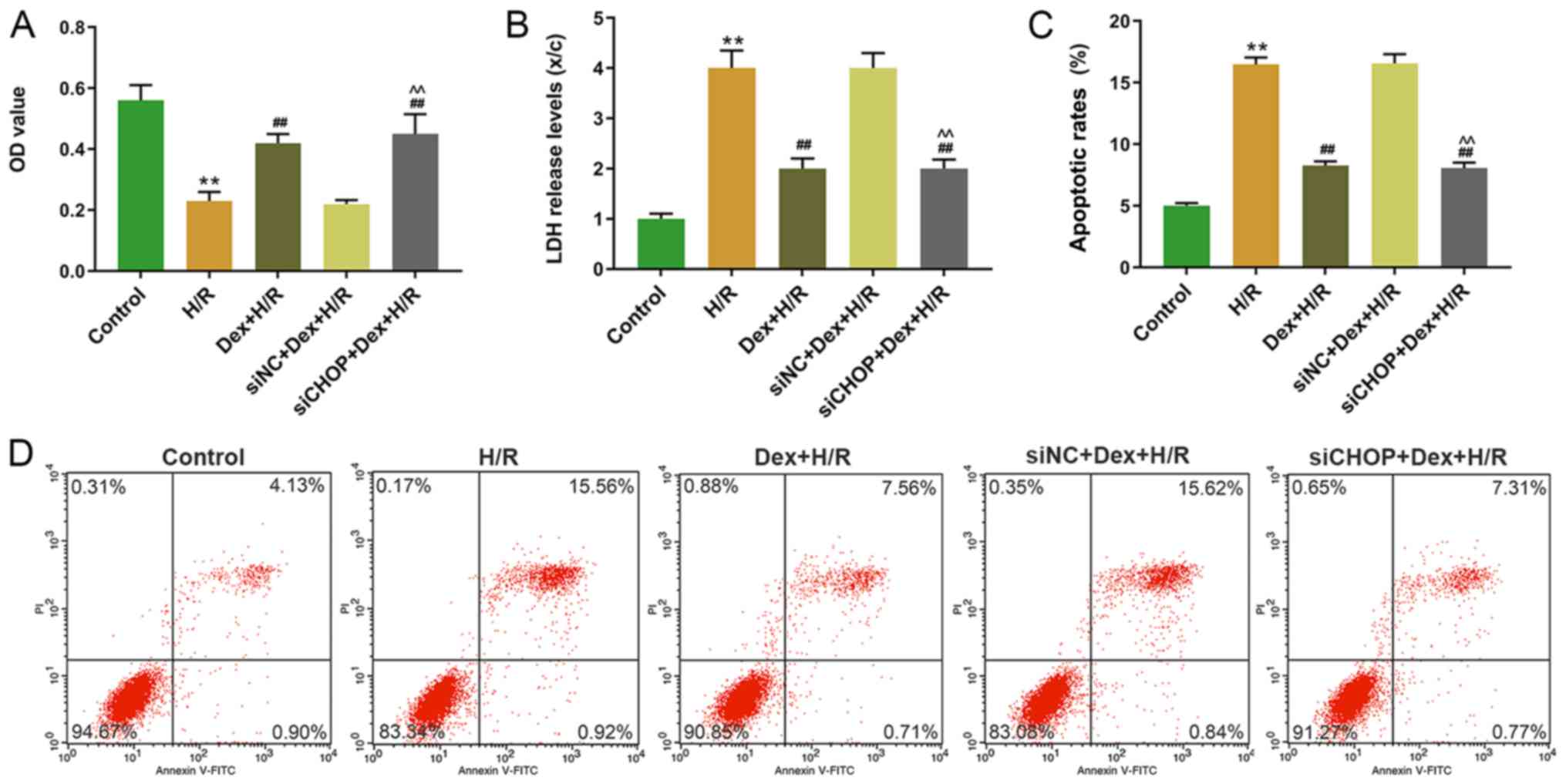
|
1
|
Kloner RA, Shi J, Dai W, Carreno J and
Zhao L: Remote ischemic conditioning in acute myocardial infarction
and shock states. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 25:3307–109. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Cooper WA, Corvera JS, Thourani VH, Puskas
JD, Craver JM, Lattouf OM and Guyton RA: Perfusion-assisted direct
coronary artery bypass provides early reperfusion of ischemic
myocardium and facilitates complete revascularization. Ann Thorac
Surg. 75:1132–1139. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Walker AC and Johnson NJ: Critical care of
the post-cardiac arrest patient. Cardiol Clin. 36:419–428. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wu D, Wang J, Li H, Xue M, Ji A and Li Y:
Role of hydrogen sulfide in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Oxid Med
Cell Longev. 2015:1869082015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Faust KB, Chiantella V, Vinten-Johansen J
and Meredith JH: Oxygen-derived free radical scavengers and
skeletal muscle ischemic/reperfusion injury. Am Surg. 54:709–719.
1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dong HJ, Li J, Zhan H, Li Y and Su RB: Tea
polyphenols promote cardiac function and energy metabolism in ex
vivo rat heart with ischemic/reperfusion injury and inhibit calcium
inward current in cultured rat cardiac myocytes. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da
Xue Xue Bao. 36:604–608. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li JP, Guo LL, Chen Z, Wang R and Wang J:
Relationship between calcium overload and myocardial ischemia
reperfusion injury and intervention strategy of Chinese herbal
medicine. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 41:2168–2173. 2016.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Francis A and Baynosa R:
Ischaemia-reperfusion injury and hyperbaric oxygen pathways: A
review of cellular mechanisms. Diving Hyperb Med. 47:110–117.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zendedel A, Gharibi Z, Anbari K,
Abbaszadeh A, Khayat ZK, Khorramabadi RM, Soleymaninejad M and
Gholami M: Selenium ameliorate peripheral nerve
ischemic-reperfusion injury via decreased TNF-α. Biol Trace Elem
Res. 176:328–337. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Halladin NL: Oxidative and inflammatory
biomarkers of ischemia and reperfusion injuries. Dan Med J.
62:B50542015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Laubach VE and Sharma AK: Mechanisms of
lung ischemia-reperfusion injury. Curr Opin Organ Transplant.
21:246–252. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li Y, Zhu X, Liu X, Du A and Yu B:
miR-200a mediates protection of thymosin β-4 in cardiac
microvascular endothelial cells as a novel mechanism under
hypoxia-reoxygenation injury. J Cell Biochem. 120:19098–19106.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gao C, Wang R, Li B, Guo Y, Yin T, Xia Y,
Zhang F, Lian K, Liu Y, Wang H, et al: TXNIP/Redd1 signalling and
excessive autophagy: A novel mechanism of myocardial
ischaemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Cardiovasc Res. 116:645–657.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Manning JR, Thapa D, Zhang M, Stoner MW,
Traba J, Corey C, Shiva S, Sack MN and Scott I: Loss of GCN5L1 in
cardiac cells disrupts glucose metabolism and promotes cell death
via reduced Akt/mTORC2 signaling. Biochem J. 476:1713–1724. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
El Baz MM and Farahat TEM: Efficacy of
adding dexmedetomidine to intra-articular levobupivacaine on
postoperative pain after knee arthroscopy. Anesth Essays Res.
13:254–258. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sha J, Zhang H, Zhao Y, Feng X, Hu X, Wang
C, Song M and Fan H: Dexmedetomidine attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced liver oxidative stress and cell
apoptosis in rats by increasing GSK-3β/MKP-1/Nrf2 pathway activity
via the α2 adrenergic receptor. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
364:144–152. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen L, Cao J, Cao D, Wang M, Xiang H,
Yang Y, Ying T and Cong H: Protective effect of dexmedetomidine
against diabetic hyperglycemia-exacerbated cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury: An in vivo and in vitro study. Life
Sci. 235:1165532019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen N, Chen X, Xie J, Wu C and Qian J:
Dexmedetomidine protects aged rats from postoperative cognitive
dysfunction by alleviating hippocampal inflammation. Mol Med Rep.
20:2119–2126. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang Q, Tan Y, Zhang N, Xu Y, Wei W, She
Y, Bi X, Zhao B and Ruan X: Dexmedetomidine inhibits activation of
the MAPK pathway and protects PC12 and NG108-15 cells from
lidocaine-induced cytotoxicity at its maximum safe dose. Biomed
Pharmacother. 91:162–166. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang CL, Tsai PS and Huang CJ: Effects of
dexmedetomidine on regulating pulmonary inflammation in a rat model
of ventilator-induced lung injury. Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan.
46:151–159. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jacob H, Stanisavljevic L, Storli KE,
Hestetun KE, Dahl O and Myklebust MP: A four-microRNA classifier as
a novel prognostic marker for tumor recurrence in stage II colon
cancer. Sci Rep. 8:61572018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu YJ, Wang DY, Yang YJ and Lei WF:
Effects and mechanism of dexmedetomidine on neuronal cell injury
induced by hypoxia-ischemia. BMC Anesthesiol. 17:1172017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gonzalez Villarreal C, Said Fernandez S,
Soto Dominguez A, Padilla Rivas G, Garza Treviño E, Rodriguez Rocha
H and Martinez Rodriguez H: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells:
Improving transgene expression level, transfection efficiency and
cell viability. J BUON. 23:1893–1903. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Peng K, Qiu Y, Li J, Zhang ZC and Ji FH:
Dexmedetomidine attenuates hypoxia/reoxygenation injury in primary
neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Exp Ther Med. 14:689–695. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu XR, Li T, Cao L, Yu YY, Chen LL, Fan
XH, Yang BB and Tan XQ: Dexmedetomidine attenuates H2O2-induced
neonatal rat cardiomyocytes apoptosis through mitochondria- and
ER-medicated oxidative stress pathways. Mol Med Rep. 17:7258–7264.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jiang J, Chen DY, Liu ZT, Chen F, Zhang
JJ, Cui J and Pang J: Effect of N-perfluorooctane on
hypoxia/reoxygenation injury in human umbilical vein endothelial
cells. Acta Cardiol Sin. 32:716–722. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chai YL, Xu JZ, Zhang YL and Sheng GT:
Effects of probucol on cultured human umbilical vein endothelial
cells injured by hypoxia/reoxygenation. Genet Mol Res.
15:150167522016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lin CX, Gu JL and Cao JM: The acute toxic
effects of platinum nanoparticles on ion channels, transmembrane
potentials of cardiomyocytes in vitro and heart rhythm in vivo in
mice. Int J Nanomedicine. 14:5595–5609. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fan L, Zhou W, Zhang L, Jiang D, Zhao Q
and Liu L: Sitagliptin protects against hypoxia/reoxygenation
(H/R)-induced cardiac microvascular endothelial cell injury. Am J
Transl Res. 11:2099–2107. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kong QR, Ji DM, Li FR, Sun HY and Wang QX:
MicroRNA-221 promotes myocardial apoptosis caused by myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion by down-regulating PTEN. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol
Sci. 23:3967–3975. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang Y, Zhang H, Zhang Z, Li S, Jiang W,
Li X and Lv J: lncRNA MALAT1 cessation antagonizes
hypoxia/reoxygenation injury in hepatocytes by inhibiting apoptosis
and inflammation via the HMGB1-TLR4 axis. Mol Immunol. 112:22–29.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ge L, Cai Y, Ying F, Liu H, Zhang D, He Y,
Pang L, Yan D, Xu A, Ma H and Xia Z: miR-181c-5p exacerbates
hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis via targeting
PTPN4. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019:19579202019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen Y, Wang H, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Liu S and
Cui L: Pretreatment of ghrelin protects H9c2 cells against
hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cell death via PI3K/AKT and AMPK
pathways. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 47:2179–2187. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yang H, Wang C, Zhang L, Lv J and Ni H:
Rutin alleviates hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced injury in myocardial
cells by up-regulating SIRT1 expression. Chem Biol Interact.
297:44–49. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Soomro AH, Khan E, Noori S, Lone MA, Syal
Z and Sheikh S: Assessment of cytokine release against oral mucosal
cell line culture (TR146) stimulated by neutrophil elastase
associated with Behcet's disease. Int J Dent. 2019:60956282019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang Q, Weng Y, Jiang Y, Zhao S, Zhou D
and Xu N: Overexpression of miR-140-5p inhibits
lipopolysaccharide-induced human intervertebral disc inflammation
and degeneration by downregulating toll-like receptor 4. Oncol Rep.
40:793–802. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Peters MC, McGrath KW, Hawkins GA, Hastie
AT, Levy BD, Israel E, Phillips BR, Mauger DT, Comhair SA, Erzurum
SC, et al: Plasma interleukin-6 concentrations, metabolic
dysfunction, and asthma severity: A cross-sectional analysis of two
cohorts. Lancet Respir Med. 4:574–584. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ren J, Li C, Liu Y, Liu H and Dong Z:
Protective effect of dexmedetomidine against myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury in rabbits. Acta Cir Bras. 33:22–30.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yu J, Yang W, Wang W, Wang Z, Pu Y, Chen
H, Wang F and Qian J: Involvement of miR-665 in protection effect
of dexmedetomidine against oxidative stress injury in myocardial
cells via CB2 and CK1. Biomed Pharmacother. 115:1088942019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Xu Z, Wang D, Zhou Z, Chen Q, Zhang D,
Chen S, Jiang H, Jia C and Liu X: Dexmedetomidine attenuates renal
and myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in a dose-dependent
manner by inhibiting inflammatory response. Ann Clin Lab Sci.
49:31–35. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yang TR, Zhang T, Mu NH, Ruan LB, Duan JL,
Zhang RP and Miao YB: Resina draconis inhibits the
endoplasmic-reticulum-induced apoptosis of myocardial cells via
regulating miR-423-3p/ERK signaling pathway in a tree shrew
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion model. J Biosci. 44:532019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Guan G, Zhang J, Liu S, Huang W, Gong Y
and Gu X: Glucagon-like peptide-1 attenuates endoplasmic reticulum
stress-induced apoptosis in H9c2 cardiomyocytes during
hypoxia/reoxygenation through the GLP-1R/PI3K/Akt pathways. Naunyn
Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 392:715–722. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hu H, Tian M, Ding C and Yu S: The C/EBP
homologous protein (CHOP) transcription factor functions in
endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis and microbial
infection. Front Immunol. 9:30832019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhao J, Xiang X, Zhang H, Jiang D, Liang
Y, Qing W, Liu L, Zhao Q and He Z: CHOP induces apoptosis by
affecting brain iron metabolism in rats with subarachnoid
hemorrhage. Exp Neurol. 302:22–33. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lei Y, Wang S, Ren B, Wang J, Chen J, Lu
J, Zhan S, Fu Y, Huang L and Tan J: CHOP favors endoplasmic
reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma
cells via inhibition of autophagy. PLoS One. 12:e01836802017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Xu JQ, Chen B, Hu HX, Yue RC, Zhang S, Xu
L, Wang H, Li Q, Tan CY, Chen HY and Zhang RY: Lycopene protects
against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury in mouse cardiomyocytes by
inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress induced apoptosis. Zhonghua
Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 44:518–523. 2016.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Cao L, Chen Y, Zhang Z, Li Y and Zhao P:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced NLRP1 inflammasome activation
contributes to myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Shock.
51:511–518. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Guan G, Yang L, Huang W, Zhang J, Zhang P,
Yu H, Liu S and Gu X: Mechanism of interactions between endoplasmic
reticulum stress and autophagy in hypoxia/reoxygenation-nduced
injury of H9c2 cardiomyocytes. Mol Med Rep. 20:350–358.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Liu C, Fu Q, Mu R, Wang F, Zhou C, Zhang
L, Yu B, Zhang Y, Fang T and Tian F: Dexmedetomidine alleviates
cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting endoplasmic
reticulum stress dependent apoptosis through the
PERK-CHOP-Caspase-11 pathway. Brain Res. 1701:246–254. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yang C, Gao C, Yu M, Li B, Lu Y and Lü G:
Effect of dexmedetomidine pretreatment on
hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced injury in human umbilical vein
endothelial cells and the possible mechanism. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za
Zhi. 94:3527–3530. 2014.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|