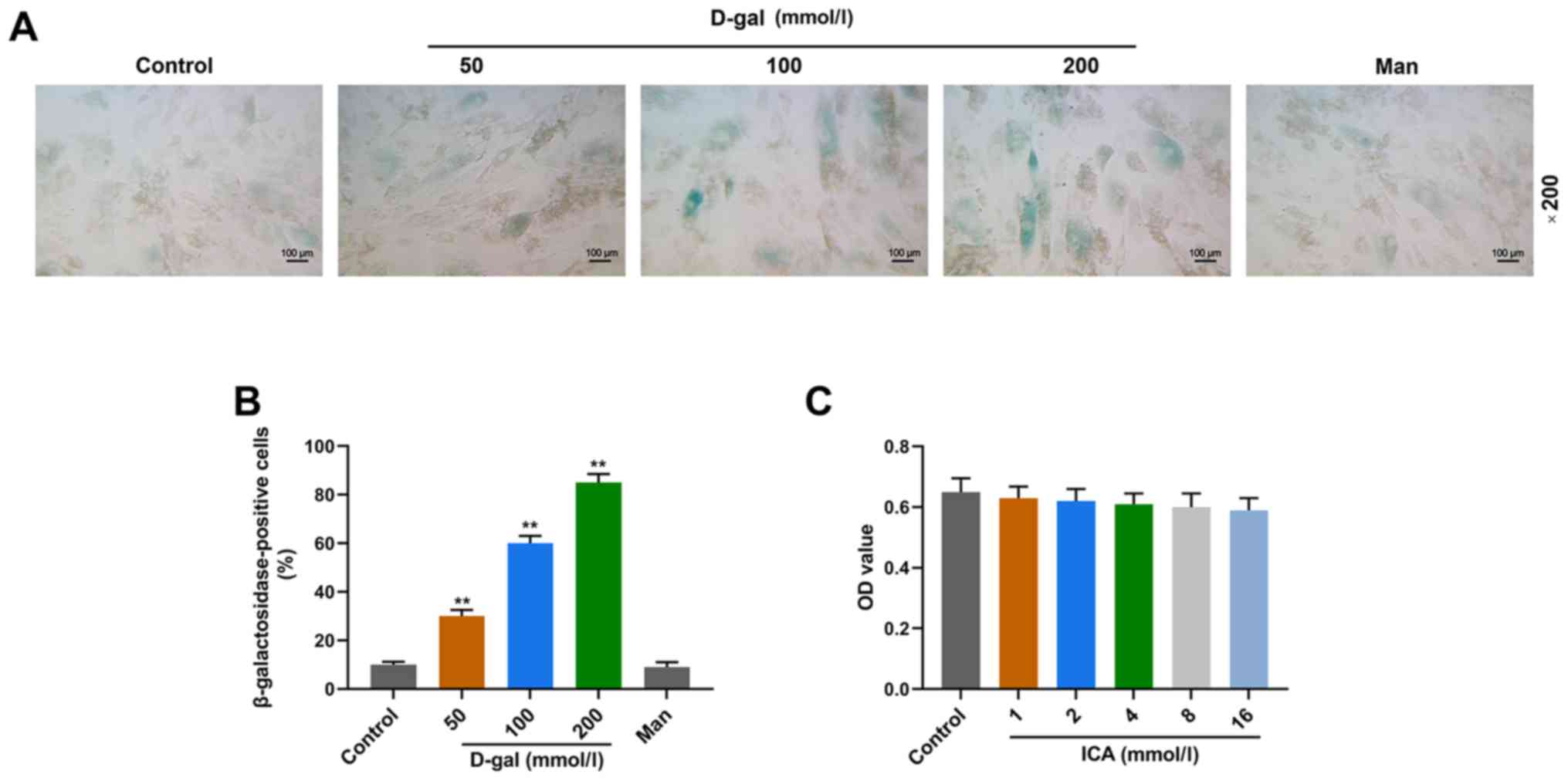
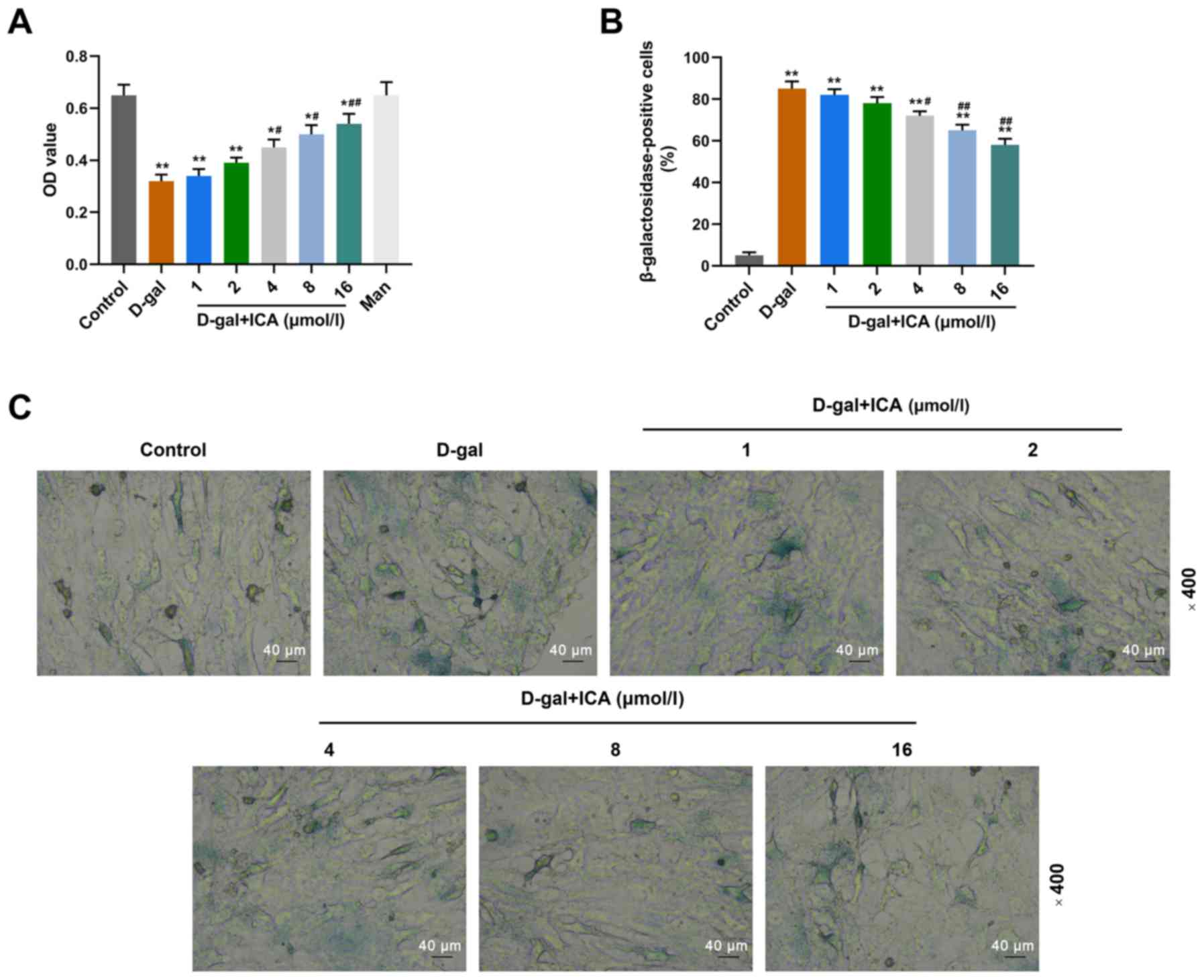
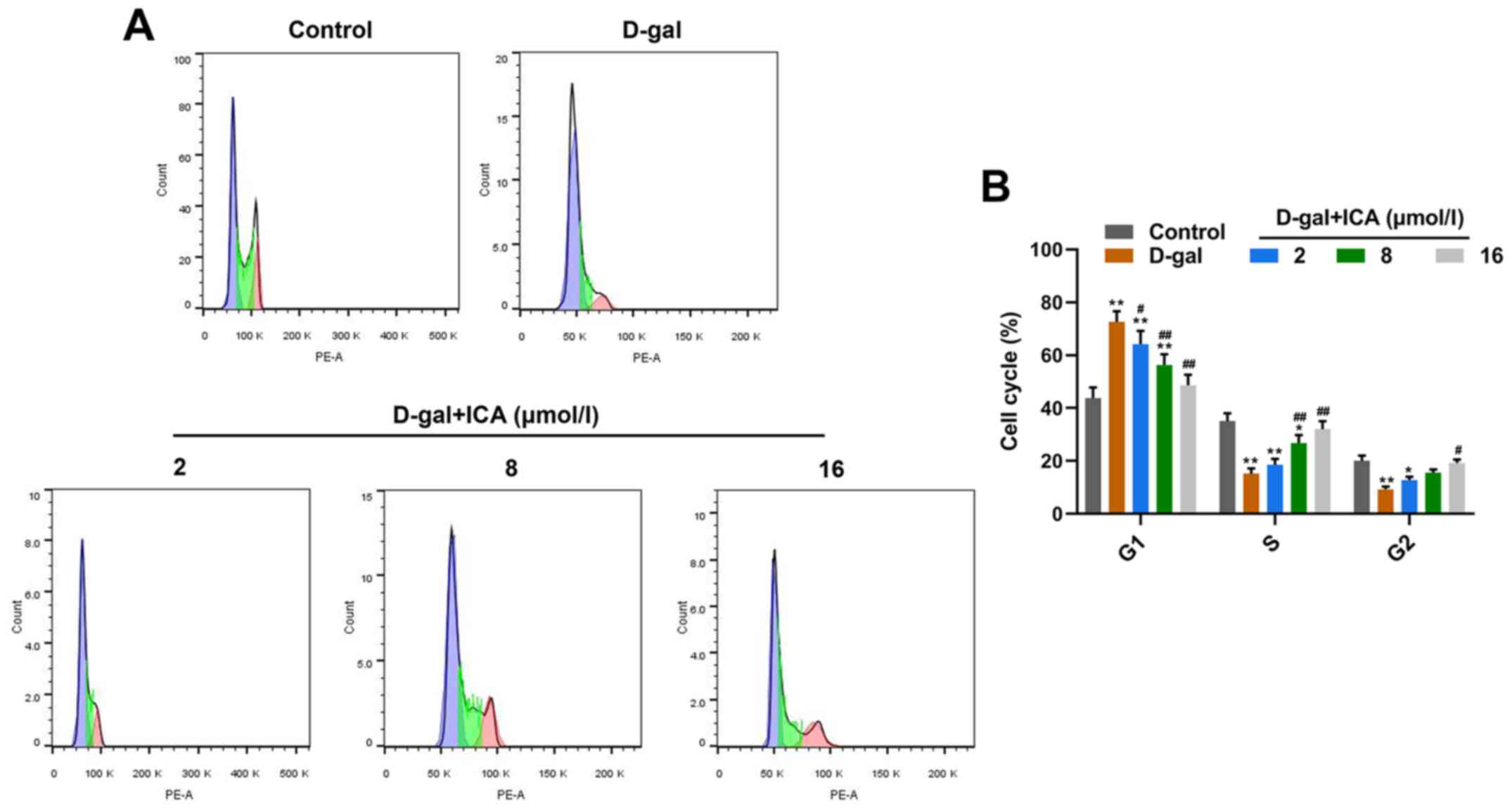
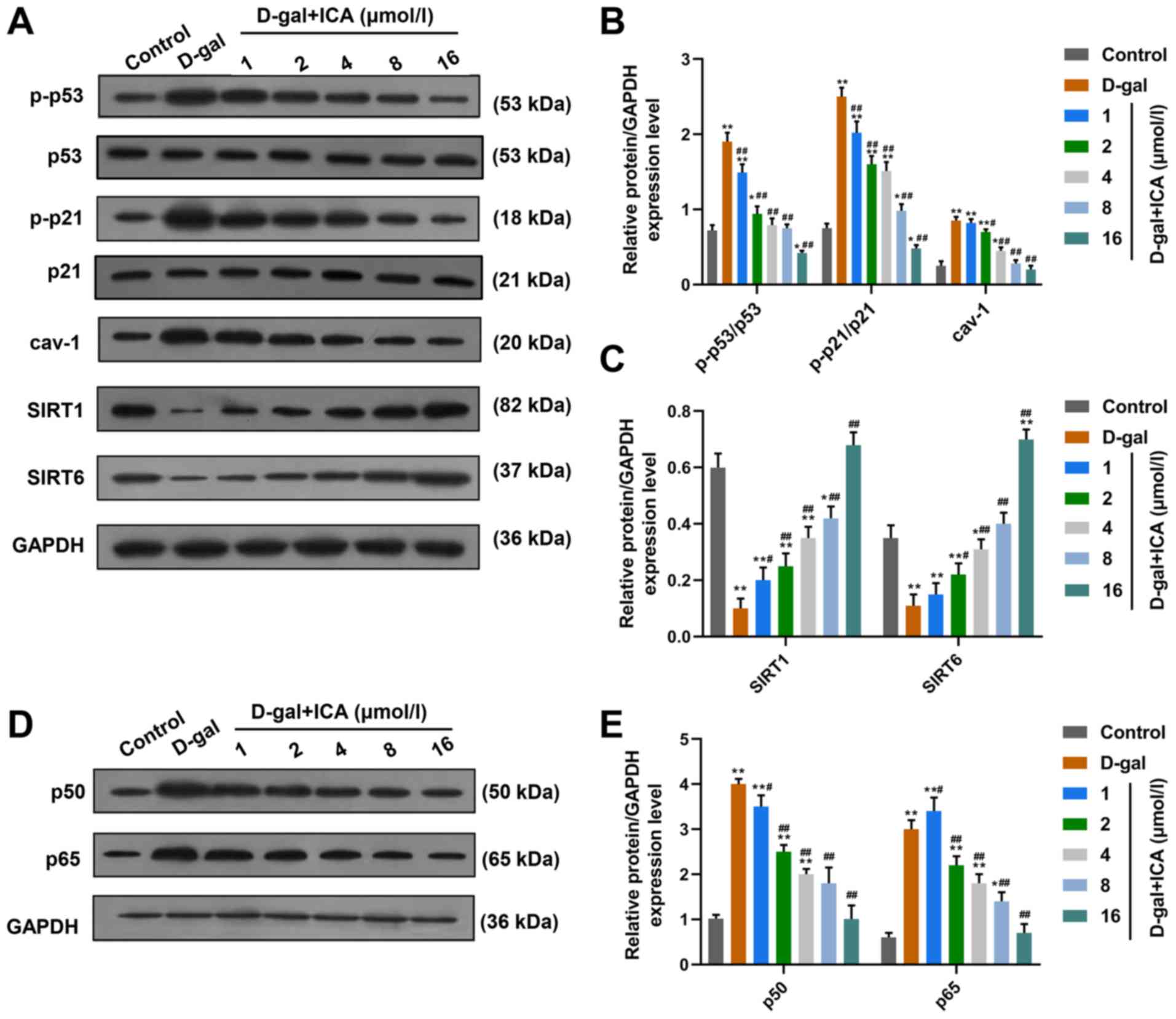
|
1
|
Wang Z, Hu S, Sang S, Luo L and Yu C:
Age-period-cohort analysis of stroke mortality in China: Data from
the global burden of disease study 2013. Stroke. 48:271–275. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li X, Sun L, Zhang W, Li H, Wang S, Mu H,
Zhou Q, Zhang Y, Tang Y, Wang Y, et al: Association of serum
glycine levels with metabolic syndrome in an elderly Chinese
population. Nutr Metab (Lond). 15:892018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lu H, Guo Z, Liu J, Zhang H, Zhao W, Wu Y,
Ni J, Liu W, Tu J, Wang J, et al: Trends in stroke incidence among
elderly low-income residents of rural China: A population-based
study from 1992 to 2016. Aging (Albany NY). 10:3438–3449. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Panicker N, Saminathan H, Jin H, Neal M,
Harischandra DS, Gordon R, Kanthasamy K, Lawana V, Sarkar S, Luo J,
et al: Fyn kinase regulates microglial neuroinflammatory responses
in cell culture and animal models of Parkinson's disease. J
Neurosci. 35:10058–10077. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Toosizadeh N, Harati H, Yen TC, Fastje C,
Mohler J, Najafi B and Dohm M: Paravertebral spinal injection for
the treatment of patients with degenerative facet osteoarthropathy:
Evidence of motor performance improvements based on objective
assessments. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 39:100–108. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gondard E, Soto-Montenegro ML, Cassol A,
Lozano AM and Hamani C: Transcranial direct current stimulation
does not improve memory deficits or alter pathological hallmarks in
a rodent model of Alzheimer's disease. J Psychiatr Res. 114:93–98.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sun K, Yang P, Zhao R, Bai Y and Guo Z:
Matrine attenuates d-galactose-induced aging-related behavior in
mice via inhibition of cellular senescence and oxidative stress.
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018:71086042018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang LF, Cao Q, Wen K, Xiao YF, Chen TT,
Guan XH, Liu Y, Zuo L, Qian YS, Deng KY and Xin HB: CD38 deficiency
alleviates d-galactose-induced myocardial cell senescence through
NAD(+)/sirt1 signaling pathway. Front Physiol. 10:11252019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang JL, Liu B, Zhang C, Wang XM, Zhen D,
Huang XM, Chen W and Gao JM: Effects of icariin on ovarian function
in d-galactose-induced aging mice. Theriogenology. 125:157–167.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sze SC, Tong Y, Ng TB, Cheng CL and Cheung
HP: Herba epimedii: Anti-oxidative properties and its medical
implications. Molecules. 15:7861–7870. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li XA, Ho YS, Chen L and Hsiao WL: The
protective effects of icariin against the homocysteine-induced
neurotoxicity in the primary embryonic cultures of rat cortical
neurons. Molecules. 21:15572016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Pei LK, Guo BL, Sun SQ and Huang WH: Study
on the identification of some species of Herba Epimedii with FTIR.
Guang Pu Xue Yu Guang Pu Fen Xi. 28:55–60. 2008.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shen CY, Jiang JG, Yang L, Wang DW and Zhu
W: Anti-ageing active ingredients from herbs and nutraceuticals
used in traditional Chinese medicine: Pharmacological mechanisms
and implications for drug discovery. Br J Pharmacol. 174:1395–1425.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hu ZW, Shen ZY and Huang JH: Experimental
study on effect of epimedium flavonoids in protecting telomere
length of senescence cells HU. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi.
24:1094–1097. 2004.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cai WJ, Zhang XM and Huang JH: Effect of
epimedium flavonoids in retarding aging of C. elegans.
Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 28:522–525. 2008.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang SQ, Cai WJ, Huang JH, Wu B, Xia SJ,
Chen XL, Zhang XM and Shen ZY: Icariin, a natural flavonol
glycoside, extends healthspan in mice. Exp Gerontol. 69:226–235.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang B, Wang G, He J, Yang Q, Li D, Li J
and Zhang F: Icariin attenuates neuroinflammation and exerts
dopamine neuroprotection via an Nrf2-dependent manner. J
Neuroinflammation. 16:922019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sanz G, Singh M, Peuget S and Selivanova
G: Inhibition of p53 inhibitors: progress, challenges and
perspectives. J Mol Cell Biol. 11:586–599. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wu D and Prives C: Relevance of the
p53-MDM2 axis to aging. Cell Death Differ. 25:169–179. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ou HL and Schumacher B: DNA damage
responses and p53 in the aging process. Blood. 131:488–495. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lessel D, Wu D, Trujillo C, Ramezani T,
Lessel I, Alwasiyah MK, Saha B, Hisama FM, Rading K, Goebel I, et
al: Dysfunction of the MDM2/p53 axis is linked to premature aging.
J Clin Invest. 127:3598–3608. 2017. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Marudamuthu AS, Shetty SK, Bhandary YP,
Karandashova S, Thompson M, Sathish V, Florova G, Hogan TB,
Pabelick CM, Prakash YS, et al: Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1
suppresses profibrotic responses in fibroblasts from fibrotic
lungs. J Biol Chem. 290:9428–9441. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jiang C, Liu G, Luckhardt T, Antony V,
Zhou Y, Carter AB, Thannickal VJ and Liu RM: Serpine 1 induces
alveolar type II cell senescence through activating p53-p21-Rb
pathway in fibrotic lung disease. Aging Cell. 16:1114–1124. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Müllers E, Silva Cascales H, Burdova K,
Macurek L and Lindqvist A: Residual Cdk1/2 activity after DNA
damage promotes senescence. Aging Cell. 16:575–584. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
De U, Son JY, Jeon Y, Ha SY, Park YJ, Yoon
S, Ha KT, Choi WS, Lee BM, Kim IS, et al: Plumbagin from a tropical
pitcher plant (Nepenthes alata Blanco) induces apoptotic cell death
via a p53-dependent pathway in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells.
Food Chem Toxicol. 123:492–500. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wheaton K: Caveolar vesicles generate DNA
damage and perpetuate cellular aging. Cell Res. 21:993–994. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wheaton K, Sampsel K, Boisvert FM, Davy A,
Robbins S and Riabowol K: Loss of functional caveolae during
senescence of human fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 187:226–235. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bai L, Deng X, Li J, Wang M, Li Q, An W, A
D and Cong YS: Regulation of cellular senescence by the essential
caveolar component PTRF/Cavin-1. Cell Res. 21:1088–1101. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ding L, Zeng Q, Wu J, Li D, Wang H, Lu W,
Jiang Z and Xu G: Caveolin-1 regulates oxidative stress-induced
senescence in nucleus pulposus cells primarily via the p53/p21
signaling pathway in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 16:9521–9527. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tennen RI and Chua KF: Chromatin
regulation and genome maintenance by mammalian SIRT6. Trends
Biochem Sci. 36:39–46. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
de Oliveira RM, Pais TF and Outeiro TF:
Sirtuins: Common targets in aging and in neurodegeneration. Curr
Drug Targets. 11:1270–1280. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Carew JS, Giles FJ and Nawrocki ST:
Histone deacetylase inhibitors: Mechanisms of cell death and
promise in combination cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 269:7–17. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chuang PY, Cai W, Li X, Fang L, Xu J,
Yacoub R, He JC and Lee K: Reduction in podocyte SIRT1 accelerates
kidney injury in aging mice. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
313:F621–F628. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tran D, Bergholz J, Zhang H, He H, Wang Y,
Zhang Y, Li Q, Kirkland JL and Xiao ZX: Insulin-like growth
factor-1 regulates the SIRT1-p53 pathway in cellular senescence.
Aging Cell. 13:669–678. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen Y, Sun T, Wu J, Kalionis B, Zhang C,
Yuan D, Huang J, Cai W, Fang H and Xia S: Icariin intervenes in
cardiac inflammaging through upregulation of SIRT6 enzyme activity
and inhibition of the NF-kappa B pathway. Biomed Res Int.
2015:8959762015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Salminen A, Ojala J, Huuskonen J,
Kauppinen A, Suuronen T and Kaarniranta K: Interaction of
aging-associated signaling cascades: Inhibition of NF-kappaB
signaling by longevity factors FoxOs and SIRT1. Cell Mol Life Sci.
65:1049–1058. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tilstra JS, Robinson AR, Wang J, Gregg SQ,
Clauson CL, Reay DP, Nasto LA, St Croix CM, Usas A, Vo N, et al:
NF-kB inhibition delays DNA damage-induced senescence and aging in
mice. J Clin Invest. 122:2601–2612. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kawahara TL, Michishita E, Adler AS,
Damian M, Berber E, Lin M, McCord RA, Ongaigui KC, Boxer LD, Chang
HY and Chua KF: SIRT6 links histone H3 lysine 9 deacetylation to
NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression and organismal life span. Cell.
136:62–74. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|