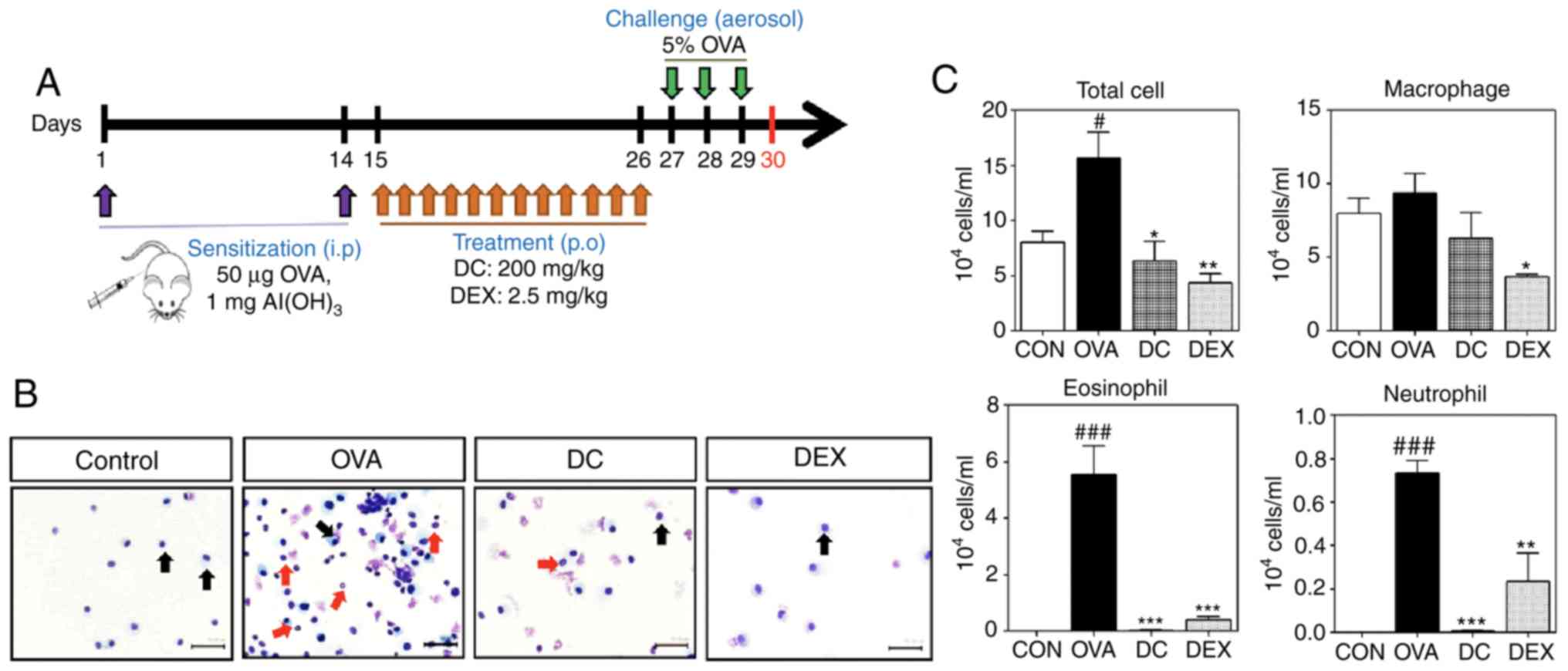
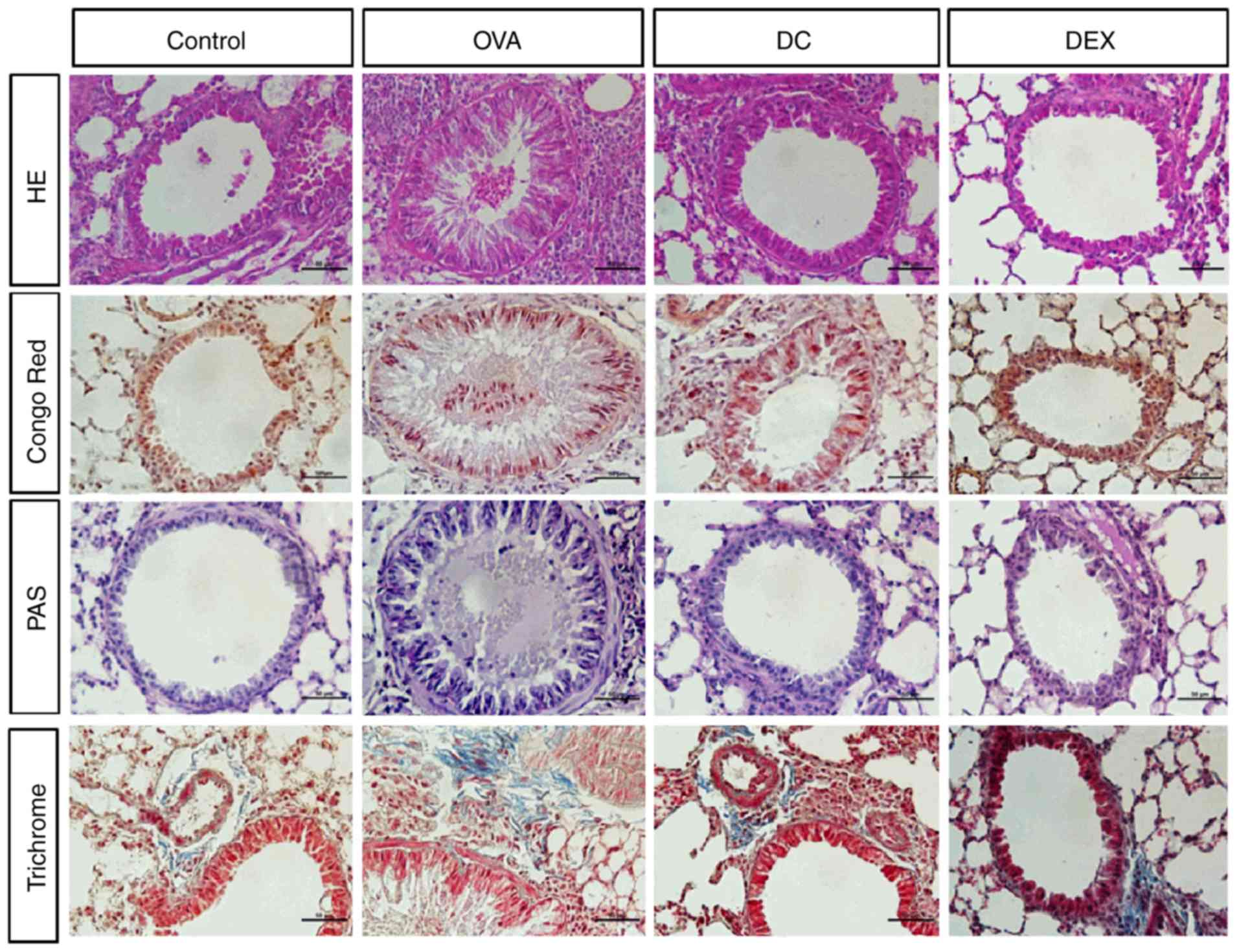
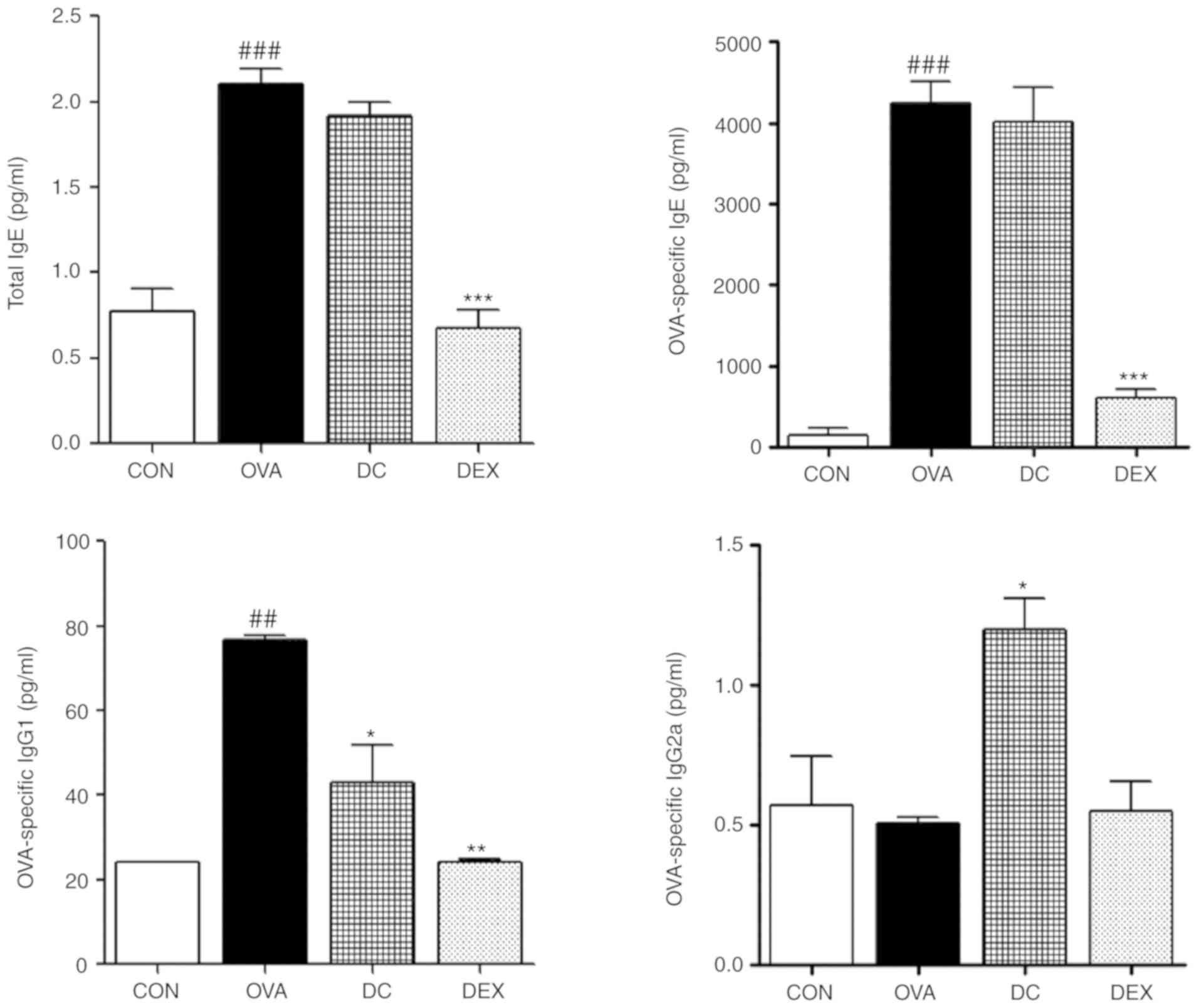
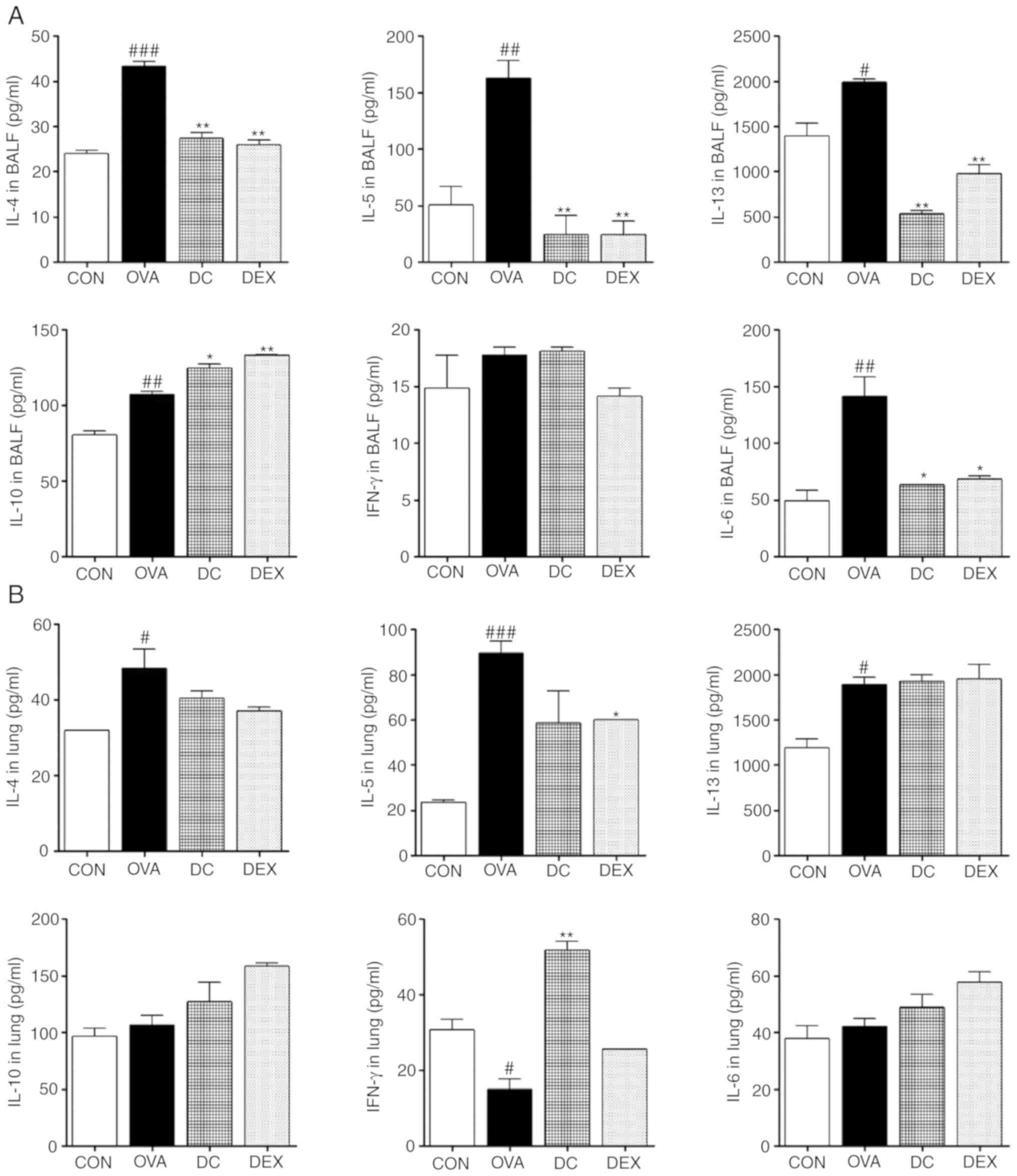
|
1
|
Hamid Q and Tulic M: Immunobiology of
asthma. Annu Rev Physiol. 71:489–507. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Spina D: Modulation of sensory nerve
function in the airways. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 11:319–330. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Barnes PJ: The cytokine network in asthma
and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Clin Invest.
118:3546–3556. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Choi IW, Kim DK, Ko HM and Lee HK:
Administration of antisense phosphorothioate oligonucleotide to the
p65 subunit of NF-kappaB inhibits established asthmatic reaction in
mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 4:1817–1828. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kang NI, Yoon HY, Lee YR, Won M, Chung MJ,
Park JW, Hur GM, Lee HK and Park BH: A20 attenuates allergic airway
inflammation in mice. J Immunol. 183:1488–1495. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Desmet C, Gosset P, Pajak B, Cataldo D,
Bentires-Alj M, Lekeux P and Bureau F: Selective blockade of
NF-kappa B activity in airway immune cells inhibits the effector
phase of experimental asthma. J Immunol. 173:5766–5775. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Oh SW, Cha JY, Jung JE, Chang BC, Kwon HJ,
Lee BR and Kim DY: Curcumin attenuates allergic airway inflammation
and hyper-responsiveness in mice through NF-κB inhibition. J
Ethnopharmacol. 136:414–421. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Surh YJ, Na HK, Lee JY and Keum YS:
Molecular mechanisms underlying anti-tumor promoting activities of
heat-processed Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer. J Korean Med Sci. 16
(Suppl):S38–S41. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Markman M: Safety issues in using
complementary and alternative medicine. J Clin Oncol. 20 (Suppl
18):S39–S41. 2002.
|
|
10
|
Wang J, Yan YT, Fu SZ, Peng B, Bao LL,
Zhang YL, Hu JH, Zeng ZP, Geng DH and Gao ZP: Anti-influenza virus
(H5N1) activity screening on the phloroglucinols from rhizomes of
Dryopteris crassirhizoma. Molecules. 22:4312017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Lee HB, Kim JC and Lee SM: Antibacterial
activity of two phloroglucinols, flavaspidic acids AB and PB, from
Dryopteris crassirhizoma. Arch Pharm Res. 32:655–659. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nakane H, Arisawa M, Fujita A, Koshimura S
and Ono K: Inhibition of HIV-reverse transcriptase activity by some
phloroglucinol derivatives. FEBS Lett. 286:83–85. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee SM, Na MK, An RB, Min BS and Lee HK:
Antioxidant activity of two phloroglucinol derivatives from
Dryopteris crassirhizoma. Biol Pharm Bull. 26:1354–1356.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee JS, Miyashiro H, Nakamura N and
Hattori M: Two new triterpenes from the Rhizome of Dryopteris
crassirhizoma, and inhibitory activities of its constituents on
human immunodeficiency virus-1 protease. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo).
56:711–714. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chang X, Li W, Koike K, Wu L and Nikaido
T: Phenolic constituents from the rhizomes of Dryopteris
crassirhizoma. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 54:748–750. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liang YH, Wang W, Yu SW, Ye M, He XH, Gong
NB, Lu Y, Khan IA and Guo DA: A new chiratane type triterpenoid
from the rhizomes of Drynaria fortunei. Fitoterapia. 81:988–991.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Grzelewska-Rzymowska I and Pietrzkowicz M:
Role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in allergic inflammation and
airway hyperresponsiveness. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 16:173–178.
2004.(In Polish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Church MK and Levi-Schaffer F: The human
mast cell. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 99:155–160. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Marini-Bettolo GB: Present aspects of the
use of plants in traditional medicine. J Ethnopharmacol. 2:5–7.
1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chang SH, Bae JH, Hong DP, Choi KD, Kim
SC, Her E, Kim SH and Kang CD: Dryopteris crassirhizoma has
anti-cancer effects through both extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic
pathways and G0/G1 phase arrest in human prostate cancer cells. J
Ethnopharmacol. 130:248–254. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jayachandran M, Zhang T, Wu Z, Liu Y and
Xu B: Isoquercetin regulates SREBP-1C via AMPK pathway in skeletal
muscle to exert antihyperlipidemic and anti-inflammatory effects in
STZ induced diabetic rats. Mol Biol Rep. 47:593–602. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Morikawa K, Nonaka M, Narahara M, Torii I,
Kawaguchi K, Yoshikawa T, Kumazawa Y and Morikawa S: Inhibitory
effect of quercetin on carrageenan-induced inflammation in rats.
Life Sci. 74:709–721. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
McKay A, Leung BP, McInnes IB, Thomson NC
and Liew FY: A novel anti-inflammatory role of simvastatin in a
murine model of allergic asthma. J Immunol. 172:2903–2908. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Piao CH, Bui TT, Song CH, Shin HS, Shon DH
and Chai OH: Trigonella foenum-graecum alleviates airway
inflammation of allergic asthma in ovalbumin-induced mouse model.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 482:1284–1288. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mueller M, Beck V and Jungbauer A: PPARα
activation by culinary herbs and spices. Planta Med. 77:497–504.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Vallabhapurapu S and Karin M: Regulation
and function of NF-kappaB transcription factors in the immune
system. Annu Rev Immunol. 27:693–733. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Edwards MR, Bartlett NW, Clarke D, Birrell
M, Belvisi M and Johnston SL: Targeting the NF-κB pathway in asthma
and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Pharmacol Ther.
121:1–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Henderson WR Jr, Chi EY, Teo JL, Nguyen C
and Kahn M: A small molecule inhibitor of redox-regulated NF-kappa
B and activator protein-1 transcription blocks allergic airway
inflammation in a mouse asthma model. J Immunol. 169:5294–5299.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Baba Y, Nishida K, Fujii Y, Hirano T,
Hikida M and Kurosaki T: Essential function for the calcium sensor
STIM1 in mast cell activation and anaphylactic responses. Nat
Immunol. 9:81–88. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Oh HA, Kim HM and Jeong HJ: Distinct
effects of imperatorin on allergic rhinitis: Imperatorin inhibits
caspase-1 activity in vivo and in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
339:72–81. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|