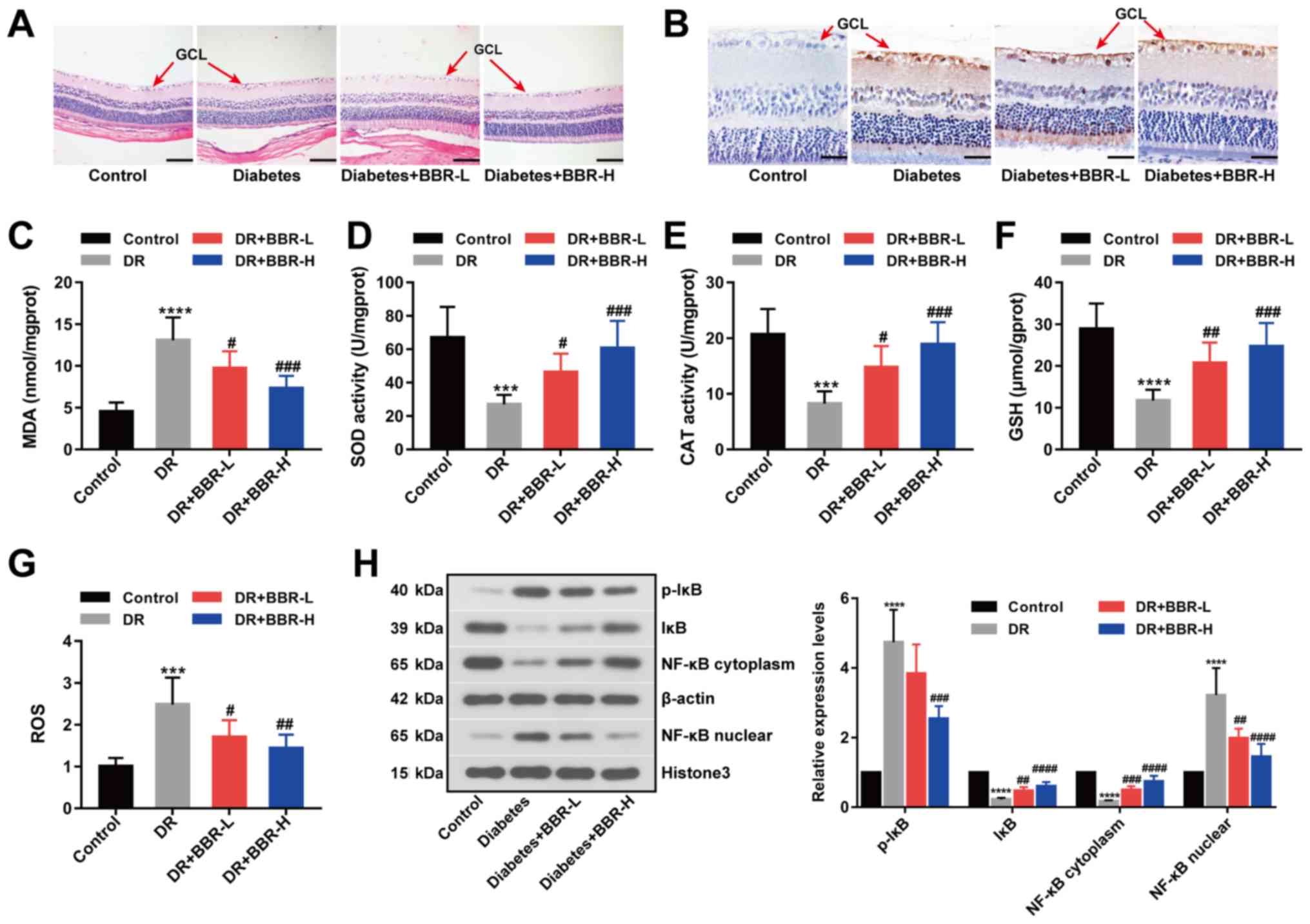
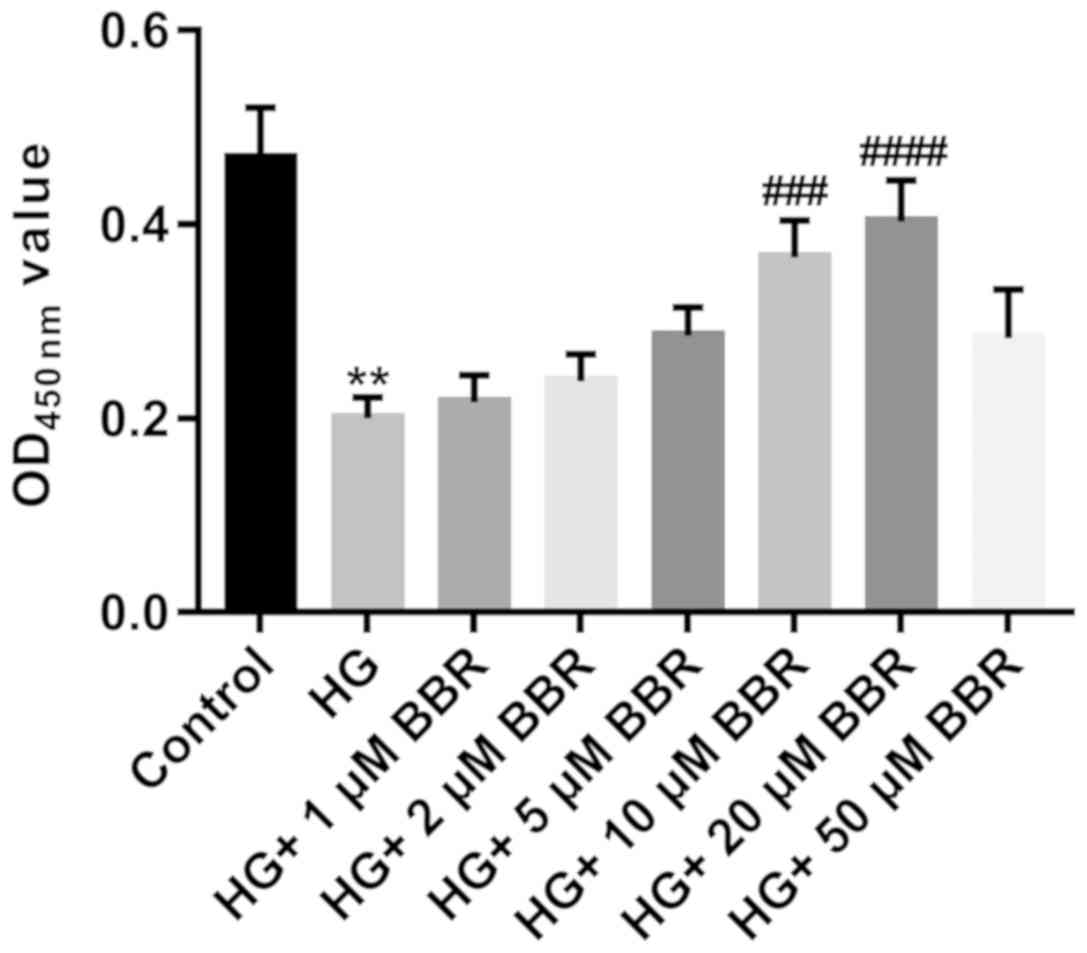
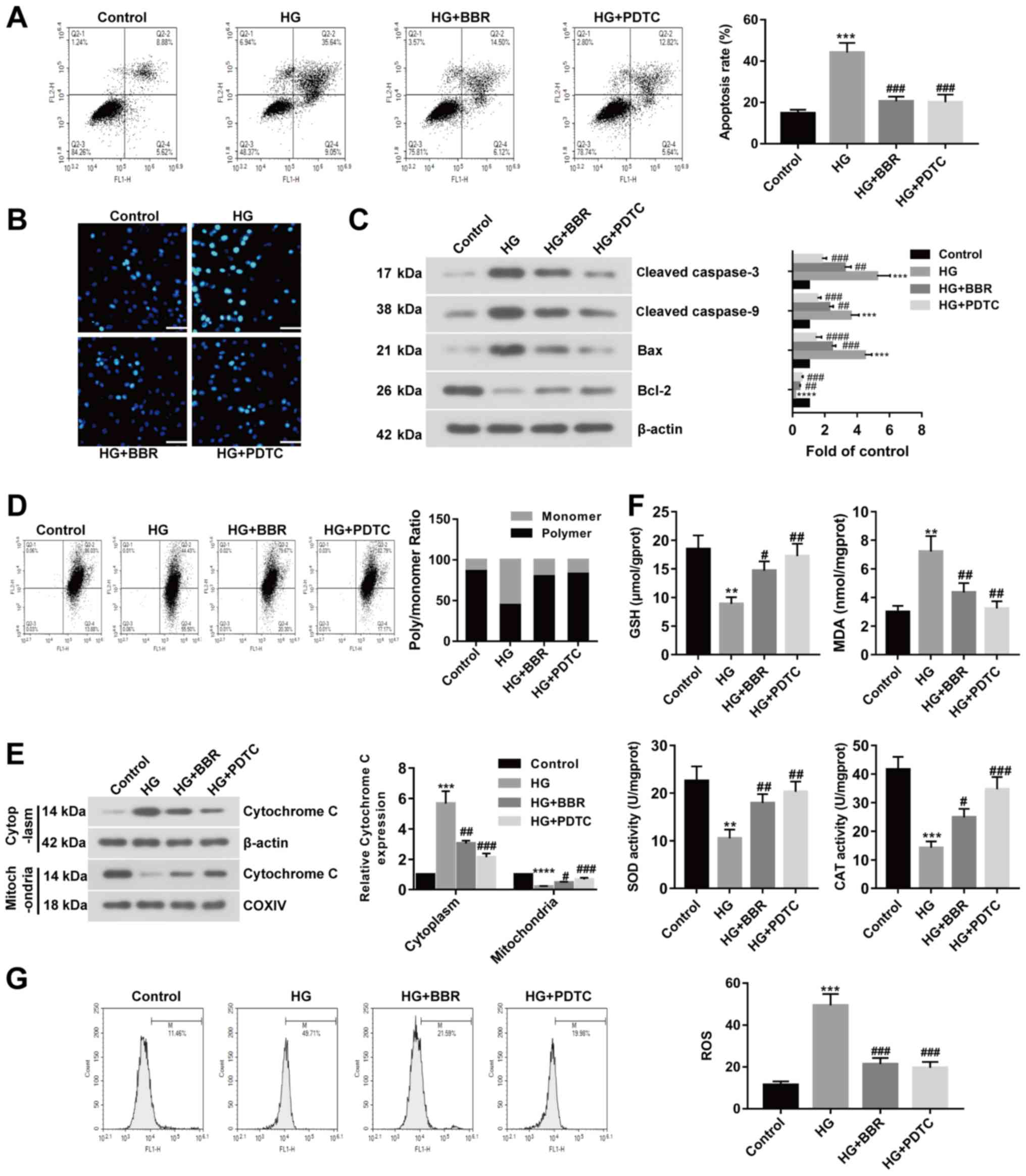
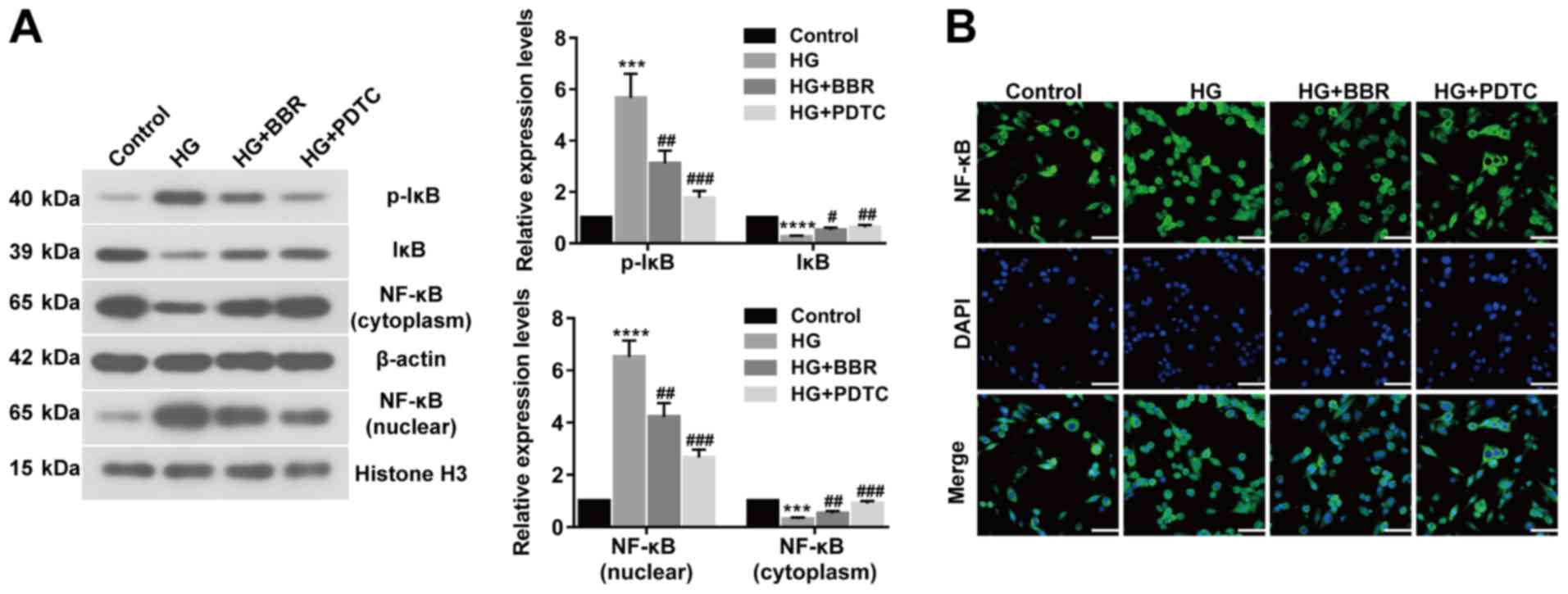
|
1
|
Cheung N, Mitchell P and Wong TY: Diabetic
retinopathy. Lancet. 376:124–136. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Porojan MD, Cătană A, Popp RA, Dumitrascu
DL and Bala C: The role of NOS2A −954G/C and vascular endothelial
growth factor +936C/T polymorphisms in type 2 diabetes mellitus and
diabetic nonproliferative retinopathy risk management. Ther Clin
Risk Manag. 11:1743–1748. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhao C, Wang W, Xu D, Li H, Li M and Wang
F: Insulin and risk of diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2
diabetes mellitus: Data from a meta-analysis of seven cohort
studies. Diagn Pathol. 9:1302014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Toft-Kehler AK, Gurubaran IS, Desler C,
Rasmussen LJ, Skytt DM and Kolko M: Oxidative stress-induced
dysfunction of muller cells during starvation. Invest Ophthalmol
Vis Sci. 57:2721–2728. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
He XF, Zhang L, Zhang CH, Zhao CR, Li H,
Zhang LF, Tian GF, Guo MF, Dai Z and Sui FG: Berberine alleviates
oxidative stress in rats with osteoporosis through receptor
activator of NF-kB/receptor activator of NF-kB
ligand/osteoprotegerin (RANK/RANKL/OPG) pathway. Bosn J Basic Med
Sci. 17:295–301. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kowluru RA, Kowluru A, Veluthakal R,
Mohammad G, Syed I, Santos JM and Mishra M: TIAM1-RAC1 signalling
axis-mediated activation of NADPH oxidase-2 initiates mitochondrial
damage in the development of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetologia.
57:1047–1056. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sun Y, Yuan X, Zhang F, Han Y, Chang X, Xu
X, Li Y and Gao X: Berberine ameliorates fatty acid-induced
oxidative stress in human hepatoma cells. Sci Rep. 7:113402017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sadeghnia HR, Kolangikhah M, Asadpour E,
Forouzanfar F and Hosseinzadeh H: Berberine protects against
glutamate-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in PC12 and N2a
cells. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 20:594–603. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hsu YY, Chen CS, Wu SN, Jong YJ and Lo YC:
Berberine activates Nrf2 nuclear translocation and protects against
oxidative damage via a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-dependent
mechanism in NSC34 motor neuron-like cells. Eur J Pharm Sci.
46:415–425. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lan J, Zhao Y, Dong F, Yan Z, Zheng W, Fan
J and Sun G: Meta-analysis of the effect and safety of berberine in
the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus, hyperlipemia and
hypertension. J Ethnopharmacol. 161:69–81. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fu D, Yu JY, Connell AR, Yang S, Hookham
MB, McLeese R and Lyons TJ: Beneficial effects of berberine on
oxidized LDL-induced cytotoxicity to human retinal muller cells.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 57:3369–3379. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tian P, Ge H, Liu H, Kern TS, Du L, Guan
L, Su S and Liu P: Leukocytes from diabetic patients kill retinal
endothelial cells: Effects of berberine. Mol Vis. 19:2092–2105.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Song D, Song J, Wang C, Li Y and Dunaief
JL: Berberine protects against light-induced photoreceptor
degeneration in the mouse retina. Exp Eye Res. 145:1–9. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kronfeld PC: The association for research
in vision and ophthalmology. Am J Ophthalmol. 76:305–306. 1973.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
National Research Council, . Guide for the
care and use of laboratory animals. (Eighth edition). Publication
No. 85–23(rev.) 327. 963–965. 2010.
|
|
16
|
Coughlin BA, Feenstra DJ and Mohr S:
Müller cells and diabetic retinopathy. Vision Res. 139:93–100.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sun Y, Xia M, Yan H, Han Y, Zhang F, Hu Z,
Cui A, Ma F, Liu Z, Gong Q, et al: Berberine attenuates hepatic
steatosis and enhances energy expenditure in mice by inducing
autophagy and fibroblast growth factor 21. Br J Pharmacol.
175:374–387. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cuenca N, Fernández-Sánchez L, Campello L,
Maneu V, De la Villa P, Lax P and Pinilla I: Cellular responses
following retinal injuries and therapeutic approaches for
neurodegenerative diseases. Prog Retin Eye Res. 43:17–75. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sadraie S, Kiasalari Z, Razavian M, Azimi
S, Sedighnejad L, Afshin-Majd S, Baluchnejadmojarad T and Roghani
M: Berberine ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced learning and
memory deficit in the rat: Insights into underlying molecular
mechanisms. Metab Brain Dis. 34:245–255. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jabbarzadeh Kaboli P, Leong MP, Ismail P
and Ling KH: Antitumor effects of berberine against EGFR, ERK1/2,
P38 and AKT in MDA-MB231 and MCF-7 breast cancer cells using
molecular modelling and in vitro study. Pharmacol Rep. 71:13–23.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liang Y, Fan C, Yan X, Lu X, Jiang H, Di
S, Ma Z, Feng Y, Zhang Z, Feng P, et al: Berberine ameliorates
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via the PERK-mediated
Nrf2/HO-1 signaling axis. Phytother Res. 33:130–148. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen K, Li G, Geng F, Zhang Z, Li J, Yang
M, Dong L and Gao F: Berberine reduces ischemia/reperfusion-induced
myocardial apoptosis via activating AMPK and PI3K-Akt signaling in
diabetic rats. Apoptosis. 19:946–957. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xu L, Zheng X, Wang Y, Fan Q, Zhang M, Li
R, Ye J, Wu X, Zhao W and Zhang Y: Berberine protects acute liver
failure in mice through inhibiting inflammation and
mitochondria-dependent apoptosis. Eur J Pharmacol. 819:161–168.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jin Y, Liu S, Ma Q, Xiao D and Chen L:
Berberine enhances the AMPK activation and autophagy and mitigates
high glucose-induced apoptosis of mouse podocytes. Eur J Pharmacol.
794:106–114. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen H, Ji Y, Yan X, Su G, Chen L and Xiao
J: Berberine attenuates apoptosis in rat retinal Müller cells
stimulated with high glucose via enhancing autophagy and the
AMPK/mTOR signaling. Biomed Pharmacother. 108:1201–1207. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li L, Wang X, Sharvan R, Gao J and Qu S:
Berberine could inhibit thyroid carcinoma cells by inducing
mitochondrial apoptosis, G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and suppressing
migration via PI3K-AKT and MAPK signaling pathways. Biomed
Pharmacother. 95:1225–1231. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dai W, Mu L, Cui Y, Li Y, Chen P, Xie H
and Wang X: Berberine promotes apoptosis of colorectal cancer via
regulation of the long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) cancer
susceptibility candidate 2 (CASC2)/AU-binding factor 1
(AUF1)/B-cell CLL/lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) axis. Med Sci Monit.
25:730–738. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li M, Zhang M, Zhang ZL, Liu N, Han XY,
Liu QC, Deng WJ and Liao CX: Induction of apoptosis by berberine in
hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells via downregulation of NF-κB.
Oncol Res. 25:233–239. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Brownlee M: The pathobiology of diabetic
complications: A unifying mechanism. Diabetes. 54:1615–1625. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kowluru RA and Shan Y: Role of oxidative
stress in epigenetic modification of MMP-9 promoter in the
development of diabetic retinopathy. Graefes Arch Clin Exp
Ophthalmol. 255:955–962. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sies H: Hydrogen peroxide as a central
redox signaling molecule in physiological oxidative stress:
Oxidative eustress. Redox Biol. 11:613–619. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Schreck R, Rieber P and Baeuerle PA:
Reactive oxygen intermediates as apparently widely used messengers
in the activation of the NF-kappa B transcription factor and HIV-1.
EMBO J. 10:2247–2258. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Toledano MB and Leonard WJ: Modulation of
transcription factor NF-kappa B binding activity by
oxidation-reduction in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 88:4328–4332.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|