|
1
|
Domingo P, Mur I, Pomar V, Corominas H,
Casademont J and de Benito N: (2020). The four horsemen of a viral
Apocalypse: The pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19).
EBioMedicine. 58. Elsevier B.V.; 2020, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
World Health Organisation (WHO), .
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Weekly Epidemiological Update.
21 August 2020. simplewww.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situation-reportsLast
accessed August 22, 2020.
|
|
3
|
Gavriatopoulou M, Korompoki E, Fotiou D,
Ntanasis- Stathopoulos I, Psaltopoulou T, Kastritis E, Terpos E and
Dimopoulos MA: Organ-specific manifestations of COVID-19 infection.
Clin Exp Med. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-020-00648-xPubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
De Felice FG, Tovar-Moll F, Moll J, Munoz
DP and Ferreira ST: Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2
(SARS-CoV-2) and the Central Nervous System. Trends Neurosci.
43:355–357. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mao L, Jin H, Wang M, Hu Y, Chen S, He Q,
Chang J, Hong C, Zhou Y, Wang D, et al: Neurologic manifestations
of hospitalized patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Wuhan,
China. JAMA Neurol. 77:6832020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mao XY and Jin WL: The COVID-19 Pandemic:
Consideration for brain infection. Neuroscience. 437:130–131. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Needham EJ, Chou SHY, Coles AJ and Menon
DK: Neurological implications of COVID-19 infections. Neurocrit
Care. 32:667–671. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hoffmann M, Kleine-Weber H, Schroeder S,
Krüger N, Herrler T, Erichsen S, Schiergens TS, Herrler G, Wu N-H,
Nitsche A, et al: SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2
and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell.
181:271–280.e8. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shang J, Wan Y, Luo C, Ye G, Geng Q,
Auerbach A and Li F: Cell entry mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 117:11727–11734. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Iwata-Yoshikawa N, Okamura T, Shimizu Y,
Hasegawa H, Takeda M and Nagata N: TMPRSS2 contributes to virus
spread and immunopathology in the airways of murine models after
coronavirus infection. J Virol. 93:e01815–18. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Katopodis P, Anikin V, Randeva HS,
Spandidos DA, Chatha K, Kyrou I and Karteris E: Pan-cancer analysis
of transmembrane protease serine 2 and cathepsin L that mediate
cellular SARS-CoV-2 infection leading to COVID-19. Int J Oncol.
57:533–539. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cui C, Huang C, Zhou W, Ji X, Zhang F,
Wang L, Zhou Y and Cui Q: AGTR2, one possible novel key gene for
the entry of SARS-CoV-2 into human cells. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput
Biol Bioinformatics. Jul 14–2020.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kerkeni M and Gharbi J: RAGE receptor: May
be a potential inflammatory mediator for SARS-COV-2 infection? Med
Hypotheses. 144:1099502020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kerslake R, Hall M, Randeva HS, Spandidos
DA, Chatha K, Kyrou I and Karteris E: Co-expression of peripheral
olfactory receptors with SARS-CoV-2 infection mediators: Potential
implications beyond loss of smell as a COVID-19 symptom. Int J Mol
Med. 46:949–956. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xia P and Dubrovska A: Tumor markers as an
entry for SARS CoV 2 infection? FEBS J. Aug 1–2020.(Epub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Bittmann S, Weissenstein A,
Moschüring-Alieva E and Villalon G and Villalon G: Neuropilin-1 in
transmission process of COVID-19. J Regen Biol Med. 2:1–2.
2020.
|
|
17
|
Cantuti-Castelvetri L, Ojha R, Pedro L,
Djannatian M, Franz J, Kuivanen S, Kallio K, Kaya T, Anastasina M,
Smura T, et al: Neuropilin-1 facilitates SARS-CoV-2 cell entry and
provides a possible pathway into the central nervous system.
bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.06.07.137802
|
|
18
|
Daly JL, Simonetti B, Antón-Plágaro C,
Kavanagh Williamson M, Shoemark DK, Simón-Gracia L, Klein K, Bauer
M, Hollandi R, Greber UF, et al: Neuropilin-1 is a host factor for
SARS-CoV-2 infection. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.06.05.134114
|
|
19
|
Guo HF and Vander Kooi CW: Neuropilin
Functions as an Essential Cell Surface Receptor. J Biol Chem.
290:29120–29126. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Roy S, Bag AK, Singh RK, Talmadge JE,
Batra SK and Datta K: Multifaceted role of neuropilins in the
immune system: potential targets for immunotherapy. Front Immunol.
8:12282017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
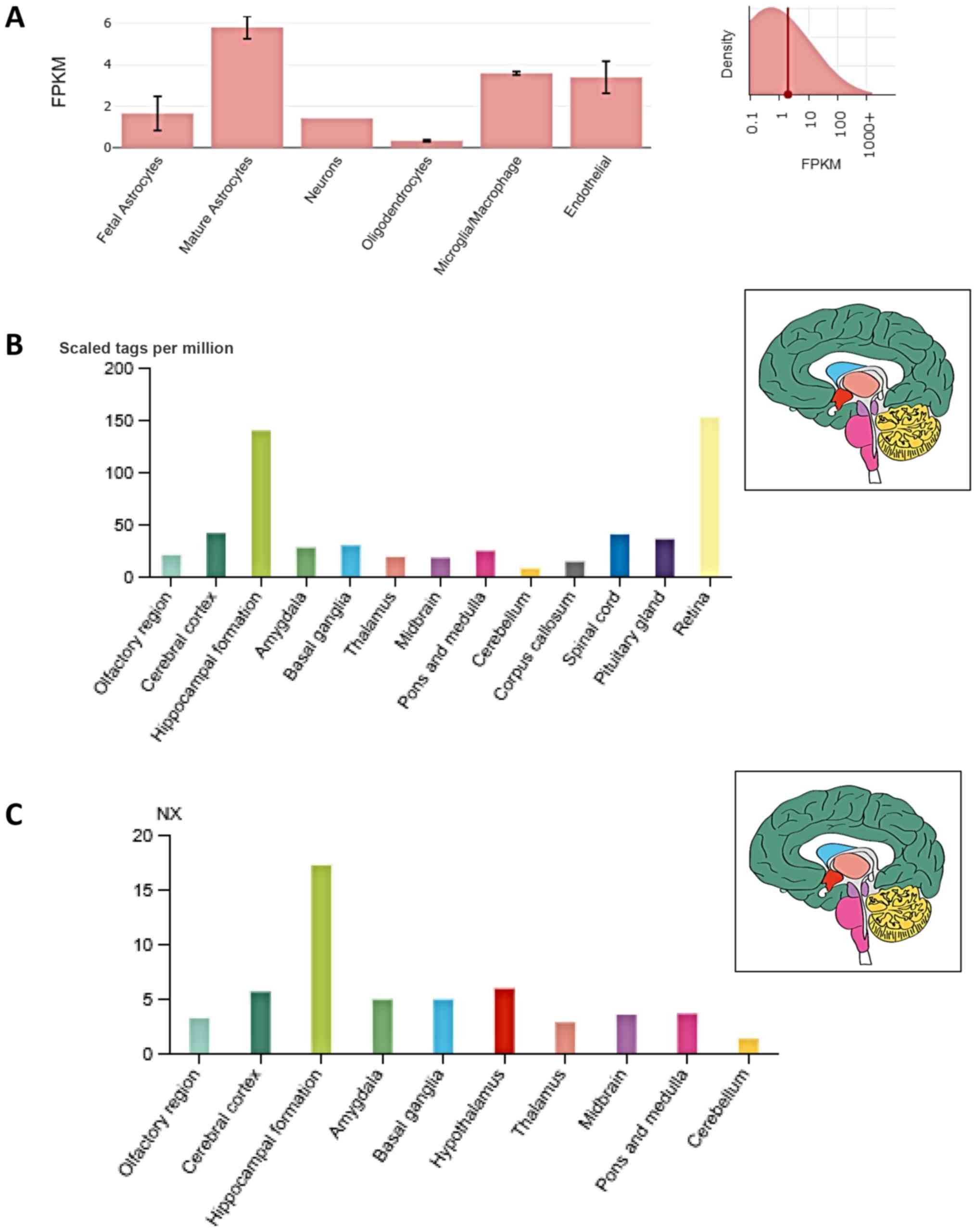
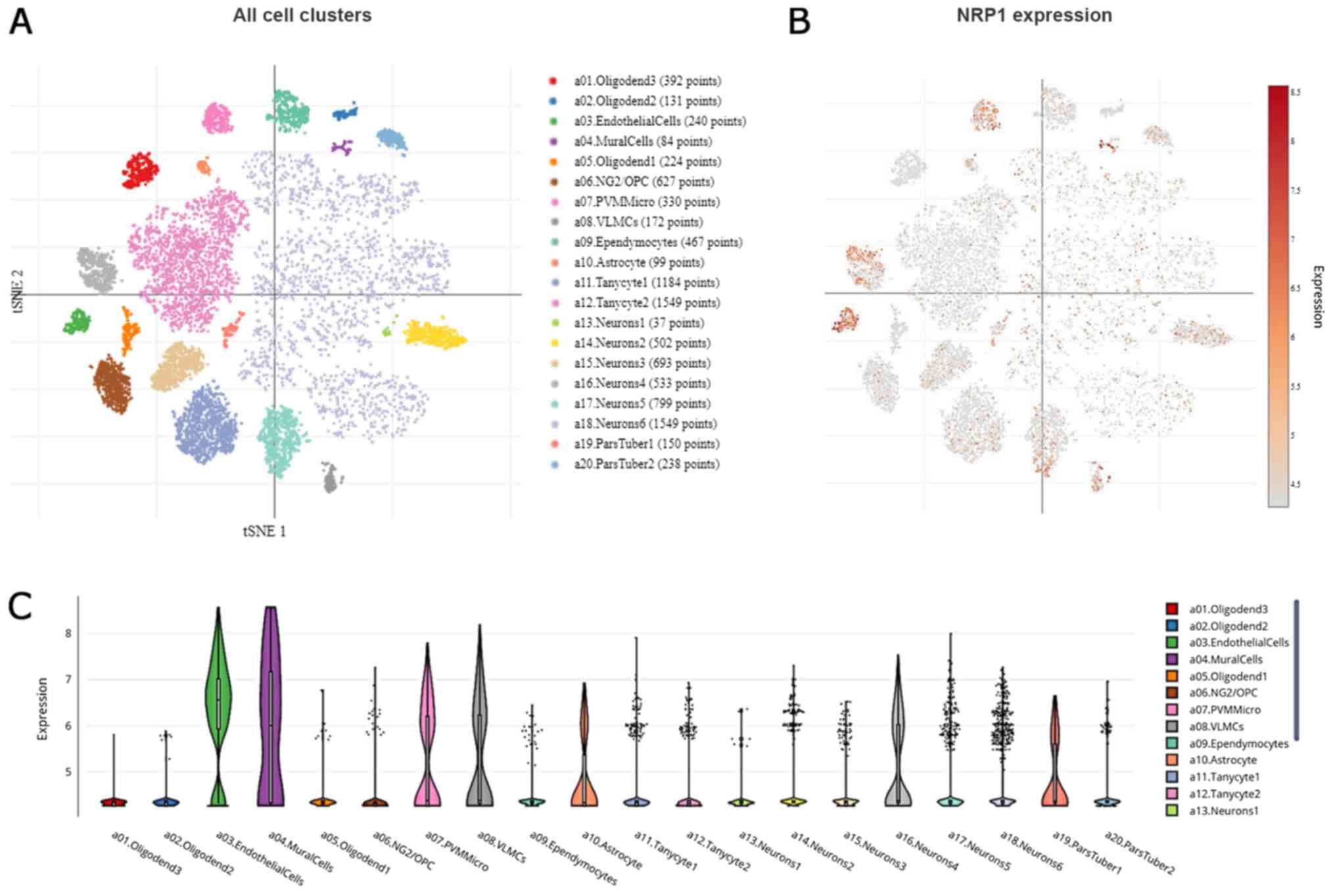
Zhang Y, Sloan SA, Clarke LE, Caneda C,
Plaza CA, Blumenthal PD, Vogel H, Steinberg GK, Edwards MSB, Li G,
et al: Purification and characterization of progenitor and mature
human astrocytes reveals transcriptional and functional differences
with mouse. Neuron. 89:37–53. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Forrest AR, Kawaji H, Rehli M, Baillie JK,
de Hoon MJ, Haberle V, Lassmann T, Kulakovskiy IV, Lizio M, Itoh M,
et al FANTOM Consortium and the RIKEN PMI and CLST (DGT), : A
promoter-level mammalian expression atlas. Nature. 507:462–470.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Thul PJ, Åkesson L, Wiking M, Mahdessian
D, Geladaki A, Ait Blal H, Alm T, Asplund A, Björk L, Breckels LM,
et al: A subcellular map of the human proteome. Science.
356:eaal33212017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Uhlén M, Fagerberg L, Hallström BM,
Lindskog C, Oksvold P, Mardinoglu A, Sivertsson Å, Kampf C,
Sjöstedt E, Asplund A, et al: Proteomics. Tissue-based map of the
human proteome. Science. 347:1260419. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
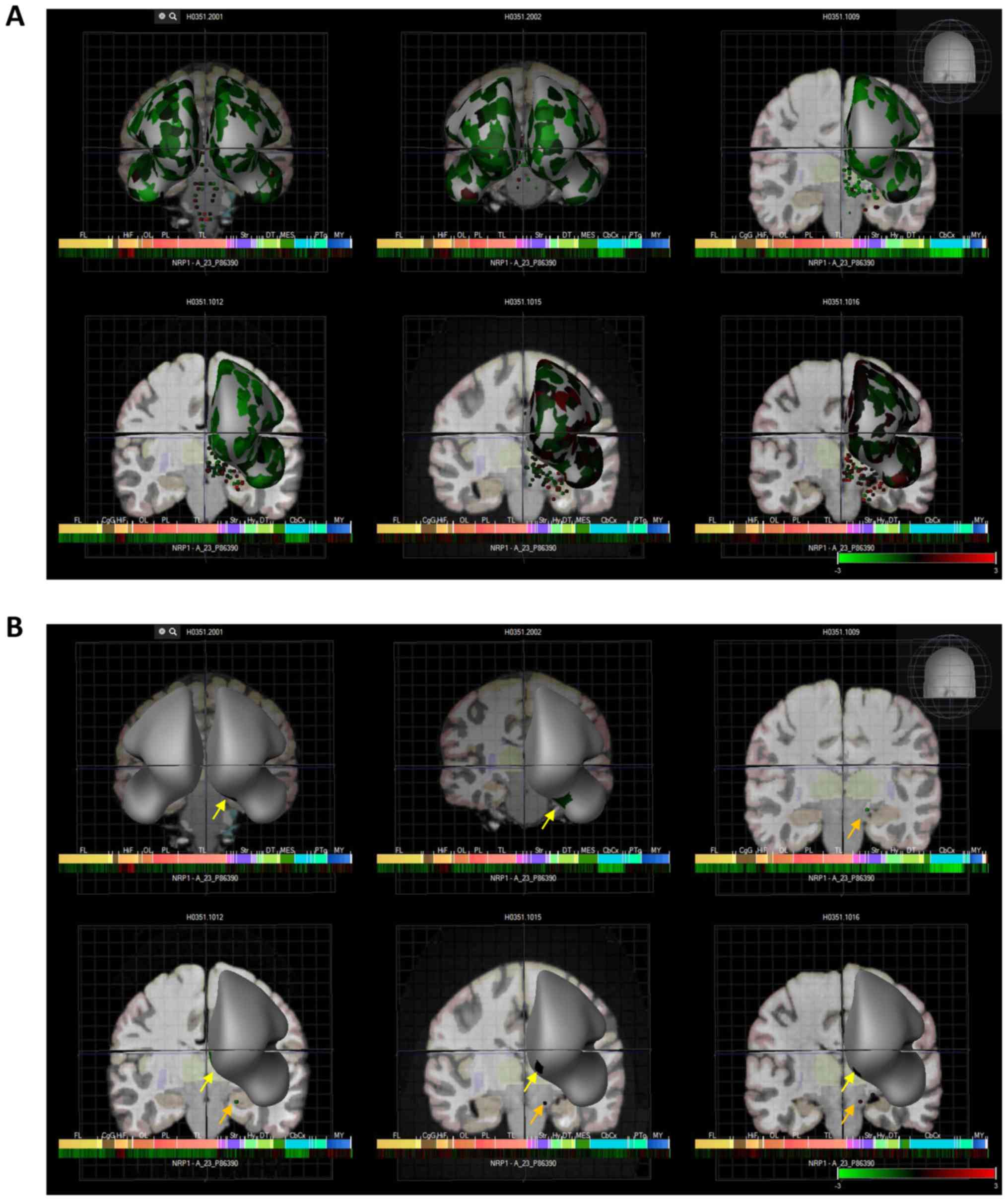
Hawrylycz MJ, Lein ES, Guillozet-Bongaarts
AL, Shen EH, Ng L, Miller JA, van de Lagemaat LN, Smith KA, Ebbert
A, Riley ZL, et al: An anatomically comprehensive atlas of the
adult human brain transcriptome. Nature. 489:391–399. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Campbell JN, Macosko EZ, Fenselau H, Pers
TH, Lyubetskaya A, Tenen D, Goldman M, Verstegen AMJ, Resch JM,
McCarroll SA, et al: A molecular census of arcuate hypothalamus and
median eminence cell types. Nat Neurosci. 20:484–496. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ikemoto S: Dopamine reward circuitry: Two
projection systems from the ventral midbrain to the nucleus
accumbens - olfactory tubercle complex. Brain Res Brain Res Rev.
56:27–78. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wesson DW and Wilson DA: Sniffing out the
contributions of the olfactory tubercle to the sense of smell:
Hedonics, sensory integration, and more? Neurosci Biobehav Rev.
35:655–668. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Arabi YM, Harthi A, Hussein J, Bouchama A,
Johani S, Hajeer AH, Saeed BT, Wahbi A, Saedy A, Al Dabbagh T, et
al: Severe neurologic syndrome associated with Middle East
respiratory syndrome corona virus (MERS-CoV). Infection.
43:495–501. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hung ECW, Chim SSC, Chan PKS, Tong YK, Ng
EKO, Chiu RWK, Leung C-B, Sung JJY, Tam JS and Lo YMD: Detection of
SARS coronavirus RNA in the cerebrospinal fluid of a patient with
severe acute respiratory syndrome. Clin Chem. 49:2108–2109. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lau KK, Yu WC, Chu CM, Lau ST, Sheng B and
Yuen KY: Possible central nervous system infection by SARS
coronavirus. Emerg Infect Dis. 10:342–344. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li K, Wohlford-Lenane C, Perlman S, Zhao
J, Jewell AK, Reznikov LR, Gibson-Corley KN, Meyerholz DK and
McCray PB Jr: Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus causes
multiple organ damage and lethal disease in mice transgenic for
human dipeptidyl peptidase 4. J Infect Dis. 213:712–722. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Helms J, Kremer S, Merdji H, Clere-Jehl R,
Schenck M, Kummerlen C, Collange O, Boulay C, Fafi-Kremer S, Ohana
M, et al: Neurologic features in severe SARS-CoV-2 infection. N
Engl J Med. 382:2268–2270. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Paterson RW, Brown RL, Benjamin L, Nortley
R, Wiethoff S, Bharucha T, Jayaseelan DL, Kumar G, Raftopoulos RE,
Zambreanu L, et al UCL Queen Square National Hospital for Neurology
and Neurosurgery COVID-19 Study Group, : The emerging spectrum of
COVID-19 neurology: Clinical, radiological and laboratory findings.
Brain. Jul 8–2020.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
von Weyhern CH, Kaufmann I, Neff F and
Kremer M: Early evidence of pronounced brain involvement in fatal
COVID-19 outcomes. Lancet. 395:e1092020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lu Y, Li X, Geng D, Mei N, Wu P-Y, Huang
C-C, Jia T, Zhao Y, Wang D, Xiao A, et al: Cerebral
micro-structural changes in COVID-19 patients - an MRI-based
3-month follow-up study. EClinicalMedicine. 25:1004842020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Conde Cardona G, Quintana Pájaro LD,
Quintero Marzola ID, Ramos Villegas Y and Moscote Salazar LR:
Neurotropism of SARS-CoV 2: Mechanisms and manifestations. J Neurol
Sci. 412:1168242020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang HB, Zhang H, Zhang JP, Li Y, Zhao B,
Feng GK, Du Y, Xiong D, Zhong Q, Liu WL, et al: Neuropilin 1 is an
entry factor that promotes EBV infection of nasopharyngeal
epithelial cells. Nat Commun. 6:62402015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|