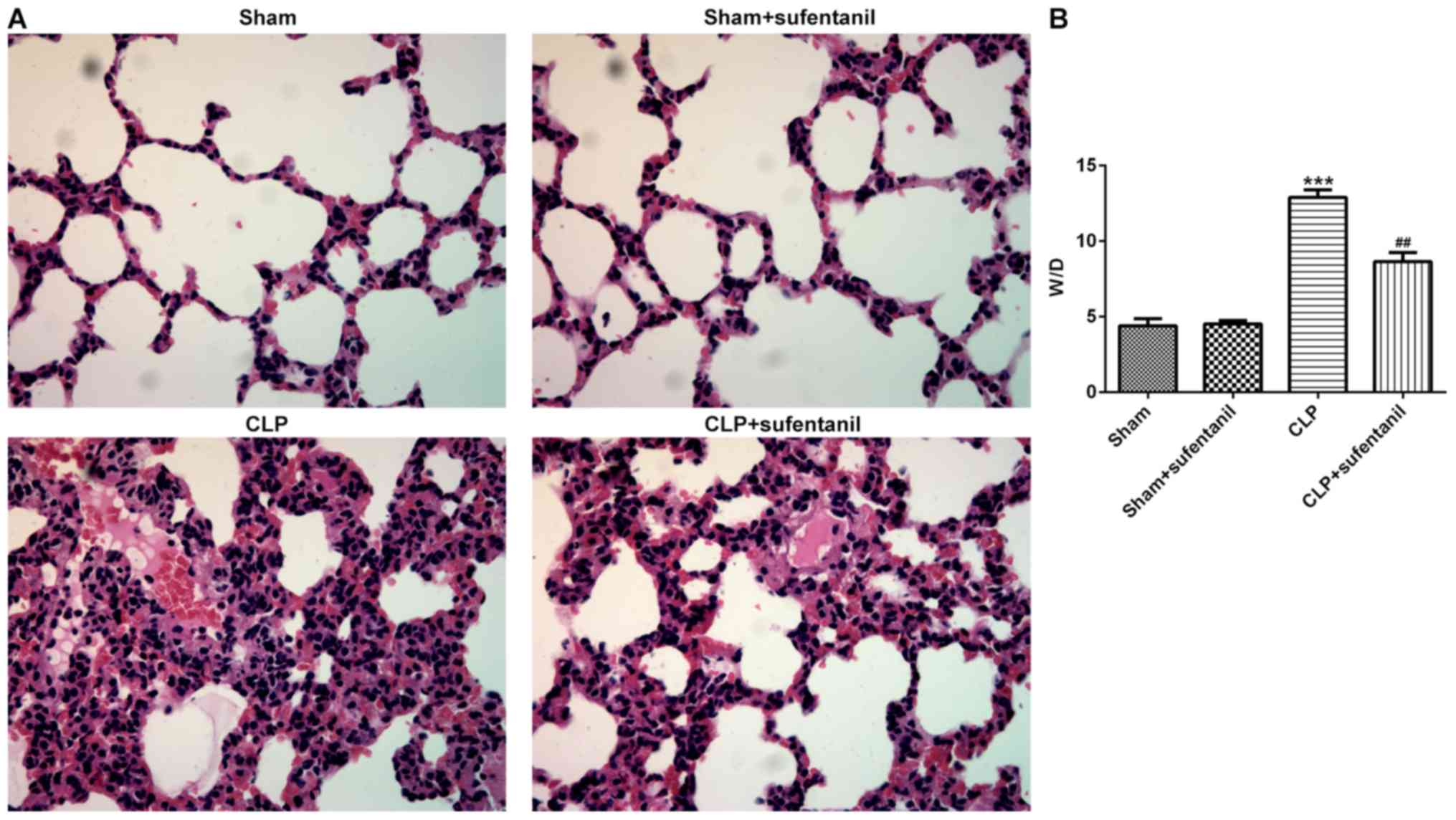
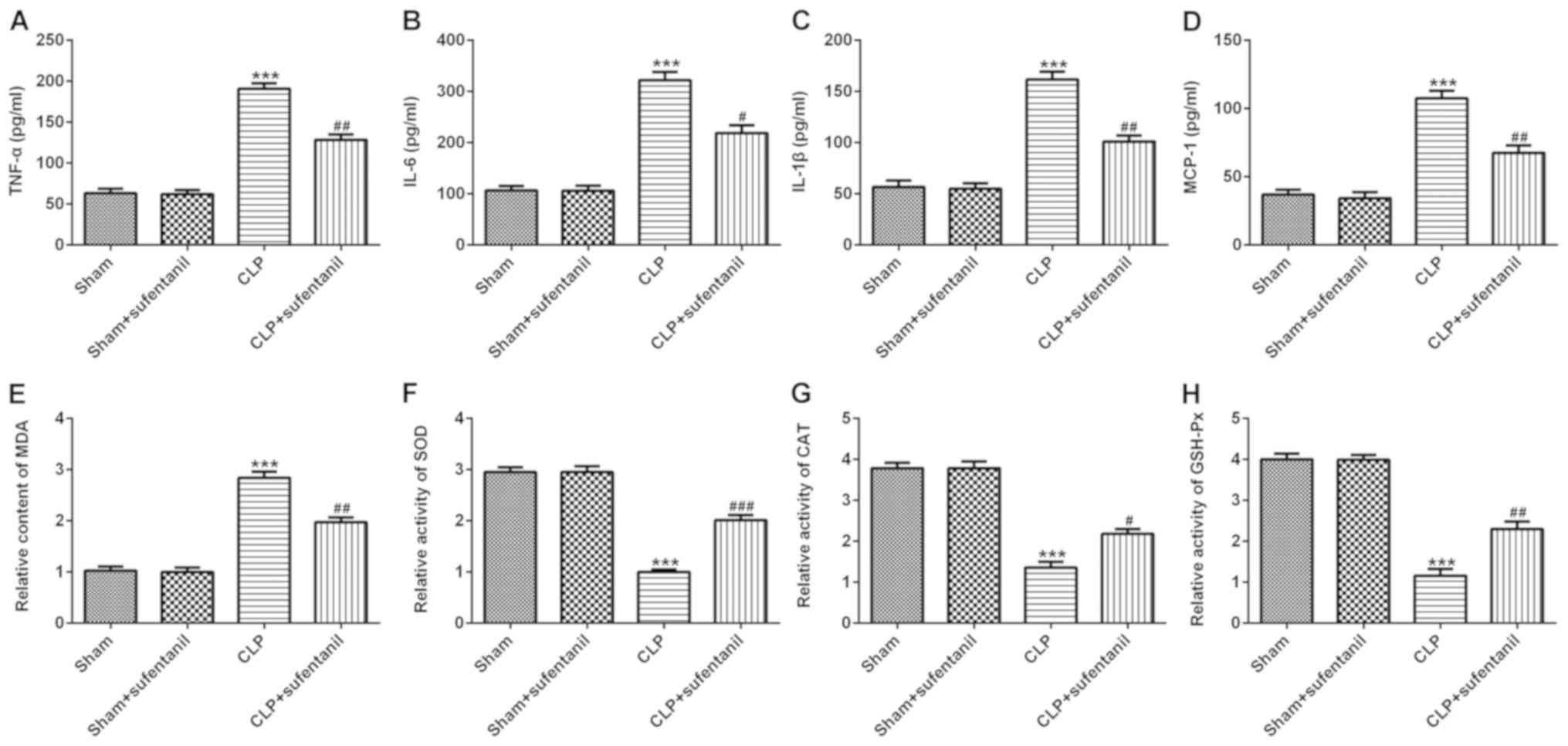
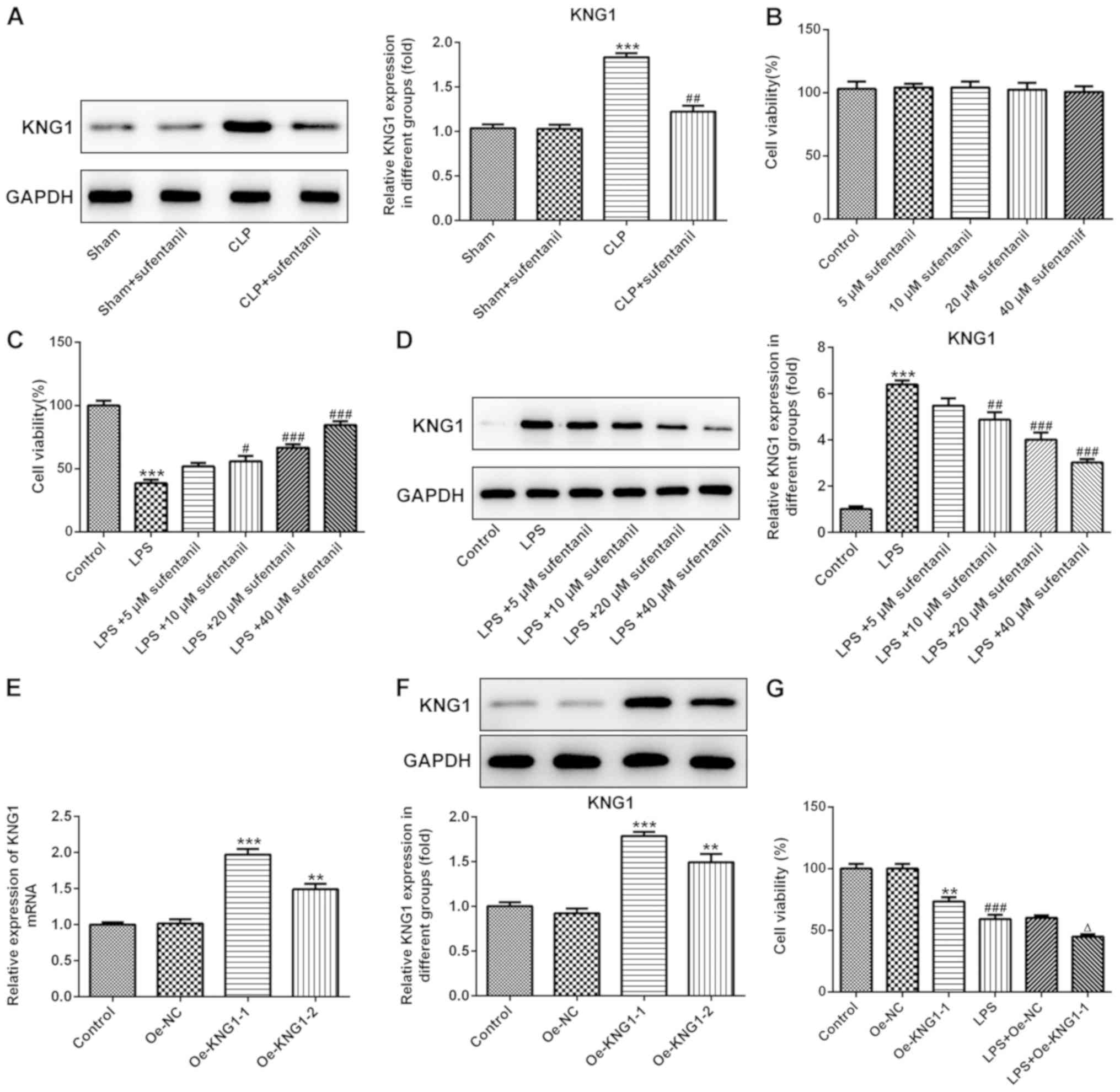
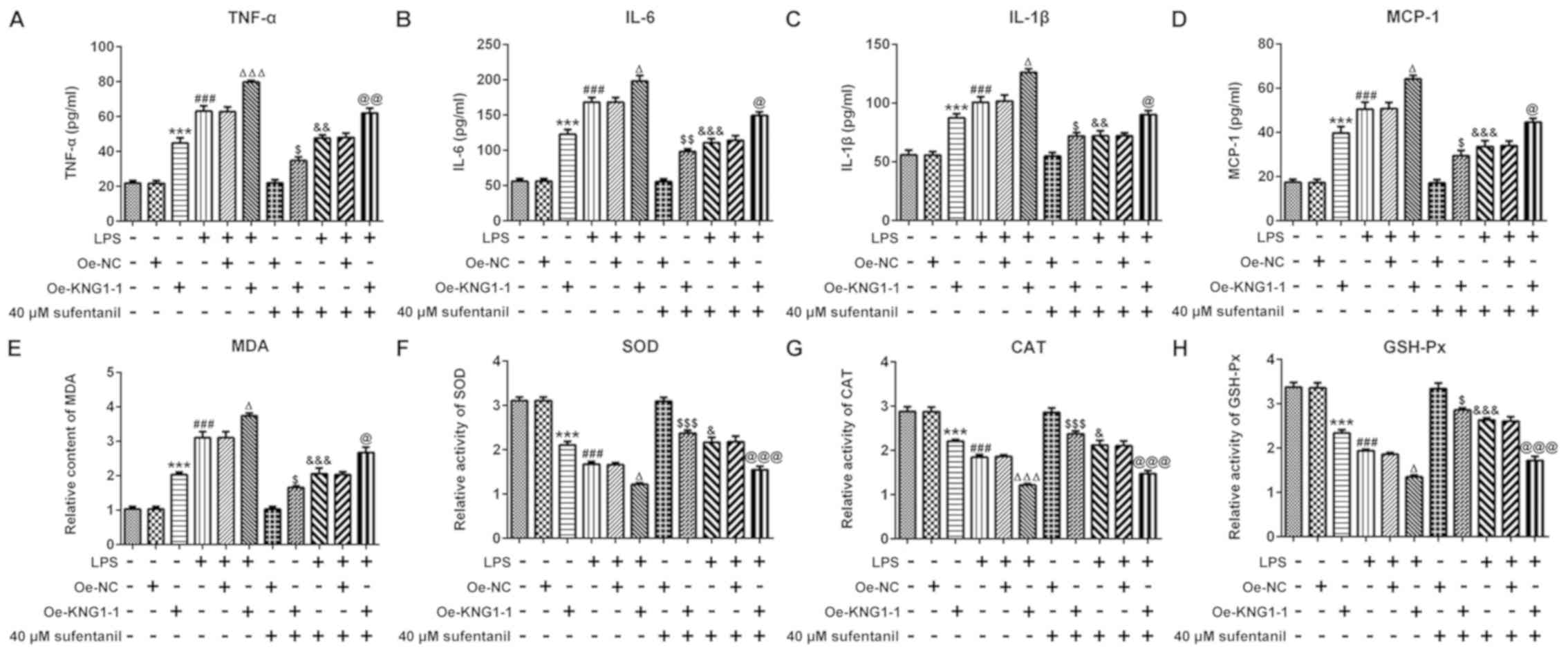
|
1
|
Bellani G, Laffey JG, Pham T, Fan E,
Brochard L, Esteban A, Gattinoni L, van Haren F, Larsson A, McAuley
DF, et al: Epidemiology, patterns of care, and mortality for
patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome in intensive care
units in 50 countries. JAMA. 315:788–800. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Peng LY, Yuan M, Shi HT, Li JH, Song K,
Huang JN, Yi PF, Fu BD and Shen HQ: Protective effect of
piceatannol against acute lung injury through protecting the
integrity of air-blood barrier and modulating the TLR4/NF-κB
signaling pathway activation. Front Pharmacol. 10:16132019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Villar J, Sulemanji D and Kacmarek RM: The
acute respiratory distress syndrome: Incidence and mortality, has
it changed? Current Opin Crit Care. 20:3–9. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Dong Y, Zhang L, Jiang Y, Dai J, Tang L
and Liu G: Emodin reactivated autophagy and alleviated inflammatory
lung injury in mice with lethal endotoxemia. Exp Anim. 68:559–568.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wu B, Miao X, Ye J and Pu X: The
protective effects of protease inhibitor MG-132 on sepsis-induced
acute lung rats and its possible mechanisms. Med Sci Monit.
25:5690–5699. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen L, Lin X, Xiao J, Tian Y, Zheng B and
Teng H: Sonchus oleraceus Linn protects against LPS-induced sepsis
and inhibits inflammatory responses in RAW264.7 cells. J
Ethnopharmacol. 236:63–69. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Guo K and Jin F: Dipeptidyl peptidase-4
(DPP-4) inhibitor saxagliptin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced
acute lung injury via regulating the Nrf-2/HO-1 and NF-κB pathways.
J Invest Surg. 1–8. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhang Y, Li RM, Wang C, Liu N, Lv S and
Xiong JY: Etomidate inhibits nuclear factor-kappaB through
decreased expression of glucocorticoid receptor in septic rats. Mol
Med Rep. 14:5760–5766. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu J, Huang X, Hu S, He H and Meng Z:
Dexmedetomidine attenuates lipopolysaccharide induced acute lung
injury in rats by inhibition of caveolin-1 downstream signaling.
Biomed Pharmacother. 118:1093142019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lian YH, Fang J, Zhou HD, Jiang HF and Xie
KJ: Sufentanil preconditioning protects against hepatic
ischemia-reperfusion injury by suppressing inflammation. Med Sci
Monit. 25:2265–2273. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang CM, Yu JL, Zhang Y, Chen LX, Cao HJ
and Wang YY: The effect of sufentanil on acute lung injury in
rabbits. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 20:108–110.
2008.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Reupke V, Walliser K, Perl T, Kimmina S,
Schraepler A, Quintel M and Kunze-Szikszay N: Total intravenous
anaesthesia using propofol and sufentanil allows controlled
long-term ventilation in rabbits without neuromuscular blocking
agents. Lab Anim. 51:284–291. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Furniss SK, Yao R and Gonzalez G:
Automatic gene prioritization in support of the inflammatory
contribution to Alzheimer's disease. AMIA Jt Summits Transl Sci
Proc. 2014:42–47. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu D, Huo M, Chen X, Zhang Y and Qiao Y:
Mechanism of tanshinones and phenolic acids from Danshen in the
treatment of coronary heart disease based on co-expression network.
BMC Complement Med Ther. 20:282020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Qin S, Wang H, Liu G, Mei H and Chen M:
miR215p ameliorates hyperoxic acute lung injury and decreases
apoptosis of AEC II cells via PTEN/AKT signaling in rats. Mol Med
Rep. 20:4953–4962. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kata D, Foldesi I, Feher LZ, Hackler L Jr,
Puskas LG and Gulya K: A novel pleiotropic effect of aspirin:
Beneficial regulation of pro- and anti-inflammatory mechanisms in
microglial cells. Brain Res Bull. 132:61–74. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li R, Ren T and Zeng J: Mitochondrial
coenzyme Q protects sepsis-induced acute lung injury by activating
PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β/mTOR pathway in rats. BioMed Res Int.
2019:52408982019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hu HY, Shi D, Hu CL, Yuan X, Zhang J and
Sun H: Dexmedetomidine mitigates CLP-stimulated acute lung injury
via restraining the RAGE pathway. Am J Transl Res. 9:5245–5258.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wu B, Miao X, Ye J and Pu X: The
protective effects of protease inhibitor MG-132 on sepsis-induced
acute lung rats and its possible mechanisms. Med Sci Monitor.
25:5690–5699. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu C, Guo Z, Zhao C, Zhang X and Wang Z:
Potential mechanism and drug candidates for sepsis-induced acute
lung injury. Exp Ther Med. 15:4689–4696. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shen N, Cheng A, Qiu M and Zang G: Allicin
improves lung injury induced by sepsis via regulation of the
toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)/myeloid differentiation primary
response 88 (MYD88)/nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathway. Med Sci
Monit. 25:2567–2576. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhou J, Fu Y, Liu K, Hou L and Zhang W:
miR-206 regulates alveolar type II epithelial cell Cx43 expression
in sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Exp Ther Med. 18:296–304.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Patel M, Chignalia AZ, Isbatan A,
Bommakanti N and Dull RO: Ropivacaine inhibits pressure-induced
lung endothelial hyperpermeability in models of acute hypertension.
Life Sci. 222:22–28. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Strosing KM, Faller S, Gyllenram V,
Engelstaedter H, Buerkle H, Spassov S and Hoetzel A: Inhaled
anesthetics exert different protective properties in a mouse model
of ventilator-induced lung injury. Anesth Analg. 123:143–151. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lin X, Ju YN, Gao W, Li DM and Guo CC:
Desflurane attenuates ventilator-induced lung injury in rats with
acute respiratory distress syndrome. Biomed Res Int.
2018:75073142018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ji S and Wang L: µ-Opioid receptor
signalling via PI3K/Akt pathway ameliorates
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. Exp
Physiol. 104:1555–1561. 2019. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dong S, Liu J, Li L, Wang H, Ma H, Zhao Y
and Zhao J: The HECT ubiquitin E3 ligase Smurf2 degrades µ-opioid
receptor 1 in the ubiquitin-proteasome system in lung epithelial
cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 316:C632–C640. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen Q, Liu J, Wang W, Liu S, Yang X, Chen
M, Cheng L, Lu J, Guo T and Huang F: Sini decoction ameliorates
sepsis-induced acute lung injury via regulating ACE2-Ang (1–7)-Mas
axis and inhibiting the MAPK signaling pathway. Biomed
Pharmacother. 115:1089712019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Qiu N, Xu X and He Y: LncRNA TUG1
alleviates sepsis-induced acute lung injury by targeting
miR-34b-5p/GAB1. BMC Pulm Med. 20:492020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang XH, Zeng JF, Lin C and Chen SB:
Effects of morphine and sufentanil preconditioning against
myocardial ischemic-reperfusion injury in rabbits. Int J Clin Exp
Med. 8:15692–15699. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang H, Tan X, Xu J, Li H, Wang M, Chen S,
Yang X, Liu Y and Wang F: Negative correlation between CSF lactate
levels and MoCA scores in male Chinese subjects. Psychiatry Res.
255:49–51. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Langhauser F, Göb E, Kraft P, Geis C,
Schmitt J, Brede M, Göbel K, Helluy X, Pham M, Bendszus M, et al:
Kininogen deficiency protects from ischemic neurodegeneration in
mice by reducing thrombosis, blood-brain barrier damage, and
inflammation. Blood. 120:4082–4092. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shi K, Chen X, Xie B, Yang SS, Liu D, Dai
G and Chen Q: Celastrol alleviates chronic obstructive pulmonary
disease by inhibiting cellular inflammation induced by cigarette
smoke via the Ednrb/Kng1 signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol.
9:12762018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xu M, Cao FL, Zhang YF, Shan L, Jiang XL,
An XJ, Xu W, Liu XZ and Wang XY: Tanshinone IIA therapeutically
reduces LPS-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting inflammation
and apoptosis in mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 36:179–187. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Qing R, Huang Z, Tang Y, Xiang Q and Yang
F: Cordycepin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung
injury via Nrf(2)/HO-1 pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 60:18–25.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhao B, Gao W, Gao X, Leng Y, Liu M, Hou J
and Wu Y: Sulforaphane attenuates acute lung injury by inhibiting
oxidative stress via Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in a rat sepsis model. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 10:9021–9028. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xu J, Li HB, Chen L, Wang YX, Lu S, Li SN,
Cui SN, Xiao HR, Qin L, Hu H, et al: BML-111 accelerates the
resolution of inflammation by modulating the Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-κB
pathways in rats with ventilator-induced lung injury. Int
Immunopharmacol. 69:289–298. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|