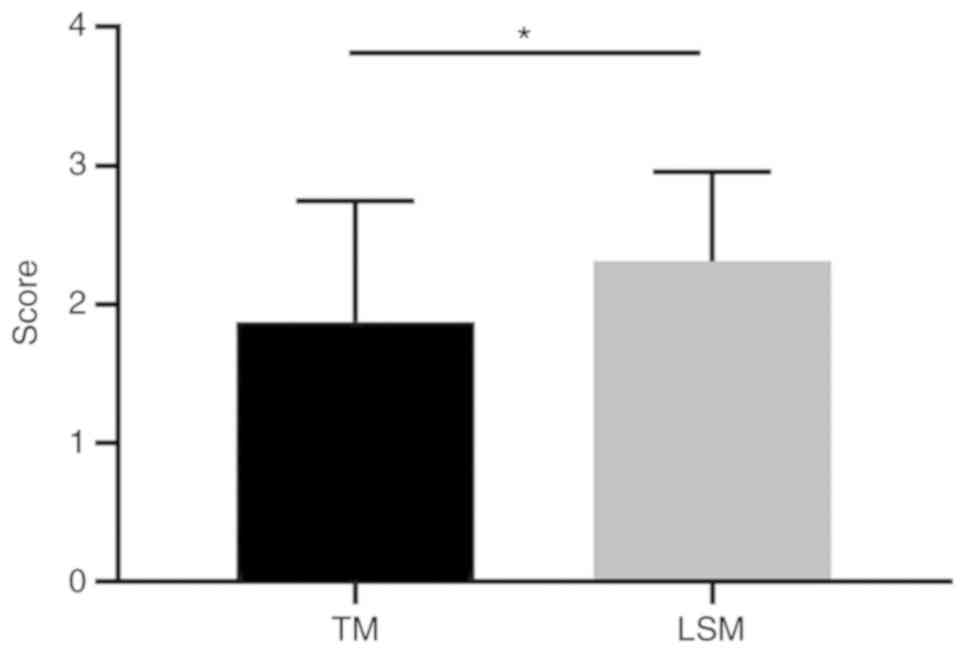
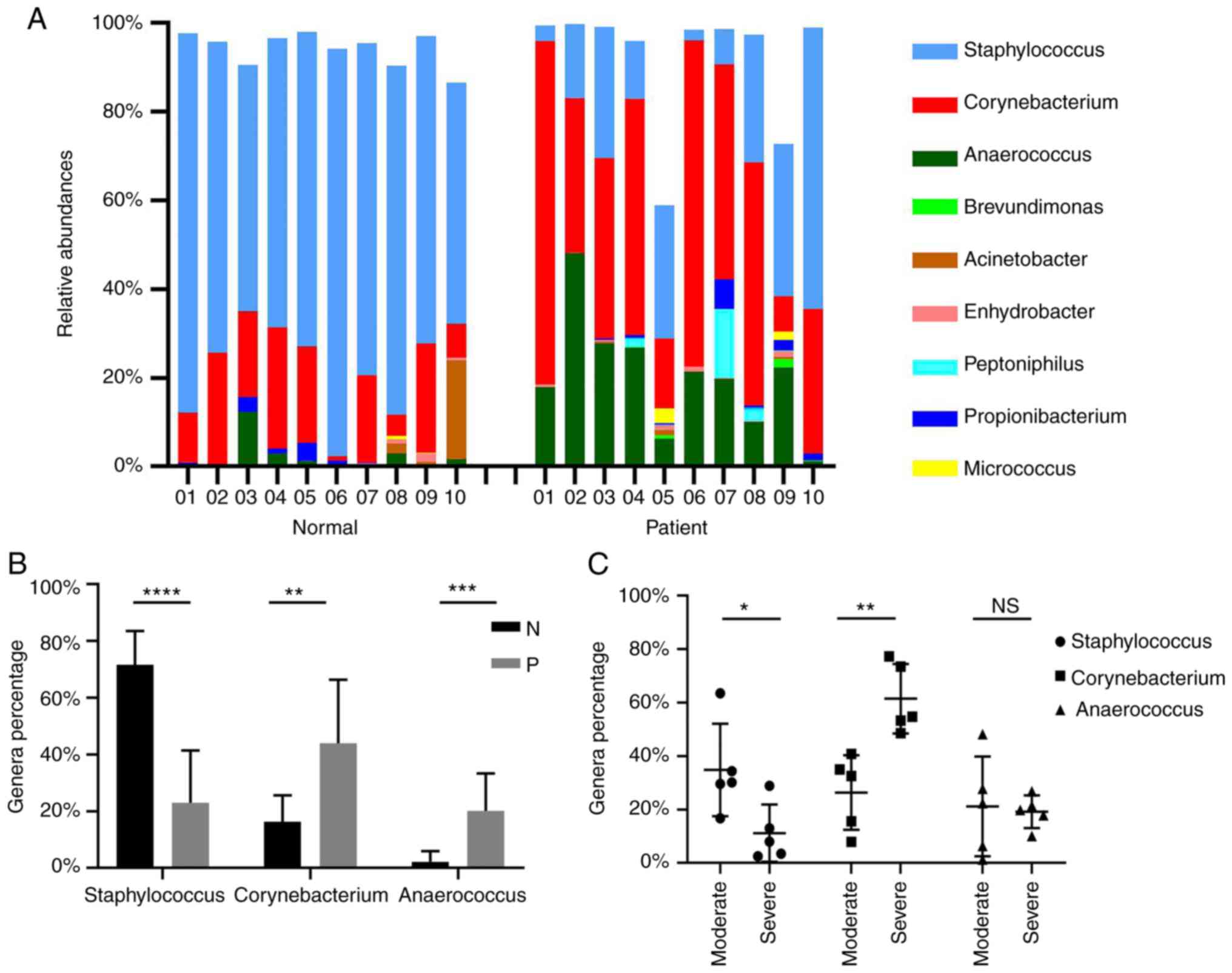
|
1
|
Toyoda Y, Gomi T, Nakagawa H, Nagakura M
and Ishikawa T: Diagnosis of human axillary osmidrosis by
genotyping of the human ABCC11 gene: Clinical practice and basic
scientific evidence. Biomed Res Int. 2016:76704832016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
James AG, Austin CJ, Cox DS, Taylor D and
Calvert R: Microbiological and biochemical origins of human
axillary odour. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 83:527–540. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wood A and Kelly D: Skin microbiology,
body odor, and methylotrophic bacteria. Handbook Hydrocarbon Lipid
Microbiol. 2010:3204–3213. 2010.
|
|
4
|
Chen H, Yang G, Li Y, Li X and Du J:
Expression of apolipoprotein D and androgen receptor in axillary
osmidrosis and its molecular mechanism. Int J Clin Exp Med.
6:497–503. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jung SW, Lee SJ and Park HR: Comparison of
outcomes of two methods of axillary osmidrosis surgery: Subdermal
excision versus liposuction combined with diode laser ablation.
Arch Aesthetic Plast Surg. 26:20–27. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wang R, Yang J and Sun J: A minimally
invasive procedure for axillary osmidrosis: Subcutaneous curettage
combined with trimming through a small incision. Aesthetic Plast
Surg. 39:106–113. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Memarian F, Amani-Tehran M and Latifi M:
Rank ordering and image processing methods aided fabric wrinkle
evaluation. Fibers Polym. 12:8302011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Egert M, Höhne HM, Weber T, Simmering R,
Banowski B and Breves R: Identification of compounds inhibiting the
C-S lyase activity of a cell extract from a Staphylococcus
sp. isolated from human skin. Lett Appl Microbiol. 57:534–539.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gao Z, Tseng CH, Pei Z and Blaser MJ:
Molecular analysis of human forearm superficial skin bacterial
biota. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:2927–2932. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fredrich E, Barzantny H, Brune I and Tauch
A: Daily battle against body odor: Towards the activity of the
axillary microbiota. Trends Microbiol. 21:305–312. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tarun J, Susan J, Suria J, Susan VJ and
Criton S: Evaluation of pH of bathing soaps and shampoos for skin
and hair care. Indian J Dermatol. 59:442–444. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ali SM and Yosipovitch G: Skin pH: From
basic science to basic skin care. Acta Derm Venereol. 93:261–267.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dai Y, Xu AE and He J: A refined surgical
treatment modality for bromhidrosis: Subcutaneous scissor with
micropore. Dermatol Ther. 30:2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
He J, Wang T and Dong J: A close positive
correlation between malodor and sweating as a marker for the
treatment of axillary bromhidrosis with botulinum toxin A. J
Dermatolog Treat. 23:461–464. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ring HC, Thorsen J, Saunte DM, Lilje B,
Bay L, Riis PT, Larsen N, Andersen LO, Nielsen HV, Miller IM, et
al: The follicular skin microbiome in patients with hidradenitis
suppurativa and healthy controls. JAMA Dermatol. 153:897–905. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Grice EA, Kong HH, Conlan S, Deming CB,
Davis J, Young AC; NISC Comparative Sequencing Program, ; Bouffard
GG, Blakesley RW, Murray PR, et al: Topographical and temporal
diversity of the human skin microbiome. Science. 324:1190–1192.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fadrosh DW, Ma B, Gajer P, Sengamalay N,
Ott S, Brotman RM and Ravel J: An improved dual-indexing approach
for multiplexed 16S rRNA gene sequencing on the Illumina MiSeq
platform. Microbiome. 2:1–6. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Troccaz M, Gaia N, Beccucci S, Schrenzel
J, Cayeux I, Starkenmann C and Lazarevic V: Mapping axillary
microbiota responsible for body odours using a culture-independent
approach. Microbiome. 3:32015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rippke F, Berardesca E and Weber TM: pH
and microbial infections. Curr Probl Dermatol. 54:87–94. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Behm B, Schreml S, Landthaler M and
Babilas P: Skin signs in diabetes mellitus. Eur Acad Dermatol
Venereol. 26:1203–1211. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kemper M, Bielfeldt S, Knie U, Wilhelm KP
and Abels C: Significant reduction of body odor in older people
with a pH 4.0 emulsion. Cosmetics. 2:136–145. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Williams S, Davids M, Reuther T, Kraus D
and Kerscher M: Gender difference of in vivo skin surface pH in the
axilla and the effect of a standardized washing procedure with tap
water. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 18:247–252. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Stenzaly-Achtert S, Schölermann A,
Schreiber J, Diec KH, Rippke F and Bielfeldt S: Axillary pH and
influence of deodorants. Skin Res Technol. 6:87–91. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ren Y, Liu W, Chen J, Wang J, Wang K, Zhou
J, Cai S, Zheng M, Liu J, Liu L and Xue D: A missense variant of
the ABCC11 gene is associated with axillary osmidrosis
susceptibility and clinical phenotypes in the Chinese han
population. Sci Rep. 7:463352017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li M, Budding AE, van der Lugt-Degen M,
Du-Thumm L, Vandeven M and Fan A: The influence of age, gender and
race/ethnicity on the composition of the human axillary microbiome.
Int J Cosmet Sci. 41:371–377. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fujii T, Shinozaki J, Kajiura T, Iwasaki K
and Fudou R: A newly discovered Anaerococcus strain
responsible for axillary odor and a new axillary odor inhibitor,
pentagalloyl glucose. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 89:198–207. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Minhas GS, Bawdon D, Herman R, Rudden M,
Stone AP, James AG, Thomas GH and Newstead S: Structural basis of
malodour precursor transport in the human axilla. Elife.
7:e349952018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Okamoto H, Koizumi S, Shimizu H, Cho O and
Sugita T: Characterization of the axillary microbiota of Japanese
male subjects with spicy and milky odor types by pyrosequencing.
Biocontrol Sci. 23:1–5. 2018. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Murphy EC and Frick IM: Gram-positive
anaerobic cocci-commensals and opportunistic pathogens. FEMS
Microbiol Rev. 37:520–553. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Badri M, Nilson B, Ragnarsson S, Senneby E
and Rasmussen M: Clinical and microbiological features of
bacteraemia with gram-positive anaerobic cocci: A population-based
retrospective study. Clin Microbiol Infect. 25:760.e1–760.e6. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|