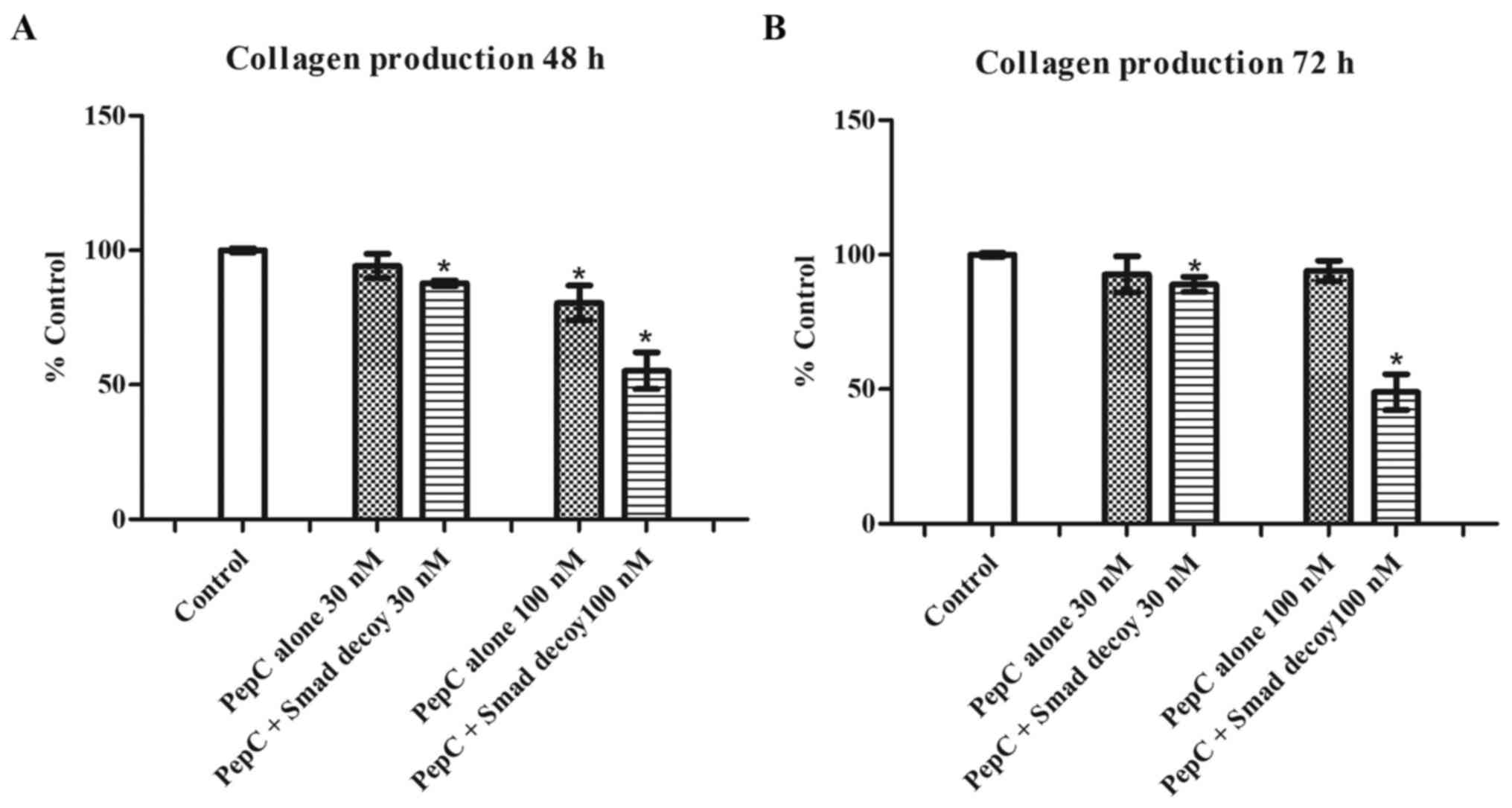
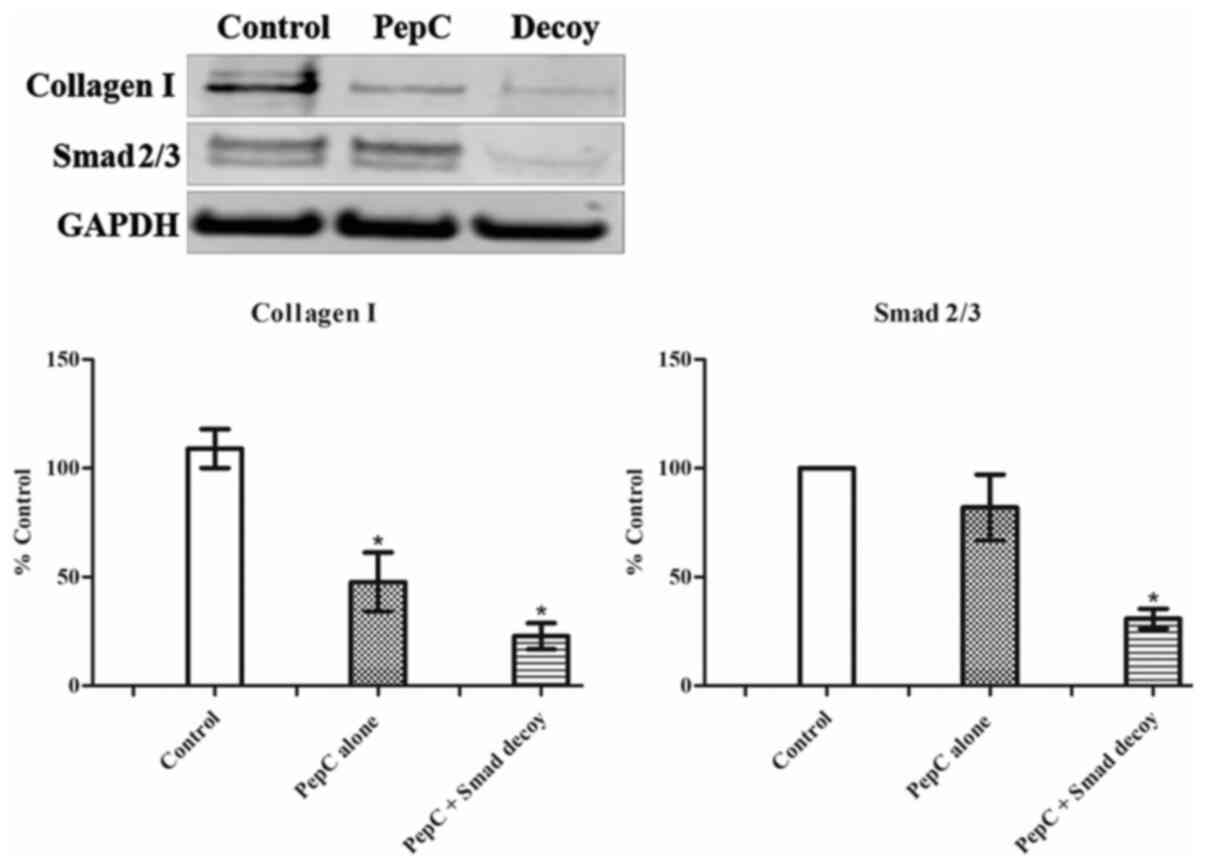
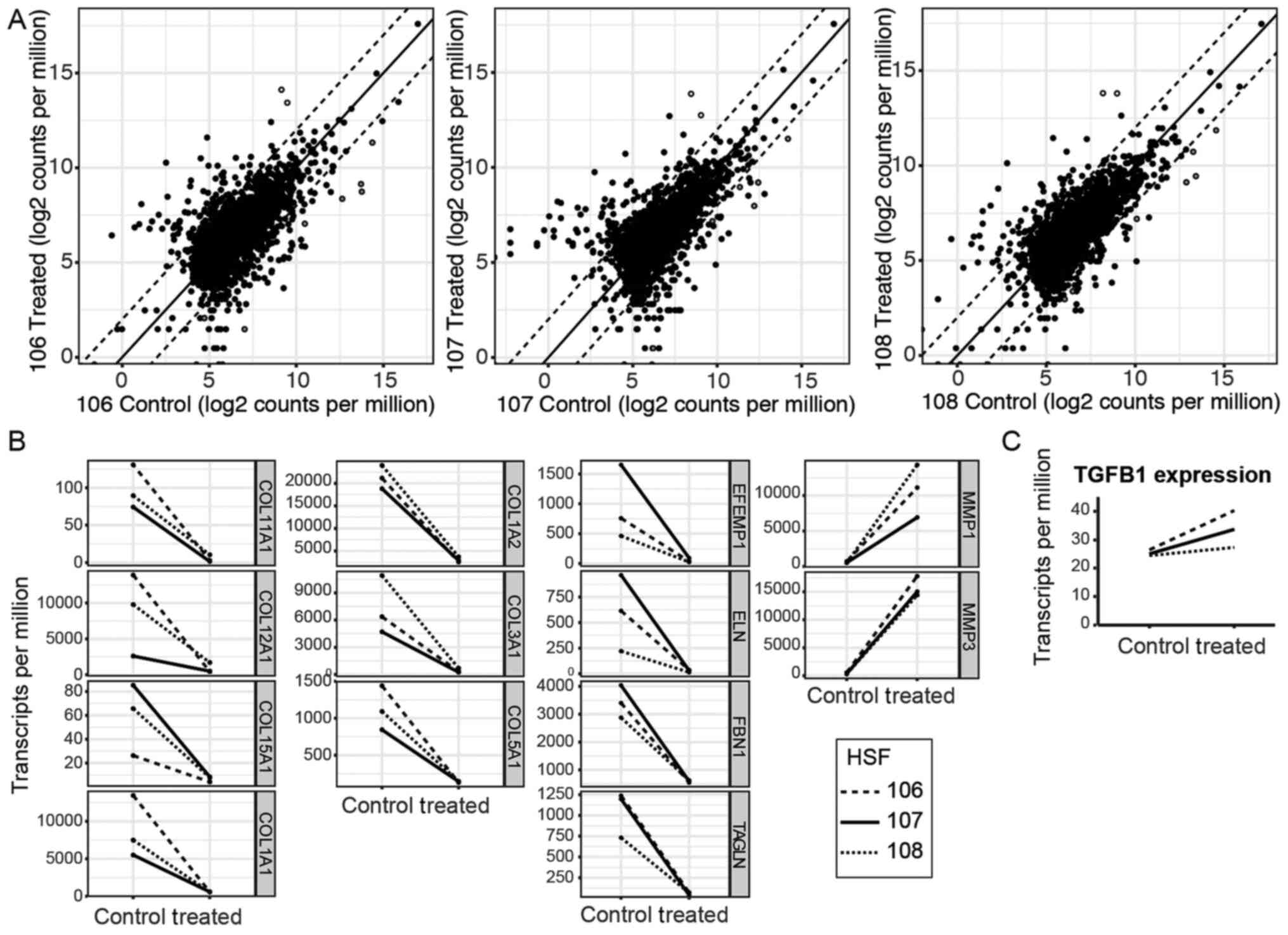
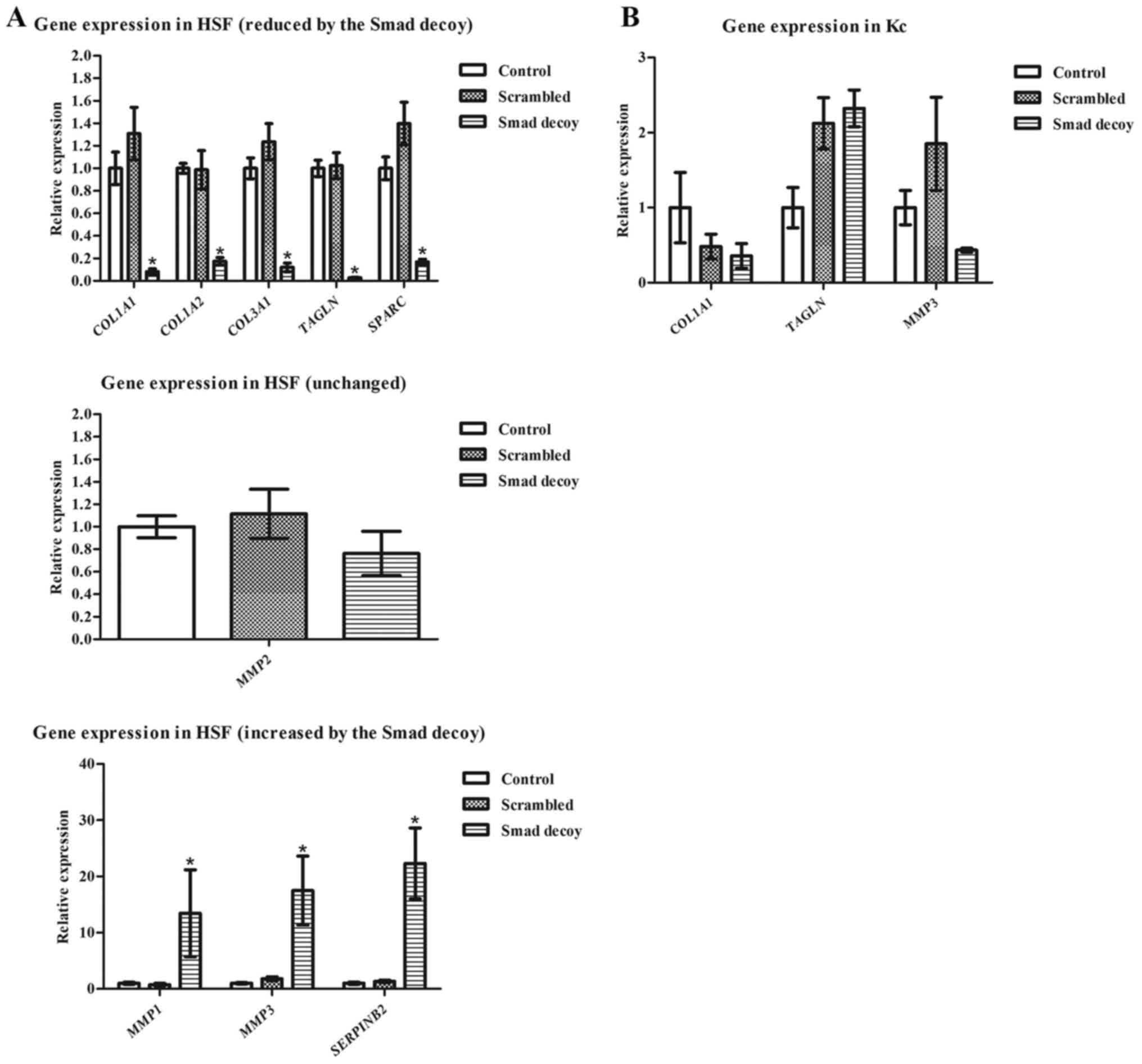
|
1
|
Ogawa R: Keloid and hypertrophic scars are
the result of chronic inflammation in the reticular dermis. Int J
Mol Sci. 18:6062017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Bombaro KM, Engrav LH, Carrougher GJ,
Wiechman SA, Faucher L, Costa BA, Heimbach DM, Rivara FP and Honari
S: What is the prevalence of hypertrophic scarring following burns?
Burns. 29:299–302. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xiao Z, Zhang M, Liu Y and Ren L:
Botulinum toxin type a inhibits connective tissue growth factor
expression in fibroblasts derived from hypertrophic scar. Aesthetic
Plast Surg. 35:802–807. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Son D and Harijan A: Overview of surgical
scar prevention and management. J Korean Med Sci. 29:751–757. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cowin AJ, Holmes TM, Brosnan P and
Ferguson MW: Expression of TGF-beta and its receptors in murine
fetal and adult dermal wounds. Eur J Dermatol. 11:424–431.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tredget EE, Yang L, Delehanty M,
Shankowsky H and Scott PG: Polarized Th2 cytokine production in
patients with hypertrophic scar following thermal injury. J
Interferon Cytokine Res. 26:179–189. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Macias MJ, Martin-Malpartida P and
Massague J: Structural determinants of Smad function in TGF-β
signaling. Trends Biochem Sci. 40:296–308. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang YE: Non-Smad pathways in TGF-beta
signaling. Cell Res. 19:128–139. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shi Y and Massague J: Mechanisms of
TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell.
113:685–700. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Meng XM, Chung AC and Lan HY: Role of the
TGF-β/BMP-7/Smad pathways in renal diseases. Clin Sci (Lond).
124:243–254. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chin GS, Liu W, Peled Z, Lee TY,
Steinbrech DS, Hsu M and Longaker MT: Differential expression of
transforming growth factor-beta receptors I and II and activation
of Smad 3 in keloid fibroblasts. Plast Reconstr Surg. 108:423–429.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Walraven M, Gouverneur M, Middelkoop E,
Beelen RH and Ulrich MM: Altered TGF-β signaling in fetal
fibroblasts: What is known about the underlying mechanisms? Wound
Repair Regen. 22:3–13. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zawel L, Dai JL, Buckhaults P, Zhou S,
Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B and Kern SE: Human Smad3 and Smad4 are
sequence-specific transcription activators. Mol Cell. 1:611–617.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rheinwald JG and Green H: Serial
cultivation of strains of human epidermal keratinocytes: The
formation of keratinizing colonies from single cells. Cell.
6:331–343. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Andaloussi SE, Lehto T, Mager I,
Rosenthal-Aizman K, Oprea II, Simonson OE, Sork H, Ezzat K,
Copolovici DM, Kurrikoff K, et al: Design of a peptide-based
vector, PepFect6, for efficient delivery of siRNA in cell culture
and systemically in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 39:3972–3987. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ezzat K, Andaloussi SE, Zaghloul EM, Lehto
T, Lindberg S, Moreno PM, Viola JR, Magdy T, Abdo R, Guterstam P,
et al: PepFect 14, a novel cell-penetrating peptide for
oligonucleotide delivery in solution and as solid formulation.
Nucleic Acids Res. 39:5284–5298. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fan C, Dong Y, Xie Y, Su Y, Zhang X,
Leavesley D and Upton Z: Shikonin reduces TGF-β1-induced collagen
production and contraction in hypertrophic scar-derived human skin
fibroblasts. Int J Mol Med. 36:985–991. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Trapnell C, Roberts A, Goff L, Pertea G,
Kim D, Kelley DR, Pimentel H, Salzberg SL, Rinn JL and Pachter L:
Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq
experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat Protoc. 7:562–578. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Anders S, Pyl PT and Huber W: HTSeq-a
Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data.
Bioinformatics. 31:166–169. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huang DW, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Applied Biosystems: Guide to performing
relative quantitation of gene expression using real-time
quantitative PCR. 2004. simplehttps://assets.thermofisher.com/TFS-Assets/LSG/manuals/cms_042380.pdf
|
|
22
|
Verrecchia F, Chu ML and Mauviel A:
Identification of novel TGF-beta/Smad gene targets in dermal
fibroblasts using a combined cDNA microarray/promoter
transactivation approach. J Biol Chem. 276:17058–17062. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fan C, Xie Y, Dong Y, Su Y and Upton Z:
Investigating the potential of Shikonin as a novel hypertrophic
scar treatment. J Biomed Sci. 22:702015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen S, Liu J, Yang M, Lai W, Ye L, Chen
J, Hou X, Ding H, Zhang W, Wu Y, et al: Fn14, a downstream target
of the TGF-β signaling pathway, regulates fibroblast activation.
PLoS One. 10:e01438022015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Perkins K, Davey RB and Wallis KA:
Silicone gel: A new treatment for burn scars and contractures.
Burns Incl Therm Inj. 9:201–204. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
de Oliveira GV, Nunes TA and Magna LA:
Silicone versus nonsilicone gel dressings: A controlled trial.
Dermatol Surg. 27:721–726. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Niessen FB, Spauwen PH, Schalkwijk J and
Kon M: On the nature of hypertrophic scars and keloids: A review.
Plast Reconstr Surg. 104:1435–1458. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Casi G and Neri D: Antibody-drug
conjugates and small molecule-drug conjugates: Opportunities and
challenges for the development of selective anticancer cytotoxic
agents. J Med Chem. 58:8751–8761. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
An S and Fu L: Small-molecule PROTACs: An
emerging and promising approach for the development of targeted
therapy drugs. EBioMedicine. 36:553–562. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang L, Yang J, Ran B, Yang X, Zheng W,
Long Y and Jiang X: Small Molecular TGF-β1-inhibitor-loaded
electrospun fibrous scaffolds for preventing hypertrophic scars.
ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 9:32545–32553. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cardarelli F, Digiacomo L, Marchini C,
Amici A, Salomone F, Fiume G, Rossetta A, Gratton E, Pozzi D and
Caracciolo G: The intracellular trafficking mechanism of
Lipofectamine-based transfection reagents and its implication for
gene delivery. Sci Rep. 6:258792016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Di Lullo GA, Sweeney SM, Korkko J,
Ala-Kokko L and San Antonio JD: Mapping the ligand-binding sites
and disease-associated mutations on the most abundant protein in
the human, type I collagen. J Biol Chem. 277:4223–4231. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhu Y, Tao H, Jin C, Liu Y, Lu X, Hu X and
Wang X: Transforming growth factor-β1 induces type II collagen and
aggrecan expression via activation of extracellular
signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and Smad2/3 signaling pathways. Mol Med
Rep. 12:5573–5579. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Santoro MM and Gaudino G: Cellular and
molecular facets of keratinocyte reepithelization during wound
healing. Exp Cell Res. 304:274–286. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Brown NJ, Kimble RM, Gramotnev G, Rodger S
and Cuttle L: Predictors of re-epithelialization in pediatric burn.
Burns. 40:751–758. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Das S, Mandal M, Chakraborti T, Mandal A
and Chakraborti S: Structure and evolutionary aspects of matrix
metalloproteinases: A brief overview. Mol Cell Biochem. 253:31–40.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Eto H, Suga H, Aoi N, Kato H, Doi K, Kuno
S, Tabata Y and Yoshimura K: Therapeutic potential of fibroblast
growth factor-2 for hypertrophic scars: Upregulation of MMP-1 and
HGF expression. Lab Invest. 92:214–223. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu J, Shen JX, Wu HT, Li XL, Wen XF, Du
CW and Zhang GJ: Collagen 1A1 (COL1A1) promotes metastasis of
breast cancer and is a potential therapeutic target. Discov Med.
25:211–223. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ma L, Gan C, Huang Y, Wang Y, Luo G and Wu
J: Comparative proteomic analysis of extracellular matrix proteins
secreted by hypertrophic scar with normal skin fibroblasts. Burns
Trauma. 2:76–83. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Seifert O, Bayat A, Geffers R, Dienus K,
Buer J, Löfgren S and Matussek A: Identification of unique gene
expression patterns within different lesional sites of keloids.
Wound Repair Regen. 16:254–265. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Amadeu TP, Braune AS, Porto LC,
Desmouliere A and Costa AM: Fibrillin-1 and elastin are
differentially expressed in hypertrophic scars and keloids. Wound
Repair Regen. 12:169–174. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liu R, Hossain MM, Chen X and Jin JP:
Mechanoregulation of SM22α/Transgelin. Biochemistry. 56:5526–5538.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Assinder SJ, Stanton JA and Prasad PD:
Transgelin: An actin-binding protein and tumour suppressor. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 41:482–486. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ulrich D, Ulrich F, Unglaub F, Piatkowski
A and Pallua N: Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of
metalloproteinases in patients with different types of scars and
keloids. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 63:1015–1021. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Poormasjedi-Meibod MS, Hartwell R, Kilani
R and Ghahary A: Anti-scarring properties of different tryptophan
derivatives. PLoS One. 9:e919552014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Martin-Malpartida P, Batet M, Kaczmarska
Z, Freier R, Gomes T, Aragón E, Zou Y, Wang Q, Xi Q, Ruiz L, et al:
Structural basis for genome wide recognition of 5-bp GC motifs by
SMAD transcription factors. Nat Commun. 8:20702017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Walton KL, Johnson KE and Harrison CA:
Targeting TGF-β Mediated SMAD signaling for the prevention of
fibrosis. Front Pharmacol. 8:4612017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Basu A, Kligman LH, Samulewicz SJ and Howe
CC: Impaired wound healing in mice deficient in a matricellular
protein SPARC (osteonectin, BM-40). BMC Cell Biol. 2:152001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chavez-Muñoz C, Hartwell R, Jalili RB,
Jafarnejad SM, Lai A, Nabai L, Ghaffari A, Hojabrpour P, Kanaan N,
Duronio V, et al: SPARC/SFN interaction, suppresses type I collagen
in dermal fibroblasts. J Cell Biochem. 113:2622–2632. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Dougherty KM, Pearson JM, Yang AY,
Westrick RJ, Baker MS and Ginsburg D: The plasminogen activator
inhibitor-2 gene is not required for normal murine development or
survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:686–691. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Rohani MG and Parks WC: Matrix remodeling
by MMPs during wound repair. Matrix Biol. 44-46:113–121. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Liu Y, Li Y, Li N, Teng W, Wang M, Zhang Y
and Xiao Z: TGF-β1 promotes scar fibroblasts proliferation and
transdifferentiation via up-regulating MicroRNA-21. Sci Rep.
6:322312016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Bai X, He T, Liu J, Wang Y, Fan L, Tao K,
Shi J, Tang C, Su L and Hu D: Loureirin B inhibits fibroblast
proliferation and extracellular matrix deposition in hypertrophic
scar via TGF-β/Smad pathway. Exp Dermatol. 24:355–360. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kim ES, Kim MS and Moon A:
TGF-beta-induced upregulation of MMP-2 and MMP-9 depends on p38
MAPK, but not ERK signaling in MCF10A human breast epithelial
cells. Int J Oncol. 25:1375–1382. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Gill SE and Parks WC: Metalloproteinases
and their inhibitors: Regulators of wound healing. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 40:1334–1347. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Qiu SS, Dotor J and Hontanilla B: Effect
of P144® (Anti-TGF-β) in an ‘in vivo’ human hypertrophic
scar model in nude mice. PLoS One. 10:e01444892015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Tredget EE, Wang R, Shen Q, Scott PG and
Ghahary A: Transforming growth factor-beta mRNA and protein in
hypertrophic scar tissues and fibroblasts: Antagonism by IFN-alpha
and IFN-gamma in vitro and in vivo. J Interferon Cytokine Res.
20:143–151. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|