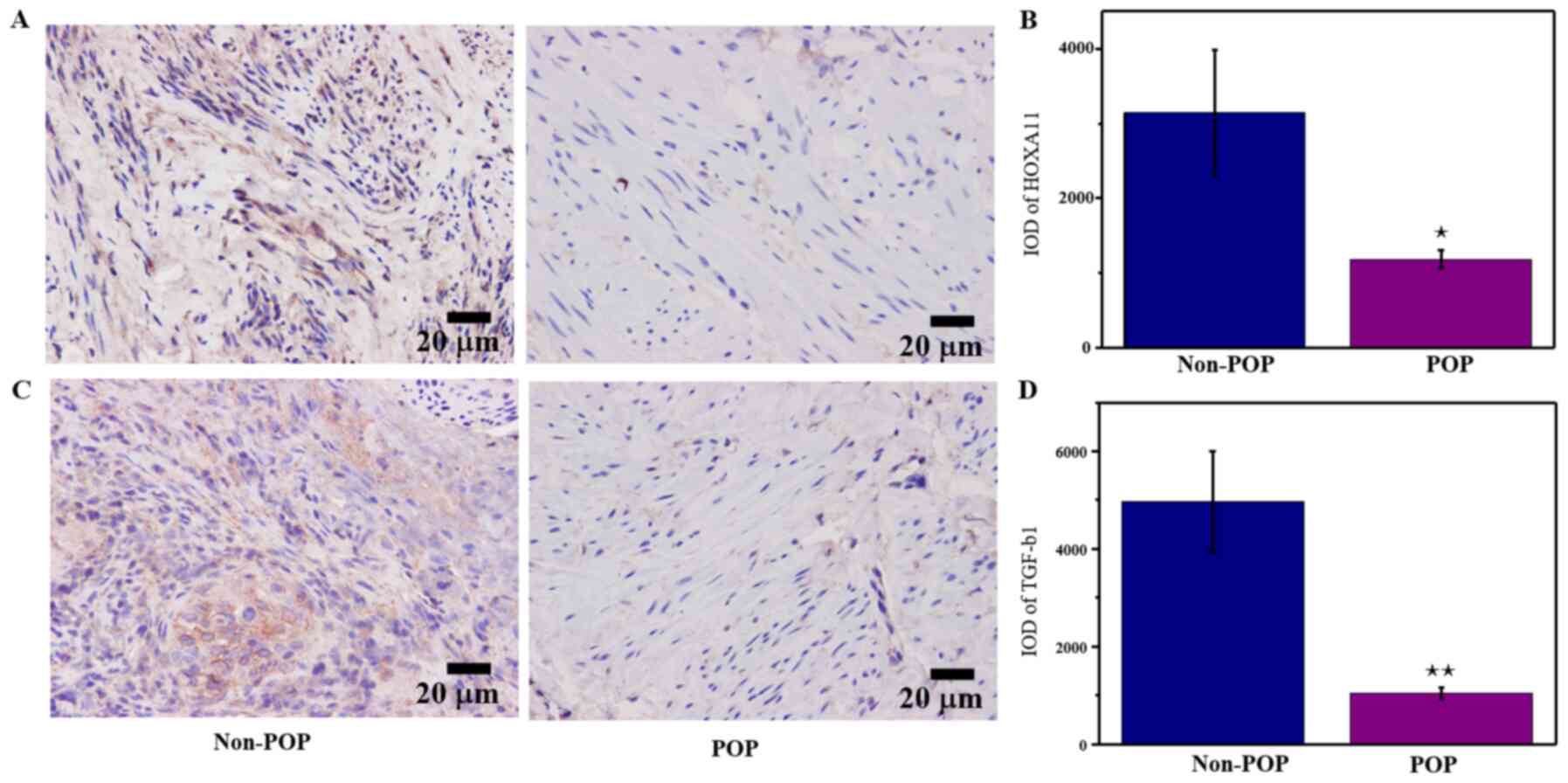
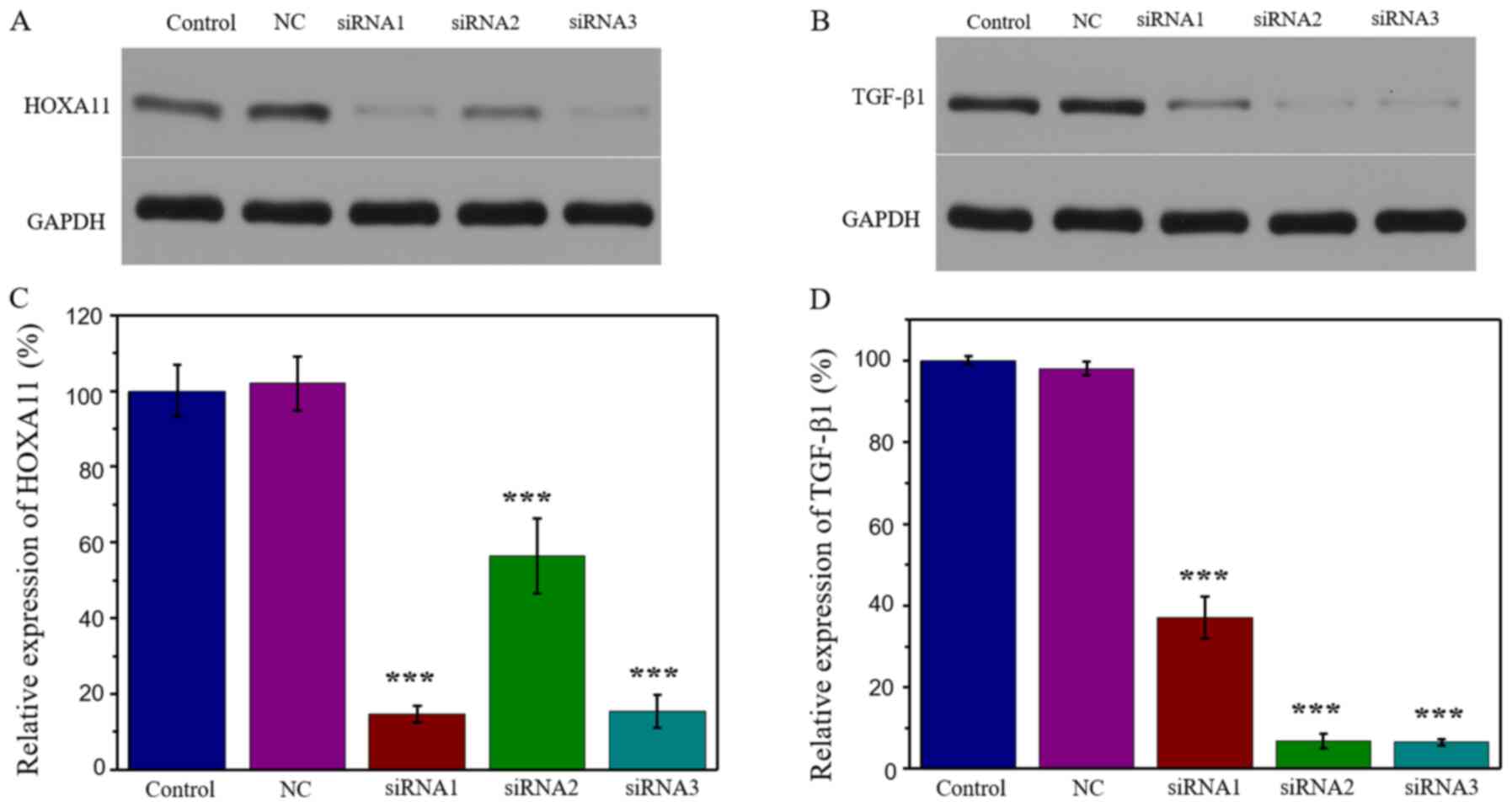
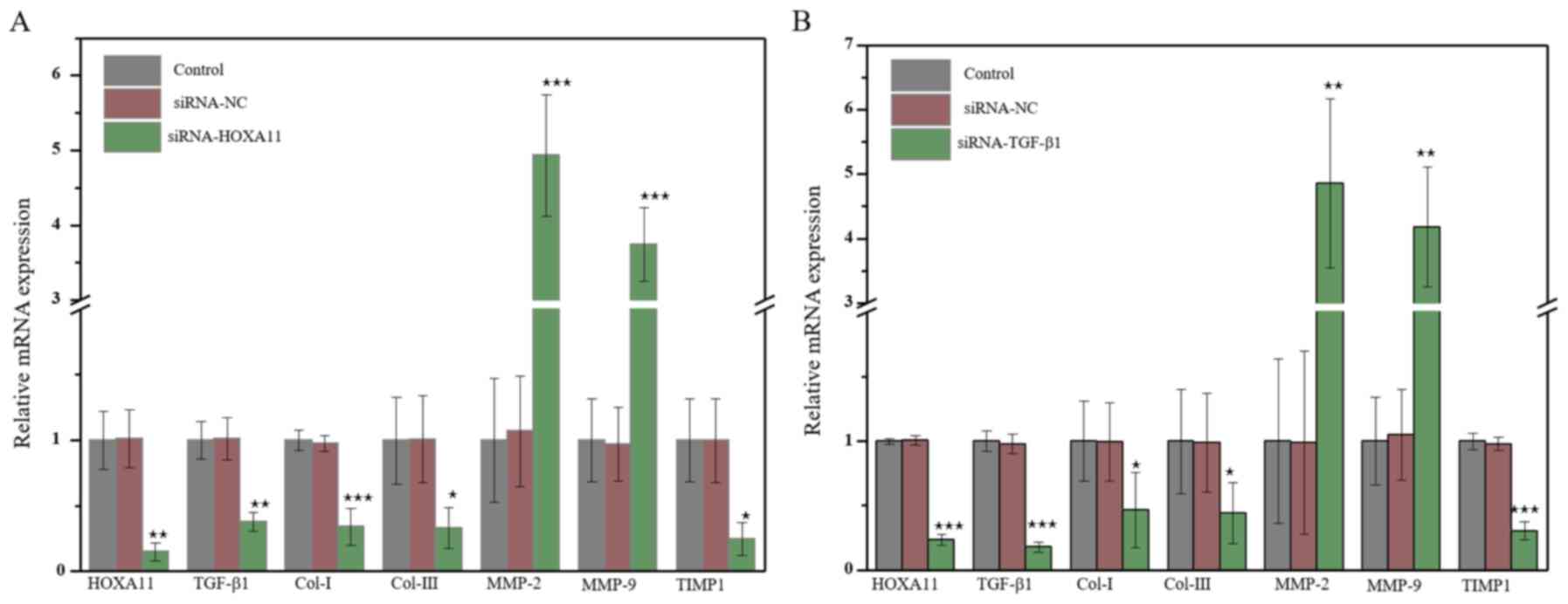
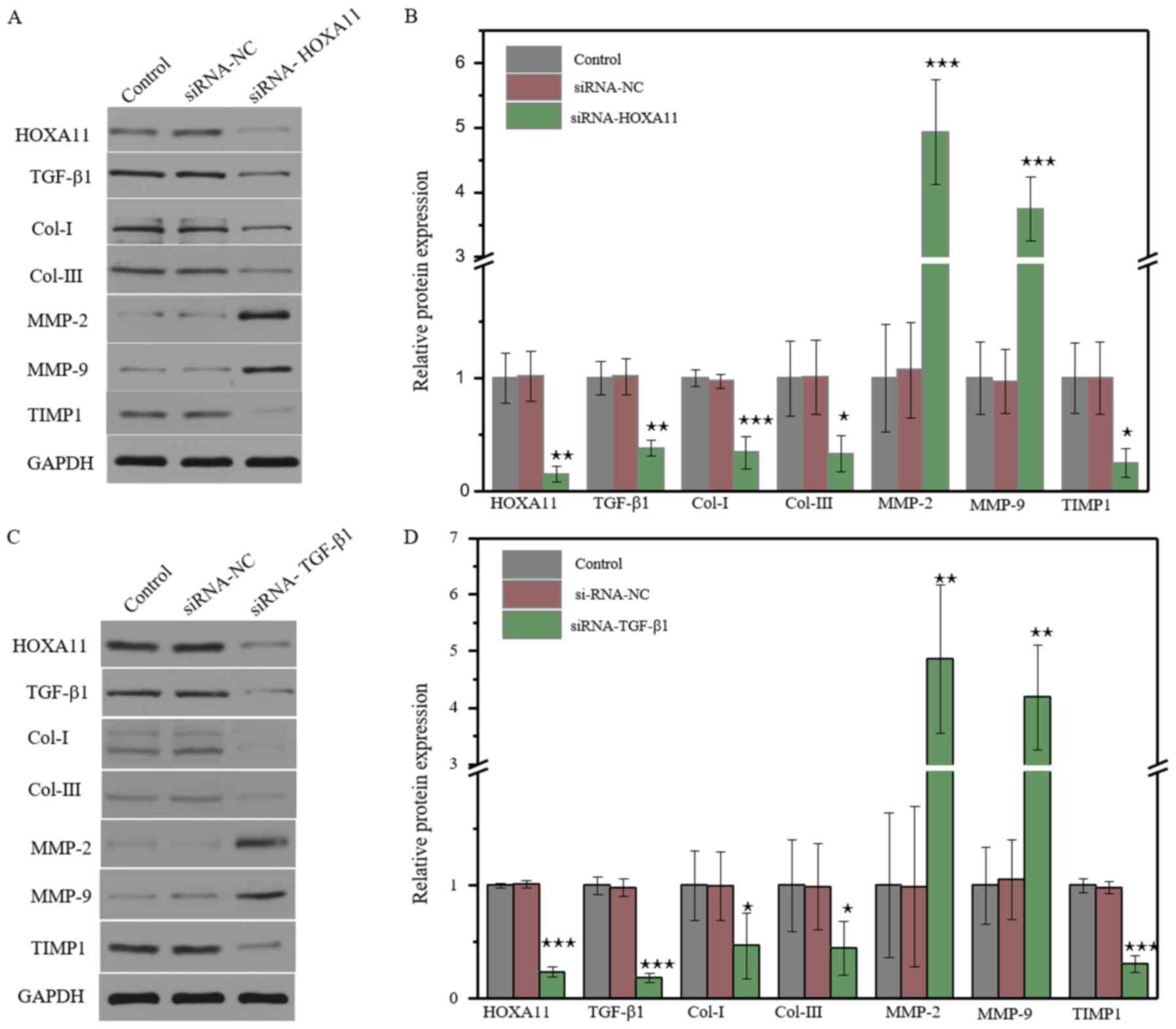
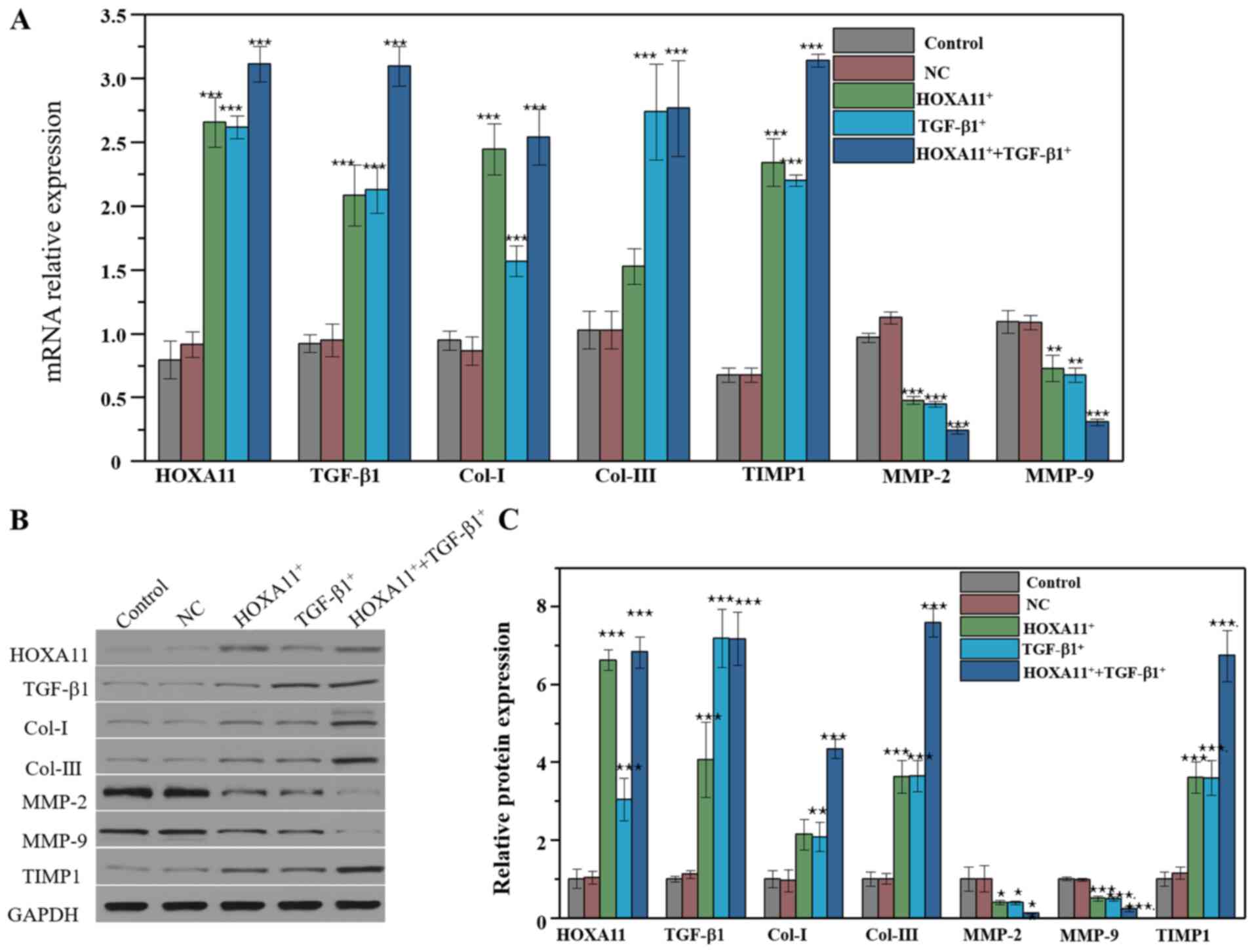
|
1
|
Vergeldt TF, Weemhoff M, IntHout J and
Kluivers KB: Risk factors for pelvic organ prolapse and its
recurrence: A systematic review. Int Urogynecol J. 26:1559–1573.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Altman D, Zetterstrom J, Schultz I,
Nordenstam J, Hjern F, Lopez A and Mellgren A: Pelvic organ
prolapse and urinary incontinence in women with surgically managed
rectal prolapse: A population-based case-control study. Dis Colon
Rectum. 49:28–35. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Clark AL, Gregory T, Smith VJ and Edwards
R: Epidemiologic evaluation of reoperation for surgically treated
pelvic organ prolapse and urinary incontinence. Am J Obstet
Gynecol. 189:1261–1267. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Olsen AL, Smith VJ, Bergstrom JO, Colling
JC and Clark AL: Epidemiology of surgically managed pelvic organ
prolapse and urinary incontinence. Obstet Gynecol. 89:501–506.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Delancey JO, Kane Low L, Miller JM, Patel
DA and Tumbarello JA: Graphic integration of causal factors of
pelvic floor disorders: An integrated life span model. Am J Obstet
Gynecol. 199:610.e1–e5. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Zhao X, Ma C, Li R, Xue J, Liu L and Liu
P: Hypoxia induces apoptosis through HIF-1α signaling pathway in
human uterosacral ligaments of pelvic organ prolapse. Biomed Res
Int. 2017:83160942017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sun MJ, Cheng YS, Liu CS and Sun R:
Changes in the PGC-1α and mtDNA copy number may play a role in the
development of pelvic organ prolapse in pre-menopausal patients.
Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 58:526–530. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang L, Zheng P, Duan A, Hao Y, Lu C and
Lu D: [Corrigendum] Genomewide DNA methylation analysis of
uterosacral ligaments in women with pelvic organ prolapse. Mol Med
Rep. 19:24582019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tyagi T, Alarab M, Leong Y, Lye S and
Shynlova O: Local oestrogen therapy modulates extracellular matrix
and immune response in the vaginal tissue of post-menopausal women
with severe pelvic organ prolapse. J Cell Mol Med. 23:2907–2919.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Alarab M, Kufaishi H, Lye S, Drutz H and
Shynlova O: Expression of extracellular matrix-remodeling proteins
is altered in vaginal tissue of premenopausal women with severe
pelvic organ prolapse. Reprod Sci. 21:704–715. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
de Landsheere L, Blacher S, Munaut C,
Nusgens B, Rubod C, Noel A, Foidart JM, Cosson M and Nisolle M:
Changes in elastin density in different locations of the vaginal
wall in women with pelvic organ prolapse. Int Urogynecol J.
25:1673–1681. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Strinic T, Vulic M, Tomic S, Capkun V,
Stipic I and Alujevic I: Increased expression of matrix
metalloproteinase-1 in uterosacral ligament tissue from women with
pelvic organ prolapse. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 89:832–834. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Budatha M, Roshanravan S, Zheng Q,
Weislander C, Chapman SL, Davis EC, Starcher B, Word RA and
Yanagisawa H: Extracellular matrix proteases contribute to
progression of pelvic organ prolapse in mice and humans. J Clin
Invest. 121:2048–2059. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Woodley DT, Krueger GG, Jorgensen CM,
Fairley JA, Atha T, Huang Y, Chan L, Keene DR and Chen M: Normal
and gene-corrected dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa fibroblasts
alone can produce type VII collagen at the basement membrane zone.
J Invest Dermatol. 121:1021–1028. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Piperi C and Papavassiliou AG: Molecular
mechanisms regulating matrix metalloproteinases. Curr Top Med Chem.
12:1095–1112. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dai W, Liang Z, Liu H, Zhao G and Ju C:
Lunasin abrogates the expression of matrix metalloproteinases and
reduction of type II collagen. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol.
47:3259–3264. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sun B, Zhou L, Wen Y, Wang C, Baer TM,
Pera RR and Chen B: Proliferative behavior of vaginal fibroblasts
from women with pelvic organ prolapse. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod
Biol. 183:1–4. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Taylor HS, Vanden Heuvel GB and Igarashi
P: A conserved Hox axis in the mouse and human female reproductive
system: Late establishment and persistent adult expression of the
Hoxa cluster genes. Biol Reprod. 57:1338–1345. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Taylor HS, Igarashi P, Olive DL and Arici
A: Sex steroids mediate HOXA11 expression in the human
peri-implantation endometrium. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
84:1129–1135. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Connell KA, Guess MK, Chen H, Andikyan V,
Bercik R and Taylor HS: HOXA11 is critical for development and
maintenance of uterosacral ligaments and deficient in pelvic
prolapse. J Clin Invest. 118:1050–1055. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ma Y, Guess M, Datar A, Hennessey A,
Cardenas I, Johnson J and Connell KA: Knockdown of Hoxa11 in vivo
in the uterosacral ligament and uterus of mice results in altered
collagen and matrix metalloproteinase activity. Biol Reprod.
86:1002012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wen Y, Polan ML and Chen B: Do
extracellular matrix protein expressions change with cyclic
reproductive hormones in pelvic connective tissue from women with
stress urinary incontinence? Hum Reprod. 21:1266–1273. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Meijerink AM, van Rijssel RH and van der
Linden PJ: Tissue composition of the vaginal wall in women with
pelvic organ prolapse. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 75:21–27. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Emmerson S, Mukherjee S, Melendez-Munoz J,
Cousins F, Edwards SL, Karjalainen P, Ng M, Tan KS, Darzi S, Bhakoo
K, et al: Composite mesh design for delivery of autologous
mesenchymal stem cells influences mesh integration, exposure and
biocompatibility in an ovine model of pelvic organ prolapse.
Biomaterials. 225:1194952019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Elneil S: Complex pelvic floor failure and
associated problems. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 23:555–573.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lee UJ, Kerkhof MH, van Leijsen SA and
Heesakkers JP: Obesity and pelvic organ prolapse. Curr Opin Urol.
27:428–434. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Qiu J, Qin M, Fan B and Chen X: Klotho
protein reduced the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-1
(MMP-1) and matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3) in fibroblasts from
patients with pelvic organ prolapse (POP) by Down-regulating the
phosphorylation of ERK1/2. Med Sci Monit. 25:3815–3824. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zeng C, Liu J, Wang H, Zhou Y, Wu J and
Yan G: Correlation between autophagy and collagen deposition in
patients with pelvic organ prolapse. Female Pelvic Med Reconstr
Surg. 24:213–221. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lachowski D, Cortes E, Rice A, Pinato D,
Rombouts K and Del Rio Hernandez A: Matrix stiffness modulates the
activity of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 in hepatic stellate cells to
perpetuate fibrosis. Sci Rep. 9:72992019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dökmeci F, Tekşen F, Çetinkaya ŞE, Özkan
T, Kaplan F and Köse K: Expressions of homeobox, collagen and
estrogen genes in women with uterine prolapse. Eur J Obstet Gynecol
Reprod Biol. 26–29. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Wang S, Lu D, Zhang Z, Jia X and Yang L:
Effects of mechanical stretching on the morphology of extracellular
polymers and the mRNA expression of collagens and small
leucine-rich repeat proteoglycans in vaginal fibroblasts from women
with pelvic organ prolapse. PLoS One. 13:e01934562018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Makker A, Goel MM, Nigam D, Bhatia V,
Mahdi AA, Das V and Pandey A: Endometrial expression of homeobox
genes and cell adhesion molecules in infertile women with
intramural fibroids during window of implantation. Reprod Sci.
24:435–444. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cunha GR, Robboy SJ, Kurita T, Isaacson D,
Shen J, Cao M and Baskin LS: Development of the human female
reproductive tract. Differentiation. 103:46–65. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nigdelioglu R, Hamanaka RB, Meliton AY,
O'Leary E, Witt LJ, Cho T, Sun K, Bonham C, Wu D, Woods PS, et al:
Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β promotes de novo serine
synthesis for collagen production. J Biol Chem. 291:27239–27251.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Leegant A, Zuckerwise LC, Downing K,
Brouwer-Visser J, Zhu C, Cossio MJ, Strube F, Xie X, Banks E and
Huang GS: Transforming growth factor β1 and extracellular matrix
protease expression in the uterosacral ligaments of patients with
and without pelvic organ prolapse. Female Pelvic Med Reconstr Surg.
21:53–58. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ventura RD, Padalhin AR, Park CM and Lee
BT: Enhanced decellularization technique of porcine dermal ECM for
tissue engineering applications. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.
104:1098412019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang Y, He RQ, Dang YW, Zhang XL, Wang X,
Huang SN, Huang WT, Jiang MT, Gan XN, Xie Y, et al: Comprehensive
analysis of the long noncoding RNA HOXA11-AS gene interaction
regulatory network in NSCLC cells. Cancer Cell Int. 16:892016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|