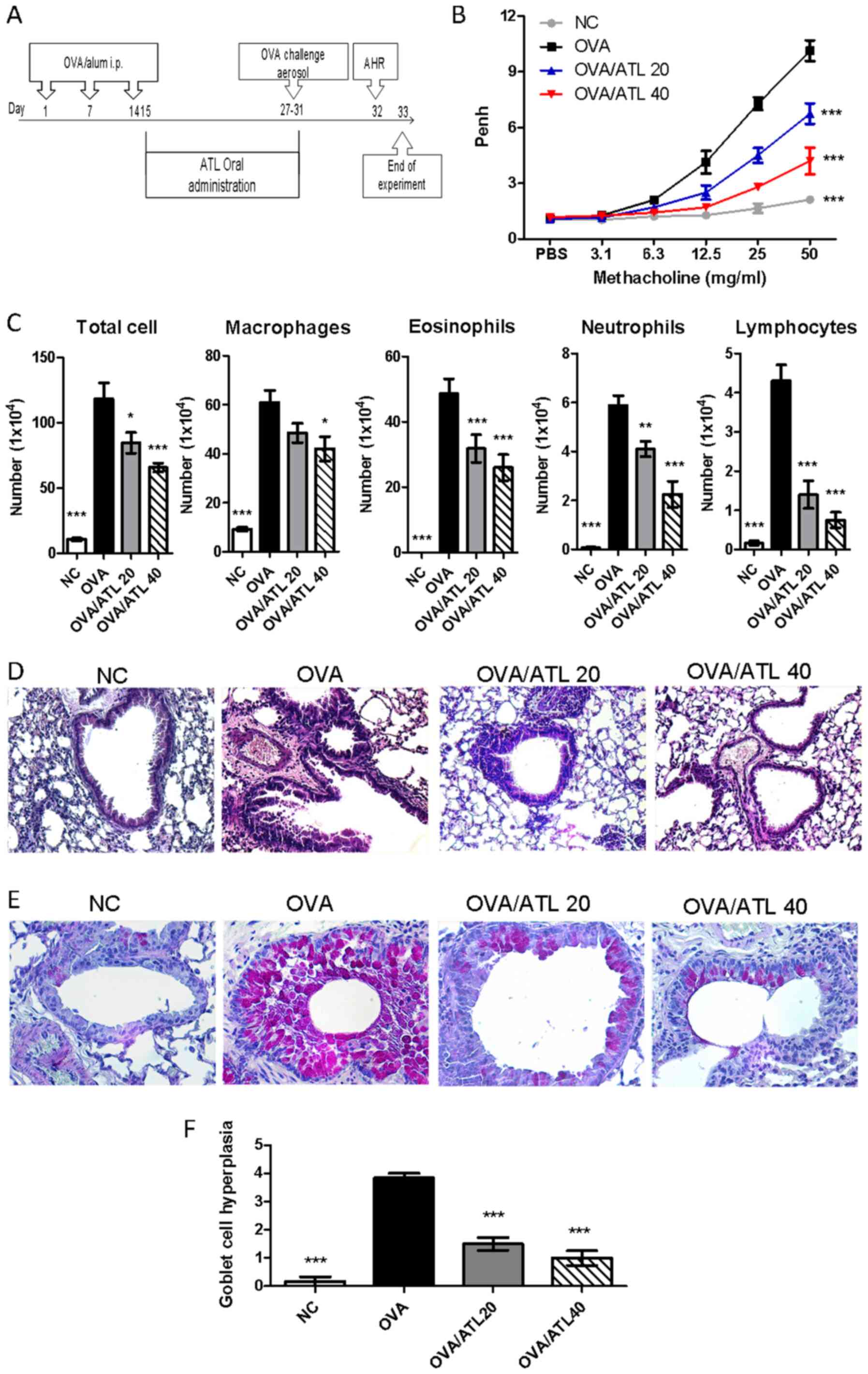
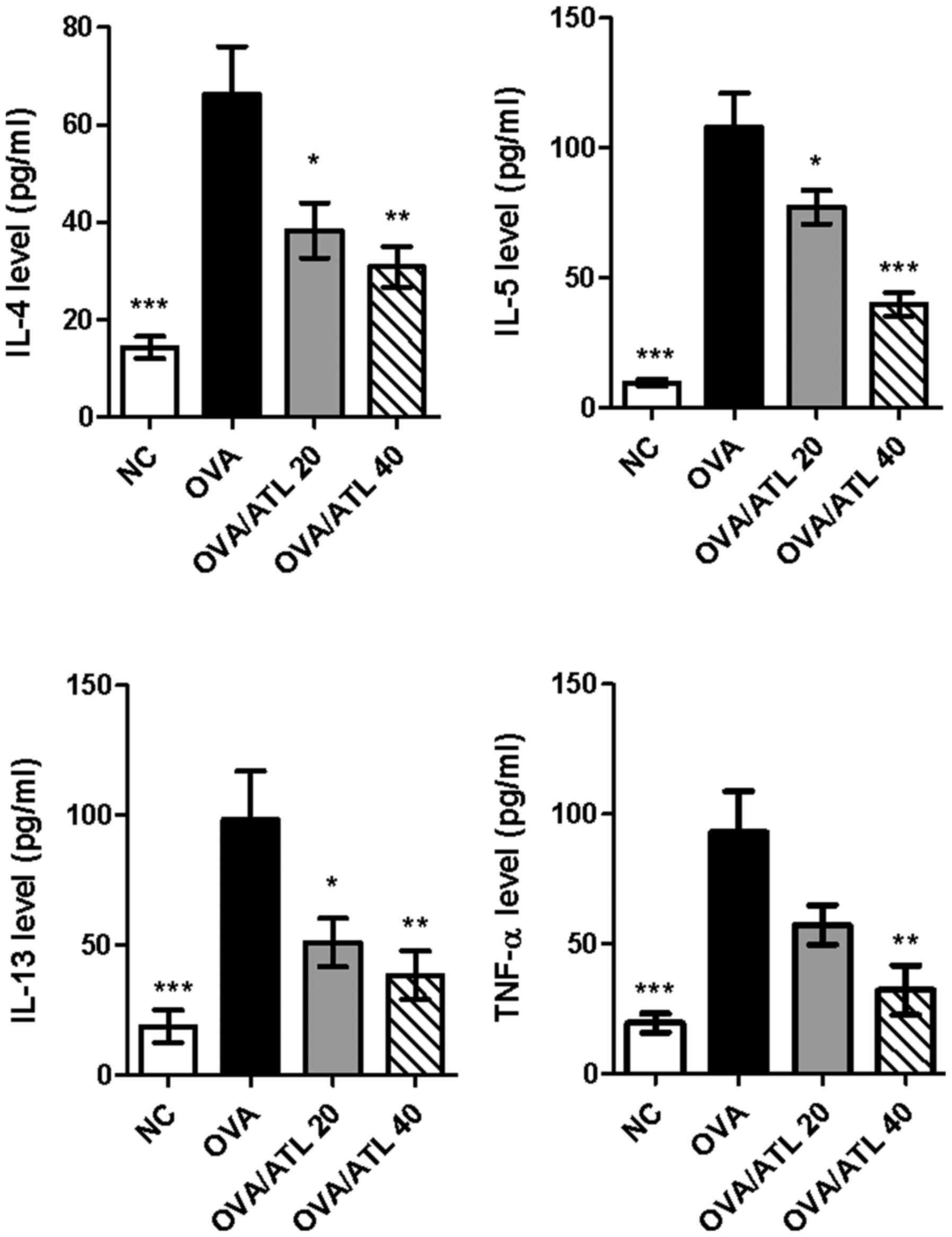
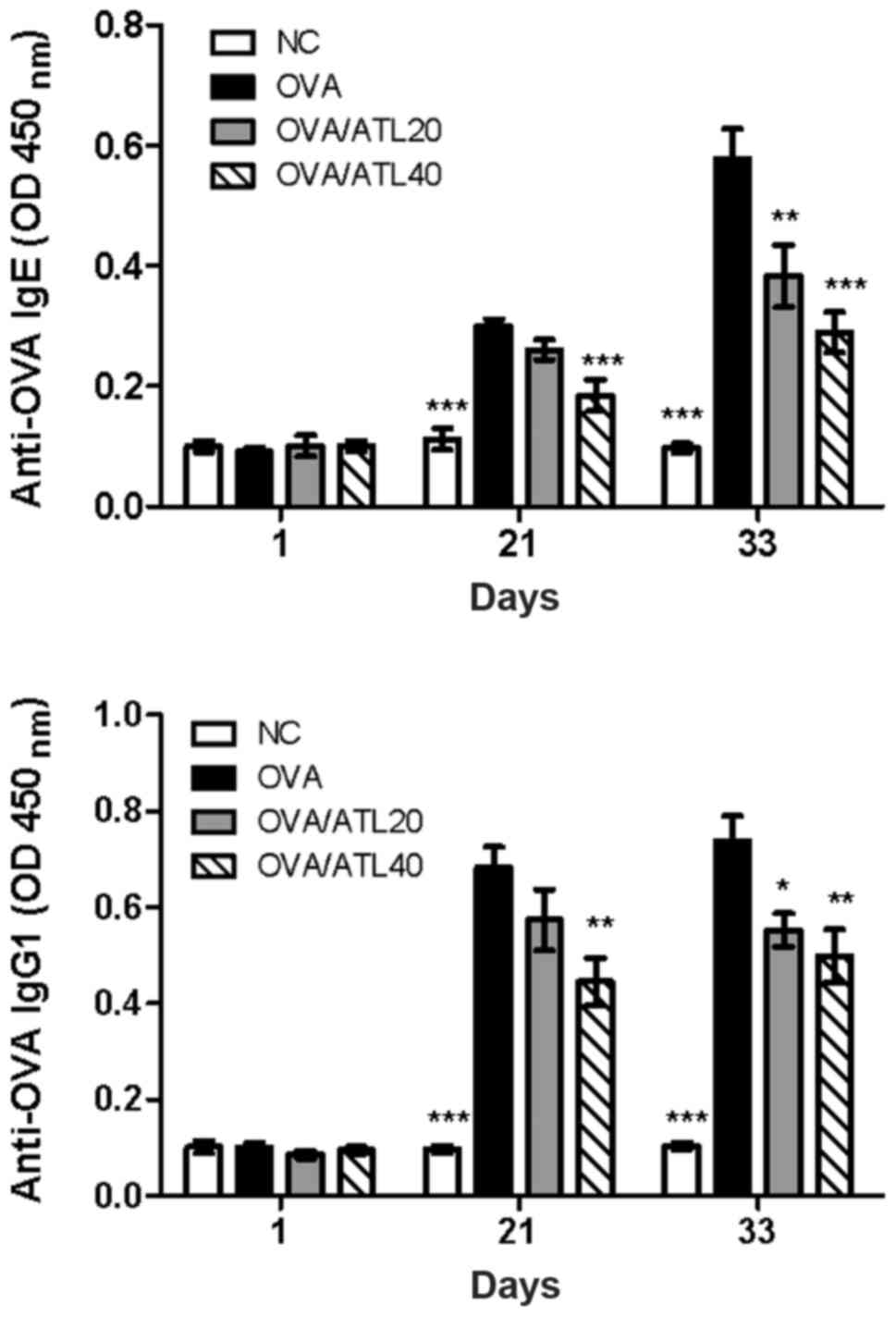
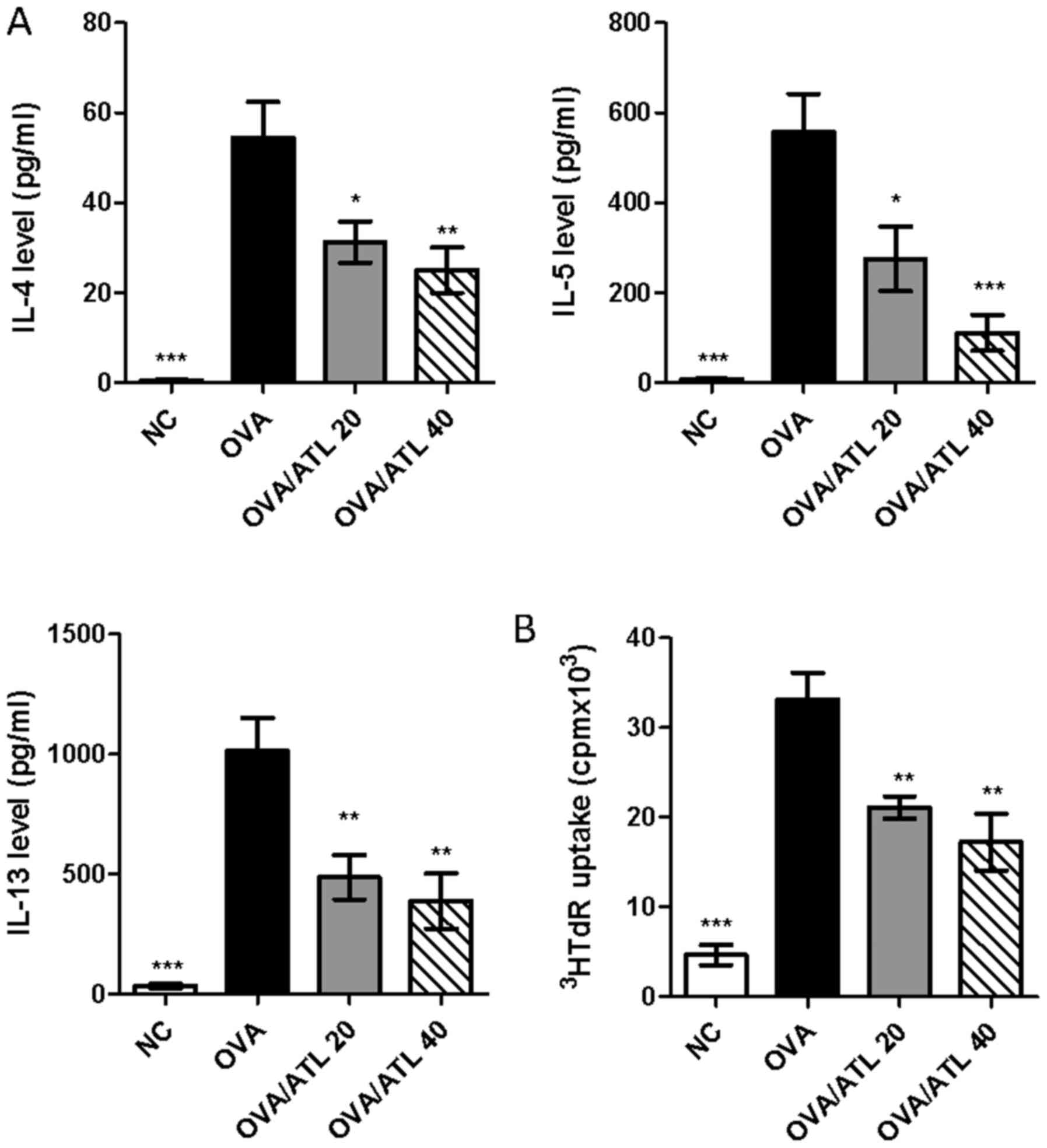
|
1
|
Collaborators GBDCRD; GBD 2015 Chronic
Respiratory Disease Collaborators, : Global, regional, and national
deaths, prevalence, disability-adjusted life years, and years lived
with disability for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and
asthma, 1990–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of
Disease Study 2015. Lancet Respir Med. 5:691–706. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Brannan JD: Bronchial hyperresponsiveness
in the assessment of asthma control: Airway hyperresponsiveness in
asthma: its measurement and clinical significance. Chest. 138
(Suppl):11S–17S. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wenzel SE: Asthma phenotypes: The
evolution from clinical to molecular approaches. Nat Med.
18:716–725. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Simpson JL, Scott R, Boyle MJ and Gibson
PG: Inflammatory subtypes in asthma: Assessment and identification
using induced sputum. Respirology. 11:54–61. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cosmi L, Maggi L, Mazzoni A, Liotta F and
Annunziato F: Biologicals targeting type 2 immunity: Lessons
learned from asthma, chronic urticaria and atopic dermatitis. Eur J
Immunol. 49:1334–1343. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lambrecht BN and Hammad H: The role of
dendritic and epithelial cells as master regulators of allergic
airway inflammation. Lancet. 376:835–843. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lambrecht BN and Hammad H: Biology of lung
dendritic cells at the origin of asthma. Immunity. 31:412–424.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xia YG, Yang BY, Wang QH, Liang J, Wang D
and Kuang HX: Species classification and quality assessment of
cangzhu (Atractylodis rhizoma) by high-performance liquid
chromatography and chemometric methods. J Anal Methods Chem.
2013:4975322013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jun X, Fu P, Lei Y and Cheng P:
Pharmacological effects of medicinal components of Atractylodes
lancea (Thunb.) DC. Chin Med. 13:592018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yu C, Xiong Y, Chen D, Li Y, Xu B, Lin Y,
Tang Z, Jiang C and Wang L: Ameliorative effects of atractylodin on
intestinal inflammation and co-occurring dysmotility in both
constipation and diarrhea prominent rats. Korean J Physiol
Pharmacol. 21:1–9. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chae HS, Kim YM and Chin YW: Atractylodin
inhibits interleukin-6 by blocking NPM-ALK activation and MAPKs in
HMC-1. Molecules. 21:11692016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Tang F, Fan K, Wang K and Bian C:
Atractylodin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung
injury by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome and TLR4 pathways. J
Pharmacol Sci. 136:203–211. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chuang CH, Cheng YC, Lin SC, Lehman CW,
Wang SP, Chen DY, Tsai SW and Lin CC: Atractylodin suppresses
dendritic cell maturation and ameliorates collagen-induced
arthritis in a mouse model. J Agric Food Chem. 67:6773–6784. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals; Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th
edition. National Academies Press (US); Washington, DC: 2011
|
|
15
|
Lyu Z, Ji X, Chen G and An B: Atractylodin
ameliorates lipopolysaccharide and d-galactosamine-induced acute
liver failure via the suppression of inflammation and oxidative
stress. Int Immunopharmacol. 72:348–357. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kim SJ, Kim CH, Ahn JH, Kim MS, Kim SC,
Lee SY, Kwon SS, Kim YK, Lim KH, Moon HS, et al: Time sequence of
airway remodeling in a mouse model of chronic asthma: the relation
with airway hyperresponsiveness. J Korean Med Sci. 22:183–191.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Padrid P, Snook S, Finucane T, Shiue P,
Cozzi P, Solway J and Leff AR: Persistent airway
hyperresponsiveness and histologic alterations after chronic
antigen challenge in cats. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 151:184–193.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chiang CY, Lee CC, Fan CK, Huang HM,
Chiang BL and Lee YL: Osthole treatment ameliorates Th2-mediated
allergic asthma and exerts immunomodulatory effects on dendritic
cell maturation and function. Cell Mol Immunol. 14:935–947. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Weng TY, Li CJ, Li CY, Hung YH, Yen MC,
Chang YW, Chen YH, Chen YL, Hsu HP, Chang JY, et al: Skin delivery
of Clec4a small hairpin RNA elicited an effective antitumor
response by enhancing CD8+ immunity in vivo. Mol Ther Nucleic
Acids. 9:419–427. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kubo M: T follicular helper and TH2 cells
in allergic responses. Allergol Int. 66:377–381. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kumar H, Kim IS, More SV, Kim BW and Choi
DK: Natural product-derived pharmacological modulators of Nrf2/ARE
pathway for chronic diseases. Nat Prod Rep. 31:109–139. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhu F, Du B and Xu B: Anti-inflammatory
effects of phytochemicals from fruits, vegetables, and food
legumes: A review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 58:1260–1270. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Schatz M and Rosenwasser L: The allergic
asthma phenotype. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2:645–648, quiz
649. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Choy DF, Hart KM, Borthwick LA, Shikotra
A, Nagarkar DR, Siddiqui S, Jia G, Ohri CM, Doran E, Vannella KM,
et al: TH2 and TH17 inflammatory pathways are reciprocally
regulated in asthma. Sci Transl Med. 7:301ra1292015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nials AT and Uddin S: Mouse models of
allergic asthma: Acute and chronic allergen challenge. Dis Model
Mech. 1:213–220. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yu QL and Chen Z: Establishment of
different experimental asthma models in mice. Exp Ther Med.
15:2492–2498. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Webb DC, Cai Y, Matthaei KI and Foster PS:
Comparative roles of IL-4, IL-13, and IL-4Ralpha in dendritic cell
maturation and CD4+ Th2 cell function. J Immunol. 178:219–227.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yi H, Zhang L, Zhen Y, He X and Zhao Y:
Dendritic cells induced in the presence of GM-CSF and IL-5.
Cytokine. 37:35–43. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ahn JS and Agrawal B: IL-4 is more
effective than IL-13 for in vitro differentiation of dendritic
cells from peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Int Immunol.
17:1337–1346. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Roper RL, Conrad DH, Brown DM, Warner GL
and Phipps RP: Prostaglandin E2 promotes IL-4-induced IgE and IgG1
synthesis. J Immunol. 145:2644–2651. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Möller GM, Overbeek SE, Van
Helden-Meeuwsen CG, Van Haarst JM, Prens EP, Mulder PG, Postma DS
and Hoogsteden HC: Increased numbers of dendritic cells in the
bronchial mucosa of atopic asthmatic patients: Downregulation by
inhaled corticosteroids. Clin Exp Allergy. 26:517–524. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li JG, Du YM, Yan ZD, Yan J, Zhuansun YX,
Chen R, Zhang W, Feng SL and Ran PX: CD80 and CD86 knockdown in
dendritic cells regulates Th1/Th2 cytokine production in asthmatic
mice. Exp Ther Med. 11:878–884. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Heron M, Grutters JC, ten Dam-Molenkamp
KM, Hijdra D, van Heugten-Roeling A, Claessen AM, Ruven HJ, van den
Bosch JM and van Velzen-Blad H: Bronchoalveolar lavage cell pattern
from healthy human lung. Clin Exp Immunol. 167:523–531. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Van Hoecke L, Job ER, Saelens X and Roose
K: Bronchoalveolar lavage of murine lungs to analyze inflammatory
cell infiltration. J Vis Exp. 4:e553982017.
|
|
36
|
Ishii T, Okuyama T, Noguchi N, Nishidono
Y, Okumura T, Kaibori M, Tanaka K, Terabayashi S, Ikeya Y and
Nishizawa M: Antiinflammatory constituents of Atractylodes
chinensis rhizome improve glomerular lesions in immunoglobulin
A nephropathy model mice. J Nat Med. 74:51–64. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|