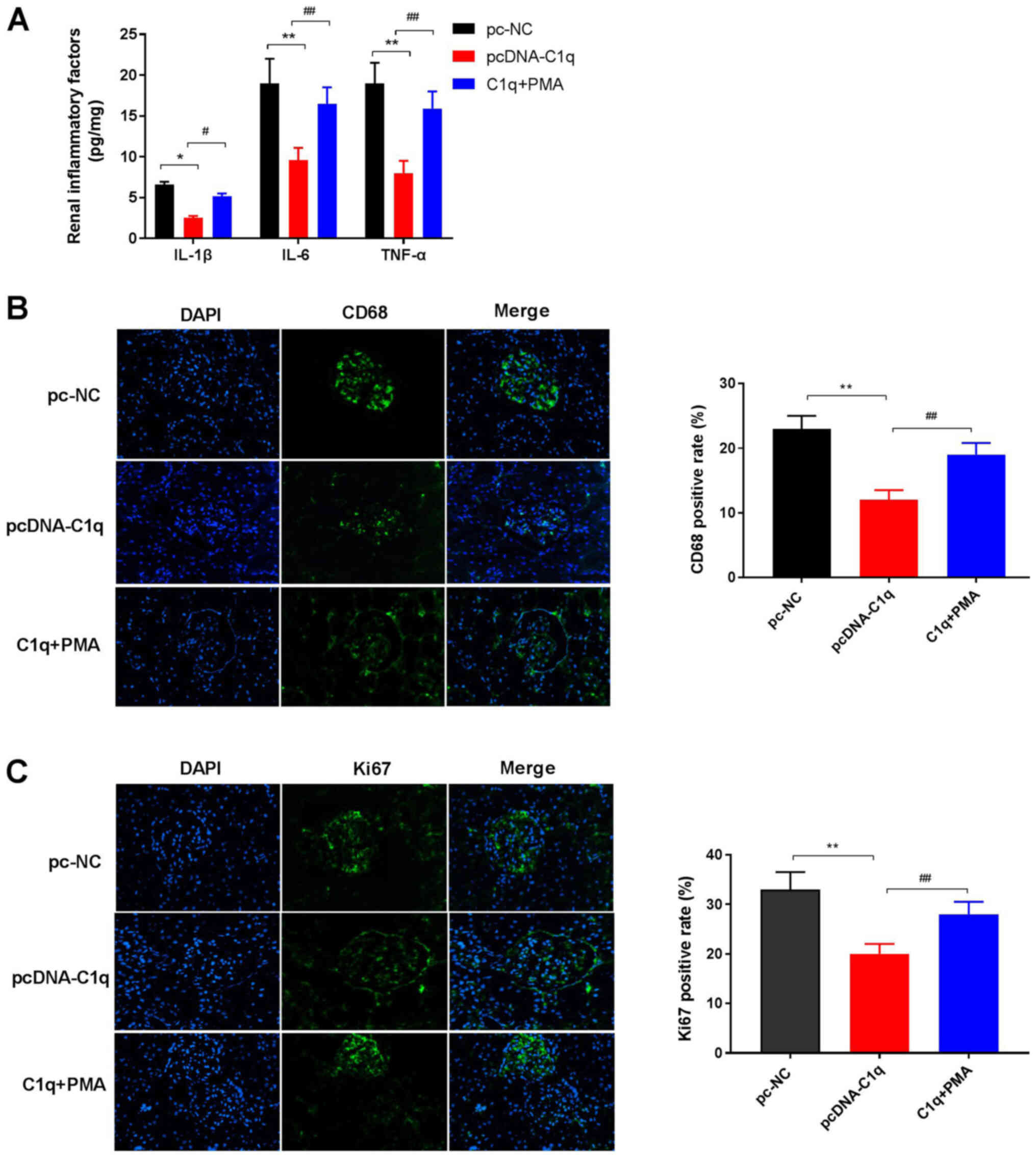
|
1
|
Davidson A, Aranow C and Mackay M: Lupus
Nephritis: Challenges and progress. Curr Opin Rheumatol.
31:682–688. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cameron JS: Lupus Nephritis. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 10:413–424. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Faurschou M, Dreyer L, Kamper AL,
Starklint H and Jacobsen S: Long-term mortality and renal outcome
in a cohort of 100 patients with lupus nephritis. Arthritis Care
Res (Hoboken). 62:873–880. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Parikh SV, Almaani S, Brodsky S and Rovin
BH: Update on lupus nephritis: Core curriculum 2020. Am J Kidney
Dis. 76:265–281. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Inoue A, Hasegawa H, Kohno M, Ito MR,
Terada M, Imai T, Yoshie O, Nose M and Fujita S: Antagonist of
fractalkine (CX3CL1) delays the initiation and ameliorates the
progression of lupus nephritis in MRL/lpr mice. Arthritis Rheum.
52:1522–1533. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mok CC, Kwok RC and Yip PS: Effect of
renal disease on the standardized mortality ratio and life
expectancy of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis
Rheum. 65:2154–2160. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Almaani S, Meara A and Rovin BH: Update on
lupus nephritis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 12:825–835. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Houssiau FA and Ginzler EM: Current
treatment of lupus nephritis. Lupus. 17:426–430. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kishore U and Reid KBM: C1q: Structure,
function, and receptors. Immunopharmacology. 49:159–170. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu G, Pang Y, Liu X and Li QW: Structure,
distribution, classification, and function of C1q protein family: A
review. Yi Chuan. 35:1072–1080. 2013.(In Chinese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang FC, Zhou B and Dong Y: The roles of
complement 1q and anti-C1q autoantibodies in pathogenesis of lupus
nephritis. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 85:955–959. 2005.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Akhter E, Burlingame RW, Seaman AL, Magder
L and Petri M: Anti-C1q antibodies have higher correlation with
flares of lupus nephritis than other serum markers. Lupus.
20:1267–1274. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sinico RA, Radice A, Ikehata M,
Giammarresi G, Corace C, Arrigo G, Bollini B and Li Vecchi M:
Anti-C1q autoantibodies in lupus nephritis: Prevalence and clinical
significance. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1050:193–200. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yin Y, Wu X, Shan G and Zhang X:
Diagnostic value of serum anti-C1q antibodies in patients with
lupus nephritis: A meta-analysis. Lupus. 21:1088–1097. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mankan AK, Lawless MW, Gray SG, Kelleher D
and McManus R: NF-κB regulation: The nuclear response. J Cell Mol
Med. 13:631–643. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ruan Q and Chen YH: Nuclear factor-κB in
immunity and inflammation: The Treg and Th17 connection. Adv Exp
Med Biol. 946:207–221. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhong J, Shi QQ, Zhu MM, Shen J, Wang HH,
Ma D and Miao CH: MFHAS1 is associated with sepsis and stimulates
TLR2/NF-κB signaling pathway following negative regulation. PLoS
One. 10:e01436622015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou Y, Fang L, Jiang L, Wen P, Cao H, He
W, Dai C and Yang J: Uric acid induces renal inflammation via
activating tubular NF-κB signaling pathway. PLoS One. 7:e397382012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xu F, Wang Y, Cui W, Yuan H, Sun J, Wu M,
Guo Q, Kong L, Wu H and Miao L: Resveratrol prevention of diabetic
nephropathy is associated with the suppression of renal
inflammation and mesangial cell proliferation: Possible roles of
Akt/NF-B Pathway. Int J Endocrinol. 2014:1–9. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Jiang X, Zhao X, Luo H and Zhu K:
Therapeutic effect of polysaccharide of large yellow croaker swim
bladder on lupus nephritis of mice. Nutrients. 6:1223–1235. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jiang T, Tian F, Zheng H, Whitman SA, Lin
Y, Zhang Z, Zhang N and Zhang DD: Nrf2 suppresses lupus nephritis
through inhibition of oxidative injury and the NF-κB-mediated
inflammatory response. Kidney Int. 85:333–343. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sun F, Teng J, Yu P, Li W, Chang J and Xu
H: Involvement of TWEAK and the NF-κB signaling pathway in lupus
nephritis. Exp Ther Med. 15:2611–2619. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Muraoka M, Hasegawa H, Kohno M, Inoue A,
Miyazaki T, Terada M, Nose M and Yasukawa M: IK cytokine
ameliorates the progression of lupus nephritis in MRL/lpr mice.
Arthritis Rheum. 54:3591–3600. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kong R, Kang OH, Seo YS, Zhou T, Kim SA,
Shin DW and Kwon DY: MAPKs and NF-κB pathway inhibitory effect of
bisdemethoxycurcumin on phorbol 12 myristate 13 acetate and A23187
induced inflammation in human mast cells. Mol Med Rep. 17:630–635.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang YY, Li HT, Lu Y, Jia XY, Li YL, Chen
S, Chai JX, Zhang JJ, Liu D and Xie CH: Protective effects of
glycyrrhizic acid against lupus nephritis in MRL/lpr mice. Nan Fang
Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 37:957–961. 2017.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu Z, Xue L, Liu Z, Huang J, Wen J, Hu J,
Bo L and Yang R: Tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of
apoptosis accelerates the progression of renal fibrosis in lupus
nephritis by activating SMAD and p38 MAPK in TGF-β1 signaling
pathway. Mediators Inflamm. 2016:1–13. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Christopher-Stine L, Petri M, Astor BC and
Fine D: Urine protein-to-creatinine ratio is a reliable measure of
proteinuria in lupus nephritis. J Rheumatol. 31:1557–1559.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang Q, Sun P, Wang R and Zhao X:
Therapeutic effect of dendrobium candidum on lupus nephritis in
mice. Pharmacogn Mag. 13:129–135. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fenton K, Fismen S, Hedberg A, Seredkina
N, Fenton C, Mortensen ES and Rekvig OP: Anti-dsDNA antibodies
promote initiation, and acquired loss of renal Dnase1 promotes
progression of lupus nephritis in autoimmune (NZBxNZW)F1 mice. PLoS
One. 4:e84742009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen Z, Wang GS, Wang GH and Li XP:
Anti-C1q antibody is a valuable biological marker for prediction of
renal pathological characteristics in lupus nephritis. Clin
Rheumatol. 31:1323–1329. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li H and Ding G: Elevated serum
inflammatory cytokines in lupus nephritis patients, in association
with promoted hsa-miR-125a. Clin Lab. 62:631–638. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang Q, Sun P, Wang R and Zhao X:
Therapeutic effect of Dendrobium candidum on lupus nephritis
in mice. Pharmacogn Mag. 13:129–135. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jin O, Hou CC, Li XQ, Zhang X, Qiu M, Lin
D, Fang L, Guo X, Lin Z, Liao Z, et al: THU0274 upregulation of
NOD2 involved in the inflammatory response by activation of MAPK
signaling pathway in lupus nephritis. Annals of the Rheumatic
Diseases. 75:282–286. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zheng CZ, Shu YB, Luo YL and Luo J: The
role of miR-146a in modulating TRAF6-induced inflammation during
lupus nephritis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:1041–1048.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Saitoh A, Ikoma M, Kamiyama C, Doi K and
Koitabashi Y: Investigation of CD68 positive monocytes/
macrophage(CD68+ Mo/M phi) in urine and infiltrated tissue of
various kidney diseases in children. Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi.
44:798–805. 2002.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ma R, Jiang W, Li Z, Sun Y and Wei Z:
Intrarenal macrophage infiltration induced by T cells is associated
with podocyte injury in lupus nephritis patients. Lupus.
25:1577–1586. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wong CY, Cheong SK, Mok PL and Leong CF:
Differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells into mesangial
cells in post-glomerular injury murine model. Pathology. 40:52–57.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Schlöndorff D and Banas B: The mesangial
cell revisited: No cell is an island. J Am Soc Nephrol.
20:1179–1187. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu J, Zhu L, Xie GL, Bao JF and Yu Q:
Let-7 miRNAs modulate the activation of NF-κB by targeting TNFAIP3
and are involved in the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis. PLoS One.
10:e01212562015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Huang F, Zhang RY and Song L: Beneficial
effect of magnolol on lupus nephritis in MRL/lpr mice by
attenuating the NLRP3 inflammasome and NF-κB signaling pathway: A
mechanistic analysis. Mol Med Rep. 16:4817–4822. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Geng C, Li J, Ding F, Wu G, Yang Q, Sun Y,
Zhang Z, Dong T and Tian X: Curcumin suppresses 4-hydroxytamoxifen
resistance in breast cancer cells by targeting SLUG/Hexokinase 2
pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 473:147–153. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Soetikno V, Sari FR, Veeraveedu PT,
Thandavarayan RA, Harima M, Sukumaran V, Lakshmanan AP, Suzuki K,
Kawachi H and Watanabe K: Curcumin ameliorates macrophage
infiltration by inhibiting NF-κB activation and proinflammatory
cytokines in streptozotocin induced-diabetic nephropathy. Nutr
Metab (Lond). 8:35. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang L, Pang S, Deng B, Qian L, Chen J,
Zou J, Zheng J, Yang L, Zhang C, Chen X, et al: High glucose
induces renal mesangial cell proliferation and fibronectin
expression through JNK/NF-κB/NADPH oxidase/ROS pathway, which is
inhibited by resveratrol. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 44:629–638.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Korashy HM and El-Kadi AOS: The role of
redox-sensitive transcription factors NF-κB and AP-1 in the
modulation of the Cyp1a1 gene by mercury, lead, and copper. Free
Radic Biol Med. 44:795–806. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wilson PC, Kashgarian M and Moeckel G:
Interstitial inflammation and interstitial fibrosis and tubular
atrophy predict renal survival in lupus nephritis. Clin Kidney J.
11:207–218. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|