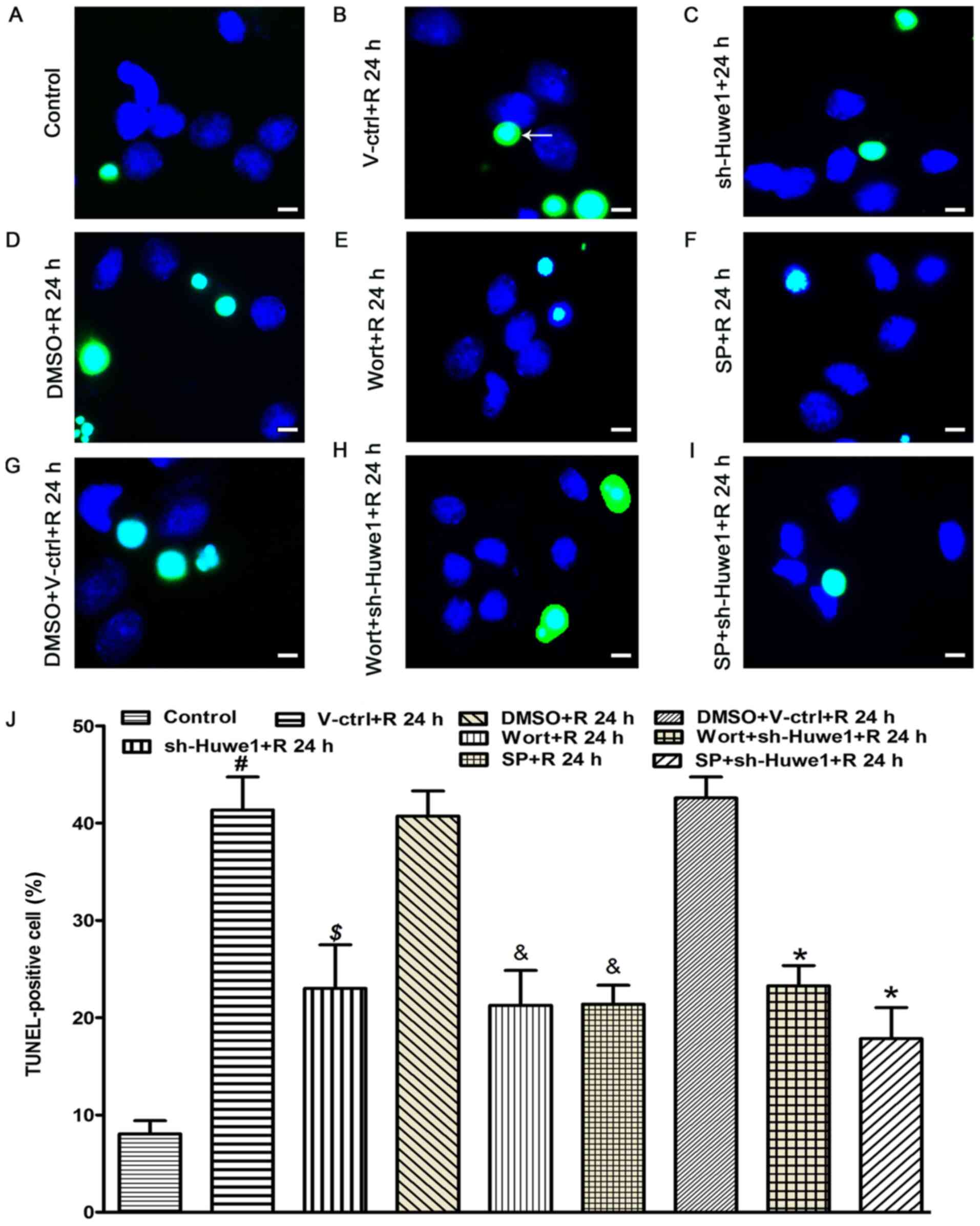
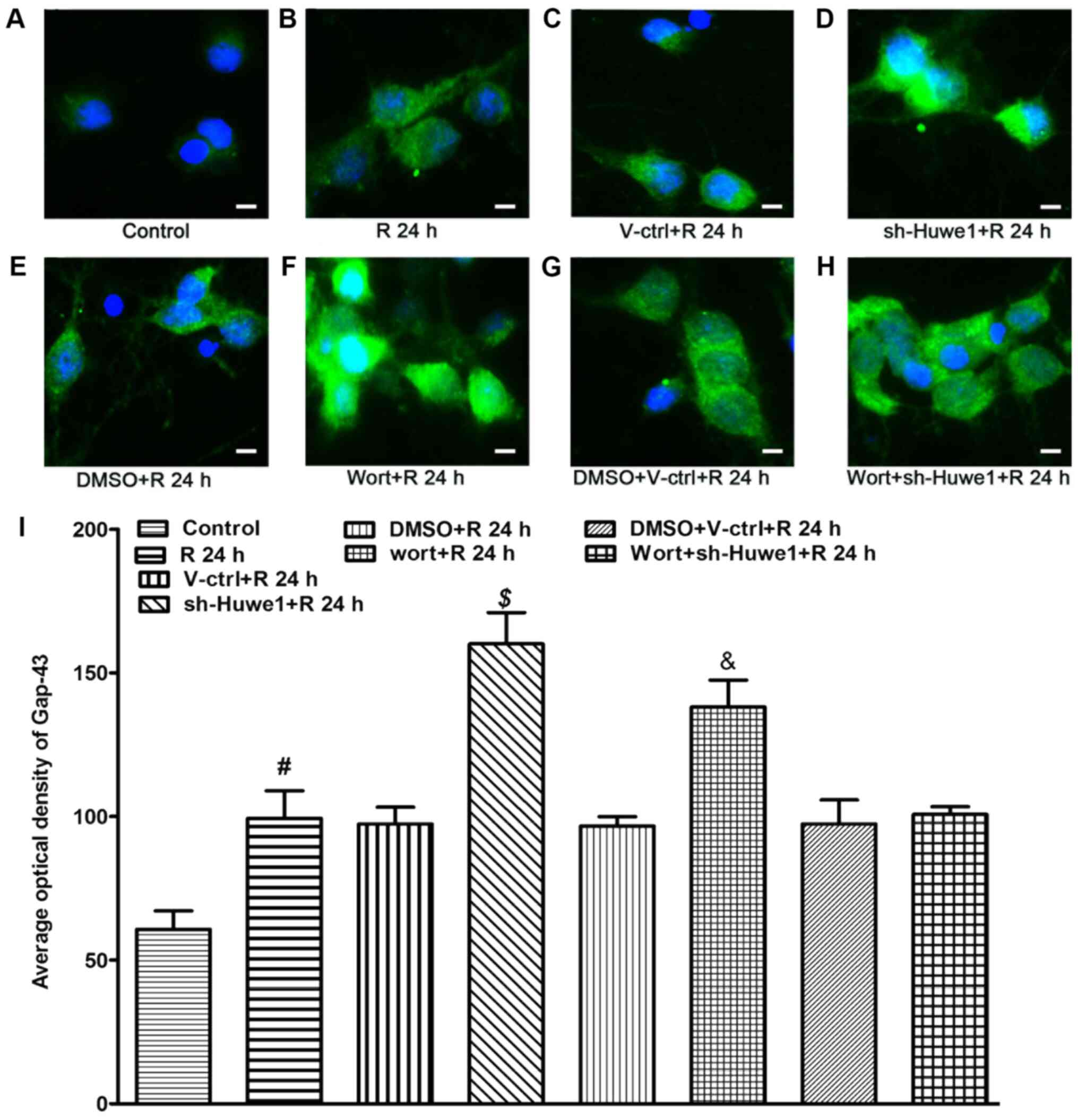
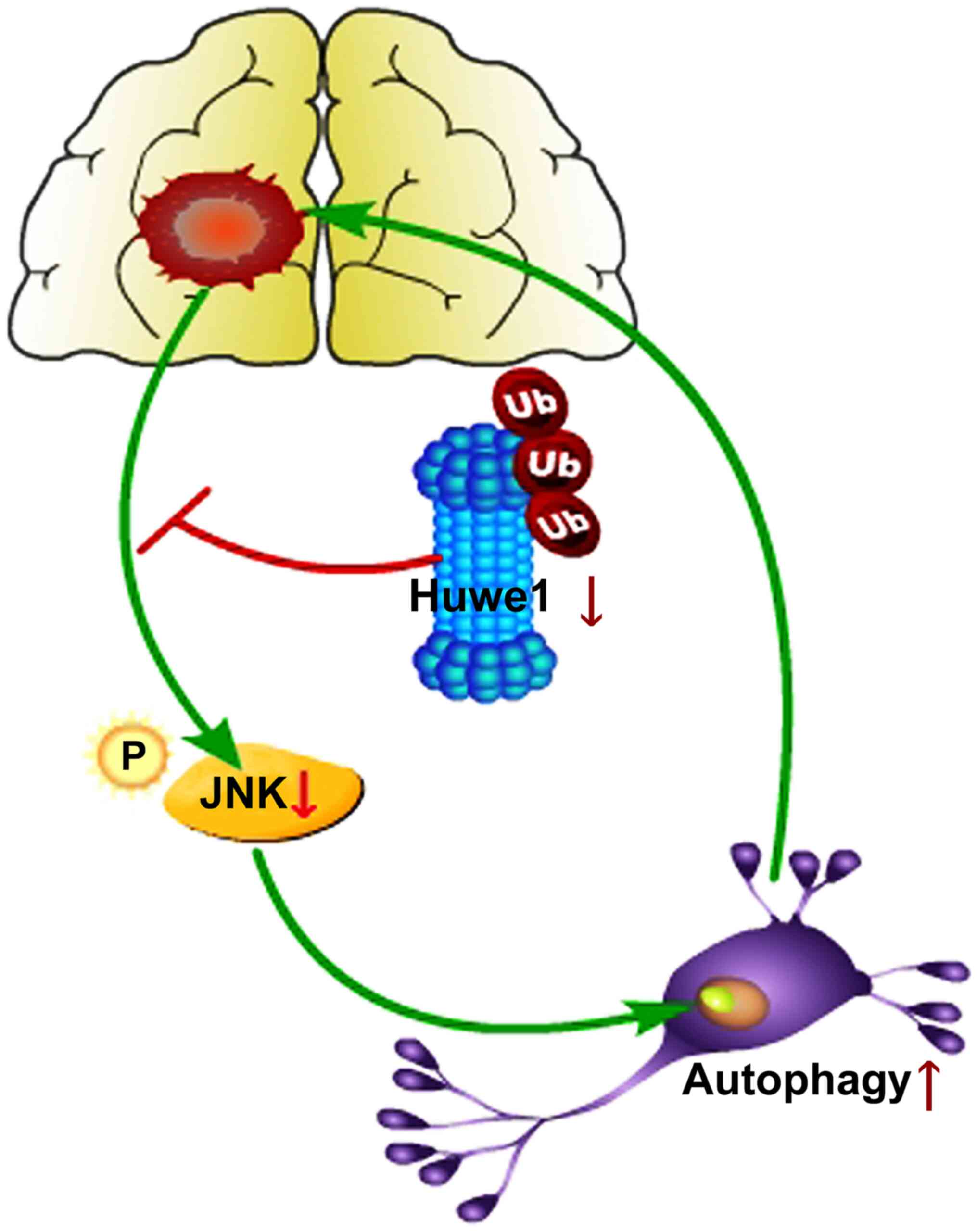
|
1
|
Dikic I: Proteasomal and autophagic
degradation systems. Annu Rev Biochem. 86:193–224. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ardley HC and Robinson PA: E3 ubiquitin
ligases. Essays Biochem. 41:15–30. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Finley D: Recognition and processing of
ubiquitin-protein conjugates by the proteasome. Annu Rev Biochem.
78:477–513. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zaffagnini G and Martens S: Mechanisms of
selective autophagy. J Mol Biol. 428:1714–1724. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Martens S and Behrends C: Molecular
mechanisms of selective autophagy. J Mol Biol. 432:1–2. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Schreiber A and Peter M: Substrate
recognition in selective autophagy and the ubiquitin-proteasome
system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1843:163–181. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ji CH and Kwon YT: Crosstalk and interplay
between the ubiquitin-proteasome system and autophagy. Mol Cells.
40:441–449. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bao X, Ren T, Huang Y, Ren C, Yang K,
Zhang H and Guo W: Bortezomib induces apoptosis and suppresses cell
growth and metastasis by inactivation of Stat3 signaling in
chondrosarcoma. Int J Oncol. 50:477–486. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lagunas-Martinez A, Garcia-Villa E,
Arellano-Gaytán M, Contreras-Ochoa CO, Dimas-González J,
López-Arellano ME, Madrid-Marina V and Gariglio P: MG132 plus
apoptosis antigen-1 (APO-1) antibody cooperate to restore p53
activity inducing autophagy and p53-dependent apoptosis in HPV16
E6-expressing keratinocytes. Apoptosis. 22:27–40. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kwon YT and Ciechanover A: The ubiquitin
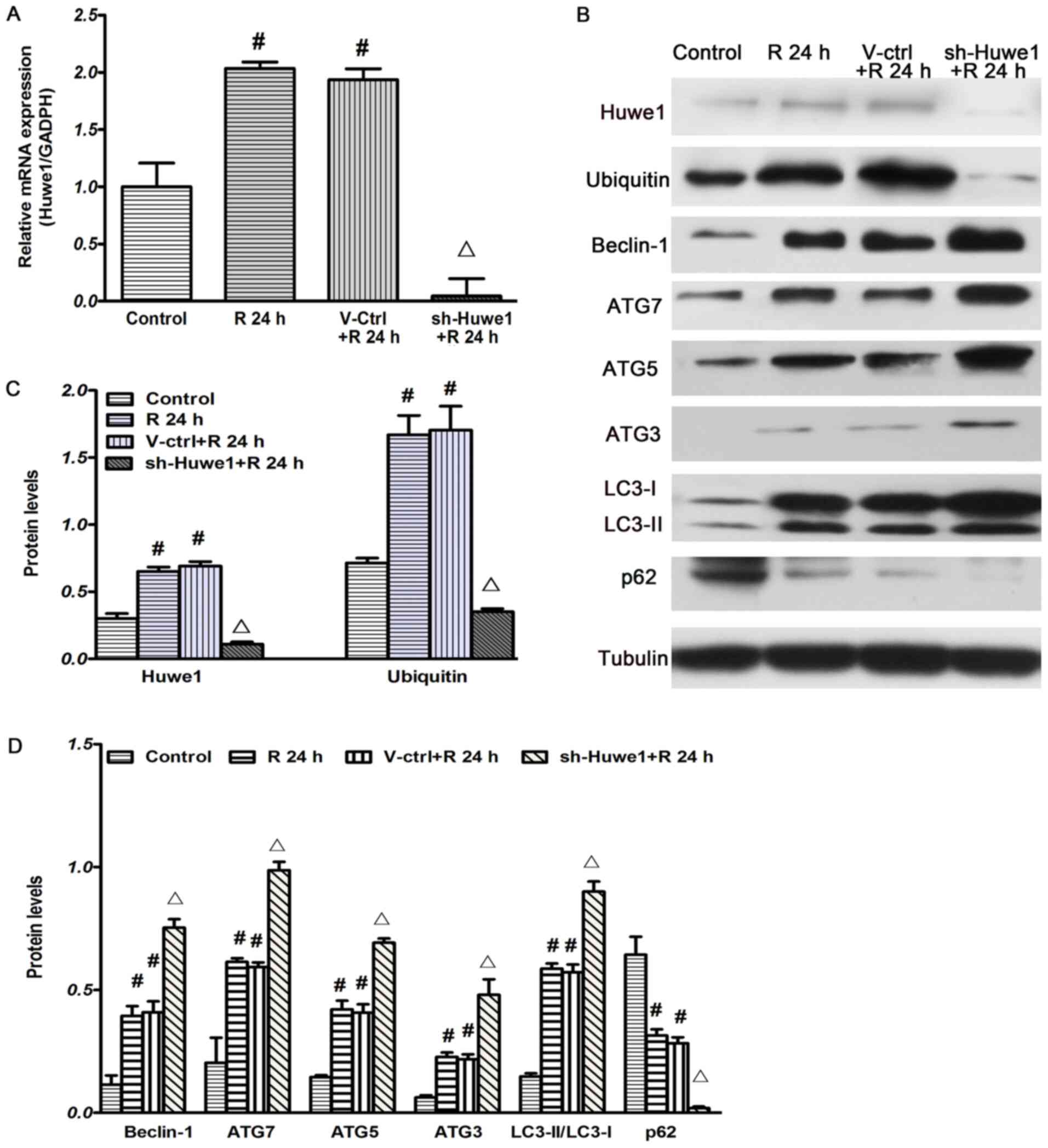
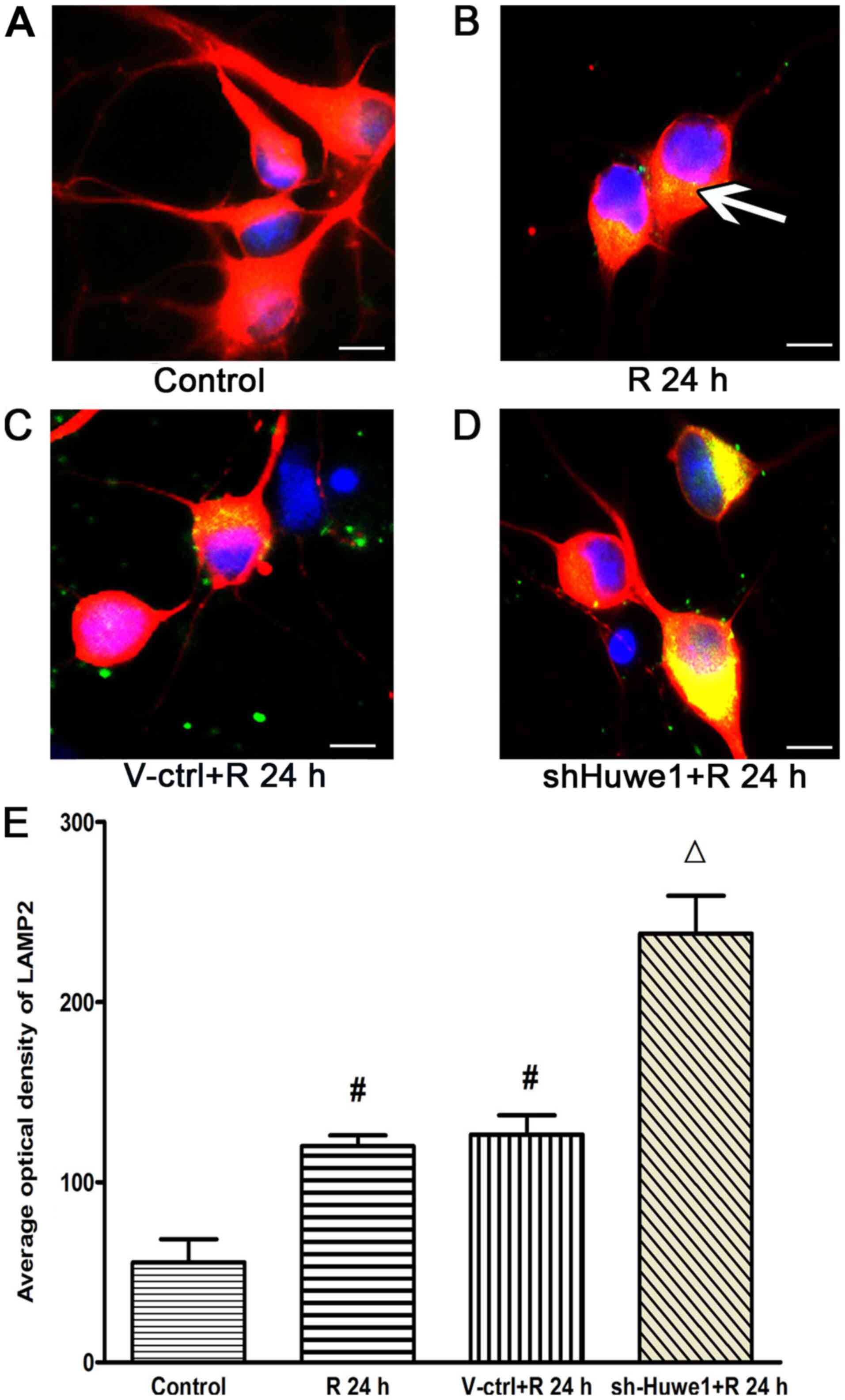
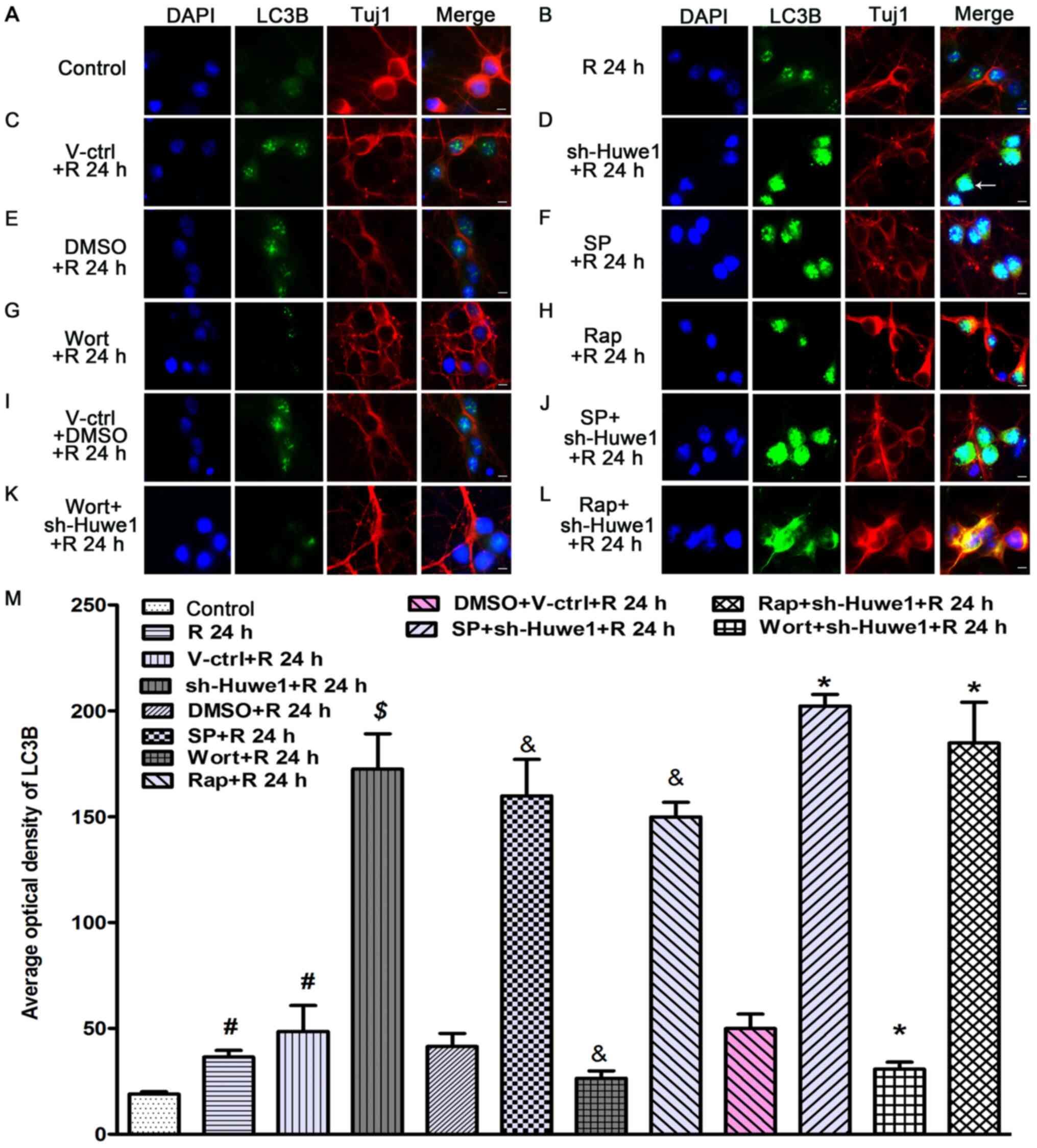
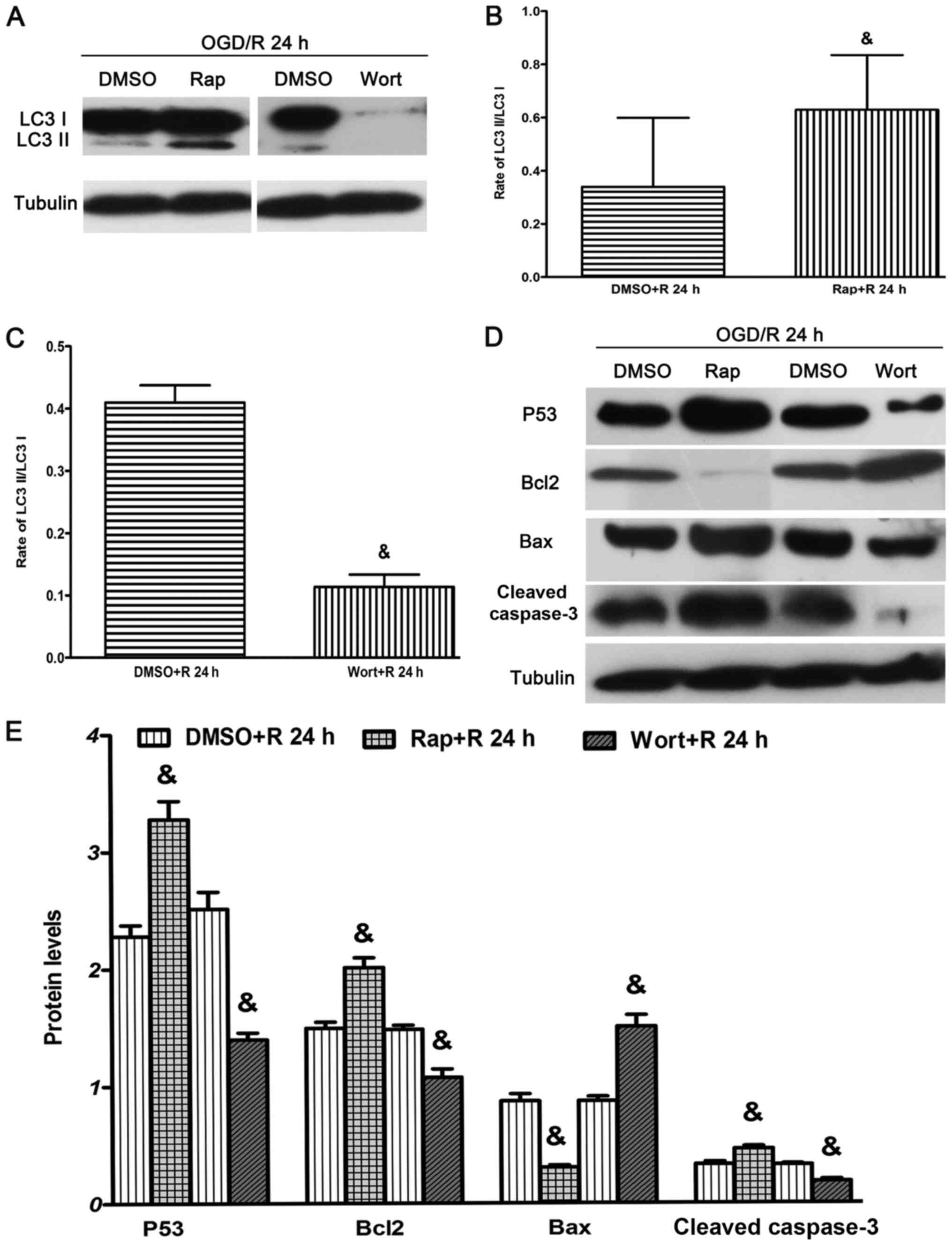
code in the ubiquitin-proteasome system and autophagy. Trends
Biochem Sci. 42:873–886. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nedelsky NB, Todd PK and Taylor JP:
Autophagy and the ubiquitin-proteasome system: Collaborators in
neuroprotection. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1782:691–699. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fan T, Huang Z, Chen L, Wang W, Zhang B,
Xu Y, Pan S, Mao Z, Hu H and Geng Q: Associations between
autophagy, the ubiquitin-proteasome system and endoplasmic
reticulum stress in hypoxia-deoxygenation or ischemia-reperfusion.
Eur J Pharmacol. 791:157–167. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nam T, Han JH, Devkota S and Lee HW:
Emerging paradigm of crosstalk between autophagy and the
ubiquitin-proteasome system. Mol Cells. 40:897–905. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zaffagnini G, Savova A, Danieli A, Romanov
J, Tremel S, Ebner M, Peterbauer T, Sztacho M, Trapannone R,
Tarafder AK, et al: p62 filaments capture and present ubiquitinated
cargos for autophagy. EMBO J. 37:e983082018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
French ME, Klosowiak JL, Aslanian A, Reed
SI, Yates JR III and Hunter T: Mechanism of ubiquitin chain
synthesis employed by a HECT domain ubiquitin ligase. J Biol Chem.
292:10398–10413. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao X, D'Arca D, Lim WK, Brahmachary M,
Carro MS, Ludwig T, Cardo CC, Guillemot F, Aldape K, Califano A, et
al: The N-Myc-DLL3 cascade is suppressed by the ubiquitin ligase
Huwe1 to inhibit proliferation and promote neurogenesis in the
developing brain. Dev Cell. 17:210–221. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhao X, Heng JI, Guardavaccaro D, Jiang R,
Pagano M, Guillemot F, Iavarone A and Lasorella A: The HECT-domain
ubiquitin ligase Huwe1 controls neural differentiation and
proliferation by destabilizing the N-Myc oncoprotein. Nat Cell
Biol. 10:643–653. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
The MULE/HUWE1 E3 ubiquitin ligase is a
tumor suppressor. Cancer Discov. 3:OF322013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou J, Liu Q, Mao M and Tong Y: Huwe1 as
a therapeutic target for neural injury. Genet Mol Res.
13:4320–4325. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li Y, Luo Y, Luo T, Lu B, Wang C, Zhang Y,
Piao M, Feng C and Ge P: Trehalose inhibits protein aggregation
caused by transient ischemic insults through preservation of
proteasome activity, not via induction of autophagy. Mol Neurobiol.
54:6857–6869. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Min JW, Lü L, Freeling JL, Martin DS and
Wang H: USP14 inhibitor attenuates cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion-induced neuronal injury in mice. J Neurochem.
140:826–833. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Baptista MS, Duarte CB and Maciel P: Role
of the ubiquitin-proteasome system in nervous system function and
disease: Using C. elegans as a dissecting tool. Cell Mol Life Sci.
69:2691–2715. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Eltzschig HK and Eckle T: Ischemia and
reperfusion-from mechanism to translation. Nat Med. 17:1391–1401.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang P, Shao BZ, Deng Z, Chen S, Yue Z and
Miao CY: Autophagy in ischemic stroke. Prog Neurobiol.
163-164:98–117. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rami A and Kögel D: Apoptosis meets
autophagy-like cell death in the ischemic penumbra: Two sides of
the same coin? Autophagy. 4:422–426. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wolf MS, Bayir H, Kochanek PM and Clark
RSB: The role of autophagy in acute brain injury: A state of flux?
Neurobiol Dis. 122:9–15. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sciarretta S, Hariharan N, Monden Y,
Zablocki D and Sadoshima J: Is autophagy in response to ischemia
and reperfusion protective or detrimental for the heart? Pediatr
Cardiol. 32:275–281. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yan W, Zhang H, Bai X, Lu Y, Dong H and
Xiong L: Autophagy activation is involved in neuroprotection
induced by hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning against focal cerebral
ischemia in rats. Brain Res. 1402:109–121. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jiang WW, Huang BS, Han Y, Deng LH and Wu
LX: Sodium hydrosulfide attenuates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion
injury by suppressing overactivated autophagy in rats. FEBS Open
Bio. 7:1686–1695. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Su J, Zhang T, Wang K, Zhu T and Li X:
Autophagy activation contributes to the neuroprotection of remote
ischemic perconditioning against focal cerebral ischemia in rats.
Neurochem Res. 39:2068–2077. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Qi Z, Dong W, Shi W, Wang R, Zhang C, Zhao
Y, Ji X, Liu KJ and Luo Y: Bcl-2 phosphorylation triggers autophagy
switch and reduces mitochondrial damage in limb remote ischemic
conditioned rats after ischemic stroke. Transl Stroke Res.
6:198–206. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wei K, Wang P and Miao CY: A double-edged
sword with therapeutic potential: An updated role of autophagy in
ischemic cerebral injury. CNS Neurosci Ther. 18:879–886. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gao L, Jiang T, Guo J, Liu Y, Cui G, Gu L,
Su L and Zhang Y: Inhibition of autophagy contributes to ischemic
postconditioning-induced neuroprotection against focal cerebral
ischemia in rats. PLoS One. 7:e460922012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xu SY, Wu YM, Ji Z, Gao XY and Pan SY: A
modified technique for culturing primary fetal rat cortical
neurons. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012:8039302012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fath T, Ke YD, Gunning P, Götz J and
Ittner LM: Primary support cultures of hippocampal and substantia
nigra neurons. Nat Protoc. 4:78–85. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu Z, Chen Z, Wang J, Zhang M, Li Z, Wang
S, Dong B, Zhang C, Gao J and Shen L: Mouse avatar models of
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma proved the potential for
EGFR-TKI afatinib and uncovered Src family kinases involved in
acquired resistance. J Hematol Oncol. 11:1092018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gertz K, Kronenberg G, Kälin RE, Baldinger
T, Werner C, Balkaya M, Eom GD, Hellmann-Regen J, Kröber J, Miller
KR, et al: Essential role of interleukin-6 in post-stroke
angiogenesis. Brain. 135:1964–1980. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jones SM, Novak AE and Elliott JP: Primary
culture of cellular subtypes from postnatal mouse for in vitro
studies of oxygen glucose deprivation. J Neurosci Methods.
199:241–248. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ding B and Kilpatrick DL: Lentiviral
vector production, titration, and transduction of primary neurons.
Methods Mol Biol. 1018:119–131. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Reich A, Spering C, Gertz K, Harms C,
Gerhardt E, Kronenberg G, Nave KA, Schwab M, Tauber SC, Drinkut A,
et al: Fas/CD95 regulatory protein Faim2 is neuroprotective after
transient brain ischemia. J Neurosci. 31:225–233. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Nagai N, Yamamoto S, Tsuboi T, Ihara H,
Urano T, Takada Y, Terakawa S and Takada A: Tissue-type plasminogen
activator is involved in the process of neuronal death induced by
oxygen-glucose deprivation in culture. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
21:631–634. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
He G, Xu W, Tong L, Li S, Su S, Tan X and
Li C: Gadd45b prevents autophagy and apoptosis against rat cerebral
neuron oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion injury. Apoptosis.
21:390–403. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhong Q, Gao W, Du F and Wang X:
Mule/ARF-BP1, a BH3-only E3 ubiquitin ligase, catalyzes the
polyubiquitination of Mcl-1 and regulates apoptosis. Cell.
121:1085–1095. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Xu F, Gu JH and Qin ZH: Neuronal autophagy
in cerebral ischemia. Neurosci Bull. 28:658–666. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hale AN, Ledbetter DJ, Gawriluk TR and
Rucker EB III: Autophagy: Regulation and role in development.
Autophagy. 9:951–972. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li W, Zhu J, Dou J, She H, Tao K, Xu H,
Yang Q and Mao Z: Phosphorylation of LAMP2A by p38 MAPK couples ER
stress to chaperone-mediated autophagy. Nat Commun. 8:17632017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Bejarano E and Cuervo AM:
Chaperone-mediated autophagy. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 7:29–39. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Penke B, Bogár F, Crul T, Sántha M, Tóth
ME and Vígh L: Heat shock proteins and autophagy pathways in
neuroprotection: From molecular bases to pharmacological
interventions. Int J Mol Sci. 19:3252018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Zhang Q, Bian H, Guo L and Zhu H:
Pharmacologic preconditioning with berberine attenuating
ischemia-induced apoptosis and promoting autophagy in neuron. Am J
Transl Res. 8:1197–1207. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lalaoui N, Lindqvist LM, Sandow JJ and
Ekert PG: The molecular relationships between apoptosis, autophagy
and necroptosis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 39:63–69. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Thorburn A: Apoptosis and autophagy:
Regulatory connections between two supposedly different processes.
Apoptosis. 13:1–9. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Delgado ME, Dyck L, Laussmann MA and Rehm
M: Modulation of apoptosis sensitivity through the interplay with
autophagic and proteasomal degradation pathways. Cell Death Dis.
5:e10112014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Mariño G, Niso-Santano M, Baehrecke EH and
Kroemer G: Self-consumption: The interplay of autophagy and
apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:81–94. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Shi R, Weng J, Zhao L, Li XM, Gao TM and
Kong J: Excessive autophagy contributes to neuron death in cerebral
ischemia. CNS Neurosci Ther. 18:250–260. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Grasselli G and Strata P: Structural
plasticity of climbing fibers and the growth-associated protein
GAP-43. Front Neural Circuits. 7:252013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Lamb CA, Yoshimori T and Tooze SA: The
autophagosome: Origins unknown, biogenesis complex. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 14:759–774. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Chen K, Cheng HH and Zhou RJ: Molecular
mechanisms and functions of autophagy and the ubiquitin-proteasome
pathway. Yi Chuan. 34:5–18. 2012.(In Chinese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Hu Z, Yang B, Mo X and Xiao H: Mechanism
and regulation of autophagy and its role in neuronal diseases. Mol
Neurobiol. 52:1190–1209. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Guo F, He XB, Li S and Le W: A central
role for phosphorylated p38α in linking proteasome
inhibition-induced apoptosis and autophagy. Mol Neurobiol.
54:7597–7609. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Liu C, Gao Y, Barrett J and Hu B:
Autophagy and protein aggregation after brain ischemia. J
Neurochem. 115:68–78. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Klionsky DJ, Abeliovich H, Agostinis P,
Agrawal DK, Aliev G, Askew DS, Baba M, Baehrecke EH, Bahr BA,
Ballabio A, et al: Guidelines for the use and interpretation of
assays for monitoring autophagy in higher eukaryotes. Autophagy.
4:151–175. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Thornton C, Leaw B, Mallard C, Nair S,
Jinnai M and Hagberg H: Cell death in the developing brain after
hypoxia-ischemia. Front Cell Neurosci. 11:2482017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Nozaki K, Nishimura M and Hashimoto N:
Mitogen-activated protein kinases and cerebral ischemia. Mol
Neurobiol. 23:1–19. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Wu D and Cederbaum AI: Inhibition of
autophagy promotes CYP2E1-dependent toxicity in HepG2 cells via
elevated oxidative stress, mitochondria dysfunction and activation
of p38 and JNK MAPK. Redox Biol. 1:552–565. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Jia G, Cheng G, Gangahar DM and Agrawal
DK: Insulin-like growth factor-1 and TNF-alpha regulate autophagy
through c-jun N-terminal kinase and Akt pathways in human
atherosclerotic vascular smooth cells. Immunol Cell Biol.
84:448–454. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Haberzettl P and Hill BG: Oxidized lipids
activate autophagy in a JNK-dependent manner by stimulating the
endoplasmic reticulum stress response. Redox Biol. 1:56–64. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Xu P, Das M, Reilly J and Davis RJ: JNK
regulates FoxO-dependent autophagy in neurons. Genes Dev.
25:310–322. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
He GQ, Xu WM, Liao HJ, Jiang C, Li CQ and
Zhang W: Silencing Huwe1 reduces apoptosis of cortical neurons
exposed to oxygen-glucose deprivation and reperfusion. Neural Regen
Res. 14:1977–1985. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Wen YD, Sheng R, Zhang LS, Han R, Zhang X,
Zhang XD, Han F, Fukunaga K and Qin ZH: Neuronal injury in rat
model of permanent focal cerebral ischemia is associated with
activation of autophagic and lysosomal pathways. Autophagy.
4:762–769. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Kost A, Kasprowska D, Labuzek K,
Wiaderkiewicz R and Gabryel B: Autophagy in brain ischemia. Postepy
Hig Med Dosw (Online). 65:524–533. 2011.(In Polish). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Balduini W, Carloni S and Buonocore G:
Autophagy in hypoxia-ischemia induced brain injury. J Matern Fetal
Neonatal Med. 25 (Suppl 1):S30–S34. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Lu Q, Harris VA, Kumar S, Mansour HM and
Black SM: Autophagy in neonatal hypoxia ischemic brain is
associated with oxidative stress. Redox Biol. 6:516–523. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Qiao L, Fu J, Xue X, Shi Y, Yao L, Huang
W, Li J, Zhang D, Liu N, Tong X, et al: Neuronalinjury and roles of
apoptosis and autophagy in a neonatal rat model of
hypoxia-ischemia-induced periventricular leukomalacia. Mol Med Rep.
17:5940–5949. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Maiuri MC, Zalckvar E, Kimchi A and
Kroemer G: Self-eating and self-killing: Crosstalk between
autophagy and apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:741–752. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
He GQ, Xu WM, Li JF, Li SS, Liu B, Tan XD
and Li CQ: Huwe1 interacts with Gadd45b under oxygen-glucose
deprivation and reperfusion injury in primary Rat cortical neuronal
cells. Mol Brain. 8:882015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Kalogeris T, Baines CP, Krenz M and
Korthuis RJ: Ischemia/reperfusion. Compr Physiol. 7:113–170. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|