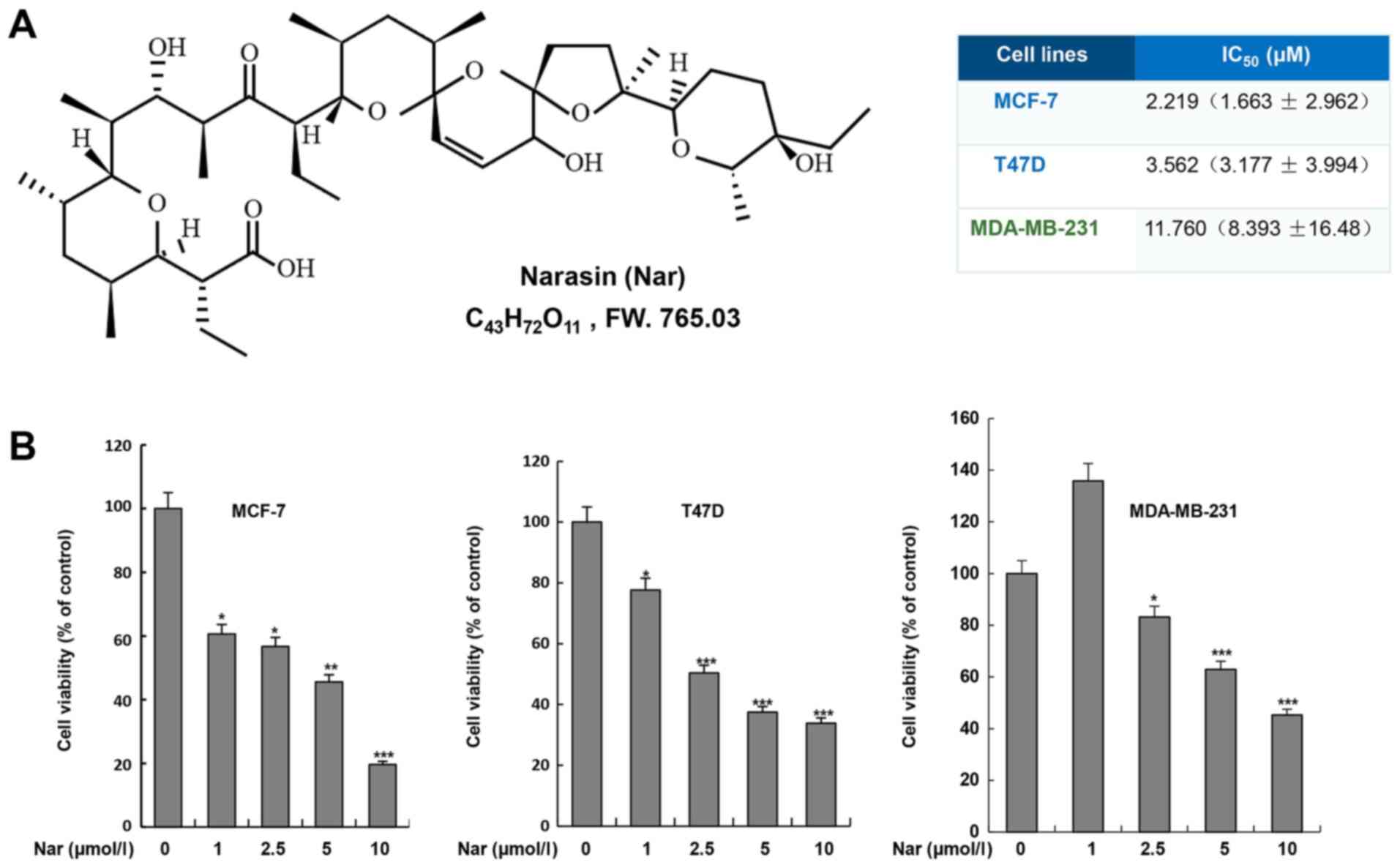
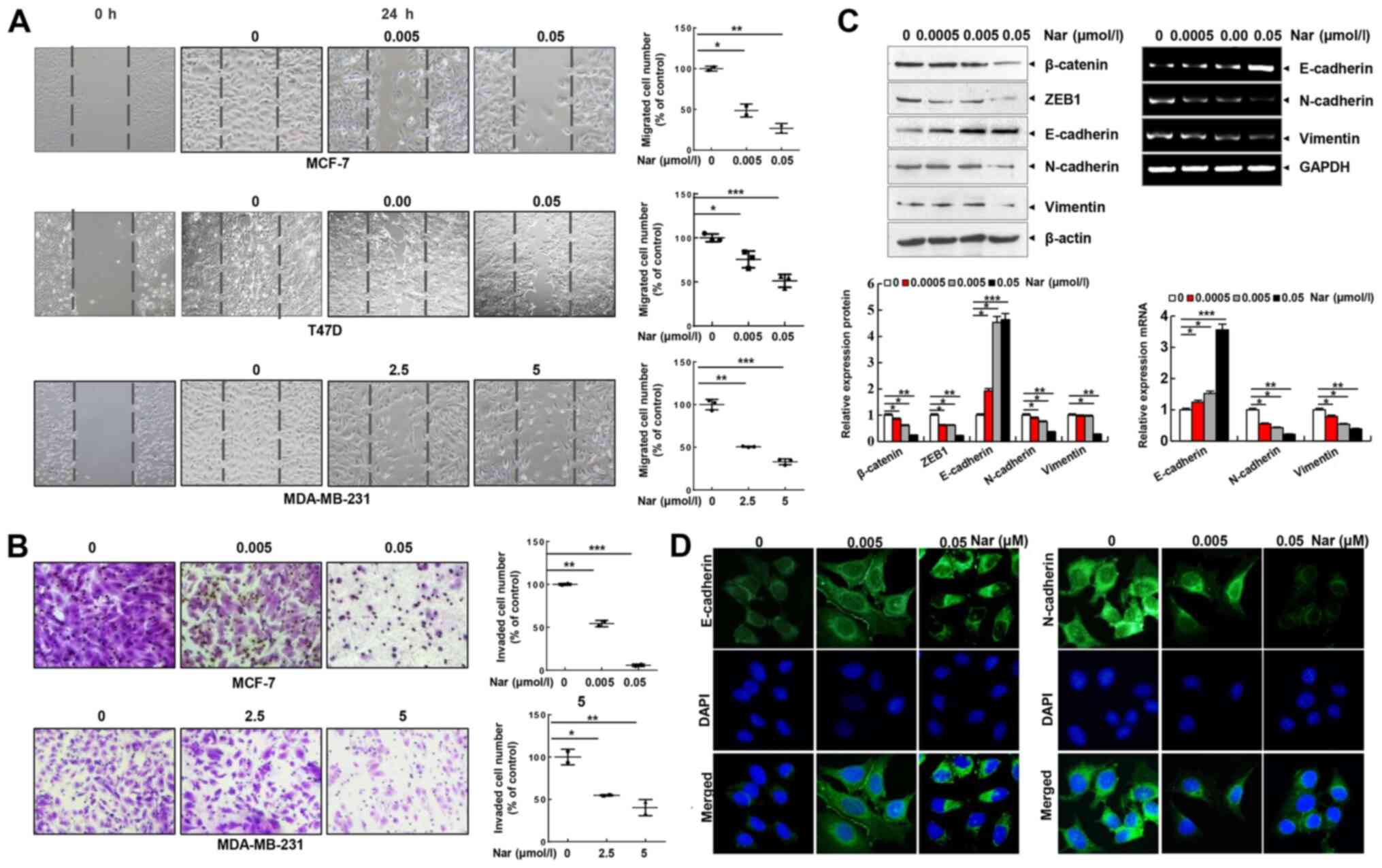
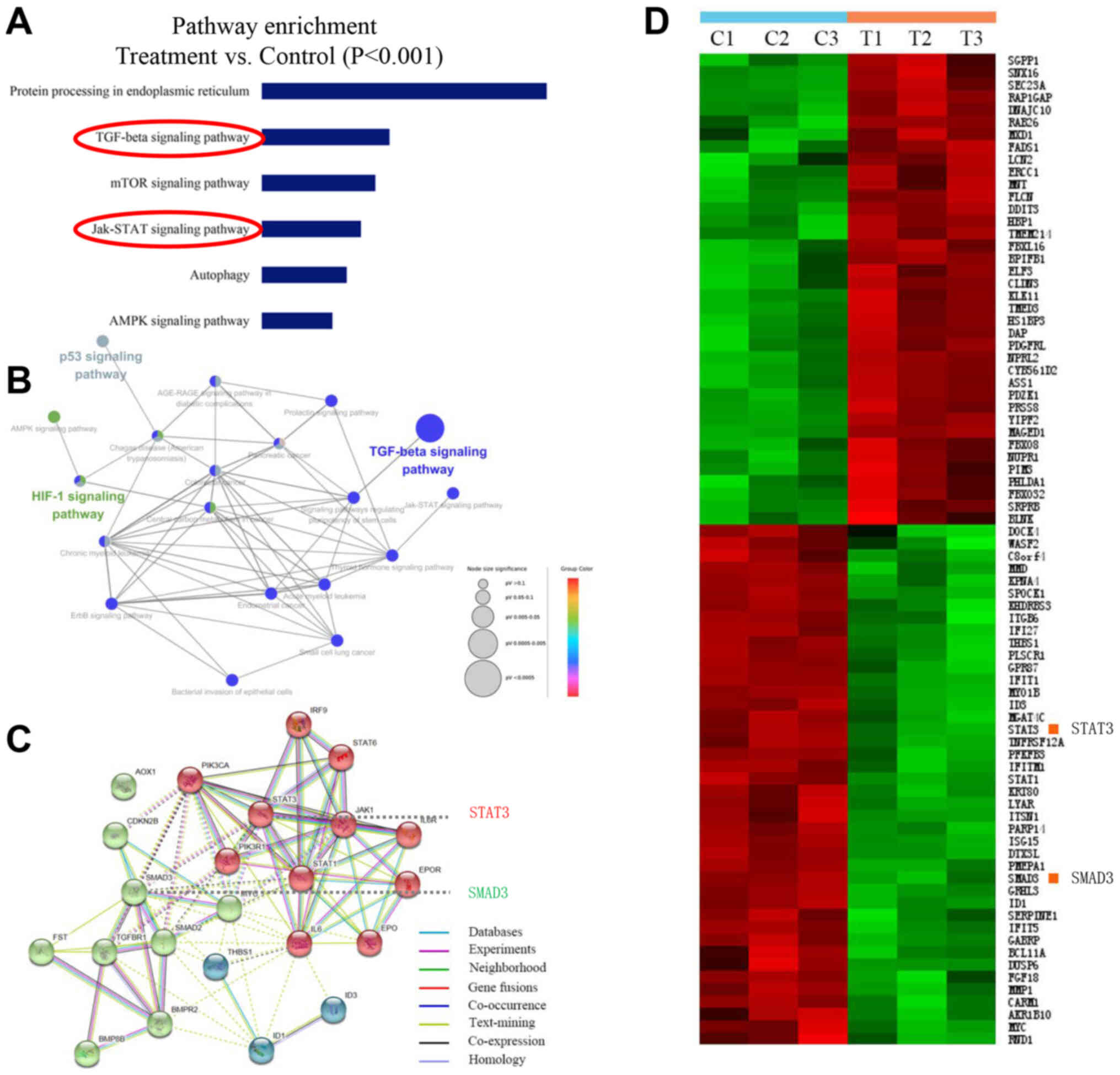
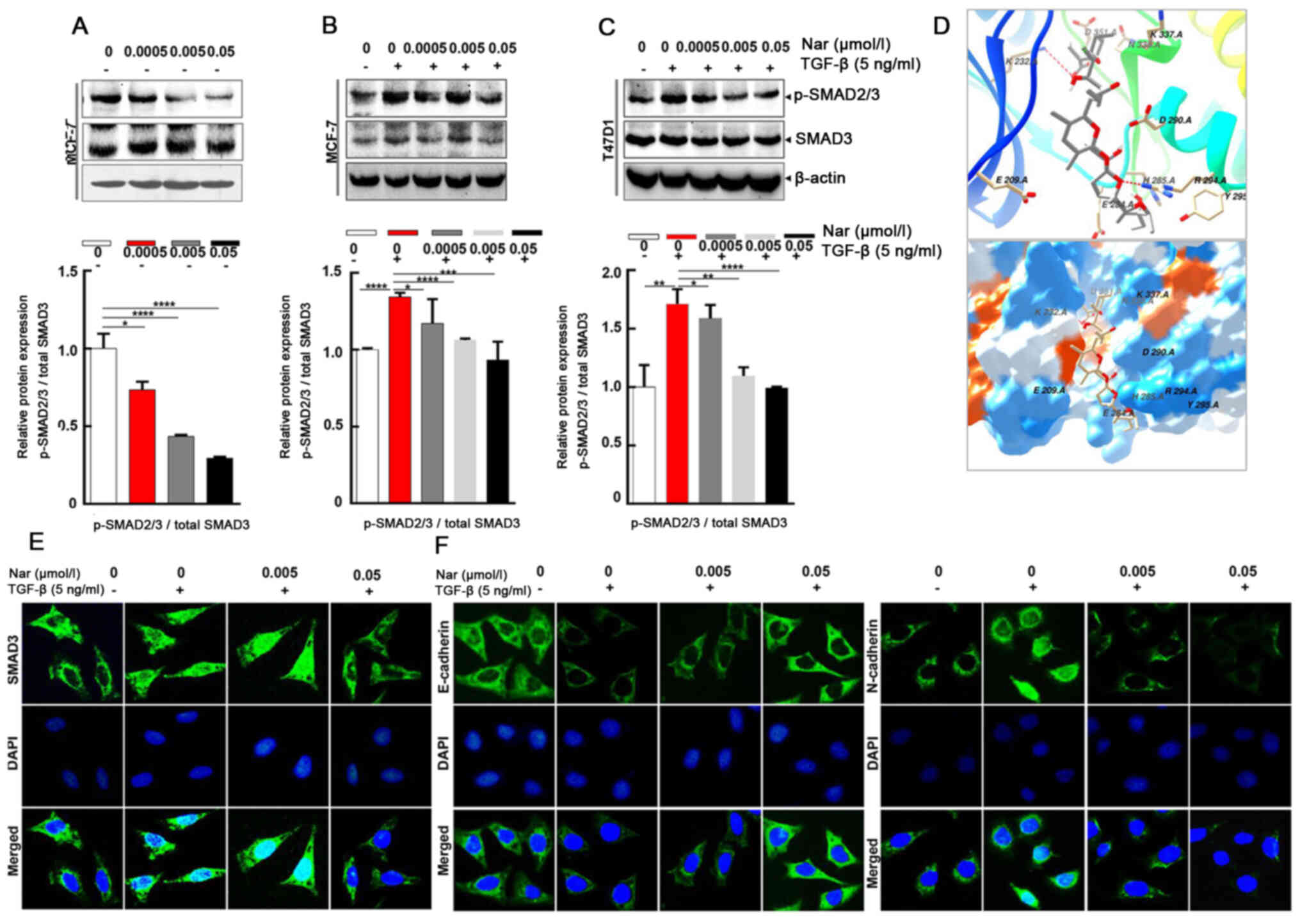
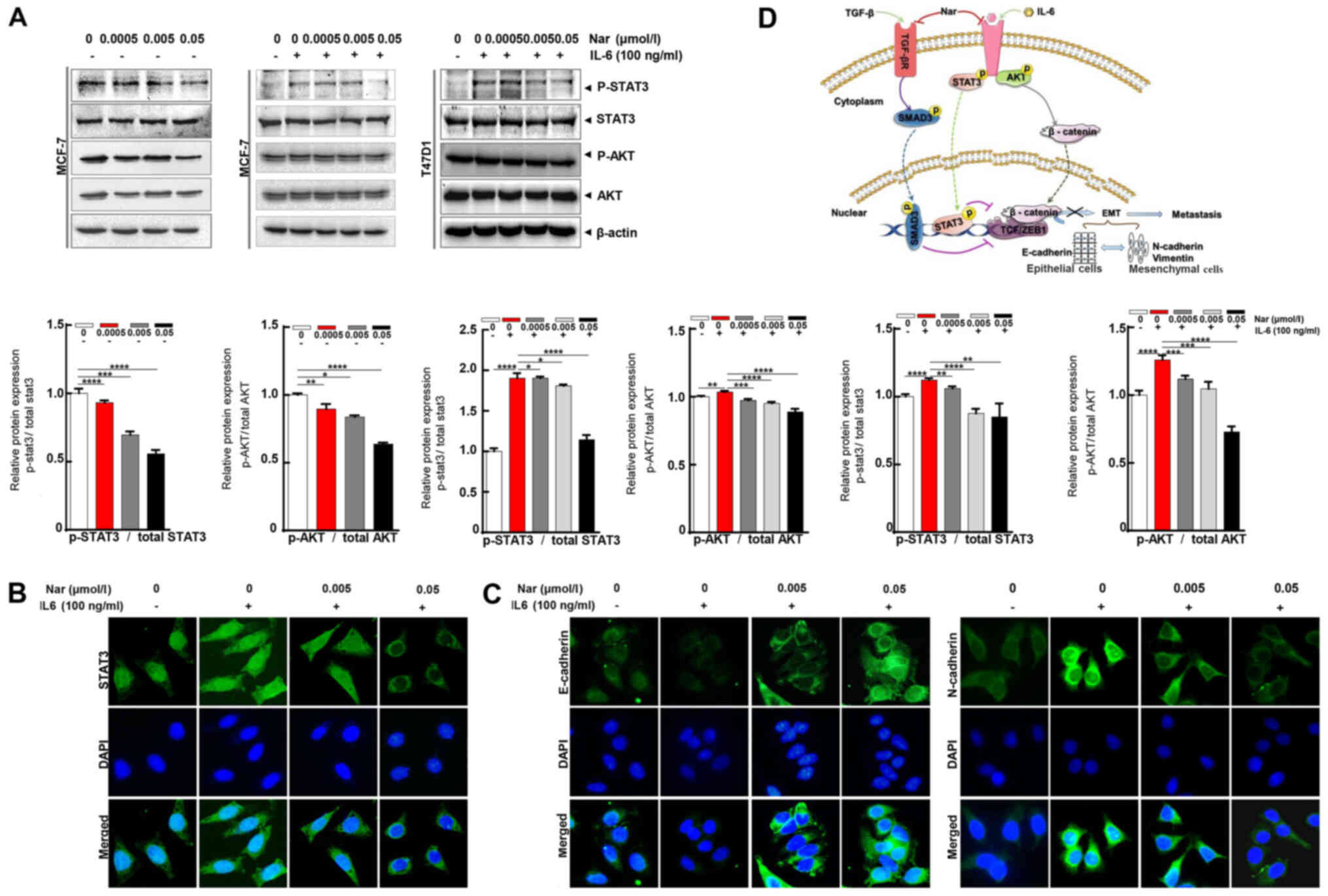
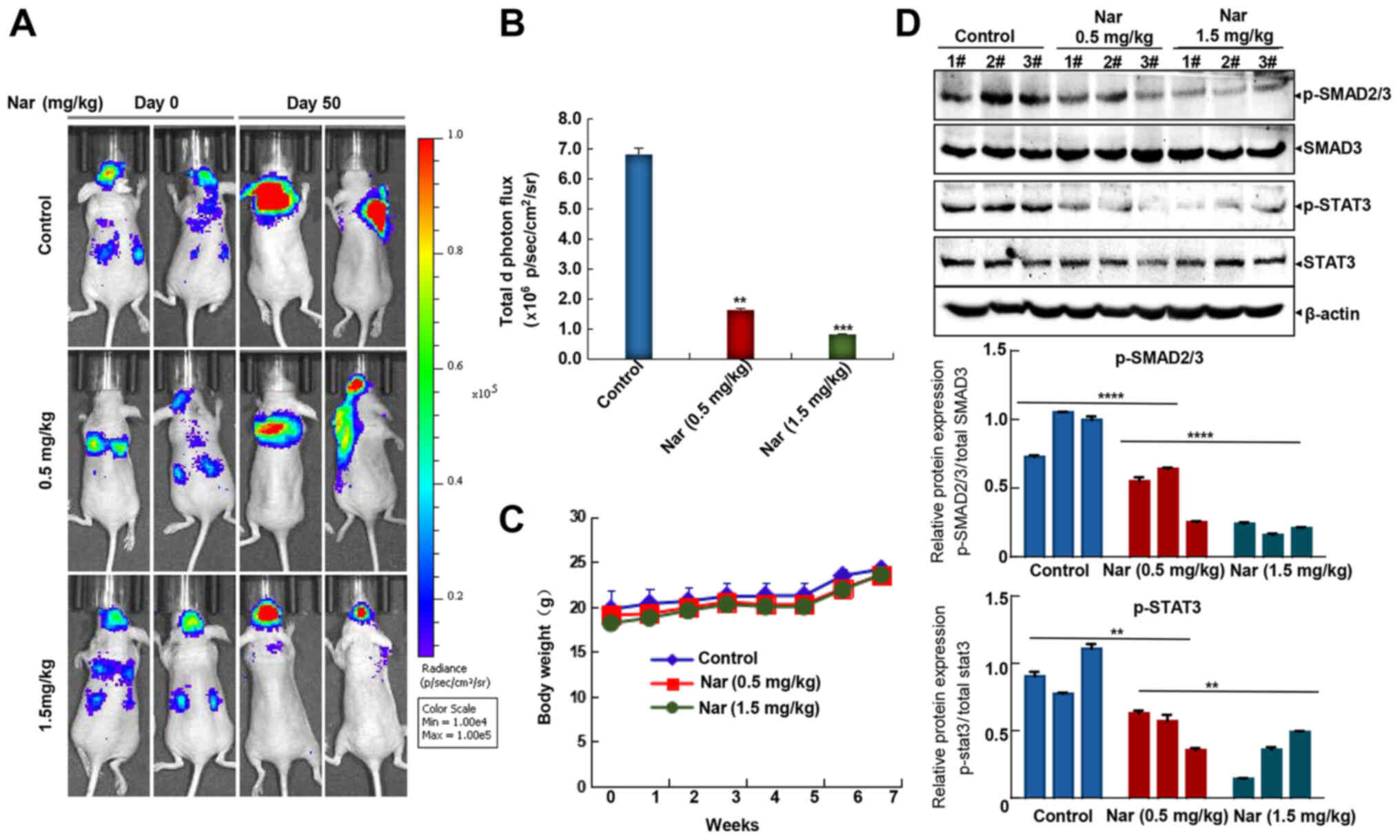
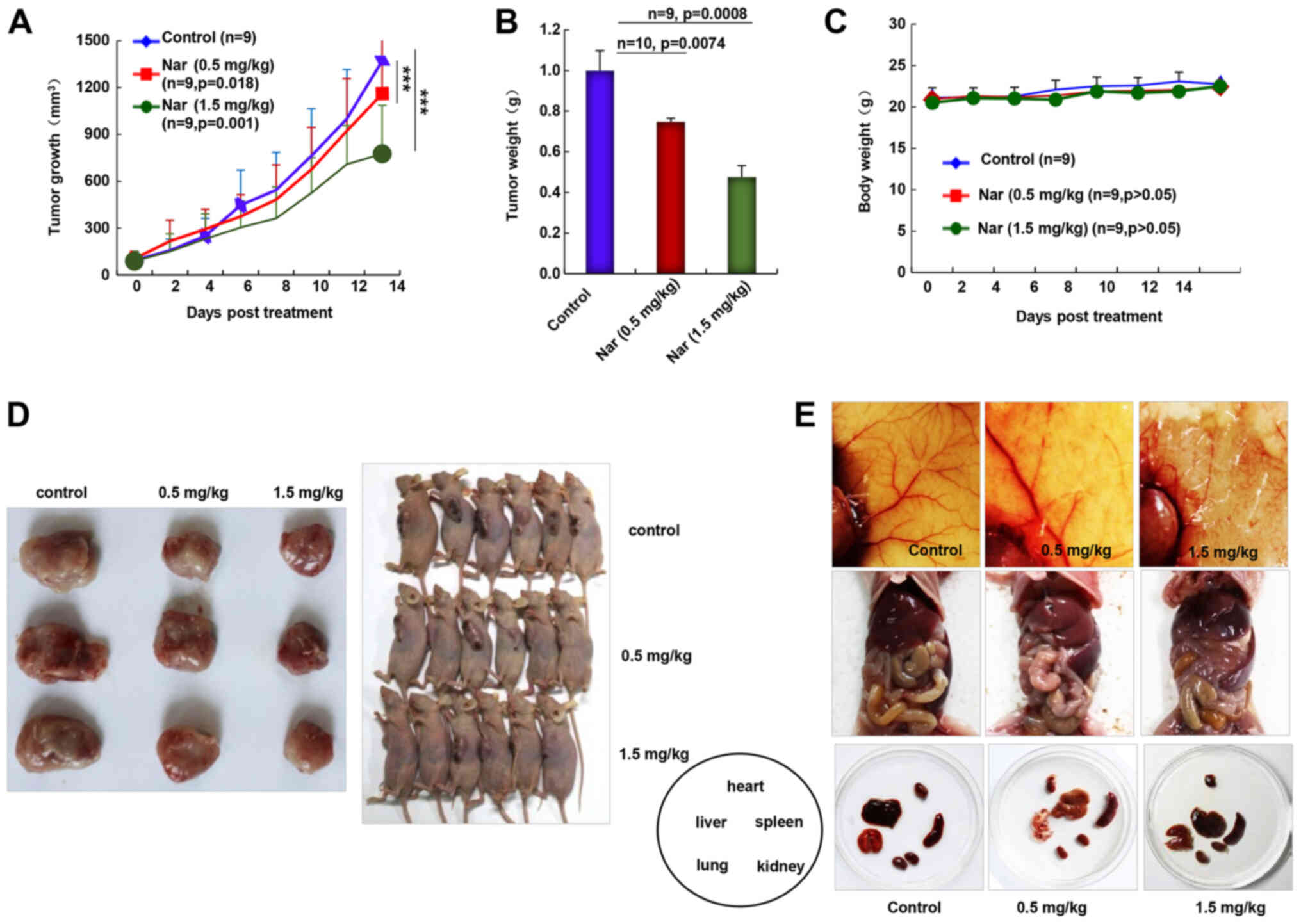
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Reiner T and Barrios CH: Optimal
management of hormone receptor positive metastatic breast cancer in
2016. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 7:304–320. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vuong D, Simpson PT, Green B, Cummings MC
and Lakhani SR: Molecular classification of breast cancer. Virchows
Arch. 465:1–14. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mikula-Pietrasik J, Uruski P, Tykarski A
and Ksiazek K: The peritoneal ‘soil’ for a cancerous ‘seed’: A
comprehensive review of the pathogenesis of intraperitoneal cancer
metastases. Cell Mol Life Sci. 75:509–525. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Riggi N, Aguet M and Stamenkovic I: Cancer
metastasis: A reappraisal of its underlying mechanisms and their
relevance to treatment. Annu Rev Pathol. 13:117–140. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lambert AW, Pattabiraman DR and Weinberg
RA: Emerging biological principles of metastasis. Cell.
168:670–691. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Brabletz T, Kalluri R, Nieto MA and
Weinberg RA: EMT in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 18:128–134. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chiu HC, Li CJ, Yiang GT, Tsai AP and Wu
MY: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition and cell biology of
molecular regulation in endometrial carcinogenesis. J Clin Med.
8:4392019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wang B, Liu T, Wu JC, Luo SZ, Chen R, Lu
LG and Xu MY: STAT3 aggravates TGF-β1-induced hepatic
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and migration. Biomed
Pharmacother. 98:214–221. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Akhurst RJ and Derynck R: TGF-beta
signaling in cancer-a Double-edged sword. Trends Cell Biol. 11
(Suppl):S44–S51. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Henke BR and Heyer D: Recent advances in
estrogen receptor modulators. Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel.
8:437–448. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Elkak AE and Mokbel K: Pure antiestrogens
and breast cancer. Curr Med Res Opin. 17:282–289. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Younus J and Vandenberg TA: A practical
overview of aromatase inhibitors in postmenopausal women with
hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Bull Cancer. 92:E39–E44.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Braga S: Resistance to targeted therapies
in breast cancer. Methods Mol Biol. 1395:105–136. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lumachi F, Santeufemia DA and Basso SM:
Current medical treatment of estrogen receptor-positive breast
cancer. World J Biol Chem. 6:231–239. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Riddell FG: Structure, conformation, and
mechanism in the membrane transport of alkali metal ions by
ionophoric antibiotics. Chirality. 14:121–125. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gupta PB, Onder TT, Jiang G, Tao K,
Kuperwasser C, Weinberg RA and Lander ES: Identification of
selective inhibitors of cancer stem cells by high-throughput
screening. Cell. 138:645–659. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Markowska A, Kaysiewicz J, Markowska J and
Huczynski A: Doxycycline, salinomycin, monensin and ivermectin
repositioned as cancer drugs. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 29:1549–1554.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jiang J, Li H, Qaed E, Zhang J, Song Y, Wu
R, Bu X, Wang Q and Tang Z: Salinomycin, as an autophagy
modulator-a new avenue to anticancer: A review. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 37:262018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cybulski W, Radko L and Rzeski W:
Cytotoxicity of monensin, narasin and salinomycin and their
interaction with silybin in HepG2, LMH and L6 cell cultures.
Toxicol In Vitro. 29:337–344. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Miller SC, Huang R, Sakamuru S, Shukla SJ,
Attene-Ramos MS, Shinn P, Van Leer D, Leister W, Austin CP and Xia
M: Identification of known drugs that act as inhibitors of
NF-kappaB signaling and their mechanism of action. Biochem
Pharmacol. 79:1272–1280. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yoon MJ, Kang YJ, Kim IY, Kim EH, Lee JA,
Lim JH, Kwon TK and Choi KS: Monensin, a polyether ionophore
antibiotic, overcomes TRAIL resistance in glioma cells via
endoplasmic reticulum stress, DR5 upregulation and c-FLIP
downregulation. Carcinogenesis. 34:1918–1928. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen J, Wang J, Lin L, He L, Wu Y, Zhang
L, Yi Z, Chen Y, Pang X and Liu M: Inhibition of STAT3 signaling
pathway by nitidine chloride suppressed the angiogenesis and growth
of human gastric cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:277–287. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li T, Liu X, Shen Q, Yang W, Huo Z, Liu Q,
Jiao H and Chen J: Salinomycin exerts anti-angiogenic and
anti-tumorigenic activities by inhibiting vascular endothelial
growth factor receptor 2-mediated angiogenesis. Oncotarget.
7:26580–26592. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kanehisa M, Sato Y, Furumichi M, Morishima
K and Tanabe M: New approach for understanding genome variations in
KEGG. Nucleic Acids Res. 47:D590–D595. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kanehisa M: Toward understanding the
origin and evolution of cellular organisms. Protein Sci.
28:1947–1951. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Galili T, O'Callaghan A, Sidi J and
Sievert C: Heatmaply: An R package for creating interactive cluster
heatmaps for online publishing. Bioinformatics. 34:1600–1602. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Amaskos C, Garmpi A, Nikolettos K,
Vavourakis M, Diamantis E, Patsouras A, Farmaki P, Nonni A,
Dimitroulis D, Mantas D, et al: Triple-negative breast cancer: The
progress of targeted therapies and future tendencies. Anticancer
Res. 39:5285–5296. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Van Themsche C, Parent S, Leblanc V,
Descôteaux C, Simard AM, Bérubé G and Asselin E: VP-128, a novel
oestradiol-platinum(II) hybrid with selective anti-tumour activity
towards hormone-dependent breast cancer cells in vivo. Endocr Relat
Cancer. 16:1185–1195. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shi JF, Yang N, Ding HJ, Zhang JX, Hu ML,
Leng Y, Han X and Sun YJ: Rα directly activated the MDR1
transcription to increase paclitaxel-resistance of ERα-positive
breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
53:35–45. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Márquez-Garbán DC, Deng G, Comin-Anduix B,
Garcia AJ, Xing Y, Chen HW, Cheung-Lau G, Hamilton N, Jung ME and
Pietras RJ: Antiestrogens in combination with immune checkpoint
inhibitors in breast cancer immunotherapy. J Steroid Biochem Mol
Biol. 193:1054152019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang J, Hu K, Guo J, Cheng F, Lv J, Jiang
W, Lu W, Liu J, Pang X and Liu M: Suppression of KRas-mutant cancer
through the combined inhibition of KRAS with PLK1 and ROCK. Nat
Commun. 7:113632016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Itoh S, Itoh F, Goumans MJ and Ten Dijke
P: Signaling of transforming growth factor-beta family members
through Smad proteins. Eur J Biochem. 267:6954–6967. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shi Y and Massagué J: Mechanisms of
TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell.
113:685–700. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mehra A and Wrana JL: TGF-beta and the
Smad signal transduction pathway. Biochem Cell Biol. 80:605–622.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Heldin CH, Landström M and Moustakas A:
Mechanism of TGF-beta signaling to growth arrest, apoptosis, and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 21:166–176.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Dumont N and Arteaga CL: Targeting the TGF
beta signaling network in human neoplasia. Cancer Cell. 3:531–536.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kandasamy M, Reilmann R, Winkler J,
Bogdahn U and Aigner L: Transforming growth factor-beta signaling
in the neural stem cell niche: A therapeutic target for
Huntington's disease. Neurol Res Int. 2011:1242562011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu S, Chen S and Zeng J: TGF-β signaling:
A complex role in tumorigenesis (Review). Mol Med Rep. 17:699–704.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lucarelli P, Schilling M, Kreutz C, Vlasov
A, Boehm ME, Iwamoto N, Steiert B, Lattermann S, Wasch M, Stepath
M, et al: Resolving the combinatorial complexity of smad protein
complex formation and its link to gene expression. Cell Syst.
6:75–89.e11. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lou W, Chen Y, Zhu KY, Deng H, Wu T and
Wang J: Polyphyllin I overcomes EMT-associated resistance to
erlotinib in lung cancer cells via IL-6/STAT3 pathway inhibition.
Biol Pharm Bull. 40:1306–1313. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Akram M, Iqbal M, Daniyal M and Khan AU:
Awareness and current knowledge of breast cancer. Biol Res.
50:332017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Majumder A, Singh M and Tyagi SC:
Post-menopausal breast cancer: From estrogen to androgen receptor.
Oncotarget. 8:102739–102758. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Guo W, Zhang S and Liu S: Establishment of
a novel orthotopic model of breast cancer metastasis to the lung.
Oncol Rep. 33:2992–2998. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ghulam J, Stuerken C, Wicklein D, Pries R,
Wollenberg B and Schumacher U: Immunohistochemical analysis of
transcription factors and markers of Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition (EMT) in human tumors. Anticancer Res. 39:5437–5448.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Li L, Zhang S, Li H and Chou H: FGFR3
promotes the growth and malignancy of melanoma by influencing EMT
and the phosphorylation of ERK, AKT, and EGFR. BMC Cancer.
19:9632019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Si L, Fu J, Liu W, Hayashi T, Nie Y,
Mizuno K, Hattori S, Fujisaki H, Onodera S and Ikejima T: Silibinin
inhibits migration and invasion of breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells
through induction of mitochondrial fusion. Mol Cell Biochem.
463:189–201. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhang LN, Huang YH and Zhao L: Fusion of
macrophages promotes breast cancer cell proliferation, migration
and invasion through activating epithelial-mesenchymal transition
and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys.
676:1081372019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Xu J, Lamouille S and Derynck R:
TGF-beta-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cell Res.
19:156–172. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Moustakas A, Souchelnytskyi S and Heldin
CH: Smad regulation in TGF-beta signal transduction. J Cell Sci.
114:4359–4369. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wang G, Yu Y, Sun C, Liu T, Liang T, Zhan
L, Lin X and Feng XH: STAT3 selectively interacts with Smad3 to
antagonize TGF-β signalling. Oncogene. 35:4388–4398. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Itoh Y, Saitoh M and Miyazawa K:
Smad3-STAT3 crosstalk in pathophysiological contexts. Acta Biochim
Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 50:82–90. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|