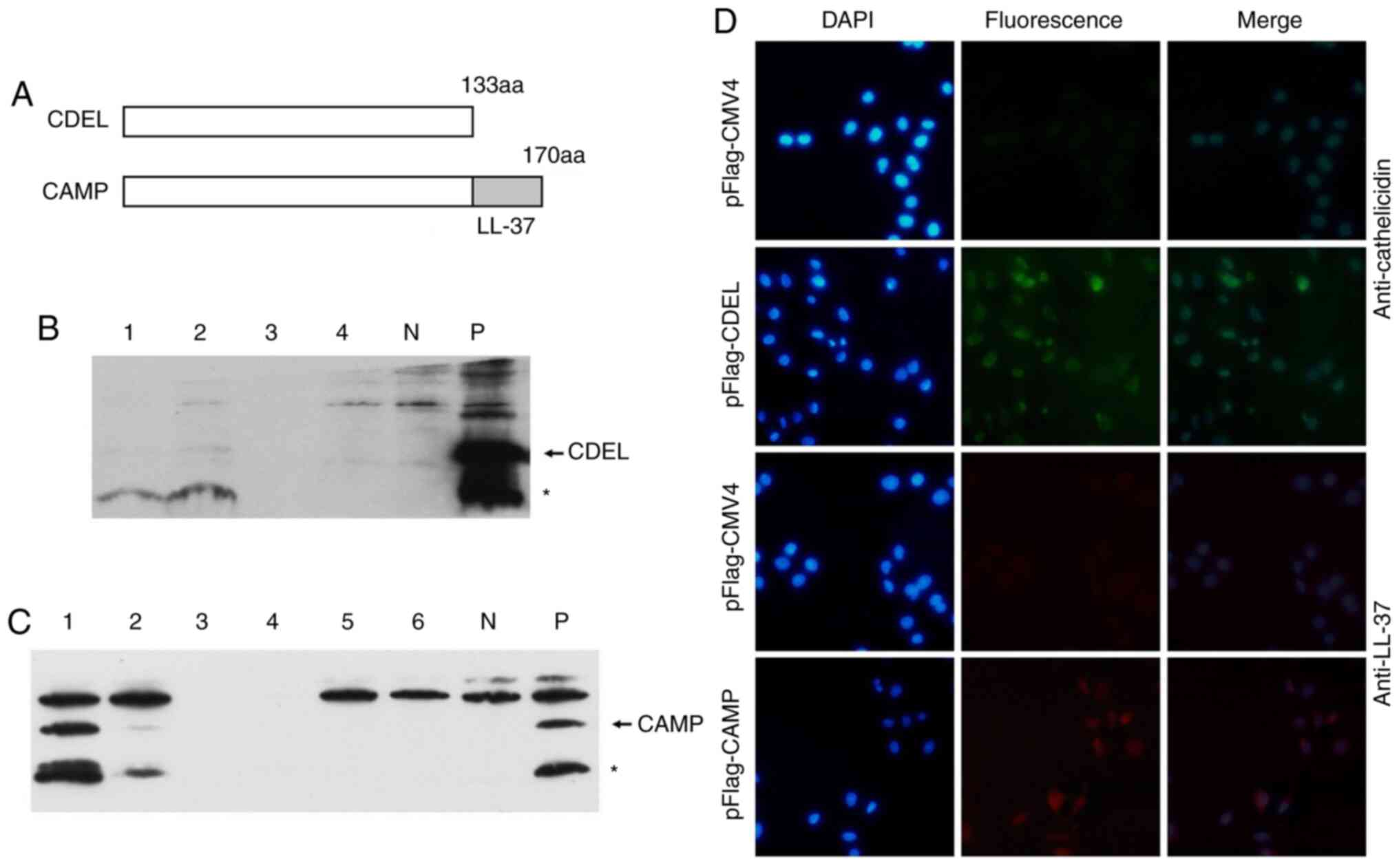
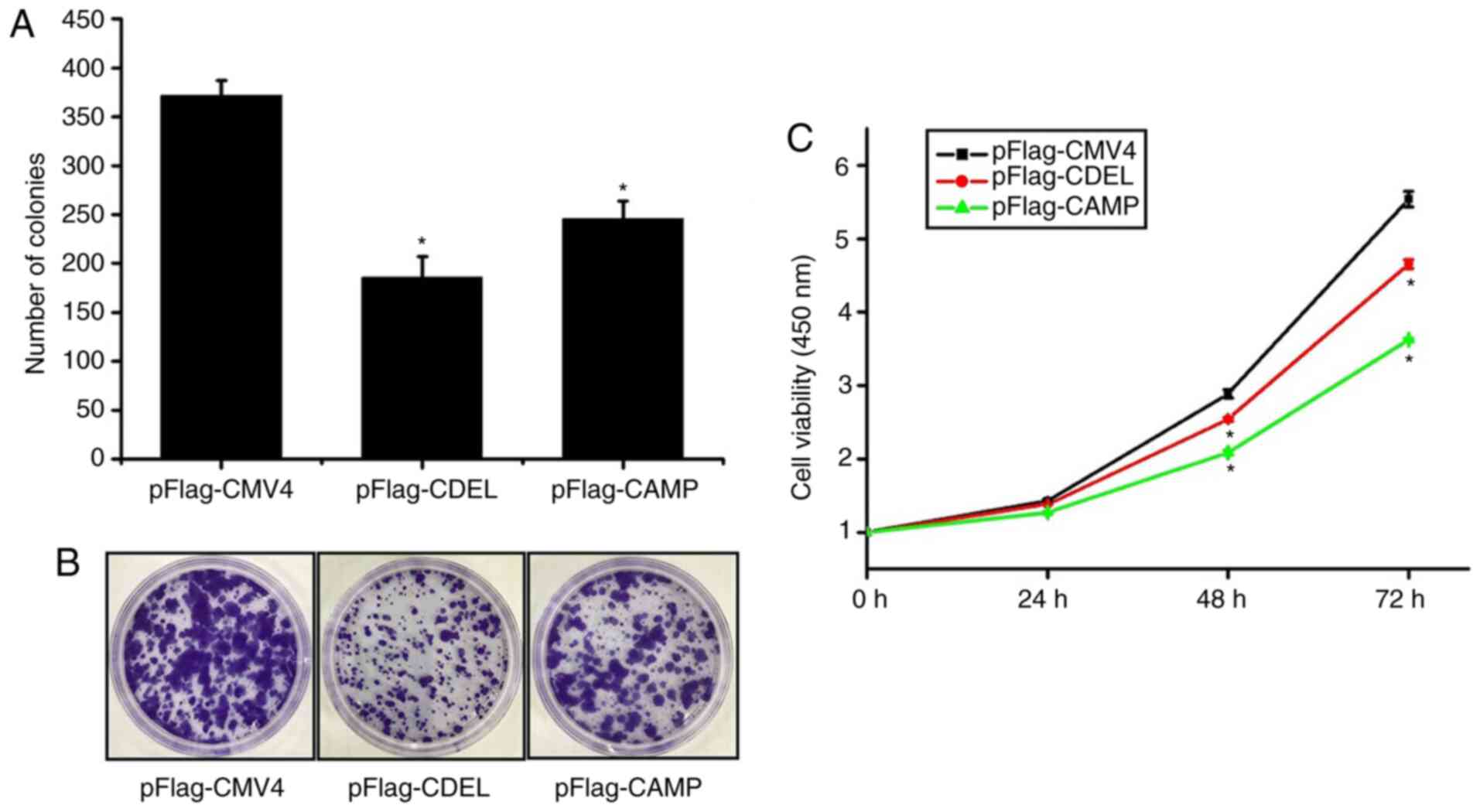
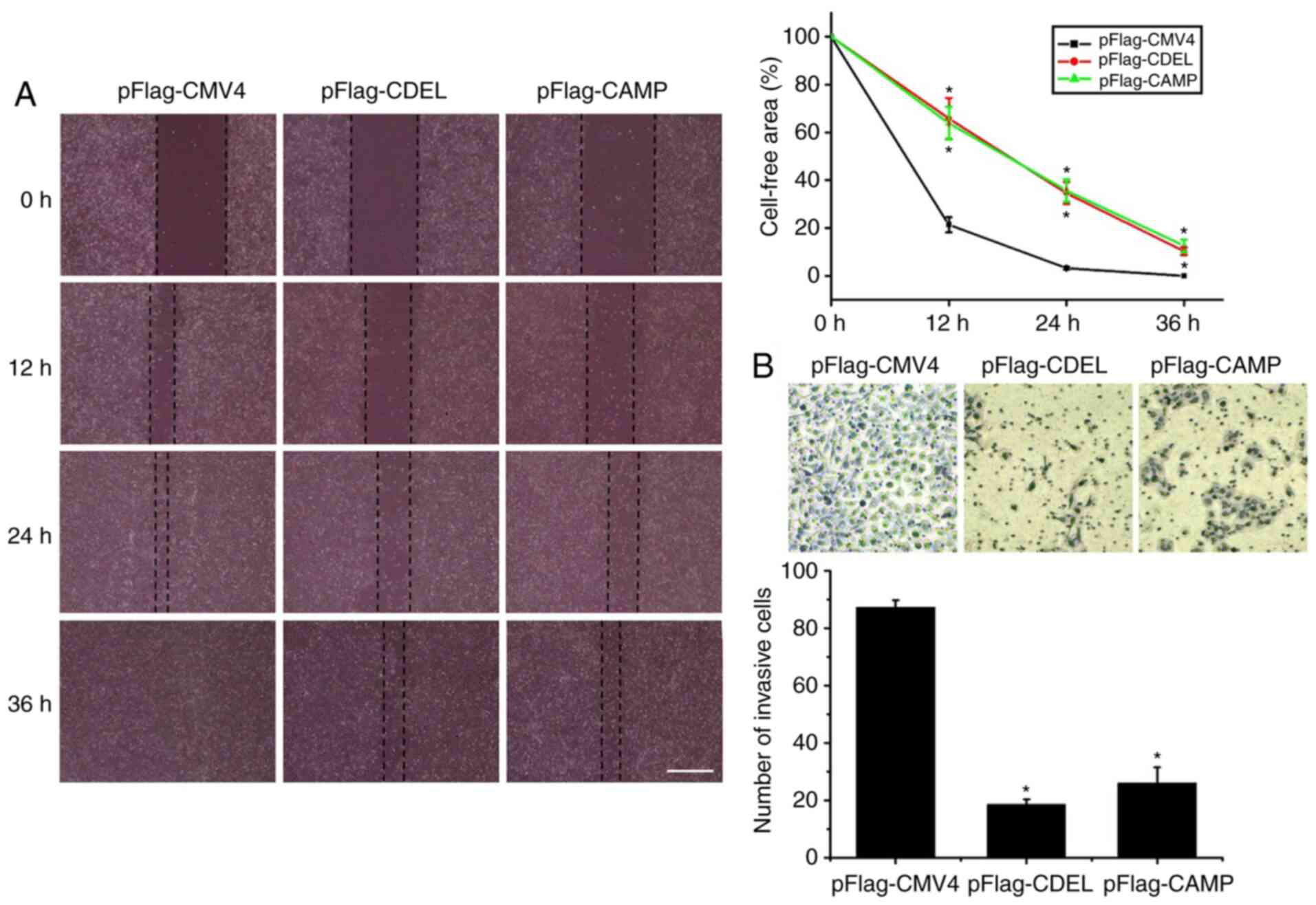
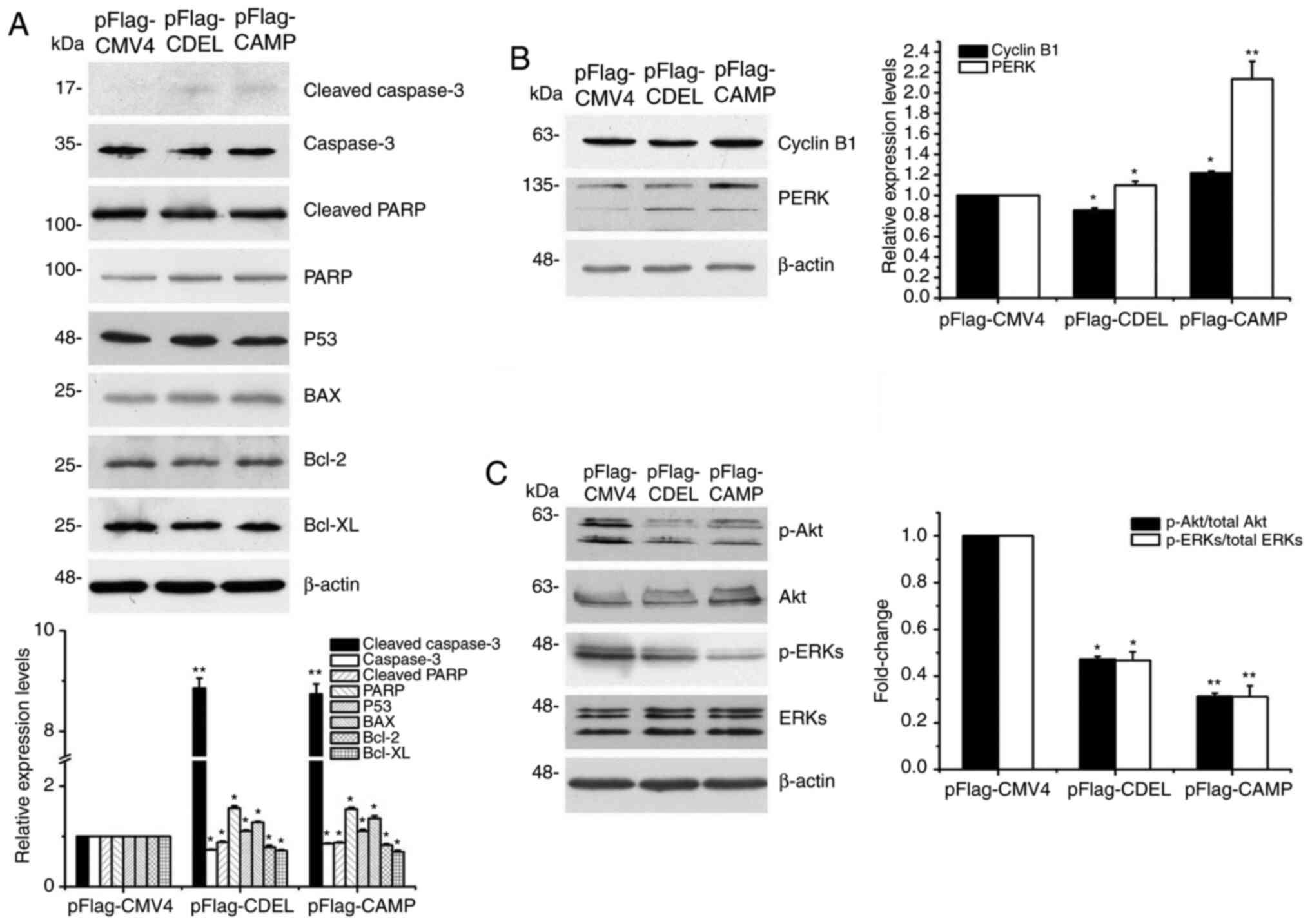
|
1
|
Alagarasu K, Patil PS, Shil P, Seervi M,
Kakade MB, Tillu H and Salunke A: In-vitro effect of human
cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide LL-37 on dengue virus type 2.
Peptides. 92:23–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Majewski K, Żelechowska P and
Brzezińska-Błaszczyk E: Circulating cathelicidin LL-37 in adult
patients with pulmonary infectious diseases. Clin Invest Med.
40:E34–E39. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tsai PW, Yang CY, Chang HT and Lan CY:
Human antimicrobial peptide LL-37 inhibits adhesion of Candida
albicans by interacting with yeast cell-wall carbohydrates.
PLoS One. 6:e177552011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Polcyn-Adamczak M and Niemir ZI:
Cathelicidin - Its structure, function and the role in autoimmune
diseases. Adv Cell Biol. 4:83–96. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kahlenberg JM and Kaplan MJ: Little
peptide, big effects: The role of LL-37 in inflammation and
autoimmune disease. J Immunol. 191:4895–4901. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Piktel E, Niemirowicz K, Wnorowska U,
Wątek M, Wollny T, Głuszek K, Góźdź S, Levental I and Bucki R: The
role of cathelicidin LL-37 in cancer development. Arch Immunol Ther
Exp (Warsz). 64:33–46. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu WK, Wang G, Coffelt SB, Betancourt AM,
Lee CW, Fan D, Wu K, Yu J, Sung JJ and Cho CH: Emerging roles of
the host defense peptide LL-37 in human cancer and its potential
therapeutic applications. Int J Cancer. 127:1741–1747. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kuroda K, Okumura K, Isogai H and Isogai
E: The human cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide LL-37 and mimics
are potential anticancer drugs. Front Oncol. 5:1442015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen X, Zou X, Qi G, Tang Y, Guo Y, Si J
and Liang L: Roles and mechanism of human cathelicidin LL-37 in
cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 47:1060–1073. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Carmona FJ, Montemurro F, Kannan S, Rossi
V, Verma C, Baselga J and Scaltriti M: AKT signaling in
ERBB2-amplified breast cancer. Pharmacol Ther. 158:63–70. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li D, Wang X, Wu JL, Quan WQ, Ma L, Yang
F, Wu KY and Wan HY: Tumor-produced versican V1 enhances
hCAP18/LL-37 expression in macrophages through activation of TLR2
and vitamin D3 signaling to promote ovarian cancer progression in
vitro. PLoS One. 8:e566162013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
von Haussen J, Koczulla R, Shaykhiev R,
Herr C, Pinkenburg O, Reimer D, Wiewrodt R, Biesterfeld S, Aigner
A, Czubayko F, et al: The host defence peptide LL-37/hCAP-18 is a
growth factor for lung cancer cells. Lung Cancer. 59:12–23. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hensel JA, Chanda D, Kumar S, Sawant A,
Grizzle WE, Siegal GP and Ponnazhagan S: LL-37 as a therapeutic
target for late stage prostate cancer. Prostate. 71:659–670. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sainz B Jr, Alcala S, Garcia E,
Sanchez-Ripoll Y, Azevedo MM, Cioffi M, Tatari M, Miranda-Lorenzo
I, Hidalgo M, Gomez-Lopez G, et al: Microenvironmental
hCAP-18/LL-37 promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by
activating its cancer stem cell compartment. Gut. 64:1921–1935.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Muñoz M, Craske M, Severino P, de Lima TM,
Labhart P, Chammas R, Velasco IT, Machado MC, Egan B, Nakaya HI, et
al: Antimicrobial peptide LL-37 participates in the transcriptional
regulation of melanoma cells. J Cancer. 7:2341–2345. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang W, Zheng Y, Jia J, Li C, Duan Q, Li
R, Wang X, Shao Y, Chen C and Yan H: Antimicrobial peptide LL-37
promotes the viability and invasion of skin squamous cell carcinoma
by upregulating YB-1. Exp Ther Med. 14:499–506. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
17. Wu WK, Sung JJ, To KF, Yu L, Li HT, Li
ZJ, Chu KM, Yu J and Cho CH: The host defense peptide LL-37
activates the tumor-suppressing bone morphogenetic protein
signaling via inhibition of proteasome in gastric cancer cells. J
Cell Physiol. 223:178–186. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ren SX, Cheng AS, To KF, Tong JH, Li MS,
Shen J, Wong CC, Zhang L, Chan RL, Wang XJ, et al: Host immune
defense peptide LL-37 activates caspase-independent apoptosis and
suppresses colon cancer. Cancer Res. 72:6512–6523. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kuroda K, Fukuda T, Krstic-Demonacos M,
Demonacos C, Okumura K, Isogai H, Hayashi M, Saito K and Isogai E:
miR-663a regulates growth of colon cancer cells, after
administration of antimicrobial peptides, by targeting CXCR4-p21
pathway. BMC Cancer. 17:332017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mader JS, Mookherjee N, Hancock RE and
Bleackley RC: The human host defense peptide LL-37 induces
apoptosis in a calpain- and apoptosis-inducing factor-dependent
manner involving Bax activity. Mol Cancer Res. 7:689–702. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
An LL, Ma XT, Yang YH, Lin YM, Song YH and
Wu KF: Marked reduction of LL-37/hCAP-18, an antimicrobial peptide,
in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Int J Hematol. 81:45–47.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Okumura K, Itoh A, Isogai E, Hirose K,
Hosokawa Y, Abiko Y, Shibata T, Hirata M and Isogai H: C-terminal
domain of human CAP18 antimicrobial peptide induces apoptosis in
oral squamous cell carcinoma SAS-H1 cells. Cancer Lett.
212:185–194. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Açil Y, Torz K, Gülses A, Wieker H, Gerle
M, Purcz N, Will OM, Eduard Meyer J and Wiltfang J: An experimental
study on antitumoral effects of KI-21-3, a synthetic fragment of
antimicrobial peptide LL-37, on oral squamous cell carcinoma. J
Craniomaxillofac Surg. 46:1586–1592. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen X, Qi G, Qin M, Zou Y, Zhong K, Tang
Y, Guo Y, Jiang X, Liang L and Zou X: DNA methylation directly
downregulates human cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide gene (CAMP)
promoter activity. Oncotarget. 8:27943–27952. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Väyrynen O, Åström P, Nyberg P, Alahuhta
I, Pirilä E, Vilen ST, Aikio M, Heljasvaara R, Risteli M, Sutinen
M, et al: Matrix metalloproteinase 9 inhibits the motility of
highly aggressive HSC-3 oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Exp
Cell Res. 376:18–26. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chang WL, Cheng FC, Wang SP, Chou ST and
Shih Y: Cinnamomum cassia essential oil and its major constituent
cinnamaldehyde induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human
oral squamous cell carcinoma HSC-3 cells. Environ Toxicol.
32:456–468. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Araújo T, Khayat A, Quintana L, Calcagno
D, Mourão R, Modesto A, Paiva J, Lima A, Moreira F, Oliveira E, et
al: Piwi like RNA-mediated gene silencing 1 gene as a possible
major player in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol.
24:5338–5350. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tang B, Qi G, Tang F, Yuan S, Wang Z,
Liang X, Li B, Yu S, Liu J, Huang Q, et al: Aberrant JMJD3
expression upregulates slug to promote migration, invasion, and
stem cell-like behaviors in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res.
76:6520–6532. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Qi G, Kudo Y, Tang B, Liu T, Jin S, Liu J,
Zuo X, Mi S, Shao W, Ma X, et al: PARP6 acts as a tumor suppressor
via downregulating Survivin expression in colorectal cancer.
Oncotarget. 7:18812–18824. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhao JG, Wang JF, Feng JF, Jin XY and Ye
WL: HHIP overexpression inhibits the proliferation, migration and
invasion of non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One.
14:e02257552019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Duan Q, Xiao Y, Zhu L, Liu Z, Mao X, Zhou
Z, Liao C, Cai J, Huang F, Liu Z, et al: BET bromodomain is a novel
regulator of TAZ and its activity. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1859:1527–1537. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mortazavi A, Williams BA, McCue K,
Schaeffer L and Wold B: Mapping and quantifying mammalian
transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat Methods. 5:621–628. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Anders S and Huber W: Differential
expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol.
11:R1062010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Vonderheide RH: Tumor-promoting
inflammatory networks in pancreatic neoplasia: Another reason to
loathe Kras. Cancer Cell. 25:553–554. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim YK, Shin JS and Nahm MH: NOD-like
receptors in infection, immunity, and diseases. Yonsei Med J.
57:5–14. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tuomela JM, Sandholm JA, Kaakinen M,
Hayden KL, Haapasaari KM, Jukkola-Vuorinen A, Kauppila JH,
Lehenkari PP, Harris KW, Graves DE, et al: Telomeric
G-quadruplex-forming DNA fragments induce TLR9-mediated and
LL-37-regulated invasion in breast cancer cells in vitro. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 155:261–271. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cheng M, Ho S, Yoo JH, Tran DH, Bakirtzi
K, Su B, Tran DH, Kubota Y, Ichikawa R and Koon HW: Cathelicidin
suppresses colon cancer development by inhibition of cancer
associated fibroblasts. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 8:13–29.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Martini M, De Santis MC, Braccini L,
Gulluni F and Hirsch E: PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and cancer: An
updated review. Ann Med. 46:372–383. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sun Y, Liu WZ, Liu T, Feng X, Yang N and
Zhou HF: Signaling pathway of MAPK/ERK in cell proliferation,
differentiation, migration, senescence and apoptosis. J Recept
Signal Transduct Res. 35:600–604. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|