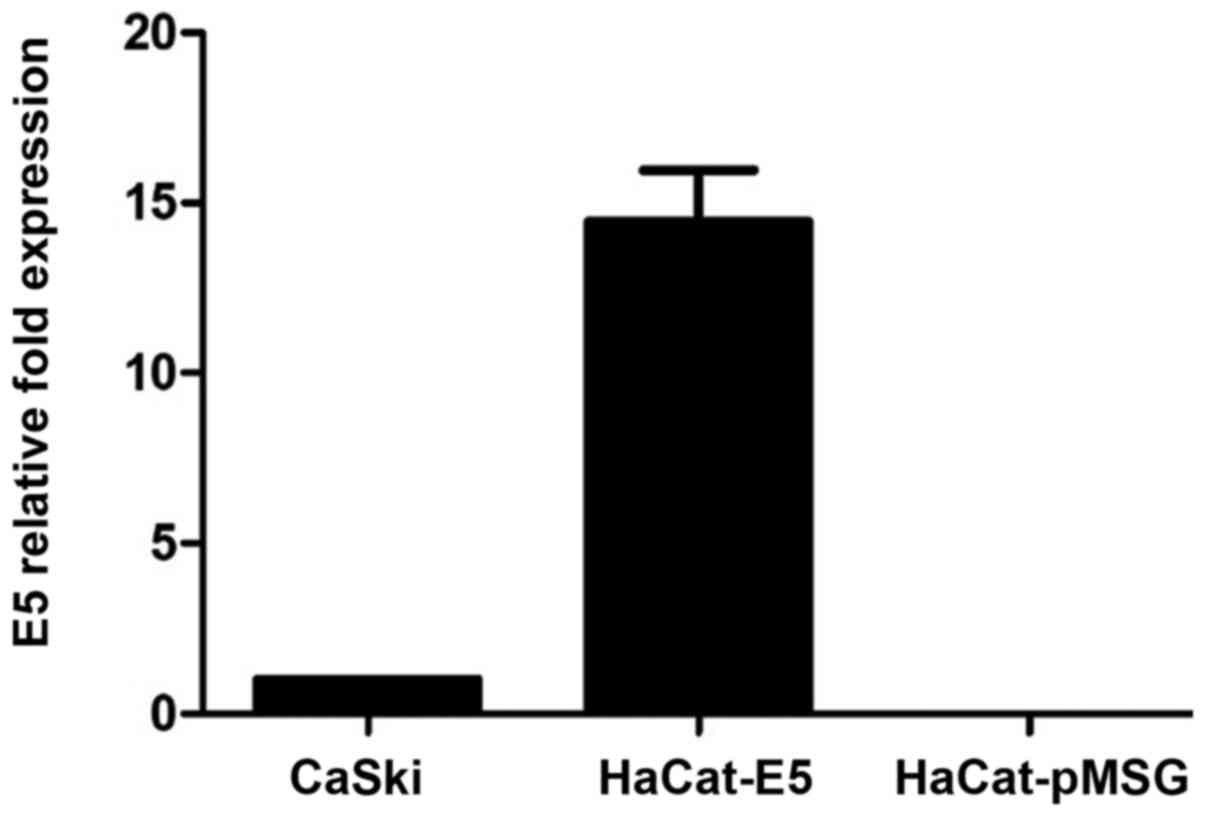
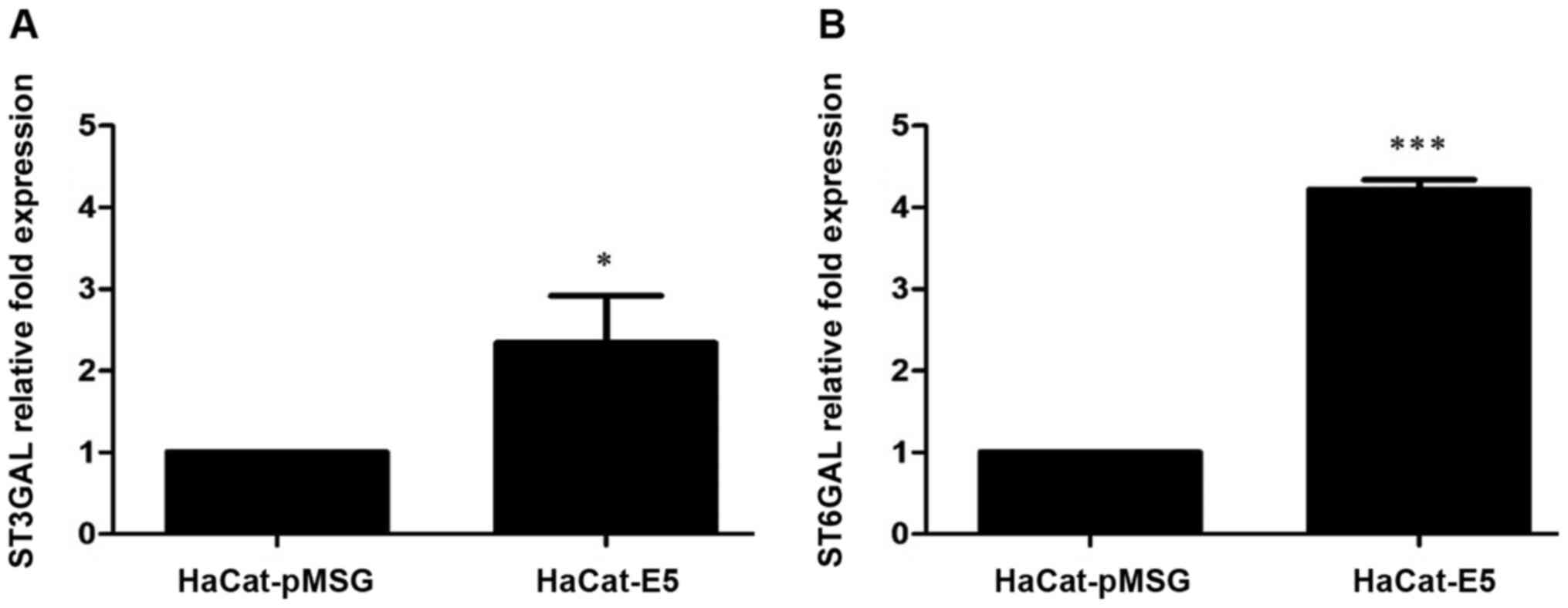
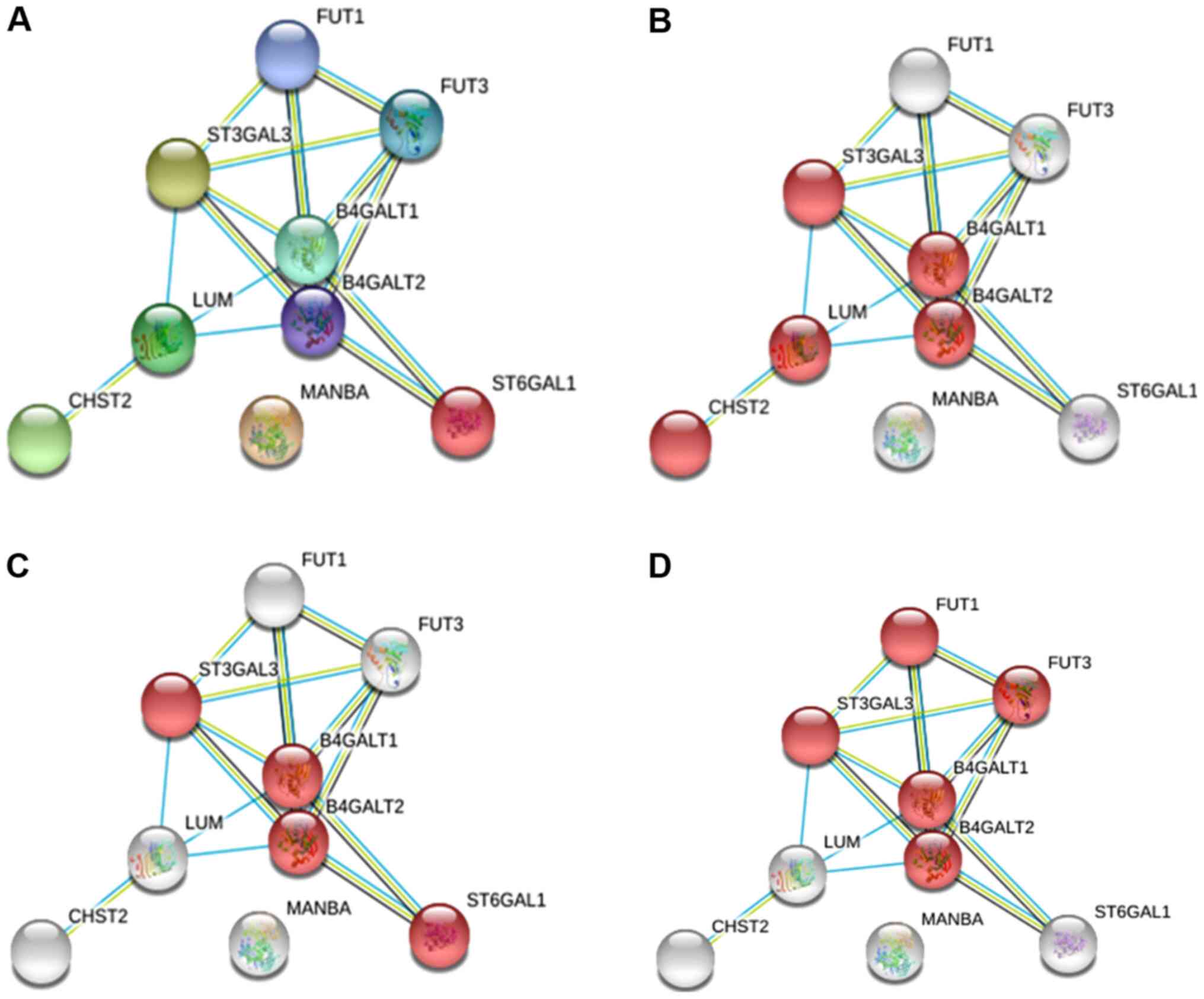
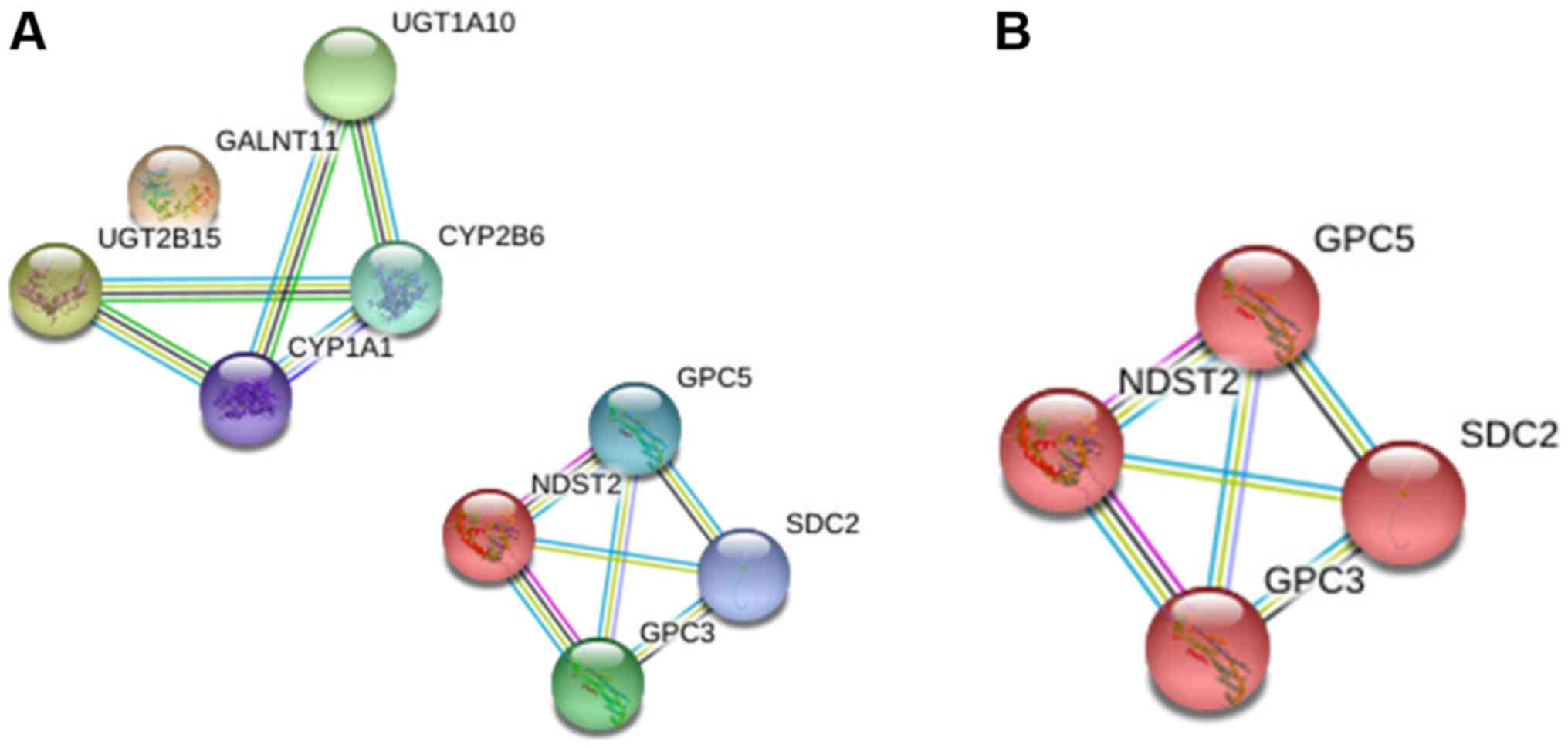
|
1
|
zur Hausen H: Papillomaviruses in the
causation of human cancers - a brief historical account. Virology.
384:260–265. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Smith JS, Lindsay L, Hoots B, Keys J,
Franceschi S, Winer R and Clifford GM: Human papillomavirus type
distribution in invasive cervical cancer and high-grade cervical
lesions: A meta-analysis update. Int J Cancer. 121:621–632. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Aguilar-Lemarroy A, Vallejo-Ruiz V,
Cortés-Gutiérrez EI, Salgado-Bernabé ME, Ramos-González NP,
Ortega-Cervantes L, Arias-Flores R, Medina-Díaz IM, Hernández-Garza
F, Santos-López G, et al IMSS Research Network on HPV, : Human
papillomavirus infections in Mexican women with normal cytology,
precancerous lesions, and cervical cancer: Type-specific prevalence
and HPV coinfections. J Med Virol. 87:871–884. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Münger K and Howley PM: Human
papillomavirus immortalization and transformation functions. Virus
Res. 89:213–228. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Conrad M, Bubb VJ and Schlegel R: The
human papillomavirus type 6 and 16 E5 proteins are
membrane-associated proteins which associate with the 16-kilodalton
pore-forming protein. J Virol. 67:6170–6178. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Venuti A, Paolini F, Nasir L, Corteggio A,
Roperto S, Campo MS and Borzacchiello G: Papillomavirus E5: The
smallest oncoprotein with many functions. Mol Cancer. 10:1402011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen SL, Huang CH, Tsai TC, Lu KY and Tsao
YP: The regulation mechanism of c-jun and junB by human
papillomavirus type 16 E5 oncoprotein. Arch Virol. 141:791–800.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen SL, Lin YK, Li LY, Tsao YP, Lo HY,
Wang WB and Tsai TC: E5 proteins of human papillomavirus types 11
and 16 transactivate the c-fos promoter through the NF1 binding
element. J Virol. 70:8558–8563. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kivi N, Greco D, Auvinen P and Auvinen E:
Genes involved in cell adhesion, cell motility and mitogenic
signaling are altered due to HPV 16 E5 protein expression.
Oncogene. 27:2532–2541. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Varki A, Kannagi R, Toole B and Stanley P:
Glycosylation Changes in Cancer. Essentials of Glycobiology
[Internet]. 3rd edition. Varki A, Cummings RD, Esko JD, Stanley P,
Hart GW, Aebi M, Darvill AG, Kinoshita T, Packer NH, Prestegard JH,
et al: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; Cold Spring Harbor, NY:
2017
|
|
11
|
Wang PH: Altered Glycosylation in Cancer:
Sialic Acids and Sialyltransferases. J Cancer Mol. 1:73–81.
2005.
|
|
12
|
Wang PH, Li YF, Juang CM, Lee YR, Chao HT,
Ng HT, Tsai YC and Yuan CC: Expression of sialyltransferase family
members in cervix squamous cell carcinoma correlates with lymph
node metastasis. Gynecol Oncol. 86:45–52. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
López-Morales D, Velázquez-Márquez N,
Valenzuela O, Santos-López G, Reyes-Leyva J and Vallejo-Ruiz V:
Enhanced sialyltransferases transcription in cervical
intraepithelial neoplasia. Invest Clin. 50:45–53. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
López-Morales D, Reyes-Leyva J,
Santos-López G, Zenteno E and Vallejo-Ruiz V: Increased expression
of sialic acid in cervical biopsies with squamous intraepithelial
lesions. Diagn Pathol. 5:742010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Roy A and Chakraborty S: Detection of
cancer cervix by estimation of sialic acid. J Indian Med Assoc.
103:589–590. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Terasawa K, Furumoto H, Kamada M and Aono
T: Expression of Tn and sialyl-Tn antigens in the neoplastic
transformation of uterine cervical epithelial cells. Cancer Res.
56:2229–2232. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Engelstaedter V, Fluegel B, Kunze S, Mayr
D, Friese K, Jeschke U and Bergauer F: Expression of the
carbohydrate tumour marker Sialyl Lewis A, Sialyl Lewis X, Lewis Y
and Thomsen-Friedenreich antigen in normal squamous epithelium of
the uterine cervix, cervical dysplasia and cervical cancer. Histol
Histopathol. 27:507–514. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Velázquez-Márquez N, Santos-López G,
Jiménez-Aranda L, Reyes-Leyva J and Vallejo-Ruiz V: Sialyl Lewis ×
expression in cervical scrapes of premalignant lesions. J Biosci.
37:999–1004. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Aco-Tlachi M, Carreño-López R,
Martínez-Morales PL, Maycotte P, Aguilar-Lemarroy A, Jave-Suárez
LF, Santos-López G, Reyes-Leyva J and Vallejo-Ruiz V: Glycogene
expression profiles based on microarray data from cervical
carcinoma HeLa cells with partially silenced E6 and E7 HPV
oncogenes. Infect Agent Cancer. 13:252018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kabsch K and Alonso A: The human
papillomavirus type 16 E5 protein impairs TRAIL- and FasL-mediated
apoptosis in HaCaT cells by different mechanisms. J Virol.
76:12162–12172. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Buettner FF, Ashikov A, Tiemann B, Lehle L
and Bakker H: C. elegans DPY-19 is a C-mannosyltransferase
glycosylating thrombospondin repeats. Mol Cell. 50:295–302. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Milde-Langosch K, Karn T, Schmidt M, zu
Eulenburg C, Oliveira-Ferrer L, Wirtz RM, Schumacher U, Witzel I,
Schütze D and Müller V: Prognostic relevance of
glycosylation-associated genes in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 145:295–305. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Recchi MA, Hebbar M, Hornez L,
Harduin-Lepers A, Peyrat JP and Delannoy P: Multiplex reverse
transcription polymerase chain reaction assessment of
sialyltransferase expression in human breast cancer. Cancer Res.
58:4066–4070. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jin XL, Zheng SS, Wang BS and Chen HL:
Correlation of glycosyltransferases mRNA expression in extrahepatic
bile duct carcinoma with clinical pathological characteristics.
Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 3:292–295. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Petretti T, Kemmner W, Schulze B and
Schlag PM: Altered mRNA expression of glycosyltransferases in human
colorectal carcinomas and liver metastases. Gut. 46:359–366. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ashkani J and Naidoo KJ:
Glycosyltransferase gene expression profiles classify cancer types
and propose prognostic subtypes. Sci Rep. 6:264512016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gretschel S, Haensch W, Schlag PM and
Kemmner W: Clinical relevance of sialyltransferases ST6GAL-I and
ST3GAL-III in gastric cancer. Oncology. 65:139–145. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang S, Lu J, Xu Z, Zou X, Sun X, Xu Y,
Shan A, Lu J, Yan X, Cui Y, et al: Differential expression of
ST6GAL1 in the tumor progression of colorectal cancer. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 486:1090–1096. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Swindall AF, Londoño-Joshi AI, Schultz MJ,
Fineberg N, Buchsbaum DJ and Bellis SL: ST6Gal-I protein expression
is upregulated in human epithelial tumors and correlates with stem
cell markers in normal tissues and colon cancer cell lines. Cancer
Res. 73:2368–2378. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Schultz MJ, Holdbrooks AT, Chakraborty A,
Grizzle WE, Landen CN, Buchsbaum DJ, Conner MG, Arend RC, Yoon KJ,
Klug CA, et al: The tumor-associated glycosyltransferase ST6Gal-I
regulates stem cell transcription factors and confers a cancer stem
cell phenotype. Cancer Res. 76:3978–3988. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Vázquez-Martín C, Gil-Martín E and
Fernández-Briera A: Elevation of ST6Gal I activity in malignant and
transitional tissue in human colorectal cancer. Oncology.
69:436–444. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chakraborty A, Dorsett KA, Trummell HQ,
Yang ES, Oliver PG, Bonner JA, Buchsbaum DJ and Bellis SL: ST6Gal-I
sialyltransferase promotes chemoresistance in pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma by abrogating gemcitabine-mediated DNA damage. J
Biol Chem. 293:984–994. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Potapenko IO, Haakensen VD, Lüders T,
Helland A, Bukholm I, Sørlie T, Kristensen VN, Lingjaerde OC and
Børresen-Dale AL: Glycan gene expression signatures in normal and
malignant breast tissue; possible role in diagnosis and
progression. Mol Oncol. 4:98–118. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen X, Yang TT, Qiu XC, Ji ZG, Li CX,
Long H, Zhou Y, Ma BA, Ma Q, Zhang X, et al: Gene expression
profiles of human osteosarcoma cell sublines with different
pulmonary metastatic potentials. Cancer Biol Ther. 11:287–292.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Warnecke-Eberz U, Metzger R, Hölscher AH,
Drebber U and Bollschweiler E: Diagnostic marker signature for
esophageal cancer from transcriptome analysis. Tumour Biol.
37:6349–6358. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Seko A, Kataoka F, Aoki D, Sakamoto M,
Nakamura T, Hatae M, Yonezawa S and Yamashita K:
N-Acetylglucosamine 6-O-sulfotransferase-2 as a tumor marker for
uterine cervical and corpus cancer. Glycoconj J. 26:1065–1073.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sud N, Sharma R, Ray R, Chattopadhyay T
and Ralhan R: Differential expression of beta mannosidase in human
esophageal cancer. Int J Cancer. 112:905–907. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Pfeiffer MJ, Smit FP, Sedelaar JP and
Schalken JA: Steroidogenic enzymes and stem cell markers are
upregulated during androgen deprivation in prostate cancer. Mol
Med. 17:657–664. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chen X, Li D, Wang N, Yang M, Liao A, Wang
S, Hu G, Zeng B, Yao Y, Liu D, et al: Bioinformatic analysis
suggests that UGT2B15 activates the Hippo YAP signaling pathway
leading to the pathogenesis of gastric cancer. Oncol Rep.
40:1855–1862. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Pâquet S, Fazli L, Grosse L, Verreault M,
Têtu B, Rennie PS, Bélanger A and Barbier O: Differential
expression of the androgen-conjugating UGT2B15 and UGT2B17 enzymes
in prostate tumor cells during cancer progression. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 97:E428–E432. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Libisch MG, Casás M, Chiribao M, Moreno P,
Cayota A, Osinaga E, Oppezzo P and Robello C: GALNT11 as a new
molecular marker in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Gene.
533:270–279. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tátrai P, Egedi K, Somorácz A, van
Kuppevelt TH, Ten Dam G, Lyon M, Deakin JA, Kiss A, Schaff Z and
Kovalszky I: Quantitative and qualitative alterations of heparan
sulfate in fibrogenic liver diseases and hepatocellular cancer. J
Histochem Cytochem. 58:429–441. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ushakov VS, Tsidulko AY, de La Bourdonnaye
G, Kazanskaya GM, Volkov AM, Kiselev RS, Kobozev VV, Kostromskaya
DV, Gaytan AS, Krivoshapkin AL, et al: Heparan sulfate biosynthetic
system is inhibited in human glioma due to EXT1/2 and HS6ST1/2
D}down-regulation. Int J Mol Sci. 18:E23012017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Cengiz B, Yumrutas O, Bozgeyik E, Borazan
E, Igci YZ, Bozgeyik I and Oztuzcu S: Differential expression of
the UGT1A family of genes in stomach cancer tissues. Tumour Biol.
36:5831–5837. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Starlard-Davenport A, Lyn-Cook B and
Radominska-Pandya A: Identification of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase
1A10 in non-malignant and malignant human breast tissues. Steroids.
73:611–620. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Pinho SS and Reis CA: Glycosylation in
cancer: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Nat Rev Cancer.
15:540–555. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Magalhães A, Duarte HO and Reis CA:
Aberrant glycosylation in cancer: A novel molecular mechanism
controlling metastasis. Cancer Cell. 31:733–735. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Harduin-Lepers A, Krzewinski-Recchi MA,
Colomb F, Foulquier F, Groux-Degroote S and Delannoy P:
Sialyltransferases functions in cancers. Front Biosci (Elite Ed).
4:499–515. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Estêvão D, Costa NR, Gil da Costa RM and
Medeiros R: Hallmarks of HPV carcinogenesis: The role of E6, E7 and
E5 oncoproteins in cellular malignancy. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene
Regul Mech. 1862:153–162. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Oetke C, Auvinen E, Pawlita M and Alonso
A: Human papillomavirus type 16 E5 protein localizes to the Golgi
apparatus but does not grossly affect cellular glycosylation. Arch
Virol. 145:2183–2191. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Vandamme V, Pierce A, Verbert A and
Delannoy P: Transcriptional induction of beta-galactoside
alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase in rat fibroblast by dexamethasone. Eur
J Biochem. 211:135–140. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Coughlan CM, Burger PG, Berger EG and
Breen KC: The biochemical consequences of alpha2,6(N)
sialyltransferase induction by dexamethasone on sialoglycoprotein
expression in the rat H411e hepatoma cell line. FEBS Lett.
413:389–393. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Caterson B and Melrose J: Keratan sulfate,
a complex glycosaminoglycan with unique functional capability.
Glycobiology. 28:182–206. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
D'Angelo G, Capasso S, Sticco L and Russo
D: Glycosphingolipids: Synthesis and functions. FEBS J.
280:6338–6353. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhuo D, Li X and Guan F: Biological roles
of aberrantly expressed glycosphingolipids and related enzymes in
human cancer development and progression. Front Physiol. 9:4662018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Suprynowicz FA, Disbrow GL, Krawczyk E,
Simic V, Lantzky K and Schlegel R: HPV-16 E5 oncoprotein
upregulates lipid raft components caveolin-1 and ganglioside GM1 at
the plasma membrane of cervical cells. Oncogene. 27:1071–1078.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Harduin-Lepers A, Vallejo-Ruiz V,
Krzewinski-Recchi MA, Samyn-Petit B, Julien S and Delannoy P: The
human sialyltransferase family. Biochimie. 83:727–737. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ohmori K, Kanda K, Mitsuoka C, Kanamori A,
Kurata-Miura K, Sasaki K, Nishi T, Tamatani T and Kannagi R: P- and
E-selectins recognize sialyl 6-sulfo Lewis X, the recently
identified L-selectin ligand. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
278:90–96. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Lu J and Gu J: Significance of
β-galactoside α2,6 sialyltranferase 1 in cancers. Molecules.
20:7509–7527. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Seales EC, Jurado GA, Brunson BA,
Wakefield JK, Frost AR and Bellis SL: Hypersialylation of beta1
integrins, observed in colon adenocarcinoma, may contribute to
cancer progression by up-regulating cell motility. Cancer Res.
65:4645–4652. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Park JJ, Yi JY, Jin YB, Lee YJ, Lee JS,
Lee YS, Ko YG and Lee M: Sialylation of epidermal growth factor
receptor regulates receptor activity and chemosensitivity to
gefitinib in colon cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 83:849–857.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Tomakidi P, Cheng H, Kohl A, Komposch G
and Alonso A: Modulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor by
the human papillomavirus type 16 E5 protein in raft cultures of
human keratinocytes. Eur J Cell Biol. 79:407–412. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Deligny A, Dierker T, Dagälv A, Lundequist
A, Eriksson I, Nairn AV, Moremen KW, Merry CLR and Kjellén L: NDST2
(N-Deacetylase/N-Sulfotransferase-2) enzyme regulates heparan
sulfate chain length. J Biol Chem. 291:18600–18607. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|