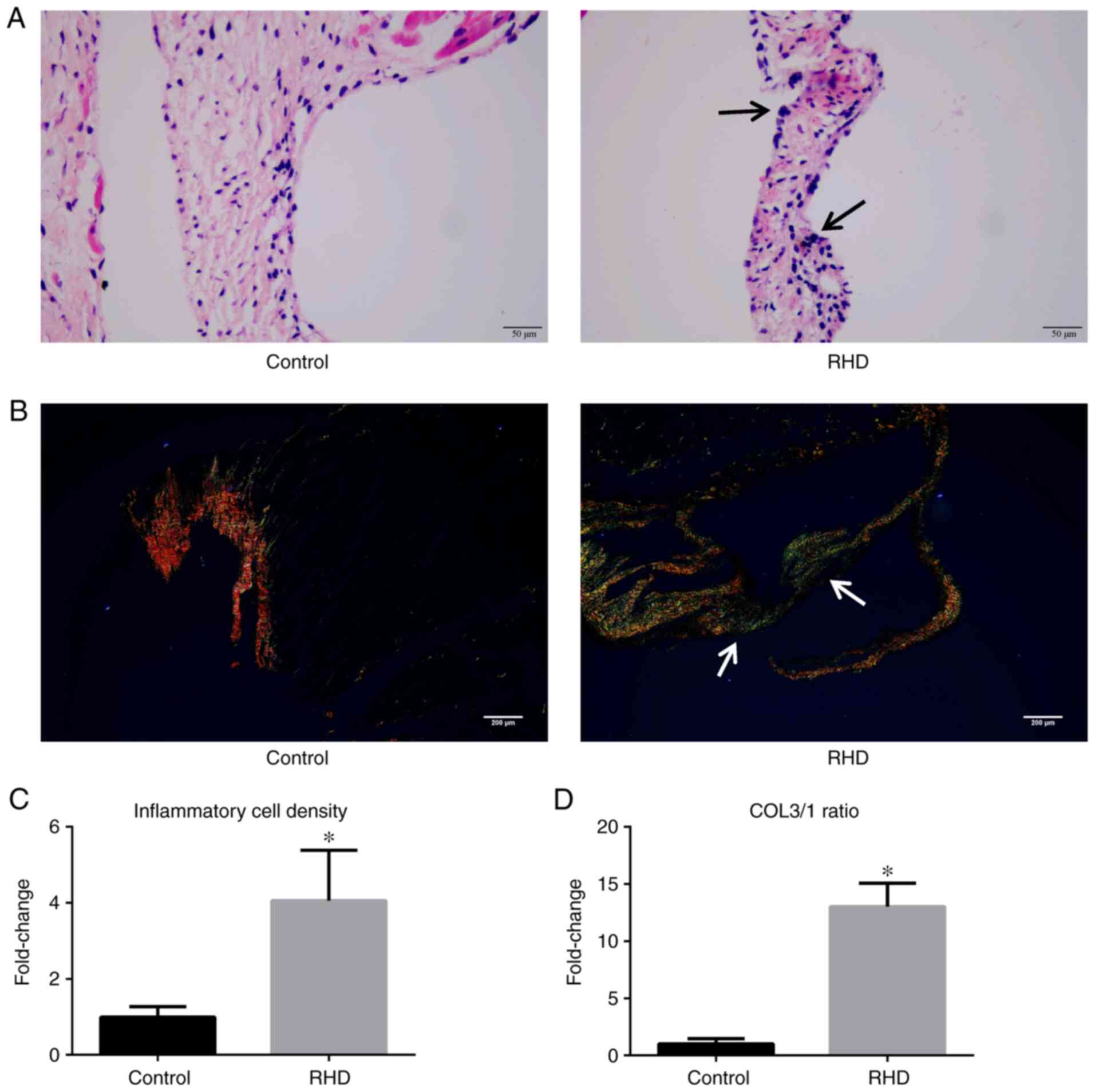
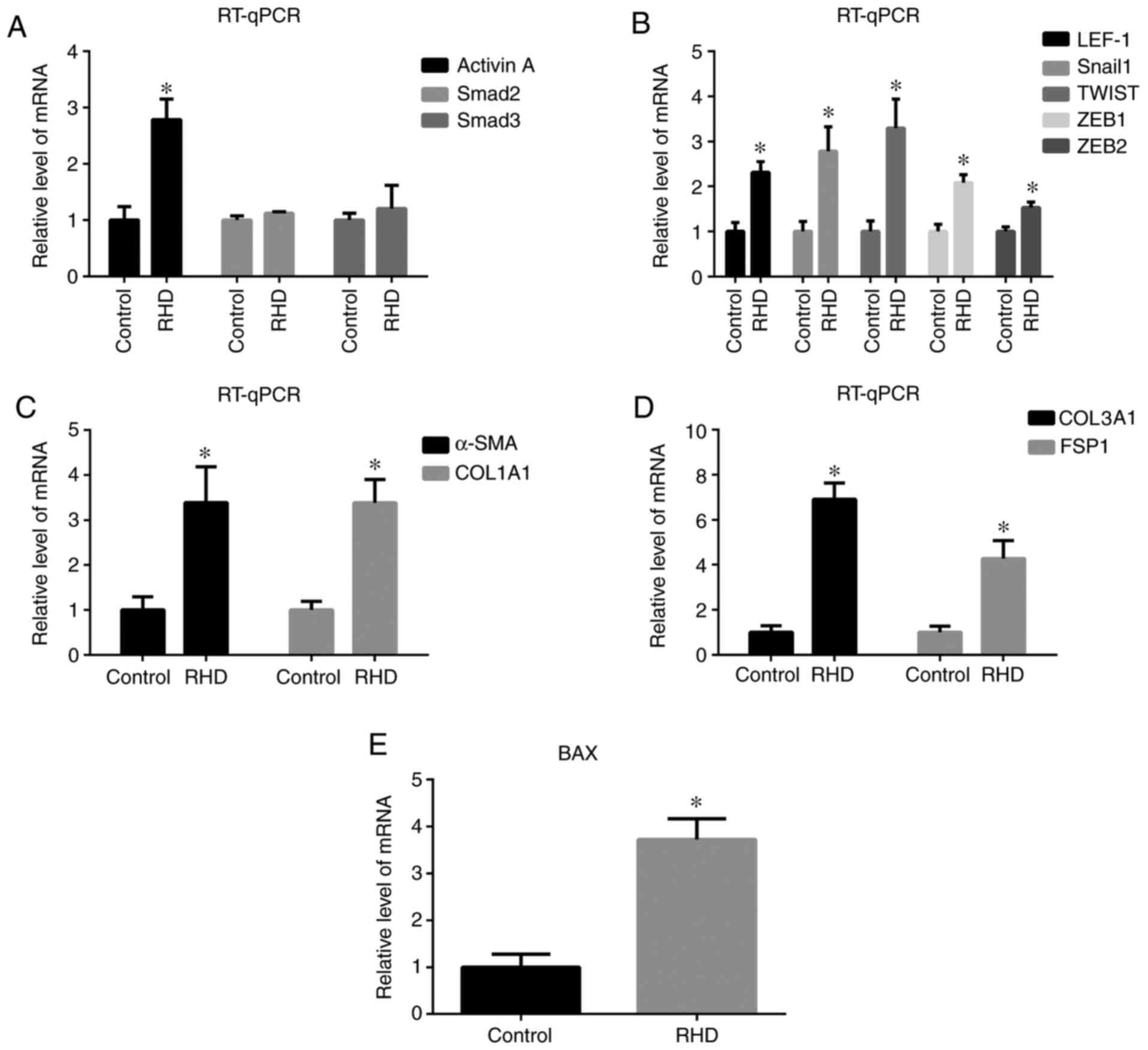
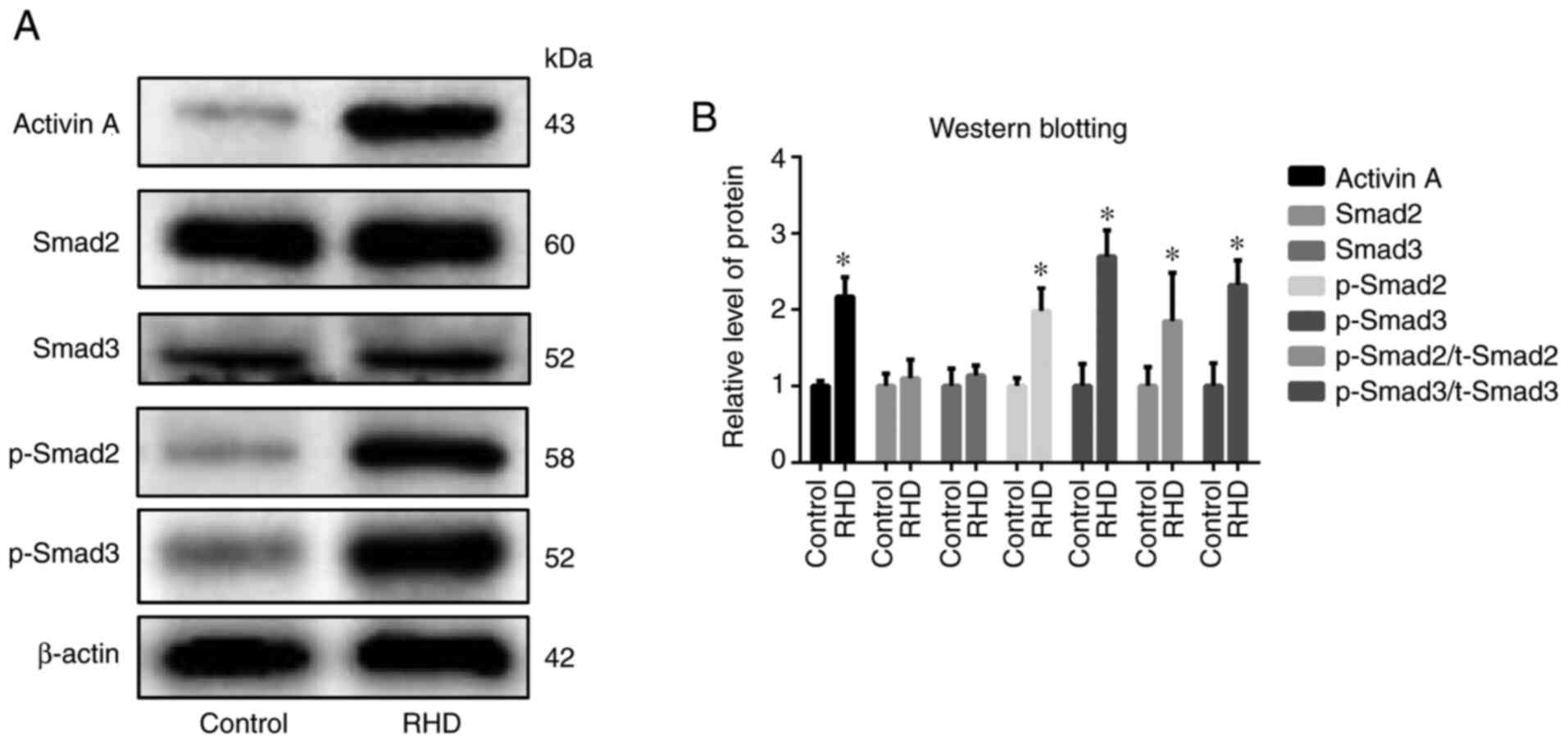
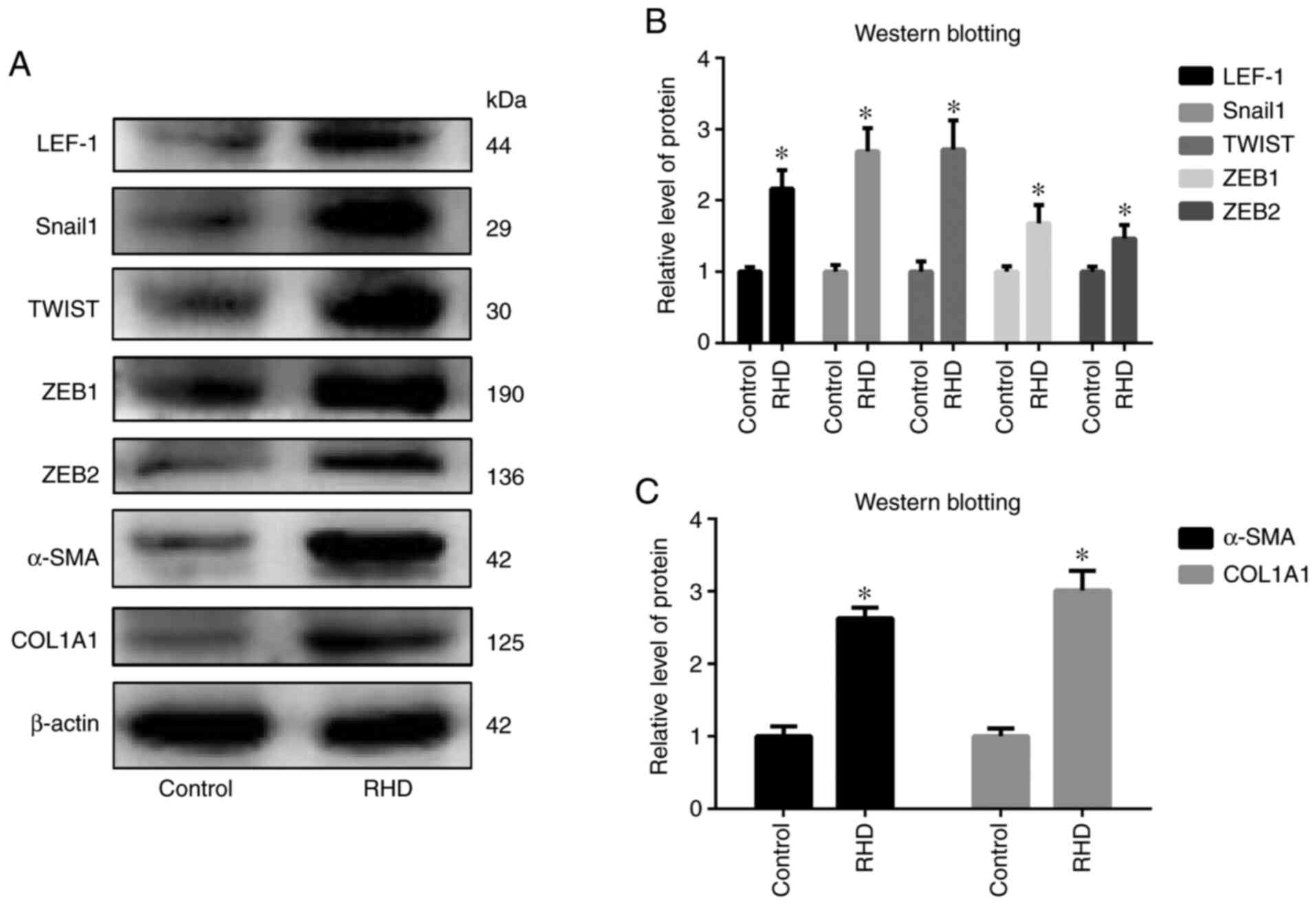
|
1
|
Watkins DA, Johnson CO, Colquhoun SM,
Karthikeyan G, Beaton A, Bukhman G, Forouzanfar MH, Longenecker CT,
Mayosi BM, Mensah GA, et al: Global, regional, and national burden
of rheumatic heart disease, 1990–2015. N Engl J Med. 377:713–722.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Remenyi B, Carapetis J, Wyber R, Taubert K
and Mayosi BM; World Heart Federation, : Position statement of the
World Heart Federation on the prevention and control of rheumatic
heart disease. Nat Rev Cardiol. 10:284–292. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Remenyi B, ElGuindy A, Smith SC Jr, Yacoub
M and Holmes DR Jr: Valvular aspects of rheumatic heart disease.
Lancet. 387:1335–1346. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Naghavi M, Abajobir AA, Abbafati C, Abbas
KM, Abd-Allah F, Abera SF, Aboyans V, Adetokunboh O, Afshin A,
Agrawal A, et al GBD 2016 Causes of Death Collaborators, : Global,
regional, and national age-sex specific mortality for 264 causes of
death, 1980–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of
Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 390:1151–1210. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Roth GA, Abate D, Abate KH, Abay SM,
Abbafati C, Abbasi N, Abbastabar H, Abd-Allah F, Abdela J,
Abdelalim A, et al GBD 2017 Causes of Death Collaborators, :
Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282
causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980–2017: A
systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017.
Lancet. 392:1736–1788. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Salem A, Abdelgawad AME and Elshemy A:
Early and midterm outcomes of rheumatic mitral valve repair. Heart
Surg Forum. 21:E352–E358. 2018. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Elsayed AAA, Abdelaal KM, Abdelghaffar
AMM, Mohamed EEH, Mahran TMA, Ahmed MSM, Ibrahim AM and Mansour AA:
Poor outcome of surgical management of acute malfunctioning
mechanical mitral valve during pregnancy. Should centers with
limited resources find different options? Heart Surg Forum.
22:E405–E410. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pagnozzi LA and Butcher JT:
Mechanotransduction mechanisms in mitral valve physiology and
disease pathogenesis. Front Cardiovasc Med. 4:832017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Songia P, Branchetti E, Parolari A,
Myasoedova V, Ferrari G, Alamanni F, Tremoli E and Poggio P: Mitral
valve endothelial cells secrete osteoprotegerin during endothelial
mesenchymal transition. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 98:48–57. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hong L, Du X, Li W, Mao Y, Sun L and Li X:
EndMT: A promising and controversial field. Eur J Cell Biol.
97:493–500. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wei WY, Zhang N, Li LL, Ma ZG, Xu M, Yuan
YP, Deng W and Tang QZ: Pioglitazone alleviates cardiac fibrosis
and inhibits endothelial to mesenchymal transition induced by
pressure overload. Cell Physiol Biochem. 45:26–36. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xiao M, Zhang M, Bie M, Wang X, Guo J and
Xiao H: Galectin-3 induces atrial fibrosis by activating the
TGF-β1/Smad pathway in patients with atrial fibrillation.
Cardiology. 145:446–455. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Thuault S, Tan EJ, Peinado H, Cano A,
Heldin CH and Moustakas A: HMGA2 and Smads co-regulate SNAIL1
expression during induction of epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. J Biol Chem. 283:33437–33446. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Vincent T, Neve EP, Johnson JR, Kukalev A,
Rojo F, Albanell J, Pietras K, Virtanen I, Philipson L, Leopold PL,
et al: A SNAIL1-SMAD3/4 transcriptional repressor complex promotes
TGF-beta mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Cell Biol.
11:943–950. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kovacic JC, Mercader N, Torres M, Boehm M
and Fuster V: Epithelial-to-mesenchymal and
endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition: From cardiovascular
development to disease. Circulation. 125:1795–1808. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Massagué J: How cells read TGF-beta
signals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 1:169–178. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Itoh S, Itoh F, Goumans MJ and Ten Dijke
P: Signaling of transforming growth factor-beta family members
through Smad proteins. Eur J Biochem. 267:6954–6967. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Moustakas A, Souchelnytskyi S and Heldin
CH: Smad regulation in TGF-beta signal transduction. J Cell Sci.
114:4359–4369. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu ZH, Zhang Y, Wang X, Fan XF, Zhang Y,
Li X, Gong YS and Han LP: SIRT1 activation attenuates cardiac
fibrosis by endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Biomed
Pharmacother. 118:1092272019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu L, Fu M, Chen D, Han W, Ostrowski MC,
Grossfeld P, Gao P and Ye M: Endothelial-specific deletion of Ets-1
attenuates Angiotensin II-induced cardiac fibrosis via suppression
of endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition. BMB Rep. 52:595–600.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Maleki S, Cottrill KA, Poujade FA,
Bhattachariya A, Bergman O, Gådin JR, Simon N, Lundströmer K,
Franco-Cereceda A, Björck HM, et al: The mir-200 family regulates
key pathogenic events in ascending aortas of individuals with
bicuspid aortic valves. J Intern Med. 285:102–114. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang B, Niu W, Dong HY, Liu M-L, Luo Y
and Li ZC: Hypoxia induces endothelial mesenchymal transition in
pulmonary vascular remodeling. Int J Mol Med. 42:270–278.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fang S, Guo H, Cheng Y, Zhou Z, Zhang W,
Han B, Luo W, Wang J, Xie W and Chao J: circHECTD1 promotes the
silica-induced pulmonary endothelial-mesenchymal transition via
HECTD1. Cell Death Dis. 9:396. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gorton D, Govan B, Olive C and Ketheesan
N: B- and T-cell responses in group a streptococcus M-protein- or
Peptide-induced experimental carditis. Infect Immun. 77:2177–2183.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gorton D, Blyth S, Gorton JG, Govan B and
Ketheesan N: An alternative technique for the induction of
autoimmune valvulitis in a rat model of rheumatic heart disease. J
Immunol Methods. 355:80–85. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lymbury RS, Olive C, Powell KA, Good MF,
Hirst RG, LaBrooy JT and Ketheesan N: Induction of autoimmune
valvulitis in Lewis rats following immunization with peptides from
the conserved region of group A streptococcal M protein. J
Autoimmun. 20:211–217. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen A, Wen J, Lu C, Lin B, Xian S, Huang
F, Wu Y and Zeng Z: Inhibition of miR-155-5p attenuates the
valvular damage induced by rheumatic heart disease. Int J Mol Med.
45:429–440. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhan Q, Zeng Q, Song R, Zhai Y, Xu D,
Fullerton DA, Dinarello CA and Meng X: IL-37 suppresses
MyD88-mediated inflammatory responses in human aortic valve
interstitial cells. Mol Med. 23:83–91. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Blake RR, Markby GR, Culshaw GJ,
Martinez-Pereira Y, Lu CC and Corcoran BM: Survival of activated
myofibroblasts in canine myxomatous mitral valve disease and the
role of apoptosis. Res Vet Sci. 128:99–106. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pande S, Tewari P, Agarwal SK, Agarwal V,
Agrawal V, Chagtoo M, Majumdar G and Tewari S: Evidence of
apoptosis in right ventricular dysfunction in rheumatic mitral
valve stenosis. Indian J Med Res. 144:718–724. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Trihia H, Siatra H, Gklisty H,
Diamantopoulos P, Arapantoni-Dadiotis P and Kalogerakos K:
Lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma of the breast: Cytological and
histological features and review of the literature. Acta Cytol.
56:85–91. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cardiff RD, Miller CH and Munn RJ: Manual
hematoxylin and eosin staining of mouse tissue sections. Cold
Spring Harb Protoc. 2014:655–658. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Purushothaman KR, Purushothaman M,
Turnbull IC, Adams DH, Anyanwu A, Krishnan P, Kini A, Sharma SK,
O'Connor WN and Moreno PR: Association of altered collagen content
and lysyl oxidase expression in degenerative mitral valve disease.
Cardiovasc Pathol. 29:11–18. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sharma N and Toor D: Interleukin-10: Role
in increasing susceptibility and pathogenesis of rheumatic
fever/rheumatic heart disease. Cytokine. 90:169–176. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dass C and Kanmanthareddy A: Rheumatic
heart disease. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing;
Treasure Island, FL: 2020
|
|
36
|
Wu XD, Zeng ZY, Gong DP, Wen JL and Huang
F: Potential involvement of S1PR1/STAT3 signaling pathway in
cardiac valve damage due to rheumatic heart disease. Biotech
Histochem. 94:398–403. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wen Y, Zeng Z, Gui C, Li L and Li W:
Changes in the expression of Th17 cell-associated cytokines in the
development of rheumatic heart disease. Cardiovasc Pathol.
24:382–387. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chockalingam A, Gnanavelu G, Elangovan S
and Chockalingam V: Clinical spectrum of chronic rheumatic heart
disease in India. J Heart Valve Dis. 12:577–581. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Trelstad RL, Hay ED and Revel JD: Cell
contact during early morphogenesis in the chick embryo. Dev Biol.
16:78–106. 1967. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bischoff J: Endothelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. Circ Res. 124:1163–1165. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kuwahara F, Kai H, Tokuda K, Kai M,
Takeshita A, Egashira K and Imaizumi T: Transforming growth
factor-beta function blocking prevents myocardial fibrosis and
diastolic dysfunction in pressure-overloaded rats. Circulation.
106:130–135. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tsai TH, Lin CJ, Hang CL and Chen WY:
Calcitriol attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiac dysfunction and
inhibits endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in mice. Cells.
8:82019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zheng G, Cai J, Chen X, Chen L, Ge W, Zhou
X and Zhou H: Relaxin ameliorates renal fibrosis and expression of
endothelial cell transition markers in rats of
isoproterenol-induced heart failure. Biol Pharm Bull. 40:960–966.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mai JT, Hu QS, Xie Y, Su SC, Qiu Q, Yuan
WL, Yang Y, Song YW, Chen YX and Wang JF: Dyssynchronous pacing
triggers endothelial-mesenchymal transition through heterogeneity
of mechanical stretch in a canine model. Circ J. 79:201–209. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chen J, Jia J, Ma L, Li B, Qin Q, Qian J
and Ge J: Nur77 deficiency exacerbates cardiac fibrosis after
myocardial infarction by promoting endothelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. J Cell Physiol. Jun 15–2020.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
46
|
Wu Y, Xu M, Bao H and Zhang JH:
Sitagliptin inhibits EndMT in vitro and improves cardiac function
of diabetic rats through the SDF-1α/PKA pathway. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 23:841–848. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Song S, Liu L, Yu Y, Zhang R, Li Y, Cao W,
Xiao Y, Fang G, Li Z, Wang X, et al: Inhibition of BRD4 attenuates
transverse aortic constriction- and TGF-β-induced
endothelial-mesenchymal transition and cardiac fibrosis. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 127:83–96. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Liu Y, Gao L, Zhao X, Guo S, Liu Y, Li R,
Liang C, Li L, Dong J, Li L, et al: Saikosaponin A protects from
pressure overload-induced cardiac fibrosis via inhibiting
fibroblast activation or endothelial cell EndMT. Int J Biol Sci.
14:1923–1934. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lai YJ, Chen IC, Li HH and Huang CC: EP4
Agonist L-902,688 suppresses EndMT and attenuates right ventricular
cardiac fibrosis in experimental pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Int J Mol Sci. 19:192018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Wang Z, Wang Z, Gao L, Xiao L, Yao R, Du
B, Li Y, Wu L, Liang C, Huang Z, et al: miR-222 inhibits cardiac
fibrosis in diabetic mice heart via regulating
Wnt/β-catenin-mediated endothelium to mesenchymal transition. J
Cell Physiol. 235:2149–2160. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wang B, Wu Y, Ge Z, Zhang X, Yan Y and Xie
Y: NLRC5 deficiency ameliorates cardiac fibrosis in diabetic
cardiomyopathy by regulating EndMT through Smad2/3 signaling
pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 528:545–553. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Souilhol C, Harmsen MC, Evans PC and
Krenning G: Endothelial-mesenchymal transition in atherosclerosis.
Cardiovasc Res. 114:565–577. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Hao YM, Yuan HQ, Ren Z, Qu SL, Liu LS, Wei
DH, Yin K, Fu M and Jiang ZS: Endothelial to mesenchymal transition
in atherosclerotic vascular remodeling. Clin Chim Acta. 490:34–38.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Song S, Ji Y, Zhang G, Zhang X, Li B, Li D
and Jiang W: Protective effect of atazanavir sulphate against
pulmonary fibrosis in vivo and in vitro. Basic Clin Pharmacol
Toxicol. 122:199–207. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Gaikwad AV, Eapen MS, McAlinden KD, Chia
C, Larby J, Myers S, Dey S, Haug G, Markos J, Glanville AR, et al:
Endothelial to mesenchymal transition (EndMT) and vascular
remodeling in pulmonary hypertension and idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis. Expert Rev Respir Med. 14:1027–1043. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Yu J, Deng Y and Han M: Blocking protein
phosphatase 2A with a peptide protects mice against
bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Exp Lung Res. 46:234–242.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhong A, Mirzaei Z and Simmons CA: The
roles of matrix stiffness and β-catenin signaling in
endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition of aortic valve endothelial
cells. Cardiovasc Eng Technol. 9:158–167. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Wylie-Sears J, Aikawa E, Levine RA, Yang
JH and Bischoff J: Mitral valve endothelial cells with osteogenic
differentiation potential. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
31:598–607. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ci HB, Ou ZJ, Chang FJ, Liu DH, He GW, Xu
Z, Yuan HY, Wang ZP, Zhang X and Ou JS: Endothelial microparticles
increase in mitral valve disease and impair mitral valve
endothelial function. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 304:E695–E702.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Shapero K, Wylie-Sears J, Levine RA, Mayer
JE Jr and Bischoff J: Reciprocal interactions between mitral valve
endothelial and interstitial cells reduce
endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition and myofibroblastic
activation. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 80:175–185. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Bischoff J, Casanovas G, Wylie-Sears J,
Kim DH, Bartko PE, Guerrero JL, Dal-Bianco JP, Beaudoin J, Garcia
ML, Sullivan SM, et al: CD45 expression in mitral valve endothelial
cells after myocardial infarction. Circ Res. 119:1215–1225. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Lan Y, Liu B, Yao H, Li F, Weng T, Yang G,
Li W, Cheng X, Mao N and Yang X: Essential role of endothelial
Smad4 in vascular remodeling and integrity. Mol Cell Biol.
27:7683–7692. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Zeisberg M, Hanai J, Sugimoto H, Mammoto
T, Charytan D, Strutz F and Kalluri R: BMP-7 counteracts
TGF-beta1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and reverses
chronic renal injury. Nat Med. 9:964–968. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Grieskamp T, Rudat C, Lüdtke TH, Norden J
and Kispert A: Notch signaling regulates smooth muscle
differentiation of epicardium-derived cells. Circ Res. 108:813–823.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Li H, Zhao Q, Chang L, Wei C, Bei H, Yin
Y, Chen M, Wang H, Liang J and Wu Y: LncRNA MALAT1 modulates ox-LDL
induced EndMT through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Lipids
Health Dis. 18:622019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Rivera-Feliciano J, Lee KH, Kong SW,
Rajagopal S, Ma Q, Springer Z, Izumo S, Tabin CJ and Pu WT:
Development of heart valves requires Gata4 expression in
endothelial-derived cells. Development. 133:3607–3618. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Jiang Y, Zhou X, Hu R and Dai A:
TGF-β1-induced SMAD2/3/4 activation promotes RELM-β transcription
to modulate the endothelium-mesenchymal transition in human
endothelial cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 105:52–60. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Pickup MW, Owens P and Moses HL: TGF-β,
bone morphogenetic protein, and activin signaling and the tumor
microenvironment. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 9:92017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Morianos I, Papadopoulou G, Semitekolou M
and Xanthou G: Activin-A in the regulation of immunity in health
and disease. J Autoimmun. 104:1023142019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Goh BC, Singhal V, Herrera AJ, Tomlinson
RE, Kim S, Faugere MC, Germain-Lee EL, Clemens TL, Lee SJ and
DiGirolamo DJ: Activin receptor type 2A (ACVR2A) functions directly
in osteoblasts as a negative regulator of bone mass. J Biol Chem.
292:13809–13822. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Peinado H, Quintanilla M and Cano A:
Transforming growth factor beta-1 induces snail transcription
factor in epithelial cell lines: Mechanisms for epithelial
mesenchymal transitions. J Biol Chem. 278:21113–21123. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Song S, Zhang R, Cao W, Fang G, Yu Y, Wan
Y, Wang C, Li Y and Wang Q: Foxm1 is a critical driver of
TGF-β-induced EndMT in endothelial cells through Smad2/3 and binds
to the Snail promoter. J Cell Physiol. 234:9052–9064. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Zheng X, Peng M, Li Y, Wang X, Lu W, Wang
X, Shan Y, Li R, Gao L and Qiu C: Cathelicidin-related
antimicrobial peptide protects against cardiac fibrosis in diabetic
mice heart by regulating endothelial-mesenchymal transition. Int J
Biol Sci. 15:2393–2407. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Mammoto T, Muyleart M, Konduri GG and
Mammoto A: Twist1 in hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension through
transforming growth factor-β-Smad signaling. Am J Respir Cell Mol
Biol. 58:194–207. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Zhu GH, Li R, Zeng Y, Zhou T, Xiong F and
Zhu M: MicroRNA-142-3p inhibits high-glucose-induced
endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition through targeting TGF-β1/Smad
pathway in primary human aortic endothelial cells. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 11:1208–1217. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|