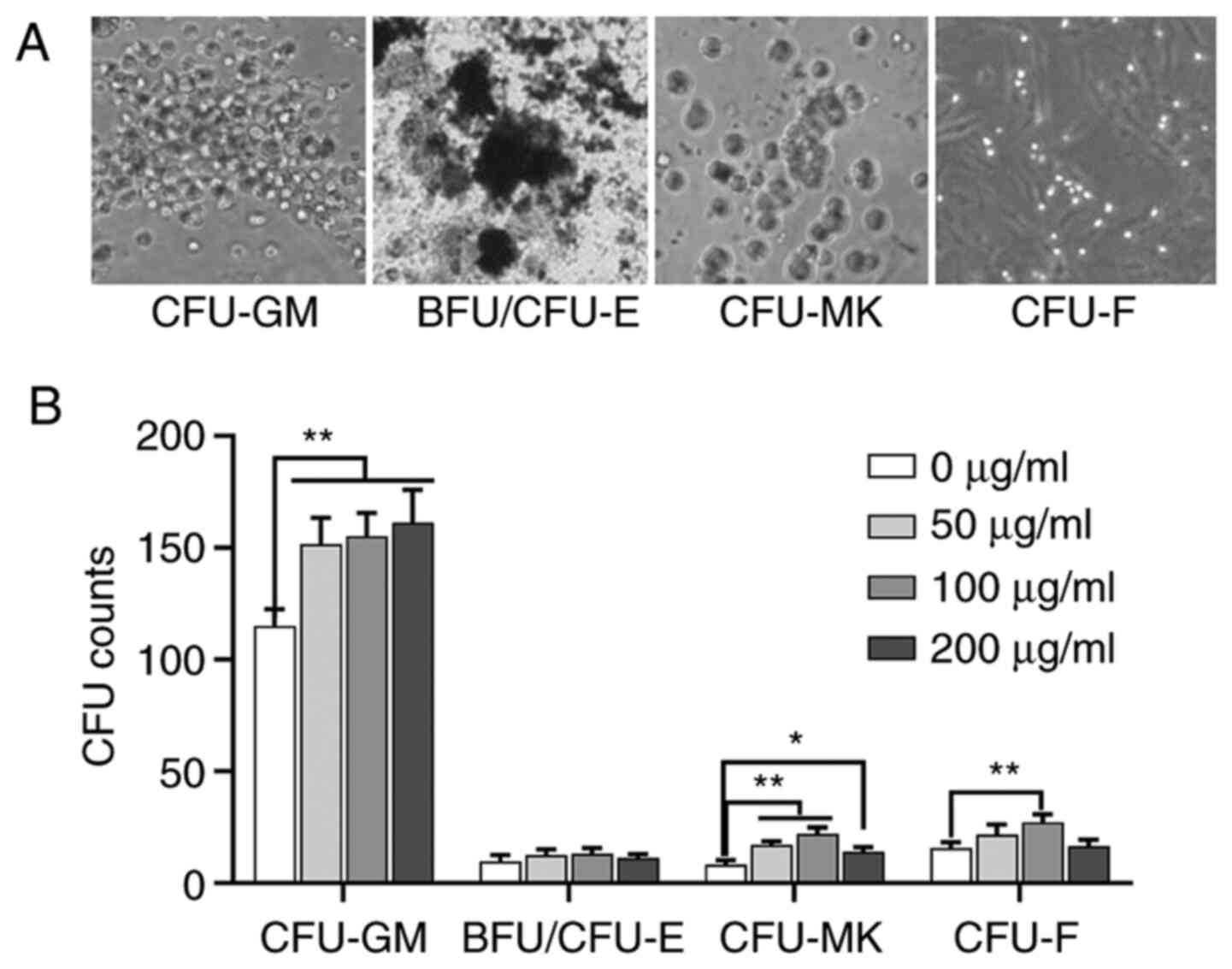
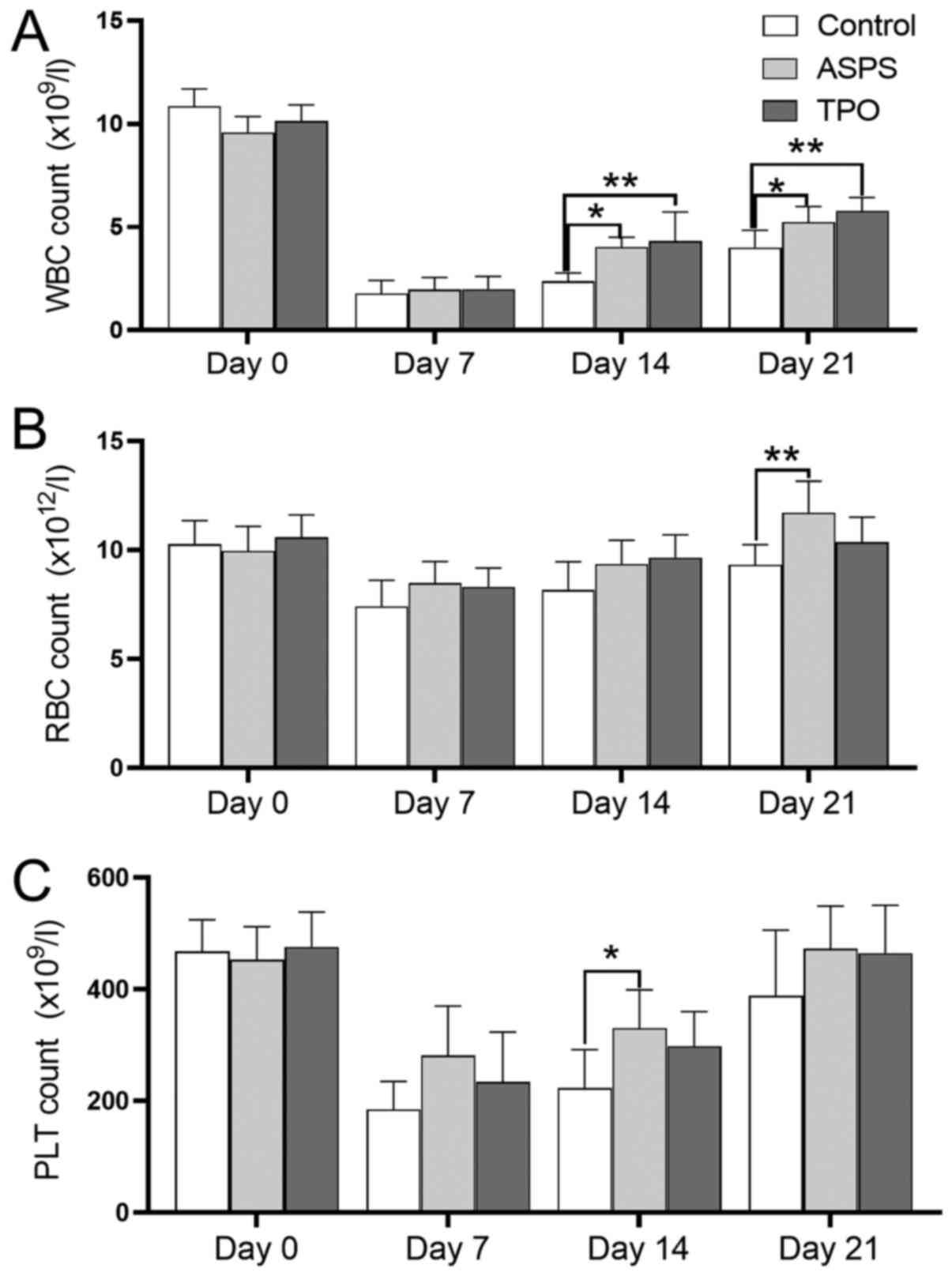
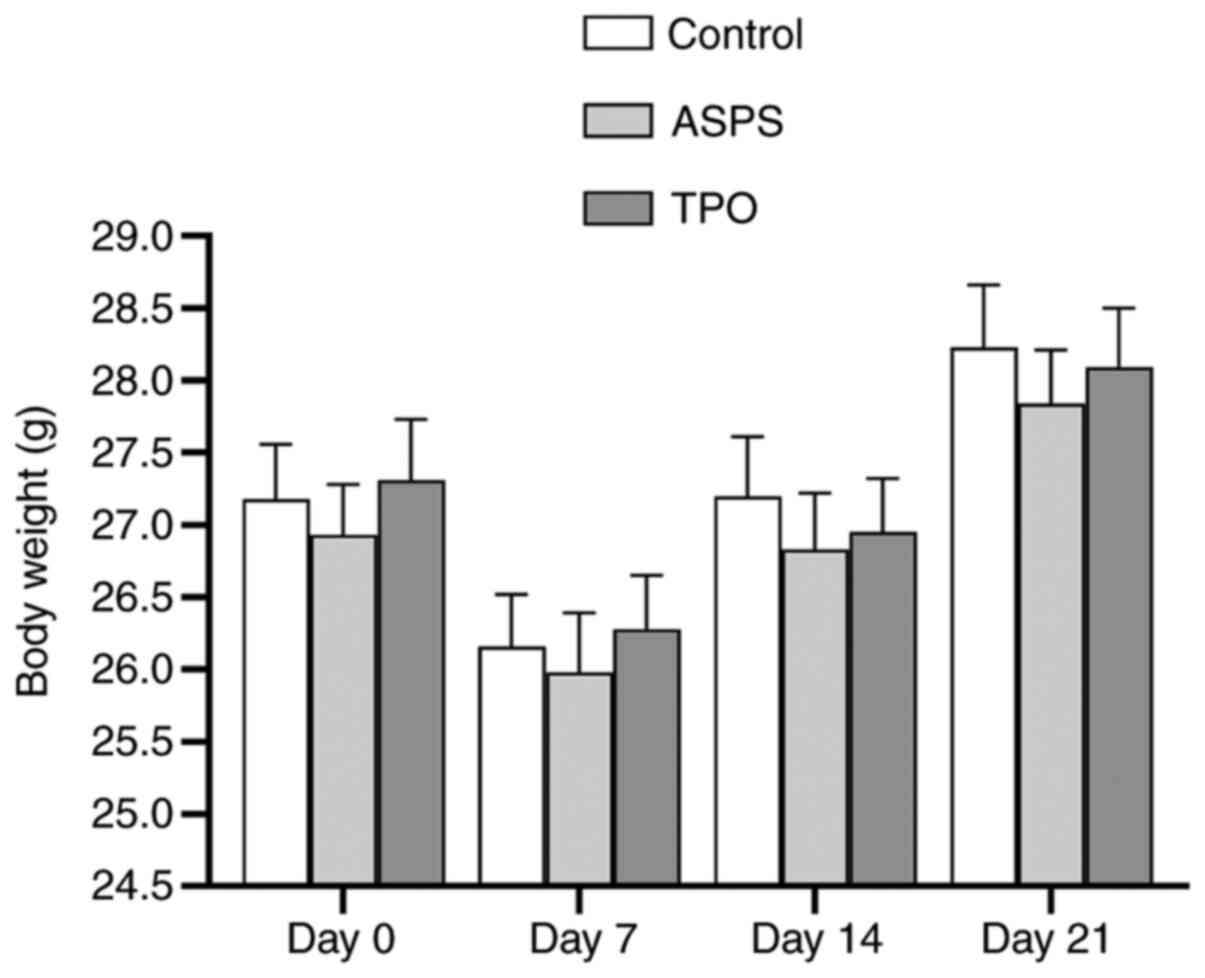
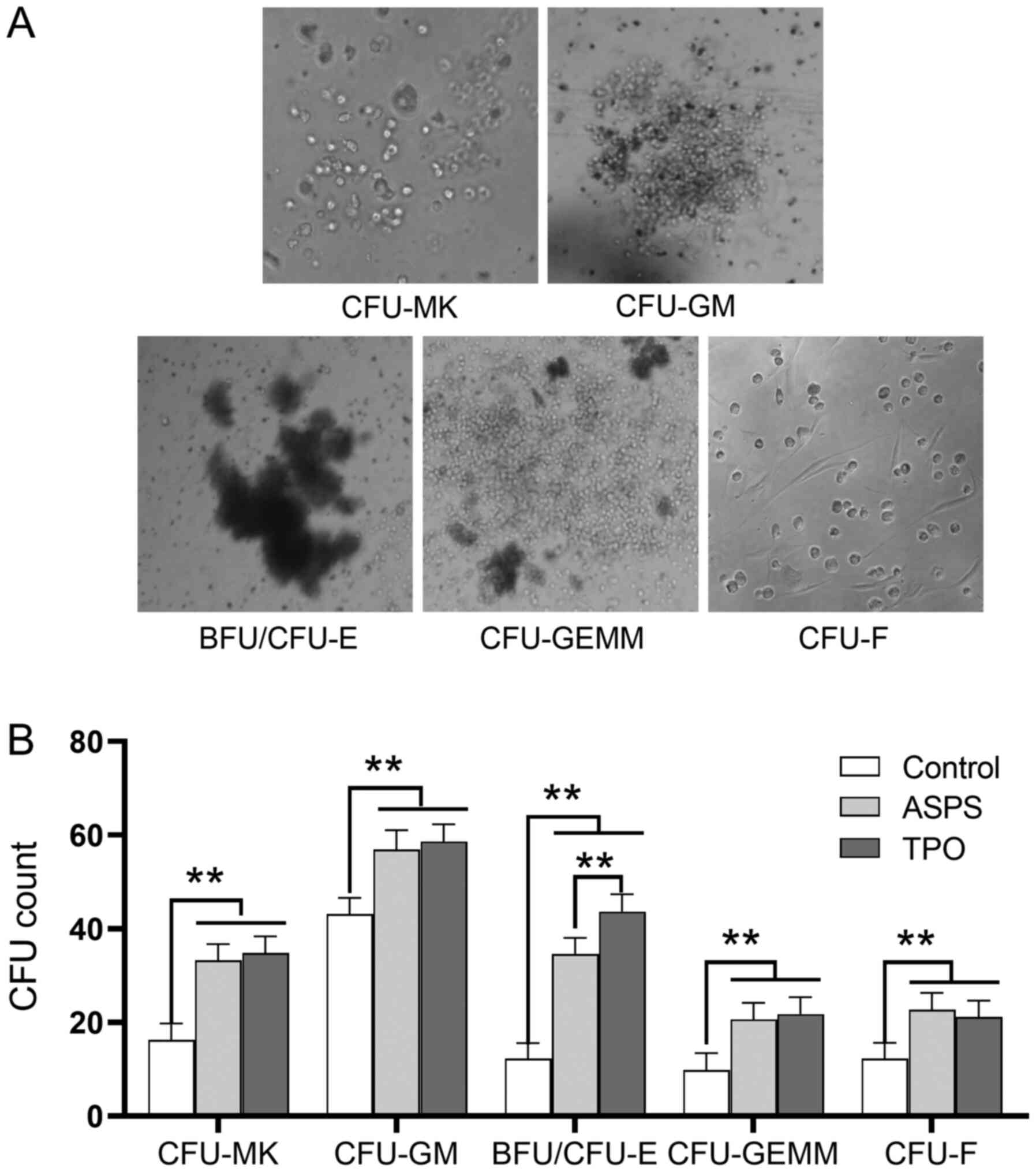
|
1
|
Liebman HA: Thrombocytopenia in cancer
patients. Thromb Res. 133 (Suppl 2):S63–S69. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lieberman L, Bercovitz RS, Sholapur NS,
Heddle NM, Stanworth SJ and Arnold DM: Platelet transfusions for
critically ill patients with thrombocytopenia. Blood.
123:1146–1151; quiz 1280. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cines DB, Gernsheimer T, Wasser J, Godeau
B, Provan D, Lyons R, Altomare I, Wang X and Lopez A: Integrated
analysis of long-term safety in patients with chronic immune
thrombocytopaenia (ITP) treated with the thrombopoietin (TPO)
receptor agonist romiplostim. Int J Hematol. 102:259–270. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Arnold DM, Vrbensky JR, Karim N, Smith JW,
Liu Y, Ivetic N, Kelton JG and Nazy I: The effect of rituximab on
anti-platelet autoantibody levels in patients with immune
thrombocytopenia. Br J Haematol. 178:302–307. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Aubron C, Flint AW, Bailey M, Pilcher D,
Cheng AC, Hegarty C, Martinelli A, Reade MC, Bellomo R and
McQuilten Z: Is platelet transfusion associated with
hospital-acquired infections in critically ill patients? Crit Care.
21:22017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Scheinberg P, Singulane CC, Barbosa LS and
Scheinberg M: Successful platelet count recovery in
lupus-associated thrombocytopenia with the thrombopoietin agonist
eltrombopag. Clin Rheumatol. 33:1347–1349. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shin SK, Pack SP, Oh JG, Kang NK, Chang
MH, Chung YH, Kim SJ, Lee JW and Heo TH: Anti-erythropoietin and
anti-thrombopoietin antibodies induced after administration of
recombinant human erythropoietin. Int Immunopharmacol.
11:2237–2241. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gong AG, Li N, Lau KM, Lee PS, Yan L, Xu
ML, Lam CT, Kong AY, Lin HQ, Dong TT, et al: Calycosin orchestrates
the functions of Danggui Buxue Tang, a Chinese herbal decoction
composing of Astragali Radix and Angelica Sinensis Radix: An
evaluation by using calycosin-knock out herbal extract. J
Ethnopharmacol. 168:150–157. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lin HQ, Gong AG, Wang HY, Duan R, Dong TT,
Zhao KJ and Tsim KW: Danggui Buxue Tang (Astragali Radix and
Angelicae Sinensis Radix) for menopausal symptoms: A review. J
Ethnopharmacol. 199:205–210. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu C, Li J, Meng FY, Liang SX, Deng R, Li
CK, Pong NH, Lau CP, Cheng SW, Ye JY, et al: Polysaccharides from
the root of Angelica sinensis promotes hematopoiesis and
thrombopoiesis through the PI3K/AKT pathway. BMC Complement Altern
Med. 10:792010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang M, Chan GC, Deng R, Ng MH, Cheng SW,
Lau CP, Ye JY, Wang L and Liu C: An herbal decoction of Radix
astragali and Radix angelicae sinensis promotes hematopoiesis and
thrombopoiesis. J Ethnopharmacol. 124:87–97. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhao M, Zhang ZF, Ding Y, Wang JB and Li
Y: Astragalus polysaccharide improves palmitate-induced insulin
resistance by inhibiting PTP1B and NF-κB in
C2C12 myotubes. Molecules. 17:7083–7092.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xie JH, Jin ML, Morris GA, Zha XQ, Chen
HQ, Yi Y, Li JE, Wang ZJ, Gao J, Nie SP, et al: Advances on
bioactive polysaccharides from medicinal plants. Crit Rev Food Sci
Nutr. 56 (Suppl 1):S60–S84. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
National Research Council, . Guide for the
Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. National Academies Press;
Washington, DC: 1985
|
|
15
|
Yuan S, Piao X, Li D, Kim S, Lee H and Guo
P: Effects of dietary Astragalus polysaccharide on growth
performance and immune function in weaned pigs. Anim Sci.
82:501–507. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Staub A: Removeal of protein-Sevag method.
Methods Carbohydr Chem. 5:5–6. 1965.
|
|
17
|
Inagaki K, Oda T, Naka Y, Shinkai H,
Komatsu N and Iwamura H: Induction of megakaryocytopoiesis and
thrombocytopoiesis by JTZ-132, a novel small molecule with
thrombopoietin mimetic activities. Blood. 104:58–64. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ye JY, Chan GC, Qiao L, Lian Q, Meng FY,
Luo XQ, Khachigian LM, Ma M, Deng R, Chen JL, et al:
Platelet-derived growth factor enhances platelet recovery in a
murine model of radiation-induced thrombocytopenia and reduces
apoptosis in megakaryocytes via its receptors and the PI3-k/Akt
pathway. Haematologica. 95:1745–1753. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang M, Li K, Chui CM, Yuen PM, Chan PK,
Chuen CK, Li CK and Fok TF: Expression of interleukin (IL) 1 type I
and type II receptors in megakaryocytic cells and enhancing effects
of IL-1beta on megakaryocytopoiesis and NF-E2 expression. Br J
Haematol. 111:371–380. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang M, Li K, Ng PC, Chuen CK, Lau TK,
Cheng YS, Liu YS, Li CK, Yuen PM, James AE, et al: Promoting
effects of serotonin on hematopoiesis: Ex vivo expansion of cord
blood CD34+ stem/progenitor cells, proliferation of bone
marrow stromal cells, and antiapoptosis. Stem Cells. 25:1800–1806.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li K, Sung RY, Huang WZ, Yang M, Pong NH,
Lee SM, Chan WY, Zhao H, To MY, Fok TF, et al: Thrombopoietin
protects against in vitro and in vivo cardiotoxicity induced by
doxorubicin. Circulation. 113:2211–2220. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Porter AG and Jänicke RU: Emerging roles
of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 6:99–104. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang J, Zhou S, Zhou Y, Feng F, Wang Q,
Zhu X, Zhao J, Fu H, Lv M, Ai H, et al: Adipose-derived mesenchymal
stem cells (ADSCs) with the potential to ameliorate platelet
recovery, enhance megakaryopoiesis, and inhibit apoptosis of bone
marrow cells in a mouse model of radiation-induced
thrombocytopenia. Cell Transplant. 25:261–273. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
MacVittie TJ, Farese AM, Smith WG, Baum
CM, Burton E and McKearn JP: Myelopoietin, an engineered chimeric
IL-3 and G-CSF receptor agonist, stimulates multilineage
hematopoietic recovery in a nonhuman primate model of
radiation-induced myelosuppression. Blood. 95:837–845. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
He X, Shu J, Xu L, Lu C and Lu A:
Inhibitory effect of Astragalus polysaccharides on
lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-α and IL-1β production in THP-1
cells. Molecules. 17:3155–3164. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xue H, Gan F, Zhang Z, Hu J, Chen X and
Huang K: Astragalus polysaccharides inhibits PCV2 replication by
inhibiting oxidative stress and blocking NF-κB pathway. Int J Biol
Macromol. 81:22–30. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Han L, Wang HX and Lu MI: Effect of
Astragalus polysaccharide on LPS-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis by
inhibiting NF-κB and JNK signaling pathway. Chinese Pharmacol Bull.
34:243–249. 2018.
|
|
28
|
Chuen CK, Li K, Yang M, Fok TF, Li CK,
Chui CM and Yuen PM: Interleukin-1β up-regulates the expression of
thrombopoietin and transcription factors c-Jun, c-Fos, GATA-1, and
NF-E2 in megakaryocytic cells. J Lab Clin Med. 143:75–88. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xiao B, Xu Y, He H, Jiang QL, Li SY, Shu
HY, Liang EY, Yi ZS, Ye JY, Huang LF, et al: Anti-apoptotic effect
of Astragalus Polysaccharide on myeloid cells. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue
Ye Xue Za Zhi. 21:1243–1247. 2013.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang M, Jiang Q, Xiao B, Liu C, Li S,
Huang L, Chong B and Meng F: Astragalus polysaccharide has
hematopoietic and thrombopoietic activities in an irradiation mouse
model. Blood. 122:42162013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Jiang X, Zeng L, Huang J, Zhou H and Liu
Y: Arctigenin, a natural lignan compound, induces apoptotic death
of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via suppression of PI3-K/Akt
signaling. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 29:458–464. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu R, Ding L, Yu MH, Wang HQ, Li WC, Cao
Z, Zhang P, Yao BC, Tang J, Ke Q, et al: Effects of
dihydrotestosterone on adhesion and proliferation via PI3-K/Akt
signaling in endothelial progenitor cells. Endocrine. 46:634–643.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Martini M, De Santis MC, Braccini L,
Gulluni F and Hirsch E: PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and cancer: An
updated review. Ann Med. 46:372–383. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hu C, Xu M, Qin R, Chen W and Xu X:
Wogonin induces apoptosis and endoplasmic reticulum stress in HL-60
leukemia cells through inhibition of the PI3K-AKT signaling
pathway. Oncol Rep. 33:3146–3154. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ma W, Wang DD, Li L, Feng YK, Gu HM, Zhu
GM, Piao JH, Yang Y, Gao X and Zhang PX: Caveolin-1 plays a key
role in the oleanolic acid-induced apoptosis of HL-60 cells. Oncol
Rep. 32:293–301. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu Y, Bi T, Wang G, Dai W, Wu G, Qian L,
Gao Q and Shen G: Lupeol inhibits proliferation and induces
apoptosis of human pancreatic cancer PCNA-1 cells through AKT/ERK
pathways. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 388:295–304. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hitchcock IS and Kaushansky K:
Thrombopoietin from beginning to end. Br J Haematol. 165:259–268.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Pulikkan JA, Madera D, Xue L, Bradley P,
Landrette SF, Kuo YH, Abbas S, Zhu LJ, Valk P and Castilla LH:
Thrombopoietin/MPL participates in initiating and maintaining
RUNX1-ETO acute myeloid leukemia via PI3K/AKT signaling. Blood.
120:868–879. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chan KY, Xiang P, Zhou L, Li K, Ng PC,
Wang CC, Zhang L, Deng HY, Pong NH, Zhao H, et al: Thrombopoietin
protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy, improves
cardiac function, and reversely alters specific signalling
networks. Eur J Heart Fail. 13:366–376. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Su RJ, Zhang XB, Li K, Yang M, Li CK, Fok
TF, James AE, Pong H and Yuen PM: Platelet-derived growth factor
promotes ex vivo expansion of CD34+ cells from human
cord blood and enhances long-term culture-initiating cells,
non-obese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficient repopulating
cells and formation of adherent cells. Br J Haematol. 117:735–746.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ye JY, Liang EY, Cheng YS, Chan GC, Ding
Y, Meng F, Ng MH, Chong BH, Lian Q and Yang M: Serotonin enhances
megakaryopoiesis and proplatelet formation via p-Erk1/2 and F-actin
reorganization. Stem Cells. 32:2973–2982. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kilkenny C, Browne WJ, Cuthill IC, Emerson
M and Altman DG: Improving bioscience research reporting: The
ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. J Pharmacol
Pharmacother. 1:94–99. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|