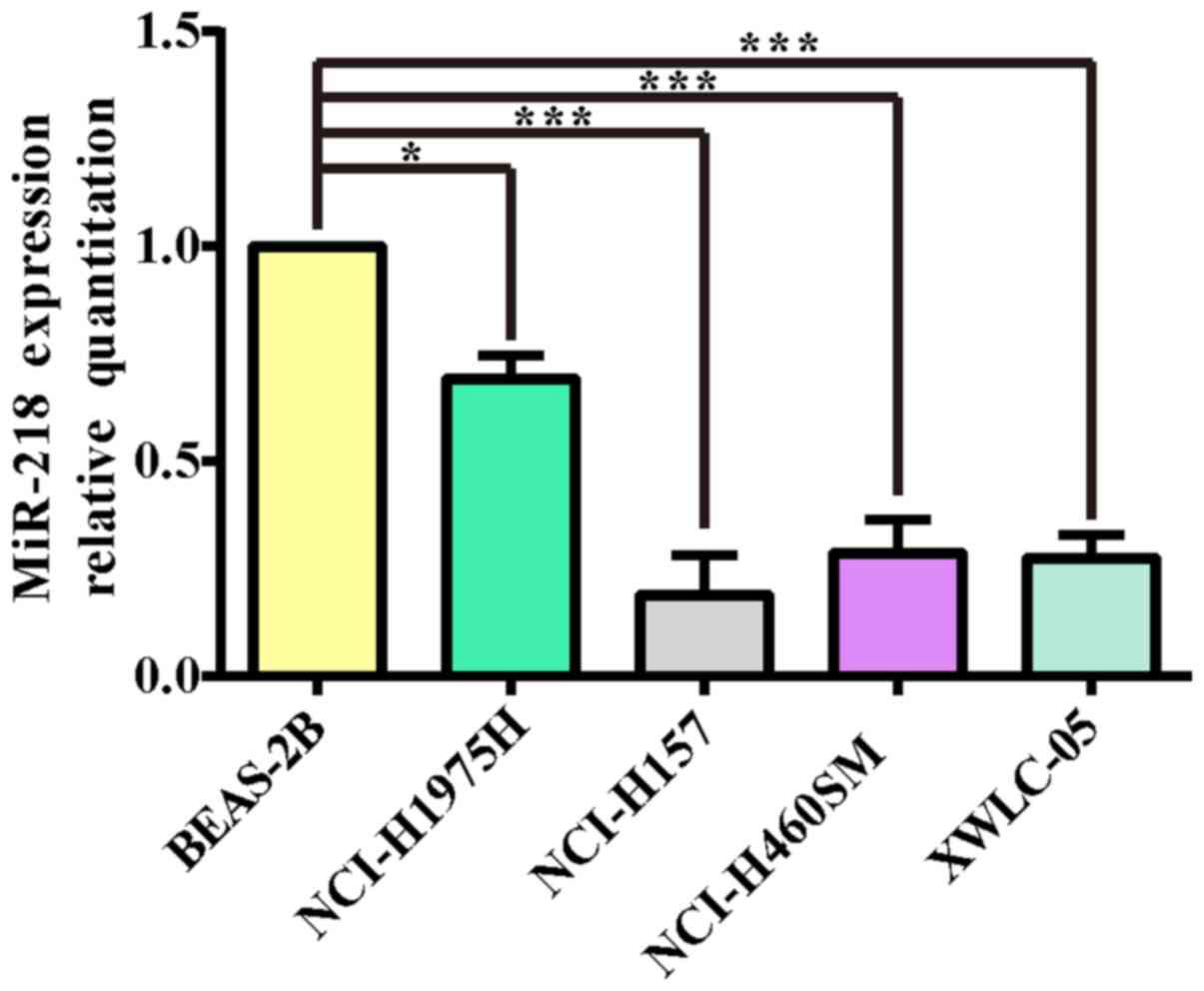
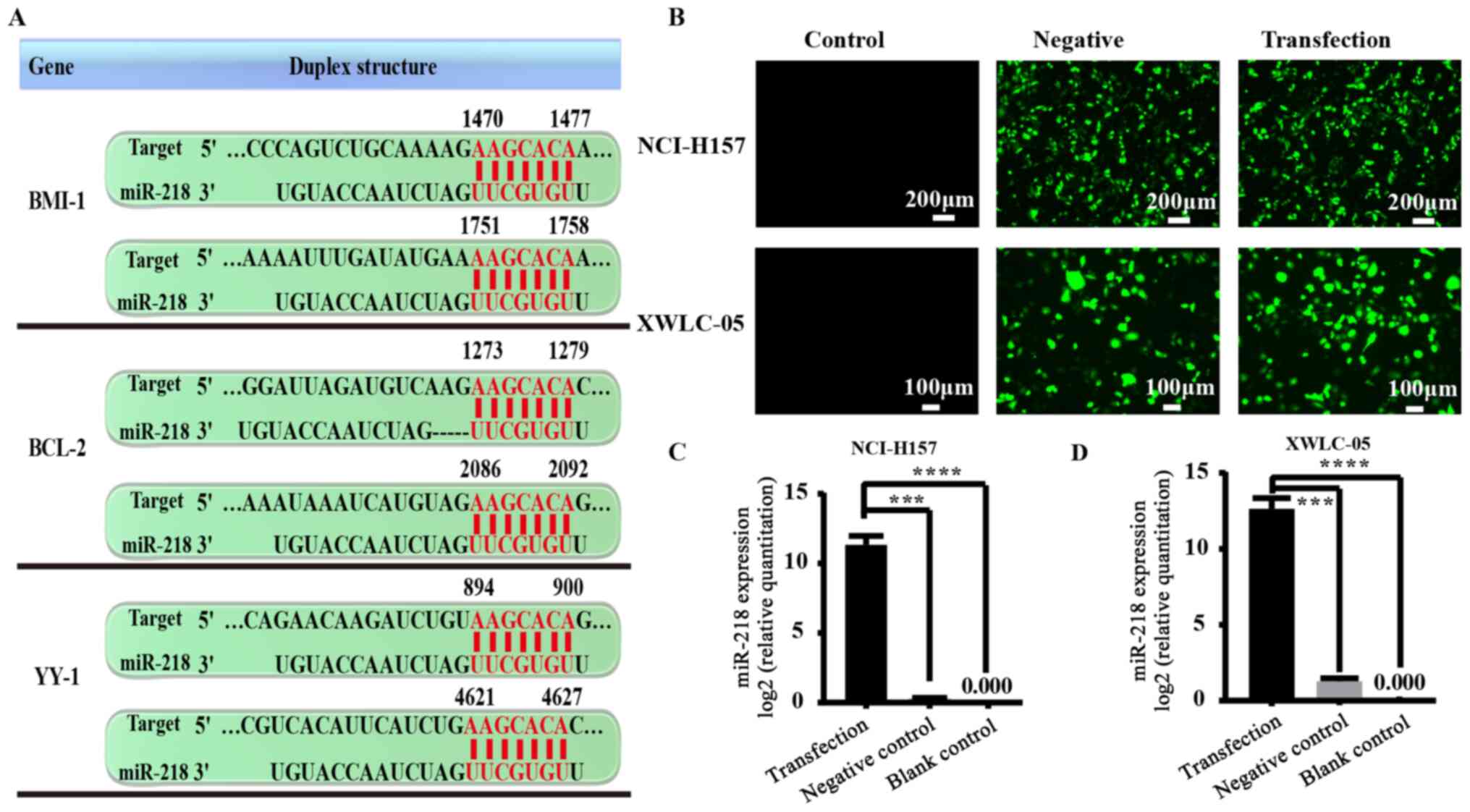
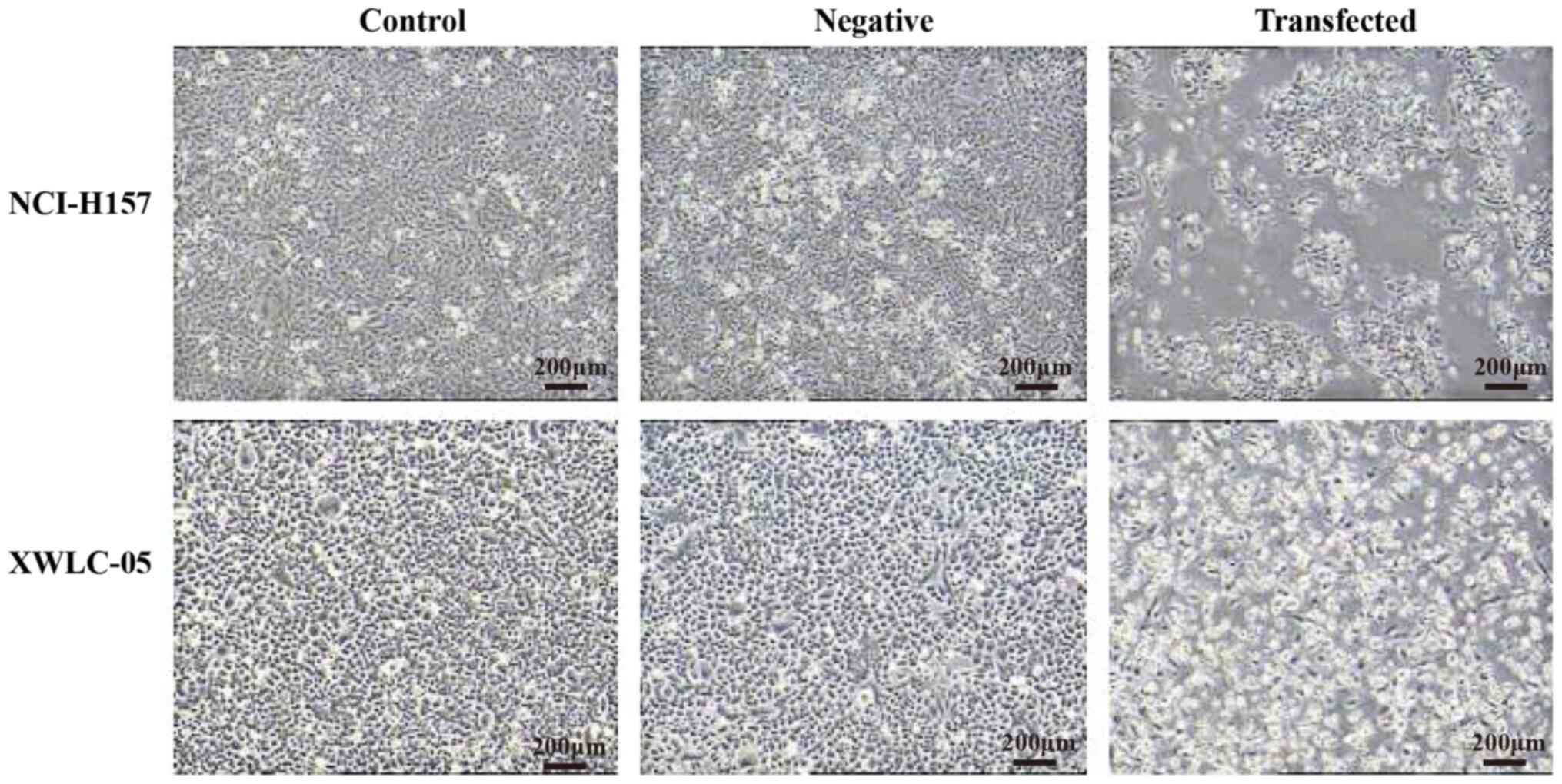
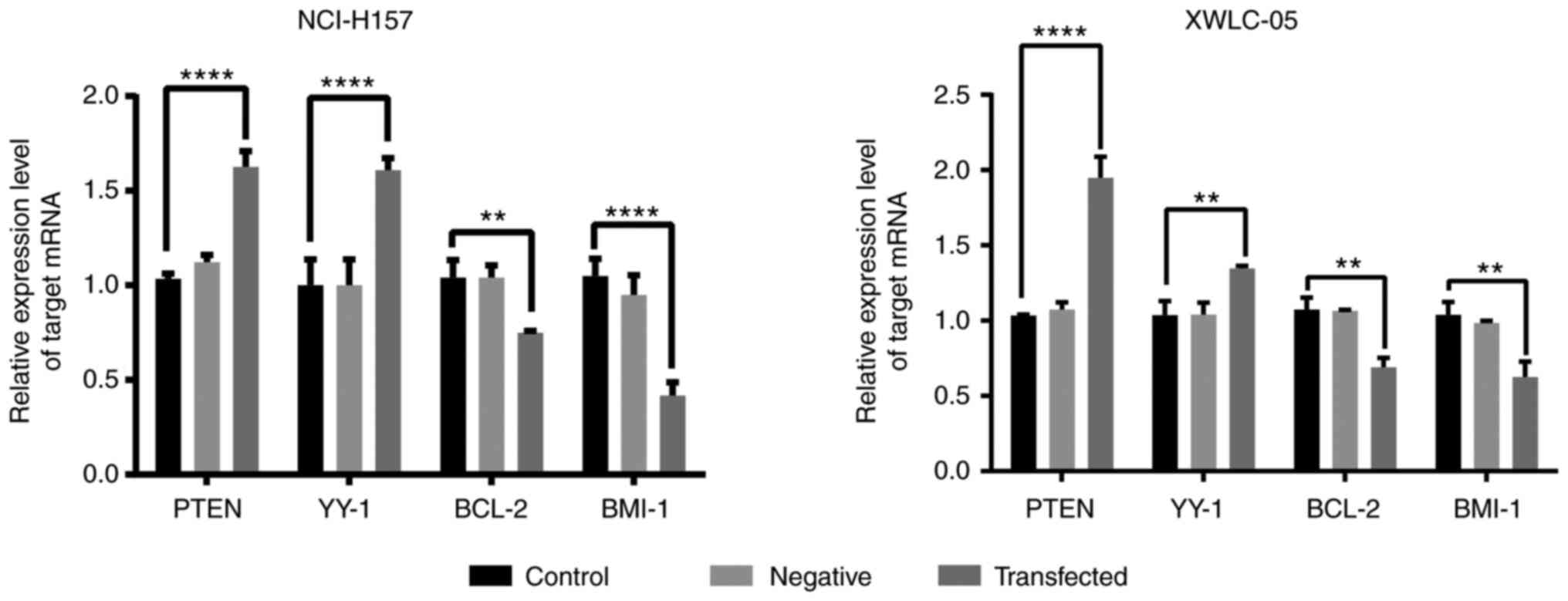
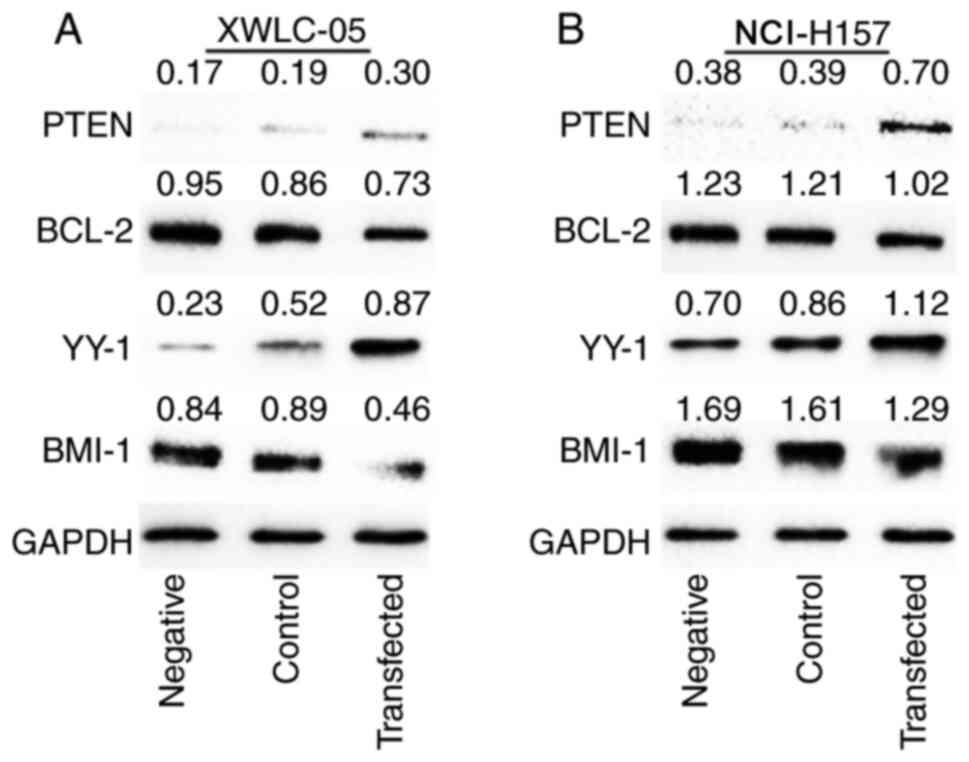
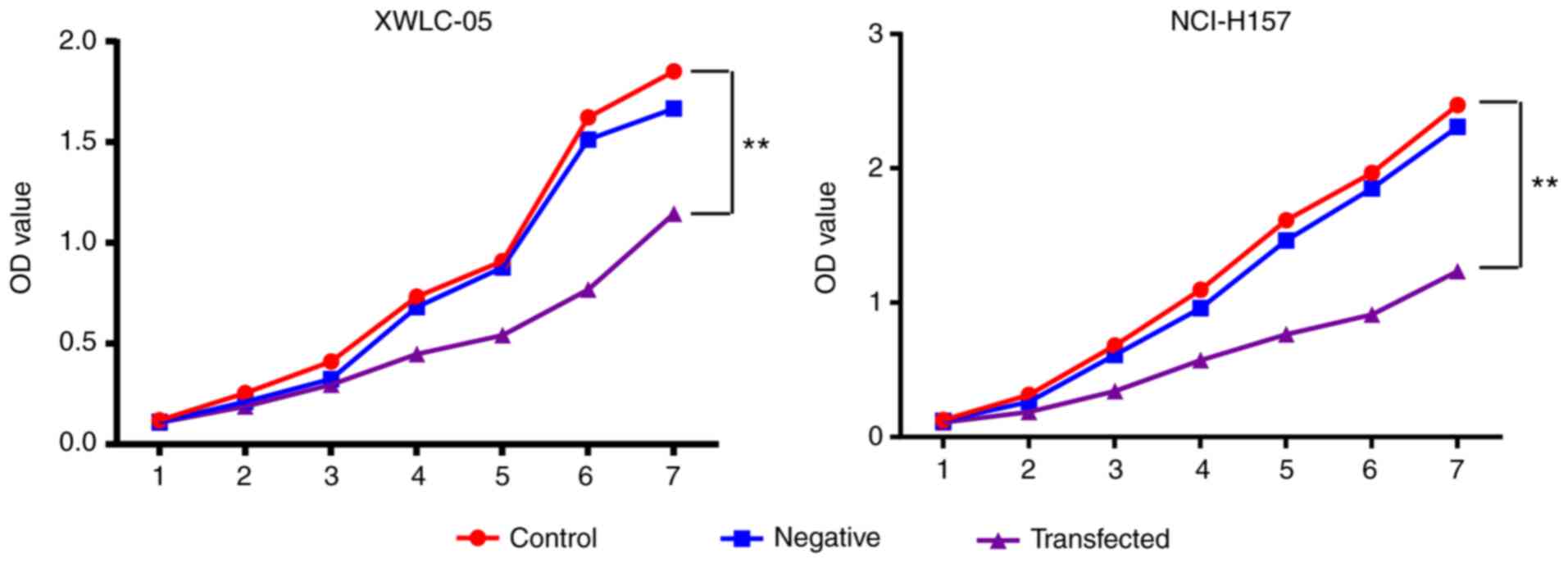
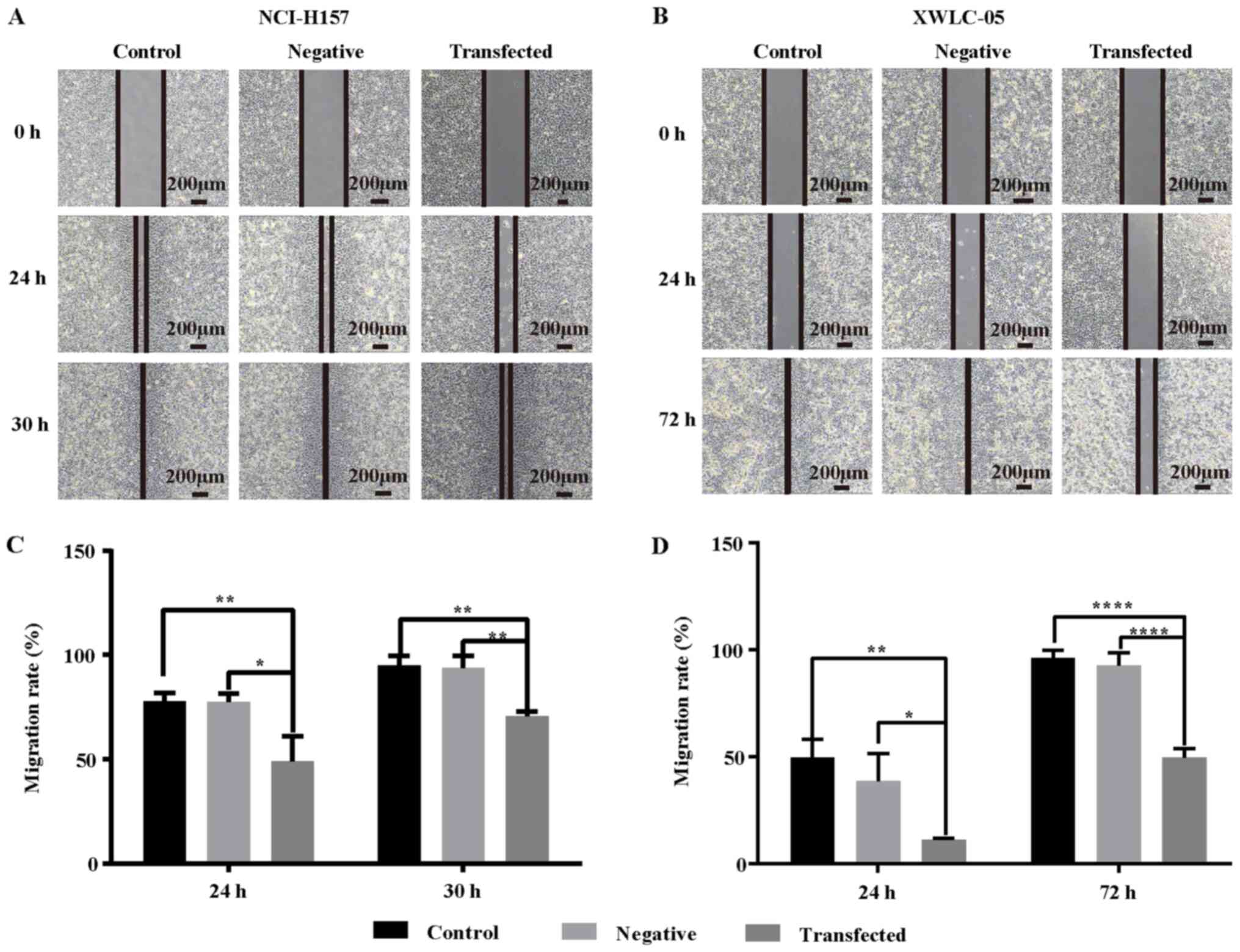
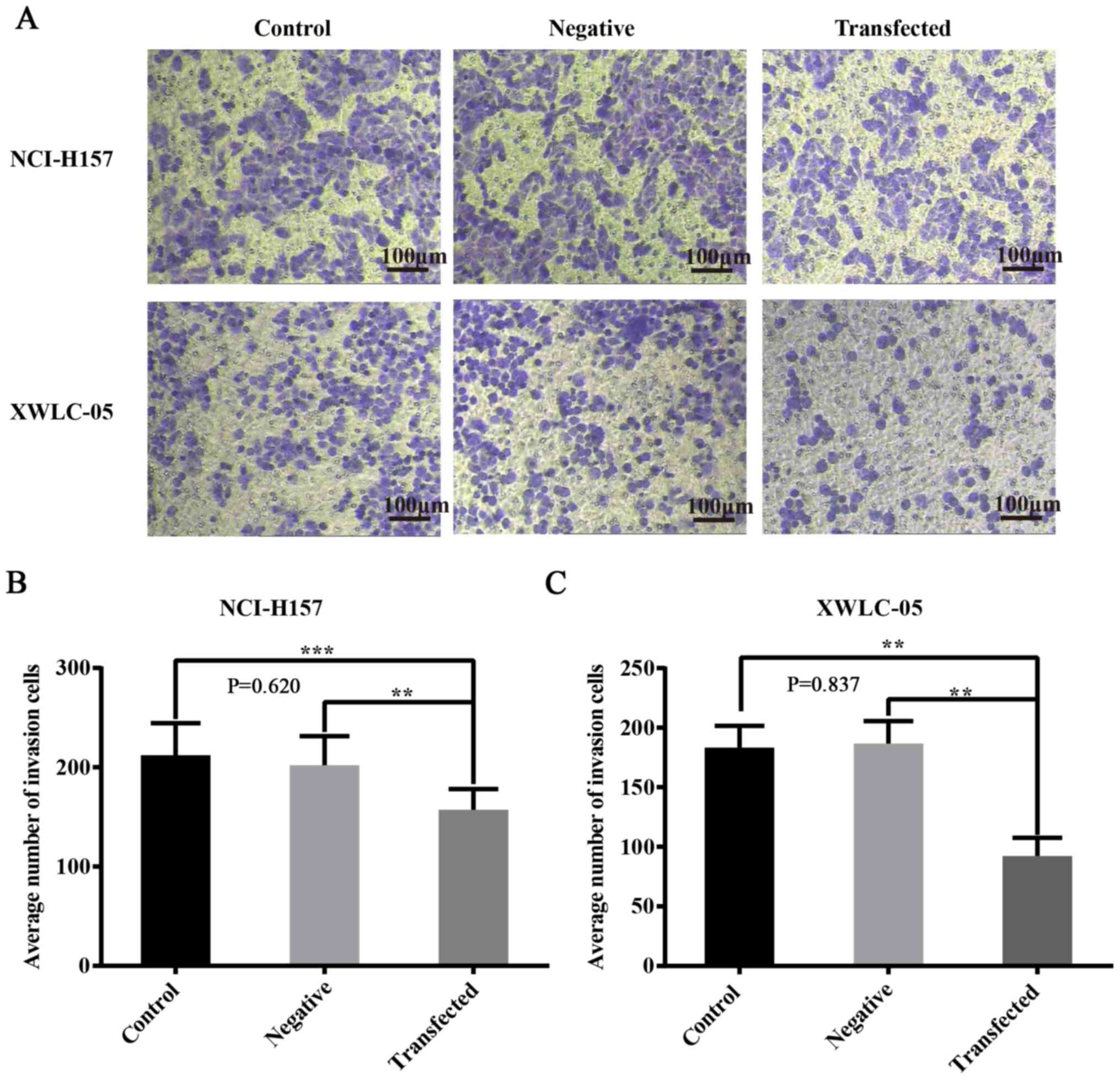
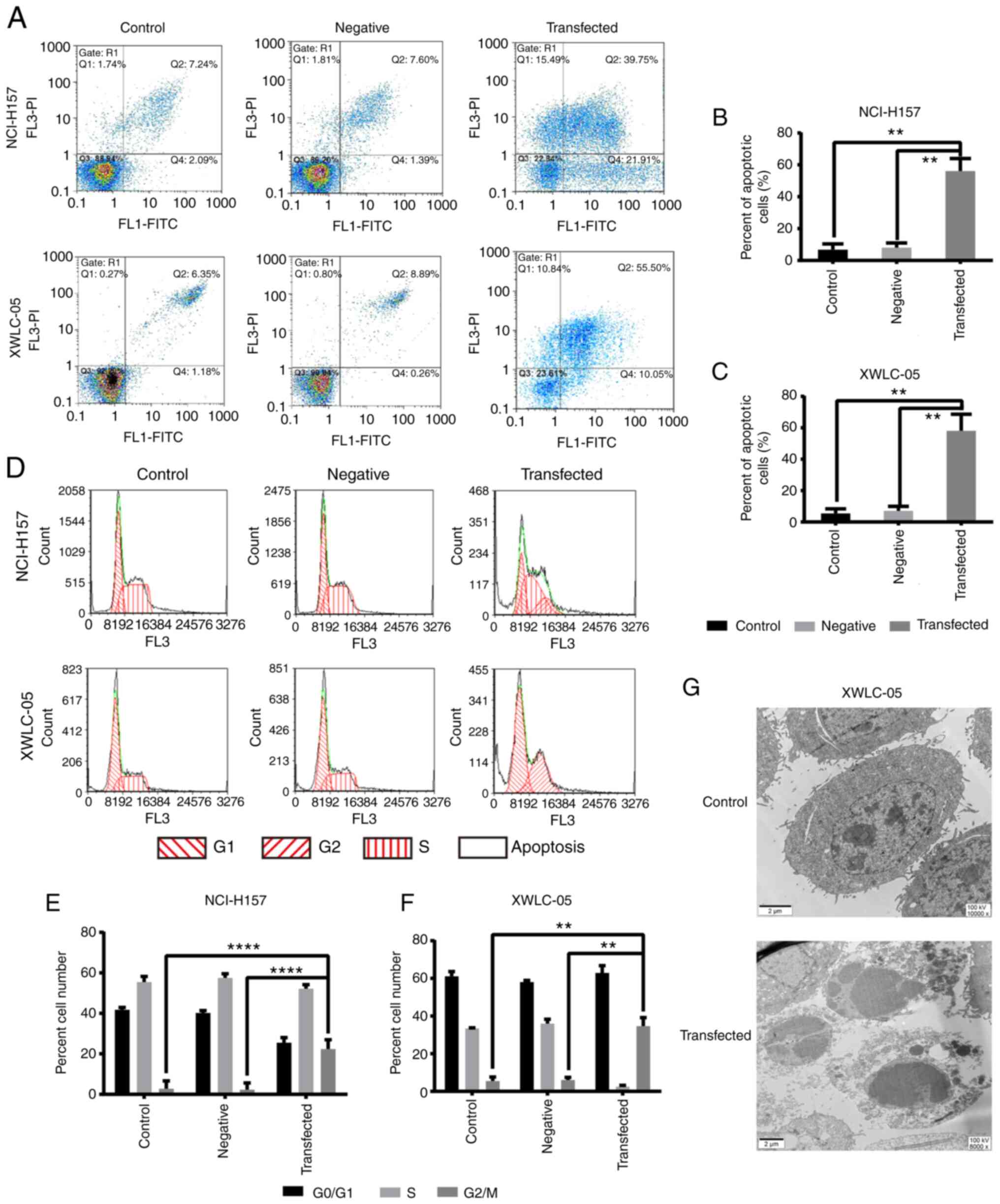
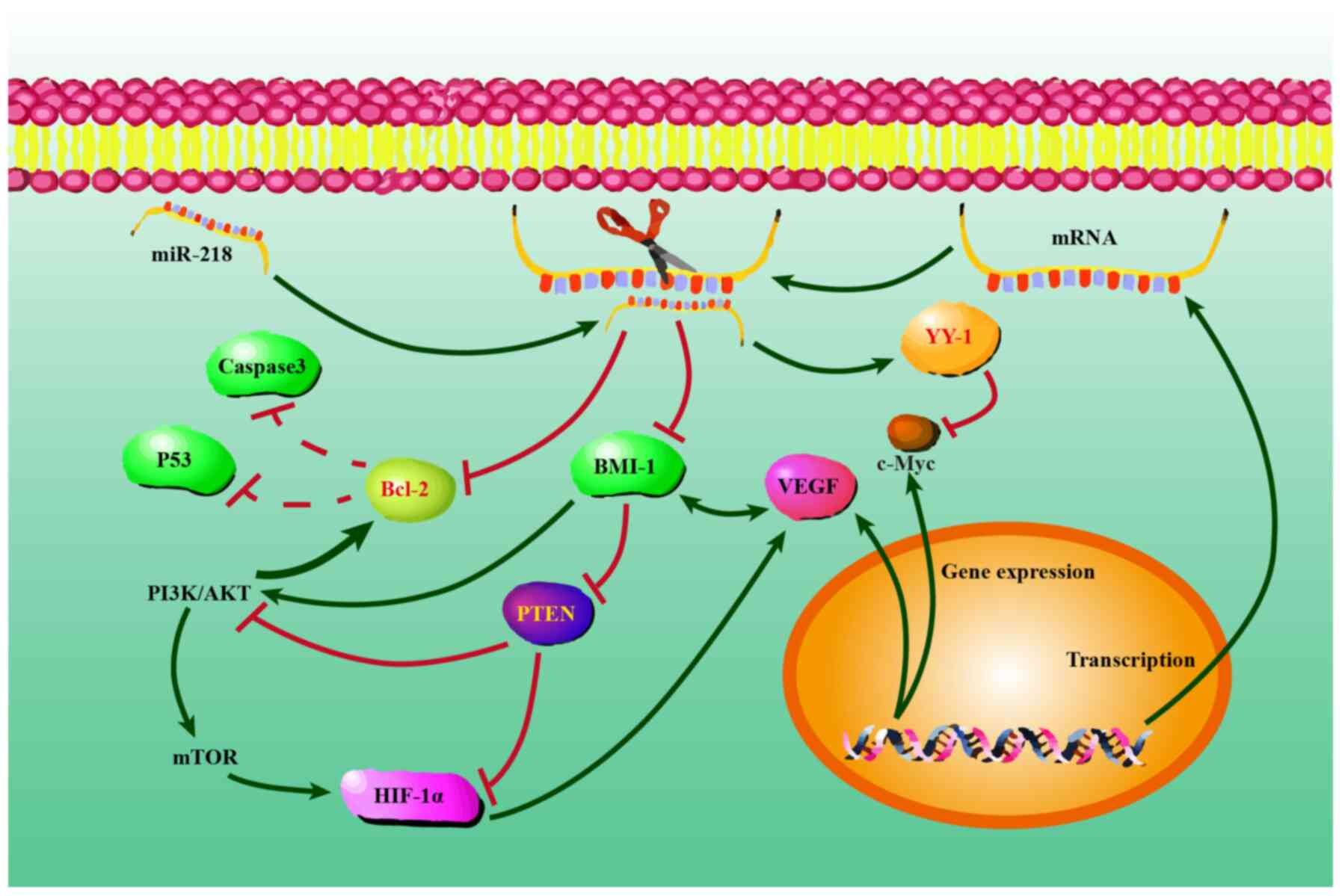
|
1
|
Miller KD, Nogueira L, Mariotto AB,
Rowland JH, Yabroff KR, Alfano CM, Jemal A, Kramer JL and Siegel
RL: Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J
Clin. 69:363–385. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li J, Guo W, Ran J, Tang R, Lin H, Chen X,
Ning B, Li J, Zhou Y, Chen LC, et al: Five-year lung cancer
mortality risk analysis and topography in Xuan Wei: A
spatiotemporal correlation analysis. BMC Public Health. 19:1732019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cao Y and Gao H: Prevalence and causes of
air pollution and lung cancer in Xuanwei City and Fuyuan County,
Yunnan Province, China. Front Med. 6:217–220. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xiao Y, Shao Y, Yu X and Zhou G: The
epidemic status and risk factors of lung cancer in Xuanwei City,
Yunnan Province, China. Front Med. 6:388–394. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang J, Duan Y, Meng QH, Gong R, Guo C,
Zhao Y and Zhang Y: Integrated analysis of DNA methylation
profiling and gene expression profiling identifies novel markers in
lung cancer in Xuanwei, China. PLoS One. 13:e02031552018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li J, Ran J, Chen LC, Costa M, Huang Y,
Chen X and Tian L: Bituminous coal combustion and Xuan Wei Lung
cancer: A review of the epidemiology, intervention, carcinogens,
and carcinogenesis. Arch Toxicol. 93:573–583. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang Y, Chen K, Zhou Y, Hu Z, Chen S and
Huang Y: Application of serum microRNA-9-5p, 21-5p, and 223-3p
combined with tumor markers in the diagnosis of non-small-cell lung
cancer in Yunnan in southwestern China. OncoTargets Ther.
11:587–597. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yan FC, Wang QQ, Ruan YH, Ma LJ, Jia JT,
Jin KW and Chin J: Establishment and biological characteristics of
lung cancer cell line XWLC-05. Ai Zheng. 26:21–25. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lei J, Li QH, Yang JL, Liu F, Wang L, Xu
WM and Zhao WX: The antitumor effects of oncolytic adenovirus H101
against lung cancer. Int J Oncol. 47:555–562. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xiong G, Chen X, Zhang Q, Fang Y, Chen W,
Li C and Zhang J: RNA interference influenced the proliferation and
invasion of XWLC-05 lung cancer cells through inhibiting aquaporin
3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 485:627–634. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang Y, He S, Mei R, Kang Y, Duan J, Wei
R, Xiang C, Wu Y, Lu X, Cai Z, et al: miR 29a suppresses IL 13
induced cell invasion by inhibiting YY1 in the AKT pathway in lung
adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Oncol Rep. 39:2613–2623. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cai L, Lin S, Girard L, Zhou Y, Yang L, Ci
B, Zhou Q, Luo D, Yao B, Tang H, et al: LCE: An open web portal to
explore gene expression and clinical associations in lung cancer.
Oncogene. 38:2551–2564. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tie J, Pan Y, Zhao L, Wu K, Liu J, Sun S,
Guo X, Wang B, Gang Y, Zhang Y, et al: MiR-218 inhibits invasion
and metastasis of gastric cancer by targeting the Robo1 receptor.
PLoS Genet. 6:e10008792010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ: Oncomirs
- microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:259–269. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL and Ambros V: The C.
elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense
complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pu M, Chen J, Tao Z, Miao L, Qi X, Wang Y
and Ren J: Regulatory network of miRNA on its target: Coordination
between transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of gene
expression. Cell Mol Life Sci. 76:441–451. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mestdagh P, Boström AK, Impens F, Fredlund
E, Van Peer G, De Antonellis P, von Stedingk K, Ghesquière B,
Schulte S, Dews M, et al: The miR-17-92 microRNA cluster regulates
multiple components of the TGF-β pathway in neuroblastoma. Mol
Cell. 40:762–773. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Naeli P, Yousefi F, Ghasemi Y,
Savardashtaki A and Mirzaei H: The role of microRNAs in lung
cancer: Implications for diagnosis and therapy. Curr Mol Med.
20:90–101. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Uddin A and Chakraborty S: Role of miRNAs
in lung cancer. J Cell Physiol. April 20–2018.(Epub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lin PY, Yu SL and Yang PC: MicroRNA in
lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 103:1144–1148. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xu LF, Wu ZP, Chen Y, Zhu QS, Hamidi S and
Navab R: MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) regulates cellular proliferation,
invasion, migration, and apoptosis by targeting PTEN, RECK and
Bcl-2 in lung squamous carcinoma, Gejiu City, China. PLoS One.
9:e1036982014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Deng M, Zeng C, Lu X, He X, Zhang R, Qiu
Q, Zheng G, Jia X, Liu H and He Z: miR-218 suppresses gastric
cancer cell cycle progression through the CDK6/Cyclin D1/E2F1 axis
in a feedback loop. Cancer Lett. 403:175–185. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Guan B, Wu K, Zeng J, Xu S, Mu L, Gao Y,
Wang K, Ma Z, Tian J, Shi Q, et al: Tumor-suppressive microRNA-218
inhibits tumor angiogenesis via targeting the mTOR component RICTOR
in prostate cancer. Oncotarget. 8:8162–8172. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jun GJ, Zhong GG and Ming ZS: miR-218
inhibits the proliferation of glioma U87 cells through the
inactivation of the CDK6/cyclin D1/p21Cip1/Waf1 pathway. Oncol
Lett. 9:2743–2749. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tu K, Li C, Zheng X, Yang W, Yao Y and Liu
Q: Prognostic significance of miR-218 in human hepatocellular
carcinoma and its role in cell growth. Oncol Rep. 32:1571–1577.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu B, Tian Y, Li F, Zhao Z, Jiang X, Zhai
C, Han X and Zhang L: Tumor-suppressing roles of miR-214 and
miR-218 in breast cancer. Oncol Rep. 35:3178–3184. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang T, Xu L, Jia R and Wei J: MiR-218
suppresses the metastasis and EMT of HCC cells via targeting
SERBP1. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 49:383–391. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang X, Shi H, Tang H, Fang Z, Wang J and
Cui S: miR-218 inhibits the invasion and migration of colon cancer
cells by targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Int J Mol
Med. 35:1301–1308. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Davidson MR, Larsen JE, Yang IA, Hayward
NK, Clarke BE, Duhig EE, Passmore LH, Bowman RV and Fong KM:
MicroRNA-218 is deleted and downregulated in lung squamous cell
carcinoma. PLoS One. 5:e125602010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wu DW, Cheng YW, Wang J, Chen CY and Lee
H: Paxillin predicts survival and relapse in non-small cell lung
cancer by microRNA-218 targeting. Cancer Res. 70:10392–10401. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang Y, Ding L, Hu Q, Xia J, Sun J, Wang
X, Xiong H, Gurbani D, Li L, Liu Y, et al: MicroRNA-218 functions
as a tumor suppressor in lung cancer by targeting IL-6/STAT3 and
negatively correlates with poor prognosis. Mol Cancer. 16:1412017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shi ZM, Wang L, Shen H, Jiang CF, Ge X, Li
DM, Wen YY, Sun HR, Pan MH, Li W, et al: Downregulation of miR-218
contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor
metastasis in lung cancer by targeting Slug/ZEB2 signaling.
Oncogene. 36:2577–2588. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhu K, Ding H, Wang W, Liao Z, Fu Z, Hong
Y, Zhou Y, Zhang CY and Chen X: Tumor-suppressive miR-218-5p
inhibits cancer cell proliferation and migration via EGFR in
non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget. 7:28075–28085. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Song L, Li D, Zhao Y, Gu Y, Zhao D, Li X,
Bai X, Sun Y, Zhang X, Sun H, et al: miR-218 suppressed the growth
of lung carcinoma by reducing MEF2D expression. Tumour Biol.
37:2891–2900. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chiu KL, Kuo TT, Kuok QY, Lin YS, Hua CH,
Lin CY, Su PY, Lai LC and Sher YP: ADAM9 enhances CDCP1 protein
expression by suppressing miR-218 for lung tumor metastasis. Sci
Rep. 5:164262015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xie J, Yu F, Li D, Zhu X, Zhang X and Lv
Z: MicroRNA-218 regulates cisplatin (DPP) chemosensitivity in
non-small cell lung cancer by targeting RUNX2. Tumour Biol.
37:1197–1204. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang C, Ge S, Hu C, Yang N and Zhang J:
MiRNA-218, a new regulator of HMGB1, suppresses cell migration and
invasion in non-small cell lung cancer. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin
(Shanghai). 45:1055–1061. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zeng F, Wang Q, Wang S, Liang S, Huang W,
Guo Y, Peng J, Li M, Zhu W and Guo L: Linc00173 promotes
chemoresistance and progression of small cell lung cancer by
sponging miR-218 to regulate Etk expression. Oncogene. 39:293–307.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jin X, Liu X, Zhang Z and Guan Y: lncRNA
CCAT1 acts as a microRNA-218 sponge to increase gefitinib
resistance in NSCLC by targeting HOXA1. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids.
19:1266–1275. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu Z, Lu C, Zhao G, Han X, Dong K, Wang
C, Guan J-Z and Wang Z: Downregulation of miR-218 by nicotine
promotes cell proliferation through targeting CDK6 in non-small
cell lung cancer. J Cell Biochem. 120:18370–18377. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li YJ, Zhang W, Xia H, Zhang BS, Chen P,
Zhao YL and Li J: miR-218 suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition by targeting Robo1 and Ecop in lung adenocarcinoma
cells. Future Oncol. 13:2571–2582. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Singh R, Letai A and Sarosiek K:
Regulation of apoptosis in health and disease: The balancing act of
BCL-2 family proteins. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 20:175–193. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Radha G and Raghavan SC: BCL2: A promising
cancer therapeutic target. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer.
1868:309–314. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hata AN, Engelman JA and Faber AC: The
BCL2 family: Key mediators of the apoptotic response to targeted
anticancer therapeutics. Cancer Discov. 5:475–487. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wang M-C, Li C-L, Cui J, Jiao M, Wu T,
Jing LI and Nan K-J: BMI-1, a promising therapeutic target for
human cancer. Oncol Lett. 10:583–588. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Meng X, Wang Y, Zheng X, Liu C, Su B, Nie
H, Zhao B, Zhao X and Yang H: shRNA-mediated knockdown of Bmi-1
inhibit lung adenocarcinoma cell migration and metastasis. Lung
Cancer. 77:24–30. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Siddique HR and Saleem M: Role of BMI1, a
stem cell factor, in cancer recurrence and chemoresistance:
Preclinical and clinical evidences. Stem Cells. 30:372–378. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Gkountakos A, Sartori G, Falcone I, Piro
G, Ciuffreda L, Carbone C, Tortora G, Scarpa A, Bria E, Milella M,
et al: PTEN in lung cancer: Dealing with the problem, building on
new knowledge and turning the game around. Cancers (Basel).
11:11412019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Álvarez-Garcia V, Tawil Y, Wise HM and
Leslie NR: Mechanisms of PTEN loss in cancer: It's all about
diversity. Semin Cancer Biol. 59:66–79. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Papa A and Pandolfi PP: The PTEN-PI3K axis
in cancer. Biomolecules. 9:1532019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Sarvagalla S, Kolapalli SP and
Vallabhapurapu S: The two sides of YY1 in cancer: A friend and a
foe. Front Oncol. 9:12302019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wang CC, Tsai MF, Hong TM, Chang GC, Chen
CY, Yang WM, Chen JJW and Yang PC: The transcriptional factor YY1
upregulates the novel invasion suppressor HLJ1 expression and
inhibits cancer cell invasion. Oncogene. 24:4081–4093. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Huang T, Wang G, Yang L, Peng B, Wen Y,
Ding G and Wang Z: Transcription factor YY1 modulates lung cancer
progression by activating lncRNA-PVT1. DNA Cell Biol. 36:947–958.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Liu J, Blackhall F, Seiden-Long I,
Jurisica I, Navab R, Liu N, Radulovich N, Wigle D, Sultan M, Hu J,
et al: Modeling of lung cancer by an orthotopically growing H460SM
variant cell line reveals novel candidate genes for systemic
metastasis. Oncogene. 23:6316–6324. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Li W, Wang W, Ding M, Zheng X, Ma S and
Wang X: MiR-1244 sensitizes the resistance of non-small cell lung
cancer A549 cell to cisplatin. Cancer Cell Int. 16:302016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Liang CC, Park AY and Guan JL: In vitro
scratch assay: A convenient and inexpensive method for analysis of
cell migration in vitro. Nat Protoc. 2:329–333. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Vermeulen R, Downward GS, Zhang J, Hu W,
Portengen L, Bassig BA, Hammond SK, Wong JYY, Li J, Reiss B, et al:
Constituents of household air pollution and risk of lung cancer
among never-smoking women in Xuanwei and Fuyuan, China. Environ
Health Perspect. 127:970012019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Chen G, Sun X, Ren H, Wan X, Huang H, Ma
X, Ning B, Zou X, Hu W and Yang G: The mortality patterns of lung
cancer between 1990 and 2013 in Xuanwei, China. Lung Cancer.
90:155–160. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Shao C, Yang F, Qin Z, Jing X, Shu Y and
Shen H: The value of miR-155 as a biomarker for the diagnosis and
prognosis of lung cancer: A systematic review with meta-analysis.
BMC Cancer. 19:11032019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Bica-Pop C, Cojocneanu-Petric R, Magdo L,
Raduly L, Gulei D and Berindan-Neagoe I: Overview upon miR-21 in
lung cancer: Focus on NSCLC. Cell Mol Life Sci. 75:3539–3551. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Zhou B, Yuan W and Li X: Long intergenic
noncoding RNA 319 (linc00319) promotes cell proliferation and
invasion in lung cancer cells by directly downregulating the tumor
suppressor miR-32. Oncol Rese. Aug 11–2017.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Zhang L, Liao Y and Tang L: MicroRNA-34
family: A potential tumor suppressor and therapeutic candidate in
cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:532019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Lu YF, Zhang L, Waye MMY, Fu WM and Zhang
JF: MiR-218 mediates tumorigenesis and metastasis: Perspectives and
implications. Exp Cell Res. 334:173–182. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
He X, Dong Y, Wu CW, Zhao Z, Ng SSM, Chan
FKL, Sung JJY and Yu J: MicroRNA-218 inhibits cell cycle
progression and promotes apoptosis in colon cancer by
downregulating BMI1 polycomb ring finger oncogene. Mol Med.
18:1491–1498. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Hu Y, Xu K and Yagüe E: miR-218 targets
survivin and regulates resistance to chemotherapeutics in breast
cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 151:269–280. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Zarogoulidis P, Petanidis S, Kioseoglou E,
Domvri K, Anestakis D and Zarogoulidis K: miR-205 and miR-218
expression is associated with carboplatin chemoresistance and
regulation of apoptosis via Mcl-1 and Survivin in lung cancer
cells. Cell Signal. 27:1576–1588. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Song LB, Li J, Liao WT, Feng Y, Yu CP, Hu
LJ, Kong QL, Xu LH, Zhang X, Liu WL, et al: The polycomb group
protein Bmi-1 represses the tumor suppressor PTEN and induces
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human nasopharyngeal
epithelial cells. J Clin Invest. 119:3626–3636. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Choi Y, Zhang J, Murga C, Yu H, Koller E,
Monia BP, Gutkind JS and Li W: PTEN, but not SHIP and SHIP2,
suppresses the PI3K/Akt pathway and induces growth inhibition and
apoptosis of myeloma cells. Oncogene. 21:5289–5300. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Lu XX, Cao LY, Chen X, Xiao J, Zou Y and
Chen Q: PTEN inhibits cell proliferation, promotes cell apoptosis,
and induces cell cycle arrest via downregulating the PI3K/AKT/
hTERT pathway in lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. BioMed Res Int.
2016:24768422016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Gao Y, Sun L, Wu Z, Xuan C, Zhang J, You Y
and Chen X: miR-218 inhibits the proliferation of human glioma
cells through downregulation of Yin Yang 1. Mol Med Rep.
17:1926–1932. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Wang CC, Tsai MF, Dai TH, Hong TM, Chan
WK, Chen JJW and Yang PC: Synergistic activation of the tumor
suppressor, HLJ1, by the transcription factors YY1 and activator
protein 1. Cancer Res. 67:4816–4826. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Tan H, Huang S, Zhang Z, Qian X, Sun P and
Zhou X: Pan-cancer analysis on microRNA-associated gene activation.
EBioMedicine. 43:82–97. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Jacobs JJ, Scheijen B, Voncken JW, Kieboom
K, Berns A and van Lohuizen M: Bmi-1 collaborates with c-Myc in
tumorigenesis by inhibiting c-Myc-induced apoptosis via INK4a/ARF.
Genes Dev. 13:2678–2690. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Shrivastava A, Saleque S, Kalpana GV,
Artandi S, Goff SP and Calame K: Inhibition of transcriptional
regulator Yin-Yang-1 by association with c-Myc. Science.
262:1889–1892. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Austen M, Cerni C, Lüscher-Firzlaff JM and
Lüscher B: YY1 can inhibit c-Myc function through a mechanism
requiring DNA binding of YY1 but neither its transactivation domain
nor direct interaction with c-Myc. Oncogene. 17:511–520. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Guo BH, Feng Y, Zhang R, Xu LH, Li MZ,
Kung HF, Song LB and Zeng MS: Bmi-1 promotes invasion and
metastasis, and its elevated expression is correlated with an
advanced stage of breast cancer. Mol Cancer. 10:102011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Xu L, Li Y, Yan D, He J and Liu D:
MicroRNA-183 inhibits gastric cancer proliferation and invasion via
directly targeting Bmi-1. Oncol Lett. 8:2345–2351. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
He Z, Xia Y, Pan C, Ma T, Liu B, Wang J,
Chen L and Chen Y: Up-regulation of miR-452 inhibits metastasis of
non-small cell lung cancer by regulating BMI1. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 37:387–398. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Guo S, Xu X, Tang Y, Zhang C, Li J, Ouyang
Y, Ju J, Bie P and Wang H: miR-15a inhibits cell proliferation and
epithelial to mesenchymal transition in pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma by down-regulating Bmi-1 expression. Cancer Lett.
344:40–46. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Tu Y, Gao X, Li G, Fu H, Cui D, Liu H, Jin
W and Zhang Y: MicroRNA-218 inhibits glioma invasion, migration,
proliferation, and cancer stem-like cell self-renewal by targeting
the polycomb group gene Bmi1. Cancer Res. 73:6046–6055. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Li X, Yang Z, Song W, Zhou L, Li Q, Tao K,
Zhou J, Wang X, Zheng Z, You N, et al: Overexpression of Bmi-1
contributes to the invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular
carcinoma by increasing the expression of matrix metalloproteinase
(MMP) 2, MMP-9 and vascular endothelial growth factor via the
PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway. Int J Oncol. 43:793–802. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Zhou Y, Wang X, Huang Y, Chen Y, Zhao G,
Yao Q, Jin C, Huang Y, Liu X and Li G: Down-regulated SOX4
expression suppresses cell proliferation, metastasis and induces
apoptosis in Xuanwei female lung cancer patients. J Cell Biochem.
116:1007–1018. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Wang D, Hao T, Pan Y, Qian X and Zhou D:
Increased expression of SOX4 is a biomarker for malignant status
and poor prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Mol
Cell Biochem. 402:75–82. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Li R, Liu Y, Wang T, Tang J, Xie L, Yao Z,
Li K, Liao Y, Zhou L, Geng Z, et al: The characteristics of lung
cancer in Xuanwei County: A review of differentially expressed
genes and noncoding RNAs on cell proliferation and migration.
Biomed Pharmacother. 119:1093122019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Hu Z, Wang X, Yang Y, Zhao Y, Shen Z and
Huang Y: MicroRNA expression profiling of lung adenocarcinoma in
Xuanwei, China: A preliminary study. Medicine (Baltimore).
98:e157172019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Yu XJ, Yang MJ, Zhou B, Wang GZ, Huang YC,
Wu LC, Cheng X, Wen ZS, Huang JY, Zhang YD, et al: Characterization
of somatic mutations in air pollution-related lung cancer.
EBioMedicine. 2:583–590. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Kanwal M, Ding XJ, Song X, Zhou GB and Cao
Y: MUC16 overexpression induced by gene mutations promotes lung
cancer cell growth and invasion. Oncotarget. 9:12226–12239. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Pan HL, Wen ZS, Huang YC, Cheng X, Wang
GZ, Zhou YC, Wang ZY, Guo YQ, Cao Y and Zhou GB: Down-regulation of
microRNA-144 in air pollution-related lung cancer. Sci Rep.
5:143312015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Zhou G: Tobacco, air pollution,
environmental carcinogenesis, and thoughts on conquering strategies
of lung cancer. Cancer Biol Med. 16:700–713. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Markou A, Zavridou M and Lianidou ES:
miRNA-21 as a novel therapeutic target in lung cancer. Lung Cancer
(Auckl). 7:19–27. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Li YL, Liu XM, Zhang CY, Zhou JB, Shao Y,
Liang C, Wang HM, Hua ZY, Lu SD and Ma ZL: MicroRNA-34a/EGFR axis
plays pivotal roles in lung tumorigenesis. Oncogenesis. 6:e3722017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Wu S, Shen W, Pan Y, Zhu M, Xie K, Geng L,
Wang Y, Liang Y, Xu J, Cao S, et al: Genetic variations in key
MicroRNAs are associated with the survival of nonsmall cell lung
cancer. Medicine (Baltimore). 94:e20842015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Liuxin Z: Role of miR-34a in local lung
cancer cell lines XWLC-05 and YTMLC-90 (unpublished PhD thesis).
Yunnan University; 2018
|