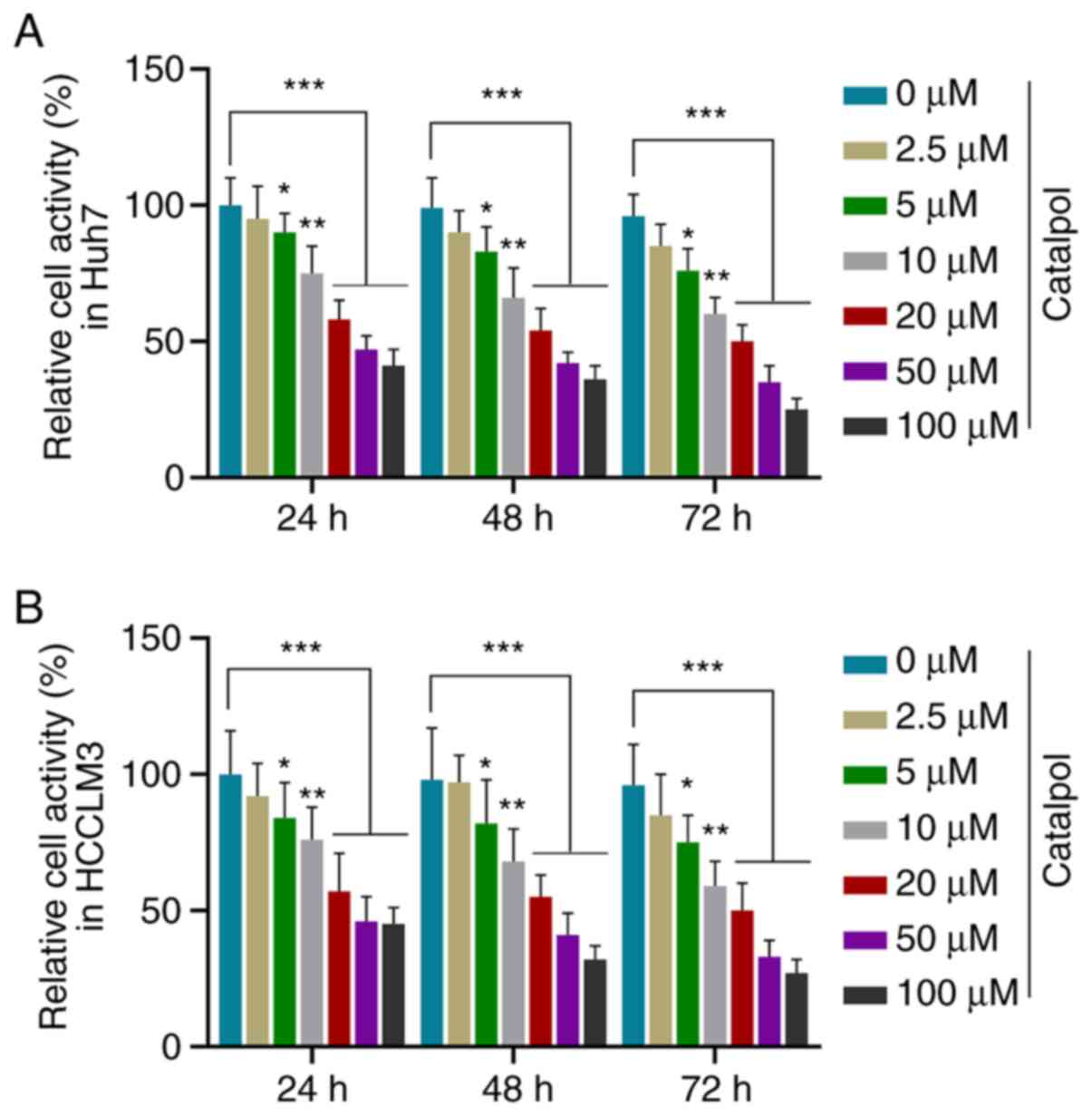
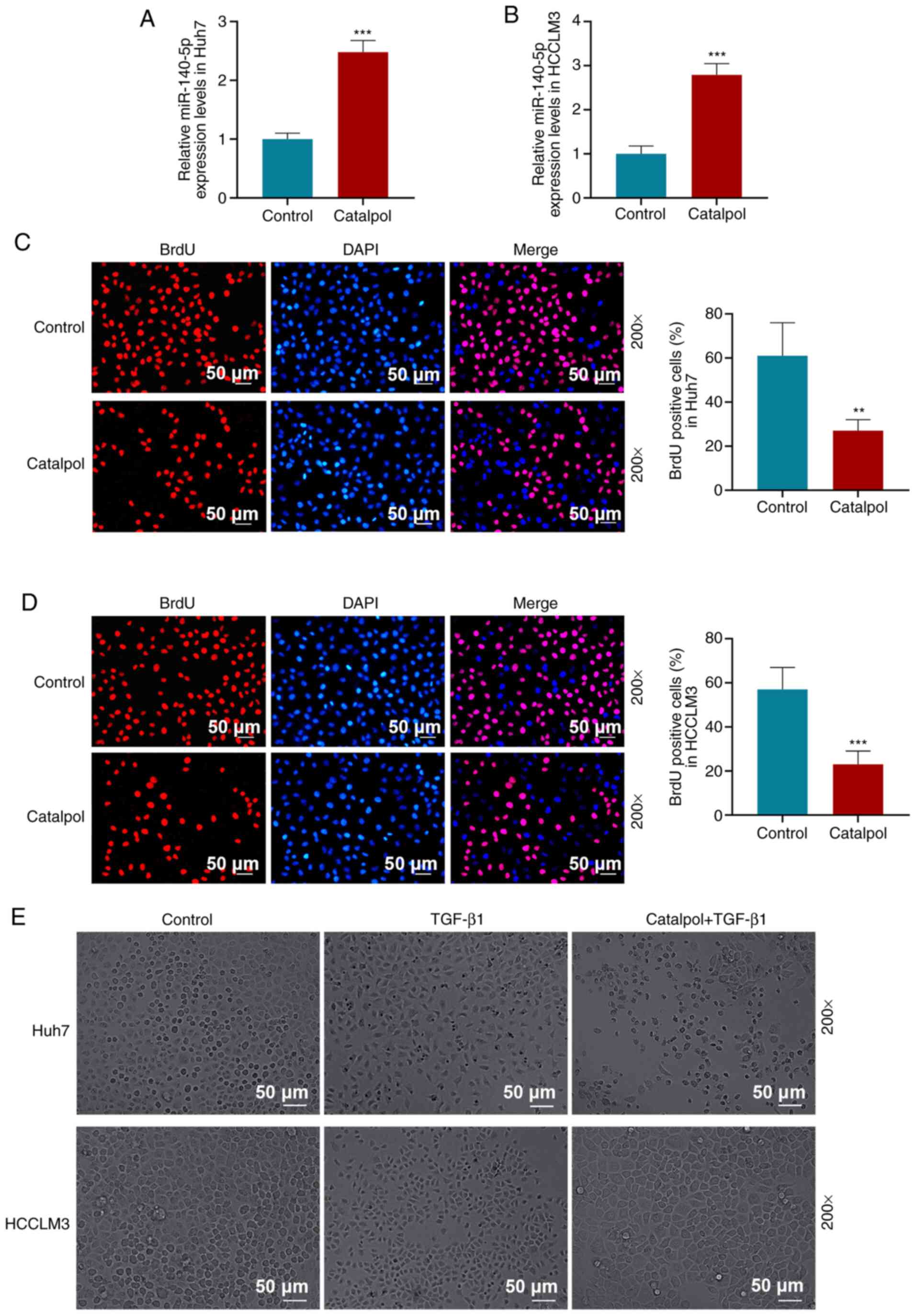
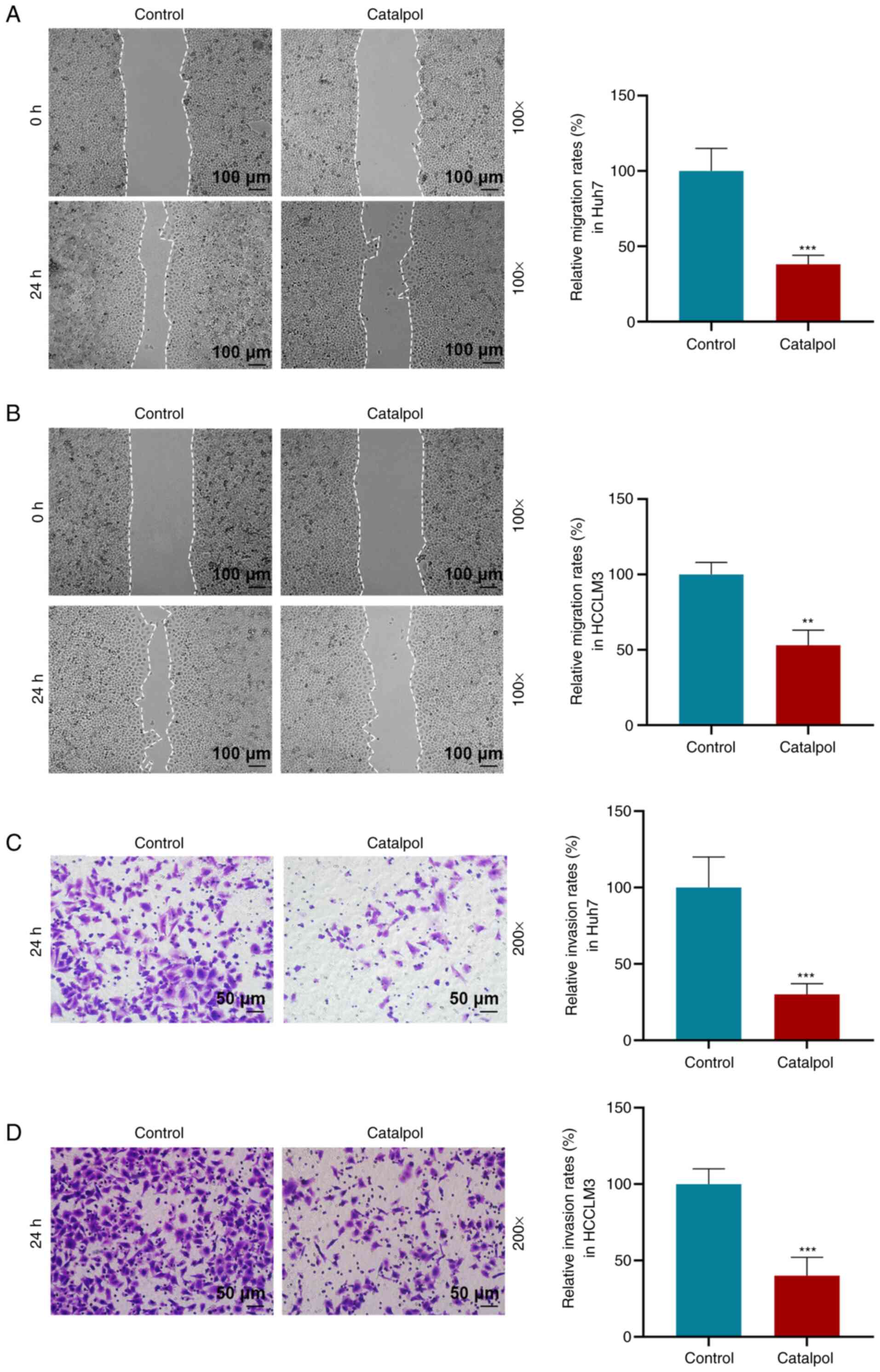
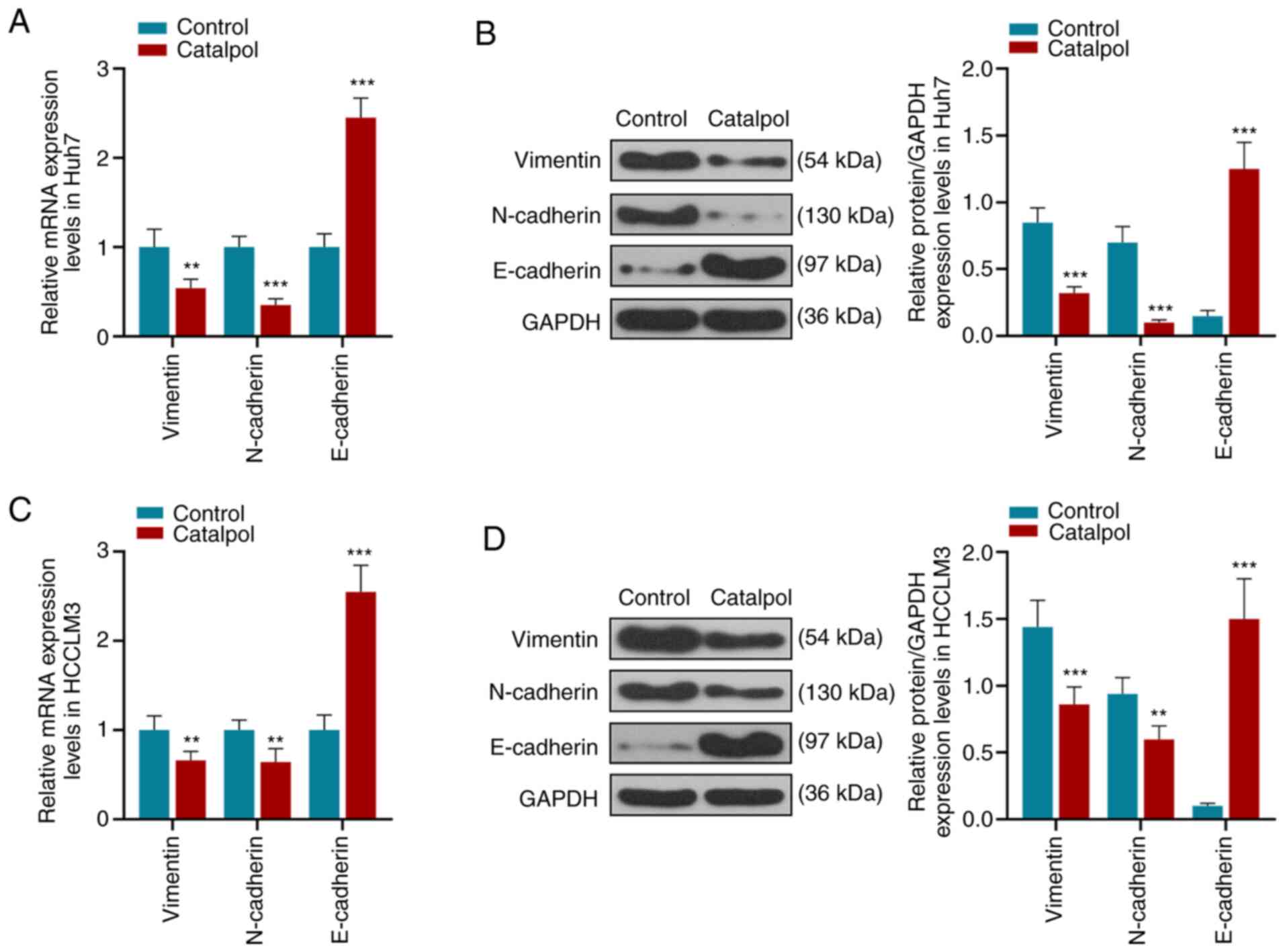
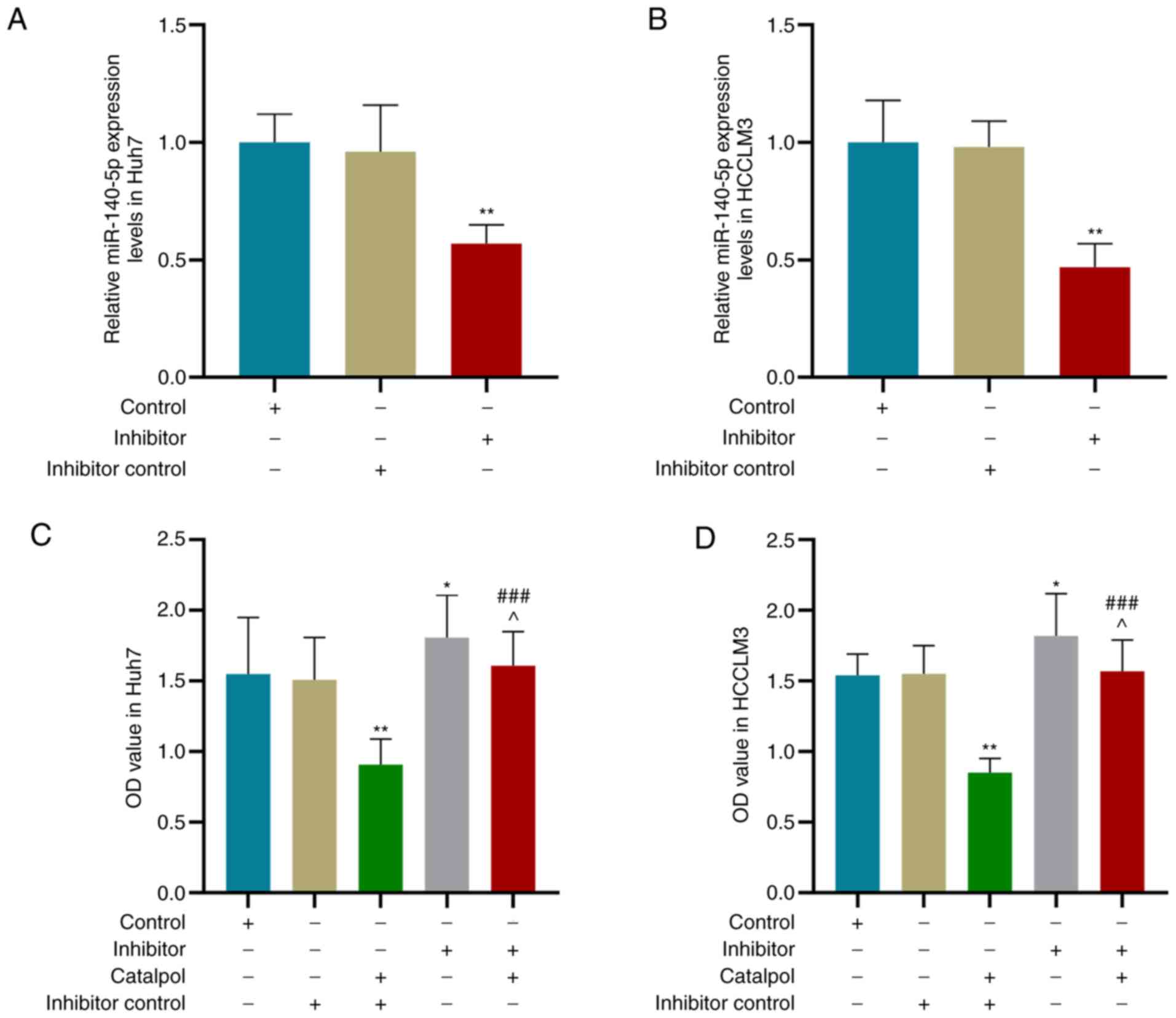
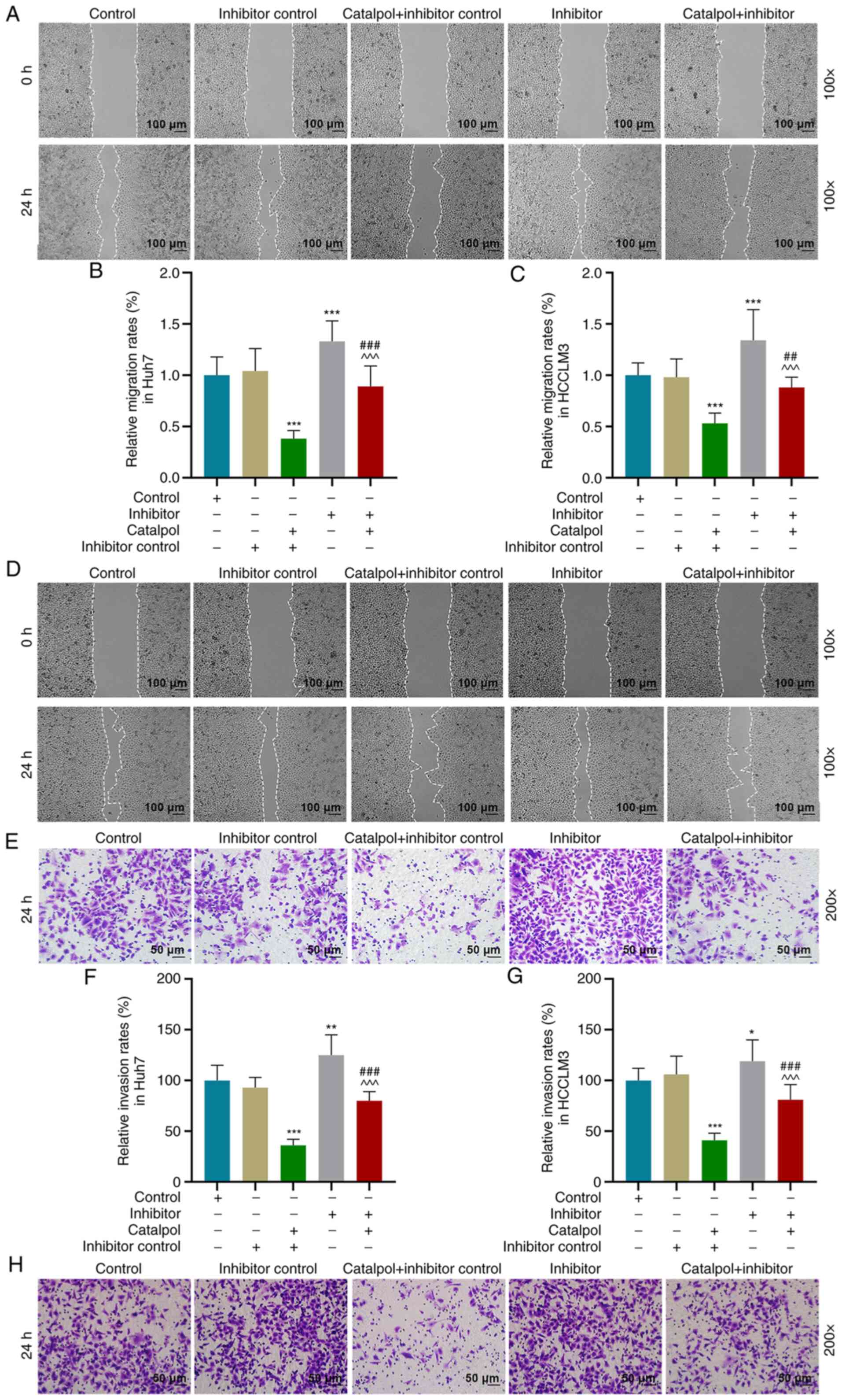
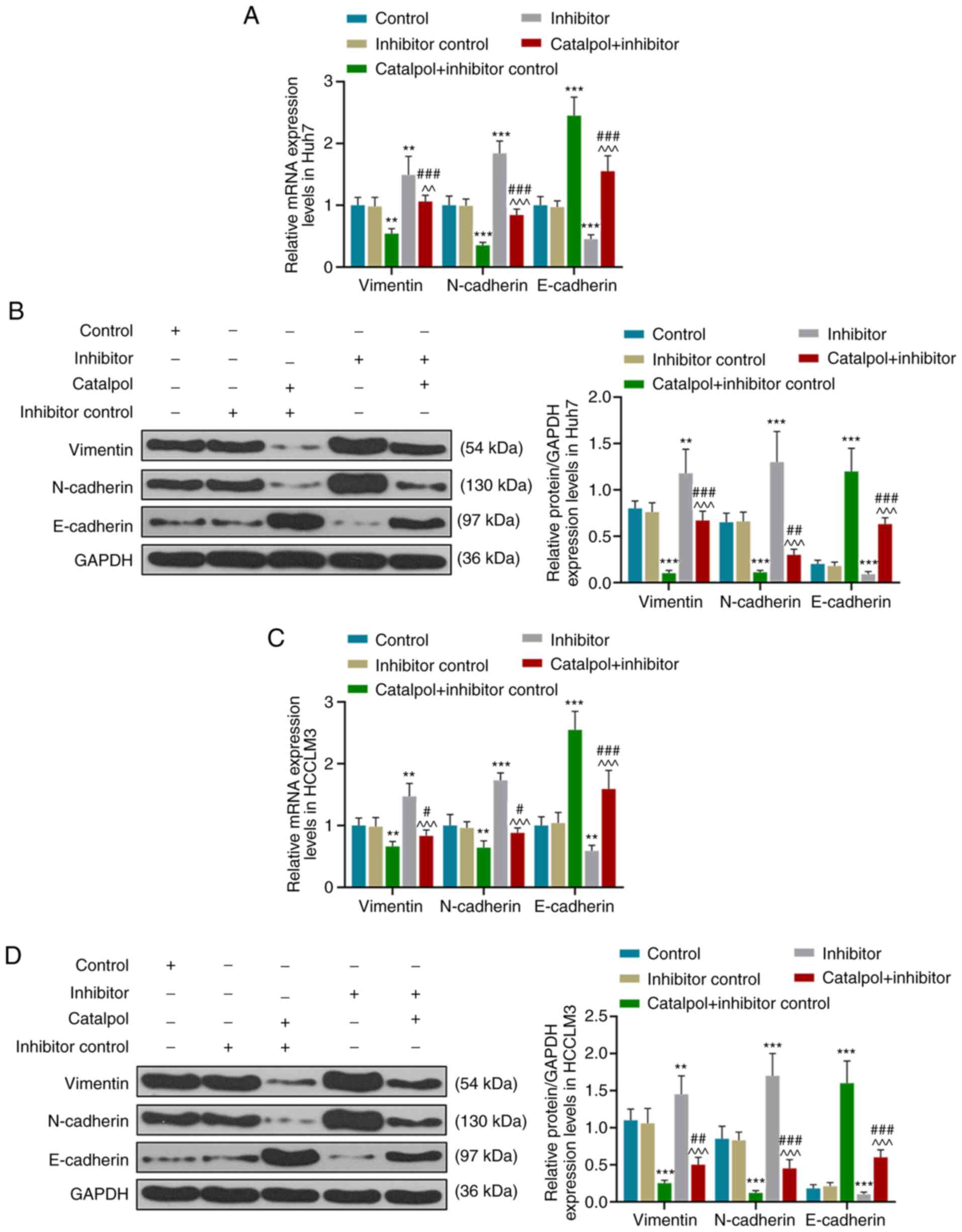
|
1
|
Intaraprasong P, Siramolpiwat S and
Vilaichone RK: Advances in management of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 17:3697–3703. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 69:7–34. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sakamoto M: Pathology of early
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res. 37 (Suppl 2):S135–S138.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wei PL, Huang CY and Chang YJ: Propyl
gallate inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth through the
induction of ROS and the activation of autophagy. PLoS One.
14:e02105132019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Deng GL, Zeng S and Shen H: Chemotherapy
and target therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: New advances and
challenges. World J Hepatol. 7:787–798. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fang F, Yang L, Tao Y and Qin W: FBI-1
promotes cell proliferation and enhances resistance to chemotherapy
of hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Cancer.
118:134–146. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Moriguchi M, Umemura A and Itoh Y: Current
status and future prospects of chemotherapy for advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin J Gastroenterol. 9:184–190. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Clark T, Maximin S, Meier J, Pokharel S
and Bhargava P: Hepatocellular carcinoma: Review of epidemiology,
screening, imaging diagnosis, response assessment, and treatment.
Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 44:479–486. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xu J: Trends in liver cancer mortality
among adults aged 25 and over in the United States, 2000–2016. NCHS
Data Brief. 1–8. 2018.
|
|
10
|
Liao CY, Lee CC, Tsai CC, Hsueh CW, Wang
CC, Chen IH, Tsai MK, Liu MY, Hsieh AT, Su KJ, et al: Novel
investigations of flavonoids as chemopreventive agents for
hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed Res Int. 2015:8405422015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu C, Ma R, Wang L, Zhu R, Liu H, Guo Y,
Zhao B, Zhao S, Tang J, Li Y, et al: Rehmanniae radix in
osteoporosis: A review of traditional Chinese medicinal uses,
phytochemistry, pharmacokinetics and pharmacology. J
Ethnopharmacol. 198:351–362. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim SH, Yook TH and Kim JU: Rehmanniae
radix, an effective treatment for patients with various
inflammatory and metabolic diseases: Results from a review of
Korean publications. J Pharmacopuncture. 20:81–88. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee B, Shim I, Lee H and Hahm DH:
Rehmannia glutinosa ameliorates scopolamine-induced learning and
memory impairment in rats. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 21:874–883.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yuan CX, Chu T, Liu L, Li HW, Wang YJ, Guo
AC and Fan YP: Catalpol induces oligodendrocyte precursor
cell-mediated remyelination in vitro. Am J Transl Res. 7:2474–2481.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu YR, Lei RY, Wang CE, Zhang BA, Lu H,
Zhu HC and Zhang GB: Effects of catalpol on ATPase and amino acids
in gerbils with cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neurol Sci.
35:1229–1233. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li MY, Cheng XR, Zhou WX and Zhang YX: The
effects of catalpol on Alzheimer's disease: Research advances.
Journal of International Pharmaceutical Research. 43:199–204.
2016.
|
|
17
|
Zhu J, Chen X, Wang H and Yan Q: Catalpol
protects mice against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury via
suppressing PI3K/Akt-eNOS signaling and inflammation. Int J Clin
Exp Med. 8:2038–2044. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang X, Zhang A, Jiang B, Bao Y, Wang J
and An L: Further pharmacological evidence of the neuroprotective
effect of catalpol from rehmannia glutinosa. Phytomedicine.
15:484–490. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhu P, Wu Y, Yang A, Fu X, Mao M and Liu
Z: Catalpol suppressed proliferation, growth and invasion of CT26
colon cancer by inhibiting inflammation and tumor angiogenesis.
Biomed Pharmacother. 95:68–76. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu C, Wu F, Liu Y and Meng C: Catalpol
suppresses proliferation and facilitates apoptosis of MCF-7 breast
cancer cells through upregulating microRNA-146a and downregulating
matrix metalloproteinase-16 expression. Mol Med Rep. 12:7609–7614.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang ZH and Sheng HZ: Catalpol inhibits
migration and induces apoptosis in gastric cancer cells and in
athymic nude mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 103:1708–1719. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Adams BD, Kasinski AL and Slack FJ:
Aberrant regulation and function of microRNAs in cancer. Curr Biol.
24:R762–R776. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Seven M, Karatas OF, Duz MB and Ozen M:
The role of miRNAs in cancer: From pathogenesis to therapeutic
implications. Future Oncol. 10:1027–1048. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fang Z, Yin S, Sun R, Zhang S, Fu M, Wu Y,
Zhang T, Khaliq J and Li Y: miR-140-5p suppresses the
proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer by
regulating YES1. Mol Cancer. 16:1392017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhai H, Fesler A, Ba Y, Wu S and Ju J:
Inhibition of colorectal cancer stem cell survival and invasive
potential by hsa-miR-140-5p mediated suppression of Smad2 and
autophagy. Oncotarget. 6:19735–19746. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lan H, Chen W, He G and Yang S: miR-140-5p
inhibits ovarian cancer growth partially by repression of PDGFRA.
Biomed Pharmacother. 75:117–122. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yan X, Zhu Z, Xu S, Yang LN, Liao XH,
Zheng M, Yang D, Wang J, Chen D, Wang L, et al: MicroRNA-140-5p
inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma by directly targeting the unique
isomerase Pin1 to block multiple cancer-driving pathways. Sci Rep.
7:459152017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li C, Zhou D, Hong H, Yang S, Zhang L, Li
S, Hu P, Ren H, Mei Z and Tang H: TGFβ1-miR-140-5p axis mediated
up-regulation of Flap endonuclease 1 promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Aging (Albany NY). 11:5593–5612. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zou G, Zhong W, Wu F, Wang X and Liu L:
Catalpol attenuates cardiomyocyte apoptosis in diabetic
cardiomyopathy via Neat1/miR-140-5p/HDAC4 axis. Biochimie.
165:90–99. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW and Bartel DP:
Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs.
ELife. 4:e050052015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Rao X, Huang X, Zhou Z and Lin X: An
improvement of the 2^(-delta delta CT) method for quantitative
real-time polymerase chain reaction data analysis. Biostat
Bioinforma Biomath. 3:71–85. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mikaelian I, Malek M, Gadet R, Viallet J,
Garcia A, Girard-Gagnepain A, Hesling C, Gillet G, Gonzalo P,
Rimokh R and Billaud M: Genetic and pharmacologic inhibition of
mTORC1 promotes EMT by a TGF-β-independent mechanism. Cancer Res.
73:6621–6631. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gheldof A and Berx G: Cadherins and
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci.
116:317–336. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yilmaz M and Christofori G: EMT, the
cytoskeleton, and cancer cell invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
28:15–33. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Villanueva A: Hepatocellular carcinoma. N
Engl J Med. 380:1450–1462. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jemal A, Ward EM, Johnson CJ, Cronin KA,
Ma J, Ryerson B, Mariotto A, Lake AJ, Wilson R, Sherman RL, et al:
Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, 1975–2014,
featuring survival. J Natl Cancer Inst. 109:djx0302017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Liang D, Xue H, Yu Y, Lv F, You W and
Zhang B: Elevated expression of UHRF1 predicts unfavorable
prognosis for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 8:9416–9421. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Reig M, da Fonseca LG and Faivre S: New
trials and results in systemic treatment of HCC. J Hepatol.
69:525–533. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bai Y, Zhu R, Tian Y, Li R, Chen B, Zhang
H, Xia B, Zhao D, Mo F, Zhang D and Gao S: Catalpol in diabetes and
its complications: A review of pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, and
safety. Molecules. 24:33022019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Lu J, Wang Y, Zhao W, Li N, Li H, Lu J,
Zeng W, Bao S and Bai Y: Effects of catalpol, L-shikonin and
paeonol extracted from radix rehmanniae, radix arnebiae and cortex
moutan on KGF-induced HaCaT cell proliferation. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za
Zhi. 94:1265–1269. 2014.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang JH, Zou L, Wan D, Huifeng Z, Wang Y
and Qin L: Review of catalpol's pleiotropic signaling pathways.
Chin Pharmacol Bull. 31:1189–1194. 2015.
|
|
42
|
Wan D, Xue L, Zhu H and Luo Y: Catalpol
induces neuroprotection and prevents memory dysfunction through the
cholinergic system and BDNF. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2013:1348522013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhou J, Xu G, Ma S, Li F, Yuan M, Xu H and
Huang K: Catalpol ameliorates high-fat diet-induced insulin
resistance and adipose tissue inflammation by suppressing the JNK
and NF-κB pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 467:853–858. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Cai Z, Xu K, Li Y, Lv Y, Bao J and Qiao L:
Long noncoding RNA in liver cancer stem cells. Discov Med.
24:87–93. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yang JY, Li D, Zhang Y, Guan BX, Gao P,
Zhou XC and Zhou CJ: The expression of MCM7 is a useful biomarker
in the early diagnostic of gastric cancer. Pathol Oncol Res.
24:367–372. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Jin D, Cao M, Mu X, Yang G, Xue W, Huang Y
and Chen H: Catalpol inhibited the proliferation of T24 human
bladder cancer cells by inducing apoptosis through the blockade of
Akt-mediated anti-apoptotic signaling. Cell Biochem Biophys.
71:1349–1356. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Brabletz T: EMT and MET in metastasis:
Where are the cancer stem cells? Cancer Cell. 22:699–701. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Heerboth S, Housman G, Leary M, Longacre
M, Byler S, Lapinska K, Willbanks A and Sarkar S: EMT and tumor
metastasis. Clin Transl Med. 4:62015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
De Craene B and Berx G: Regulatory
networks defining EMT during cancer initiation and progression. Nat
Rev Cancer. 13:97–110. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Tiwari N, Gheldof A, Tatari M and
Christofori G: EMT as the ultimate survival mechanism of cancer
cells. Semin Cancer Biol. 22:194–207. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wang L and Xue GB: Catalpol suppresses
osteosarcoma cell proliferation through blocking
epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and inducing apoptosis.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 495:27–34. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wu J, Zhang T, Chen Y and Ha S: MiR-139-5p
influences hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion and proliferation
capacities via decreasing SLITRK4 expression. Biosci Rep.
40:BSR201932952020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wang Y, Zhang P, Yuan M and Li X:
Overexpression of miRNA-21 promotes the proliferation and invasion
in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via suppressing SMAD7. Technol
Cancer Res Treat. 18:15330338198786862019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kong Q, Liang C, Jin Y, Pan Y, Tong D,
Kong Q and Zhou J: The lncRNA MIR4435-2HG is upregulated in
hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes cancer cell proliferation by
upregulating miRNA-487a. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 24:262019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Lv J, Fan HX, Zhao XP, Lv P, Fan JY, Zhang
Y, Liu M and Tang H: Long non-coding RNA Unigene56159 promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition by acting as a ceRNA of
miR-140-5p in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett.
382:166–175. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zhao L, Wang Y and Liu Q: Catalpol
inhibits cell proliferation, invasion and migration through
regulating miR-22-3p/MTA3 signalling in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Exp Mol Pathol. 109:51–60. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|